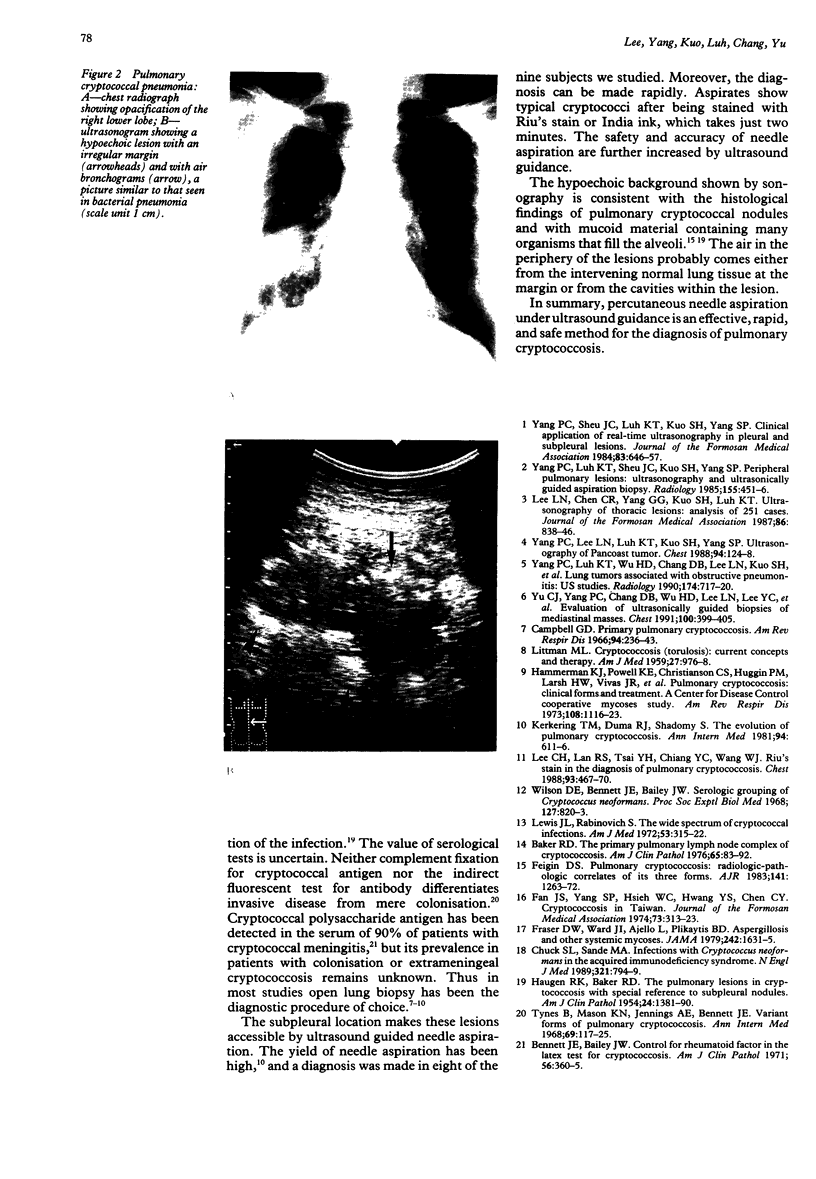
Abstract
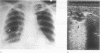
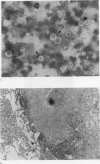
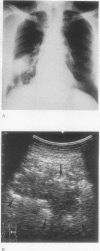
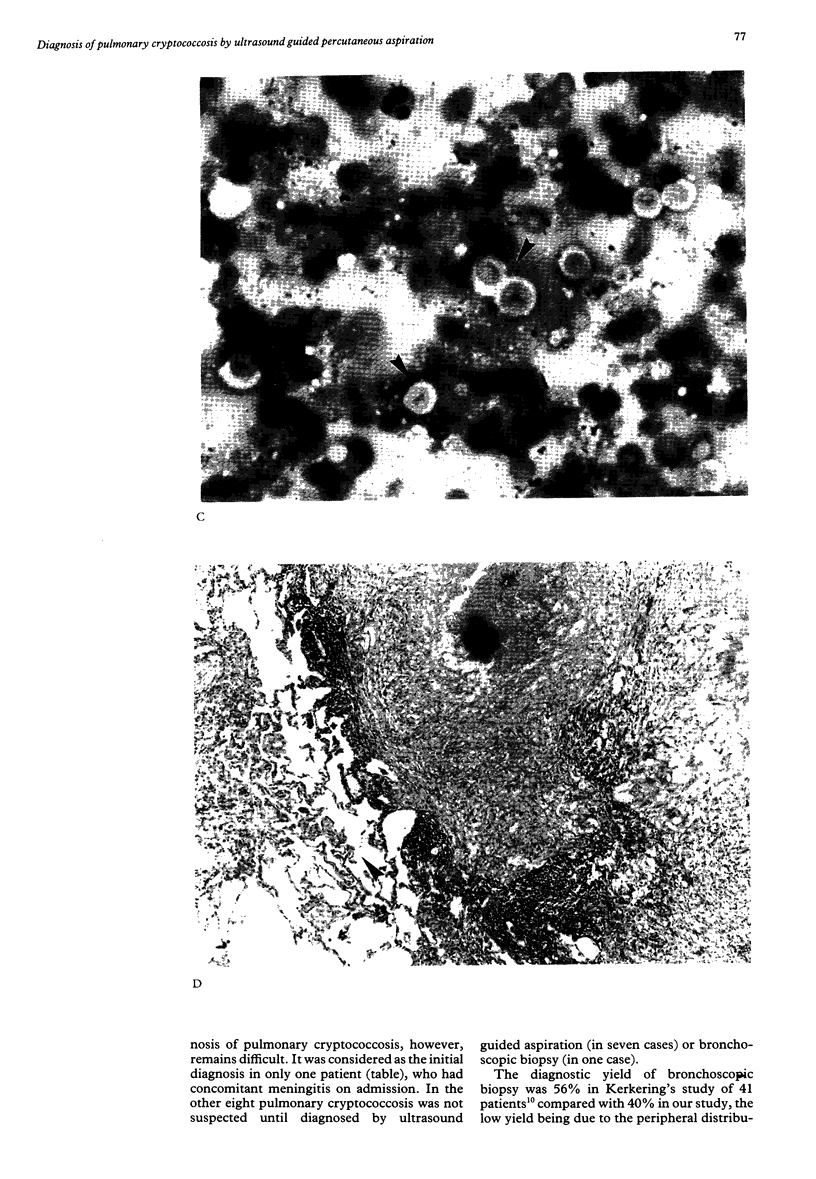
BACKGROUND: Ultrasound is useful for locating thoracic lesions and guiding biopsy procedures. The use of sonographic appearances and ultrasound guided needle aspiration has led to the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis at this hospital. METHODS: Six hundred and eight patients who had ultrasound guided lung aspirations were reviewed retrospectively and nine with documented pulmonary cryptococcosis were collected. All patients had nodules or infiltrates on the chest radiograph. The needle aspirates obtained under ultrasound guidance were stained by Riu's or Papanicolaou's method or with India ink, and six were sent for culture. Five patients also underwent bronchoscopy and biopsy. RESULTS: The nine patients had 18 pulmonary lesions, of which 15 were nodules and three infiltrates. Fifteen lesions were detectable by ultrasound, which showed the nodules to be hypoechoic with eccentrically located air echoes. In eight of the nine cases cryptococci were detected after the lung aspirates had been stained with Riu's or Papanicolaou stain or with India ink. In five of the six aspirates sent for fungal culture Cryptococcus neoformans was isolated. The diagnostic yield was higher than that of bronchoscopy. None developed post-aspiration pneumothorax or any evidence of late dissemination. CONCLUSIONS: Because they tend to be subpleural pulmonary cryptococcal lesions seem to be identifiable by ultrasound. Ultrasound guided lung aspiration is an effective, rapid, and safe method for diagnosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott W. M., Cumming G., Horsfield K. Alveolar ventilation. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jul;69(1):1–12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. D. The primary pulmonary lymph node complex of crytptococcosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jan;65(1):83–92. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/65.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E., Bailey J. W. Control for rheumatoid factor in the latex test for cryptococcosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;56(3):360–365. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.3.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. D. Primary pulmonary cryptococcosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Aug;94(2):236–243. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.94.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Sande M. A. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 21;321(12):794–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909213211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. S., Yang S. P., Hsieh W. C., Hwang Y. S., Chen C. Y. Cryptococcosis in Taiwan. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1974 Jun;73(6):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Ward J. I., Ajello L., Plikaytis B. D. Aspergillosis and other systemic mycoses. The growing problem. JAMA. 1979 Oct 12;242(15):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGEN R. K., BAKER R. D. The pulmonary lesions in cryptococcosis with special reference to subpleural nodules. Am J Clin Pathol. 1954 Dec;24(12):1381–1390. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/24.12.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkering T. M., Duma R. J., Shadomy S. The evolution of pulmonary cryptococcosis: clinical implications from a study of 41 patients with and without compromising host factors. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):611–616. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTMAN M. L. Cryptococcosis (torulosis). Current concepts and therapy. Am J Med. 1959 Dec;27:976–998. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Lan R. S., Tsai Y. H., Chiang Y. C., Wang W. J. Riu's stain in the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis. Introduction of a new diagnostic method. Chest. 1988 Mar;93(3):467–470. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. N., Chen C. R., Yang P. C., Yang G. G., Kuo S. H., Luh K. T. Ultrasonography of thoracic lesions: analysis of 251 cases. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1987 Aug;86(8):838–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. L., Rabinovich S. The wide spectrum of cryptococcal infections. Am J Med. 1972 Sep;53(3):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebow A. A. The J. Burns Amberson lecture--pulmonary angiitis and granulomatosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):1–18. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Bennett J. E., Bailey J. W. Serologic grouping of Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Mar;127(3):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. C., Lee L. N., Luh K. T., Kuo S. H., Yang S. P. Ultrasonography of Pancoast tumor. Chest. 1988 Jul;94(1):124–128. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. C., Luh K. T., Sheu J. C., Kuo S. H., Yang S. P. Peripheral pulmonary lesions: ultrasonography and ultrasonically guided aspiration biopsy. Radiology. 1985 May;155(2):451–456. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.2.3885310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. C., Luh K. T., Wu H. D., Chang D. B., Lee L. N., Kuo S. H., Yang S. P. Lung tumors associated with obstructive pneumonitis: US studies. Radiology. 1990 Mar;174(3 Pt 1):717–720. doi: 10.1148/radiology.174.3.2406780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P. C., Sheu J. C., Luh K. T., Kuo S. H., Yang S. P. Clinical application of real-time ultrasonography in pleural and subpleural lesions. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1984 Jul;83(7):646–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. J., Yang P. C., Chang D. B., Wu H. D., Lee L. N., Lee Y. C., Kuo S. H., Luh K. T. Evaluation of ultrasonically guided biopsies of mediastinal masses. Chest. 1991 Aug;100(2):399–405. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]