Abstract
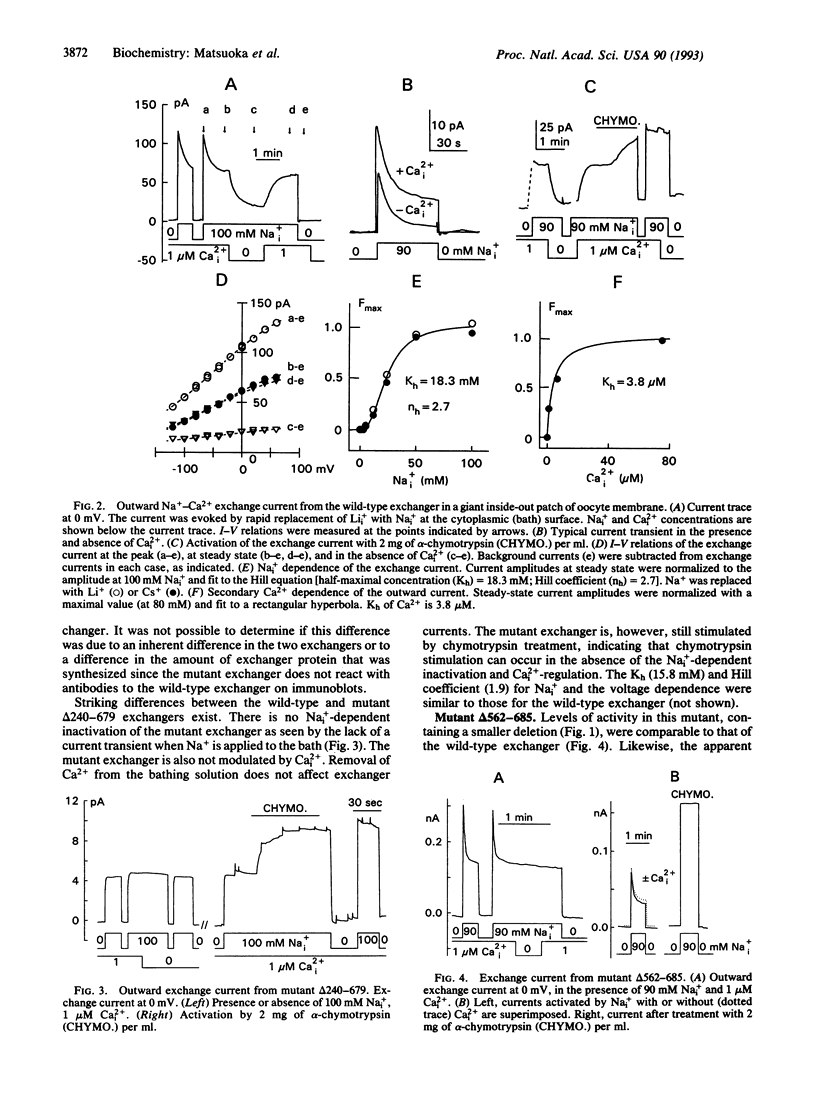
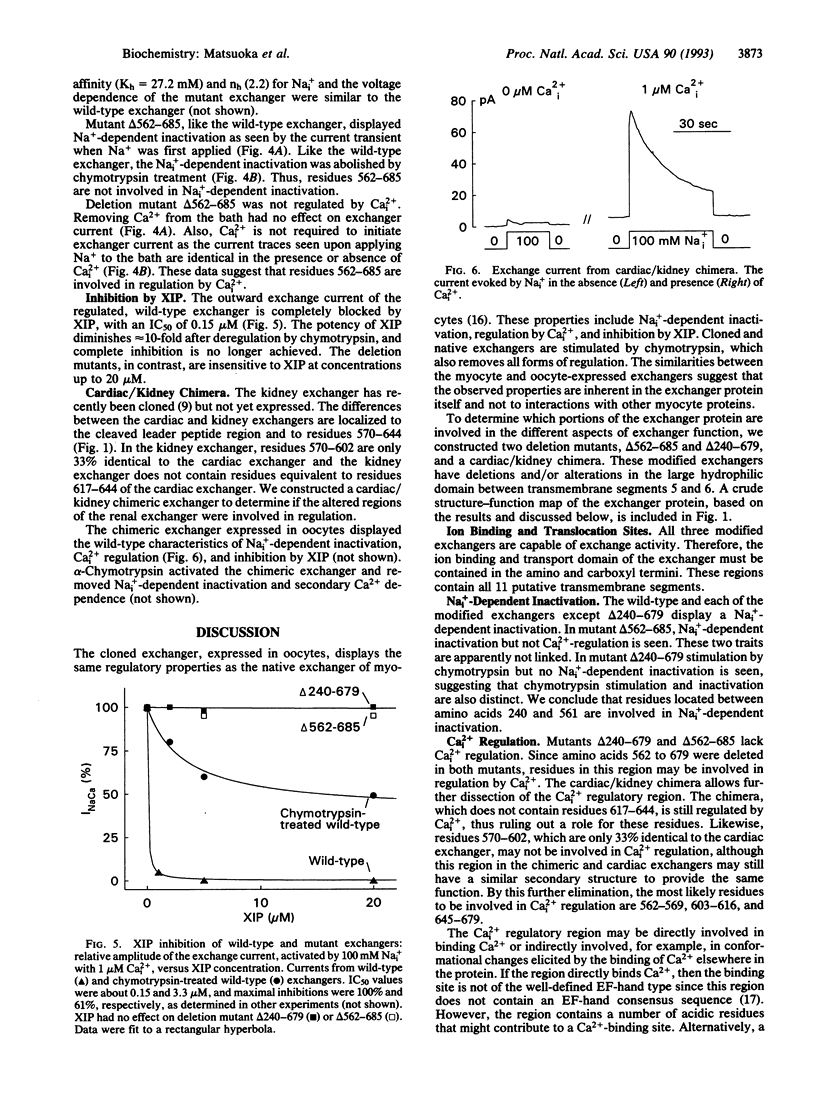
We have analyzed the regulatory properties of the wild-type cardiac Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes using the giant excised patch technique. The exchanger is activated by cytoplasmic application of chymotrypsin and exhibits a number of properties that can be changed or abolished by chymotrypsin treatment, including cytoplasmic Na(+)-dependent inactivation, secondary regulation by free cytoplasmic Ca2+, and inhibition by exchanger inhibitory peptide. Thus, the cloned exchanger expressed in oocytes exhibits regulatory properties similar to those of the native sarcolemmal exchanger. The exchanger protein contains a large (520 amino acids) hydrophilic domain modeled to be intracellular. The role of this region in exchanger function and regulation was examined by deletion mutagenesis. Mutants with residues 240-679 and 562-685 deleted exhibited exchange activity, indicating that this extensive region is not essential for transport function. Both mutants were stimulated by chymotrypsin treatment. Neither mutant demonstrated regulation by free cytoplasmic Ca2+ (Ca2+i) or inhibition by exchanger inhibitory peptide (XIP). However, mutant delta 562-685 but not delta 240-679 displayed Na(+)-dependent inactivation. The data suggest that the binding sites for XIP and regulatory Ca2+ may reside in the region encompassed by residues 562-685. A chimera made from renal and cardiac exchangers has normal regulatory characteristics and helps to further define these sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridge J. H., Smolley J. R., Spitzer K. W. The relationship between charge movements associated with ICa and INa-Ca in cardiac myocytes. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):376–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2158147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A., Somlyo A. V., Hilgemann D. W. The giant cardiac membrane patch method: stimulation of outward Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange current by MgATP. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:27–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W., Collins A., Cash D. P., Nagel G. A. Cardiac Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange system in giant membrane patches. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;639:126–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb17296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W., Collins A. Mechanism of cardiac Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange current stimulation by MgATP: possible involvement of aminophospholipid translocase. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:59–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W. Extracellular calcium transients and action potential configuration changes related to post-stimulatory potentiation in rabbit atrium. J Gen Physiol. 1986 May;87(5):675–706. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W., Nicoll D. A., Philipson K. D. Charge movement during Na+ translocation by native and cloned cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):715–718. doi: 10.1038/352715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W. Regulation and deregulation of cardiac Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange in giant excised sarcolemmal membrane patches. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):242–245. doi: 10.1038/344242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Nicoll D. A., Collins A., Hilgemann D. W., Filoteo A. G., Penniston J. T., Weiss J. N., Tomich J. M., Philipson K. D. Identification of a peptide inhibitor of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1014–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden B. J., Shaw G. S., Sykes B. D. Calcium binding proteins. Elucidating the contributions to calcium affinity from an analysis of species variants and peptide fragments. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;68(3):587–601. doi: 10.1139/o90-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll D. A., Longoni S., Philipson K. D. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1700476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll D. A., Philipson K. D. Molecular studies of the cardiac sarcolemmal sodium-calcium exchanger. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;639:181–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb17305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D., Nishimoto A. Y. Stimulation of Na+-Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by proteinase pretreatment. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C191–C195. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. F., Shugrue C. A. cDNA cloning of a renal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):F1105–F1109. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.6.F1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. M., Aylwin M. Niflumic and flufenamic acids are potent reversible blockers of Ca2(+)-activated Cl- channels in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



