Abstract
Peanut diseases, such as leaf spot and spotted wilt caused by Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus, can significantly reduce yield and quality. Application of marker assisted plant breeding requires the development and validation of different types of DNA molecular markers. Nearly 10,000 SSR-based molecular markers have been identified by various research groups around the world, but less than 14.5% showed polymorphism in peanut and only 6.4% have been mapped. Low levels of polymorphism limit the application of marker assisted selection (MAS) in peanut breeding programs. Insertion/deletion (InDel) markers have been reported to be more polymorphic than SSRs in some crops. The goals of this study were to identify novel InDel markers and to evaluate the potential use in peanut breeding. Forty-eight InDel markers were developed from conserved sequences of functional genes and tested in a diverse panel of 118 accessions covering six botanical types of cultivated peanut, of which 104 were from the U.S. mini-core. Results showed that 16 InDel markers were polymorphic with polymorphic information content (PIC) among InDels ranged from 0.017 to 0.660. With respect to botanical types, PICs varied from 0.176 for fastigiata var., 0.181 for hypogaea var., 0.306 for vulgaris var., 0.534 for aequatoriana var., 0.556 for peruviana var., to 0.660 for hirsuta var., implying that aequatoriana var., peruviana var., and hirsuta var. have higher genetic diversity than the other types and provide a basis for gene functional studies. Single marker analysis was conducted to associate specific marker to disease resistant traits. Five InDels from functional genes were identified to be significantly correlated to tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) infection and leaf spot, and these novel markers will be utilized to identify disease resistant genotype in breeding populations.
Keywords: InDel markers, cultivated peanut, genetic diversity, disease resistances
Introduction
Various types of molecular markers, such as random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) (Williams et al., 1990; Burow et al., 1996; Subramanian et al., 2000); amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) (Vos et al., 1995; He and Prakash, 1997); inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers (Zietkiewicz et al., 1994; Raina et al., 2001) and simple sequence repeats (SSR) (Tautz, 1989; Liang et al., 2009), have been used in detecting the genetic diversity of plant germplasm resources (Cuc et al., 2008; Jiang et al., 2010; Moretzsohn et al., 2013), construction of genetic linkage maps (Varshney et al., 2009; Hong et al., 2010; Gautami et al., 2012; Nagy et al., 2012; Qin et al., 2012; Shirasawa et al., 2013), molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS) and mapping and cloning of genes/QTL (Chu et al., 2011; Ravi et al., 2011; Sujay et al., 2012) in peanut. Microsatellite or simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers have been developed using sequences derived from SSR-enriched genomic libraries and expressed sequence tags (ESTs) (Guo et al., 2009; Koilkonda et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2012) and have been utilized to investigate genetic diversity for the US peanut mini-core collection (Belamkar et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2014), Chinese peanut mini-core collection (Jiang et al., 2010, 2014), and ICRISAT peanut mini-core collections (Ren et al., 2010; Mukri et al., 2012; Upadhyaya et al., 2012). The functional SNP markers from FAD2A/FAD2B genes have been used to screen the U.S. mini-core collection (Wang et al., 2013). Another new kind of marker called Start codon targeted polymorphism (SCoT) was also developed and showed the potential use for studying the genetic diversity and relationship in cultivated peanut (Xiong et al., 2011). Approximately 10,000 molecular markers have been identified by various research groups around the world, but only 14.5% showed polymorphism in peanut and only 6.4% were mapped (Zhao et al., 2012), mainly due to the fact that cultivated peanut possesses an extremely narrow genetic basis (Xiong et al., 2011). Low genetic diversity among cultivated peanut accessions is likely due to the single hybridization event between two ancient diploid species, likely Arachis duranensis (A genome) and Arachis ipaensis (B genome) (Burow et al., 2009; Nagy et al., 2012; Shirasawa et al., 2013). Low level of polymorphism limits the application of molecular markers in peanut breeding and genetics studies.
InDels have been recognized as an abundant source of genetic markers that are widely spread across the genome, and there is an increasing focus on polymorphisms of the type short insertions and deletions (InDels) in genomic and breeding research (Lv et al., 2013; Yamaki et al., 2013). Short sequence and homonucleotide repeats tend to accumulate InDels due to polymerase slippage during replication and frame shift InDels in coding regions can result loss of function or non-sense mutation (Rockah-Shmuel et al., 2013). It has been reported that insertions and deletions (InDels) markers were more polymorphic than SSRs in some crops (Liu et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2014). No research of InDel marker in peanut has been reported for trait association. Therefore, it is vital to develop InDel markers in peanut and to apply these markers to associate important traits, such as disease resistance. The objectives of this research were: (1) to develop the gene-specific InDel markers; (2) to evaluate the potential use in genetic diversity study for cultivated peanut; and (3) to identify novel InDel markers that related to the disease-resistant traits.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and phenotyping of TSWV and leaf spot
One hundred and eighteen peanut accessions from the USDA peanut germplasm collection in Griffin, GA were used in the study, in which 104 accessions were selected from the US peanut mini-core collection and an additional 14 accessions were selected to represent two botanical types (hirsuta var. and aequatoriana var.) of cultivated peanut that are not present in the mini-core (Table 1). Twenty seed of each 118 Arachis hypogaea accessions were planted at Dawson, GA (31°45′ latitude, −84°30′ longitude) in 2010, 2012, and 2013 under irrigated conditions. The genotypes were planted in two-row plots 3 m long and 0.91 m between rows at a seeding rate of 3 seed m−1 in early May with three replications. Before planting, the field area was cultivated and irrigated with 15 mm of water to ensure adequate moisture for uniform seed germination. Crop management for all entries was according to best management practices for soil nutrients, herbicides, and pesticides. For evaluation of TSWV resistance, all plots of each PI were visually rated immediately prior to digging for foliar symptoms on a percentage basis, similar to the 1–10 method described by Tillman et al. (2007) where 1 = no disease and 10 = all plants severely diseased. Disease evaluations for leaf spot resistance were conducted in the field under a reduced fungicide-treatment with one application of 1.5 pt/A chlorothalonil in 2010 and no fungicide application in 2012 and 2013. Plants were rated using the Florida leaf spot scoring system during flowering, 2 weeks before harvest, and immediately prior to harvest (Chiteka et al., 1988). The data was analyzed using SAS Institute (version 9.2, 2009) with PROC GLM under the general linear model. Means were separated using Fisher's Protected LSD at p < 0.05.
Table 1.
One hundred eighteen accessions from six botanical varieties of cultivated peanuts used for disease evaluation and the InDel marker analysis.
| Code | PI Number | Botanical variety | Origin | Code | PI Number | Botanical variety | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G001 | PI 152146 | fastigiata | Uruguay | G060 | PI 372305 | hypogaea | Nigeria |
| G002 | PI 155107 | vulgaris | Uruguay | G061 | PI 399581 | hypogaea | Nigeria |
| G003 | PI 157542 | vulgaris | China | G062 | PI 403813 | vulgaris | Argentina |
| G004 | PI 158854 | fastigiata | China | G063 | PI 407667 | vulgaris | Thailand |
| G005 | PI 159786 | hypogaea | Senegal | G064 | PI 429420 | fastigiata | Zimbabwe |
| G006 | PI 162655 | hypogaea | Uruguay | G065 | PI 442768 | hypogaea | Zimbabwe |
| G007 | PI 162857 | hypogaea | Sudan | G066 | PI 461434 | hypogaea | China |
| G008 | PI 196622 | hypogaea | Cote D'Ivoire | G067 | PI 471952 | hypogaea | Zimbabwe |
| G009 | PI 196635 | hypogaea | Madagascar | G068 | PI 471954 | fastigiata | Zimbabwe |
| G010 | PI 200441 | fastigiata | Japan | G069 | PI 476432 | hypogaea | Nigeria |
| G011 | PI 240560 | hypogaea | South Africa | G070 | PI 476636 | hypogaea | Nigeria |
| G012 | PI 259617 | fastigiata | Cuba | G071 | PI 478819 | vulgaris | India |
| G013 | PI 259658 | hypogaea | Cuba | G072 | PI 478850 | fastigiata | Uganda |
| G014 | PI 259836 | fastigiata | Malawi | G073 | PI 481795 | hypogaea | Zambezia |
| G015 | PI 259851 | hypogaea | Malawi | G074 | PI 482120 | hypogaea | Zimbabwe |
| G016 | PI 262038 | fastigiata | Brazil | G075 | PI 482189 | fastigiata | Zimbabwe |
| G017 | PI 268586 | hypogaea | Zambia | G076 | PI 494795 | hypogaea | Zambia |
| G018 | PI 268696 | hypogaea | South Africa | G077 | PI 496401 | hypogaea | Burkina |
| G019 | PI 268755 | hypogaea | Zambia | G078 | PI 496448 | hypogaea | Burkina |
| G020 | PI 268806 | hypogaea | Zambia | G079 | PI 502040 | fastigiata | Peru |
| G021 | PI 268868 | hypogaea | Sudan | G080 | PI 502111 | peruviana | Peru |
| G022 | PI 268996 | hypogaea | Zambia | G081 | PI 502120 | peruviana | Peru |
| G023 | PI 270786 | hypogaea | Zambia | G082 | PI 504614 | hypogaea | Colombia |
| G024 | PI 270905 | hypogaea | Zambia | G083 | PI 475863 | fastigiata | Bolivia |
| G025 | PI 270907 | hypogaea | Zambia | G084 | PI 475918 | fastigiata | Bolivia |
| G026 | PI 270998 | vulgaris | Zambia | G085 | PI 476025 | fastigiata | Peru |
| G027 | PI 271019 | vulgaris | Zambia | G086 | PI 493329 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G028 | PI 274193 | hypogaea | Bolivia | G087 | PI 493356 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G029 | PI 288146 | vulgaris | India | G088 | PI 493547 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G030 | PI 290536 | hypogaea | India | G089 | PI 493581 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G031 | PI 290560 | vulgaris | India | G090 | PI 493631 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G032 | PI 290566 | fastigiata | India | G091 | PI 493693 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G033 | PI 290594 | hypogaea | India | G092 | PI 493717 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G034 | PI 290620 | fastigiata | Argentina | G093 | PI 493729 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G035 | PI 292950 | hypogaea | South Africa | G094 | PI 493880 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G036 | PI 295250 | hypogaea | Israel | G095 | PI 493938 | fastigiata | Argentina |
| G037 | PI 295309 | hypogaea | Israel | G096 | PI 497517 | fastigiata | Brazil |
| G038 | PI 295730 | fastigiata | India | G097 | PI 497639 | fastigiata | Ecuador |
| G039 | PI 296550 | hypogaea | Israel | G098 | PI 497318 | hypogaea | Bolivia |
| G040 | PI 296558 | hypogaea | Israel | G099 | PI 497395 | hypogaea | Bolivia |
| G041 | PI 298854 | hypogaea | South Africa | G100 | PI 494018 | vulgaris | Argentina |
| G042 | PI 313129 | fastigiata | Taiwan | G101 | PI 494034 | vulgaris | Argentina |
| G043 | PI 319768 | hypogaea | Israel | G102 | PI 288210 | vulgaris | India |
| G044 | PI 323268 | hypogaea | Pakistan | G103 | PI 371521 | hypogaea | Israel |
| G045 | PI 325943 | hypogaea | Venezuela | G104 | PI 461427 | hypogaea | China |
| G046 | PI 331297 | hypogaea | Argentina | G105 | PI 576613 | hirsuta | Mexico |
| G047 | PI 331314 | hypogaea | Argentina | G106 | Grif 14051 | aequatoriana | Guatemala |
| G048 | PI 337293 | hypogaea | Brazil | G107 | PI 576634 | hirsuta | Mexico |
| G049 | PI 337399 | hypogaea | Morocco | G108 | PI 648241 | hirsuta | Ecuador |
| G050 | PI 337406 | fastigiata | Paraguay | G109 | PI 648250 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G051 | PI 338338 | peruviana | Venezuela | G110 | PI 576616 | hirsuta | Mexico |
| G052 | PI 339960 | fastigiata | Argentina | G111 | PI 648249 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G053 | PI 343384 | hypogaea | Israel | G112 | PI 648242 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G054 | PI 343398 | fastigiata | Israel | G113 | PI 648245 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G055 | PI 355268 | hypogaea | Mexico | G114 | Grif 12579 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G056 | PI 355271 | hypogaea | Mexico | G115 | PI 576614 | hirsuta | Mexico |
| G057 | PI 356004 | fastigiata | Argentina | G116 | Grif 12545 | aequatoriana | Ecuador |
| G058 | PI 370331 | hypogaea | Israel | G117 | PI 576636 | hirsuta | Mexico |
| G059 | PI 372271 | hypogaea | Unknown | G118 | PI 576637 | hirsuta | Mexico |
Identification of InDels and primer design
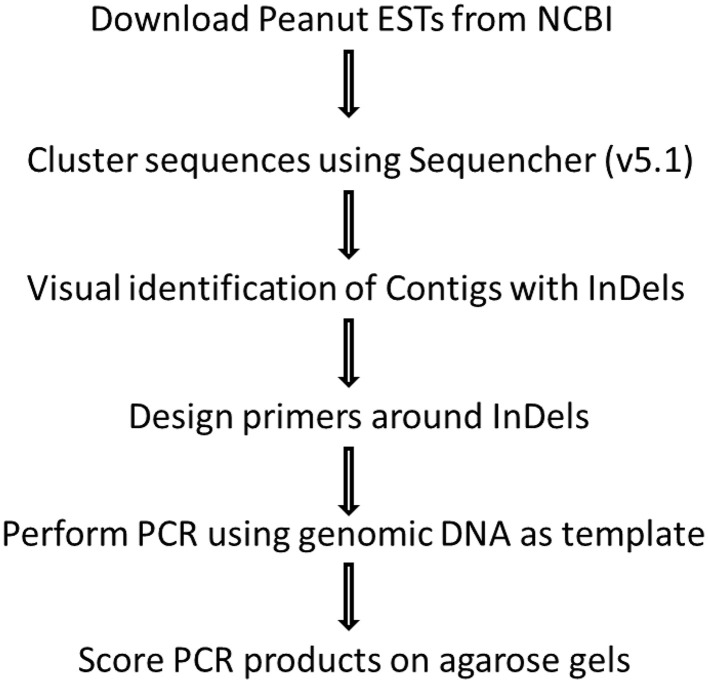
Publically available peanut expressed sequence tags (ESTs) derived from various tissues, developmental stages, and under different biotic and abiotic stresses (Feng et al., 2012) were utilized to identify potential InDel markers. Sequences were downloaded and alignment was performed by Sequencher v5.1 (Gene Codes, Ann Arbor, MI). Individual clusters or contigs were visually observed to identify potential InDels and selected contigs were reassembled using “large gap” criteria for assembly algorithm, resulting in the identification of 48 InDels. Primers were designed using Primer Express 3.0 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) for the sizes of 150–500 bp. Potential plant gene function was identified through BLASTx (NCBI) and comparison of the sequences according to conserved sequences of functional genes. The procedure of identification of peanut EST InDels, primer design and marker scoring was illustrated by flowchart (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart showing identification of peanut EST InDels, primer design, and marker scoring.
DNA extraction and PCR
Genomic DNA extraction from dry seeds was performed following the method of Dang and Chen (2013). A Nano-Drop 2000c spectrophotometer (Nano Drop Technologies, USA) was used to evaluate the quality and concentration of all DNA. DNA samples were diluted to 20 ng/μL and PCR conditions were applied: 94°C for 1 min, 30 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 50°C for 1.0 min, 72°C for 1.5 min, and 1 cycle at 72°C for 10 min. PCR products and DNA molecular weight marker (Promega, Madison, WI) were separated on a 1.2% TAE-agarose gel and image was captured on a Gel Logic 200 Imaging System (Kodak, Rochester, NY).
Data analysis
Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) based on allelic frequencies among 118 genotypes was calculated for each InDel marker using the following formula: PIC = 1- where xi is the relative frequency of the ith allele of the SSR loci. Clustering analyses were performed using SAS (SAS 9.3; SAS Institute, 2009) to calculate the genetic similarity matrices, and a neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm (Saitou and Nei, 1987) was used to construct a phylogram from a distance matrix using the MEGA4 software (Tamura et al., 2007). Single marker analysis (SMA) method was used for trait-marker analysis (Jansen and Stam, 1994). It was carried out by PROC GLM of SAS (SAS 9.3; SAS Institute, 2009) with the following linear model: Yiklm = u + Ei + Mk + F(M)kl + E x F(M)ikl + eiklm, where Yiklm is each observed phenotype, u is the population mean, Ei is the effect of year (i = 1, 2), Mk is the effect of marker genotype (k = 1, 2), F(M) kl is the effect of PIs within marker genotype (l = 1, …, 118), E x F(M)ikl is the interaction between the effect of year and the effect of PIs within marker genotype, and eiklm is residual error. Threshold for declaring a marker significant was chosen to be marker-wise p < 0.0001, which is approximately equal to an experiment-wise p < 0.05 in this study based on 16 polymorphic markers.
Results
Polymorphic information of the InDel markers and genetic diversity of the different botanical types based on InDel markers
Forty-eight primer-pairs of InDel markers were designed from coding and non-coding regions of the 48 functional genes (Table 2). All 48 primer-pairs generated PCR bands, of which 16 were polymorphic, with different sizes from 200 to 470 bp (Figure 2). The polymorphic information content (PIC) values of each primer ranged from 0.0169 of InDel-03 to 0.5960 of InDel-18 with an average of 0.1349 (Table 3). The distributions of 16 polymorphic InDel markers among the six botanical types were quite different. More polymorphic markers were detected in the botanical types of hirsuta var., aequatoriana var., hypogaea var., and fastigiata var. than the other two types of peruviana var. and vulgaris var. (12, 9, 9, 7, vs. 2, 2) (Table 3). The least polymorphic marker was InDel-03 which only showed in hirsuta var., while InDel-16 and InDel-18 showed polymorphism in five of six botanical types. In respect to the different botanical types, PICs varied from 0.176 for fastigiata var., 0.181 for hypogaea var., 0.306 for vulgaris var., 0.534 for aequatoriana var., 0.556 for peruviana var., to 0.660 for hirsuta var., which implied that hirsuta var., peruviana var., and aequatoriana var. have higher genetic diversity than the other types (Table 4).
Table 2.
The sequence and annotations of the 48 InDel markers that were developed and used in this study.
| InDels Primer | Sequence from 5′ to 3′ | Contig | Annotation | bp difference | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indel-001- F | AATTCGAGGGTGCTGAAATG | [0016] | Metallothionein, type 2 | 6 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-001-R | TCAAGGATGCAGCAAGACAC | ||||
| Indel-002_F | GCTCAACCGGTTCCAGAATA | [0023] | Allergen II | 5 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-002_R | AGGCAATGCCATAAAAGCAC | ||||
| Indel-003_F | GGCCCATGACAAAAGGACTA | [0031] | Peroxidase | 6 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-003_R | GAACTGTGACTGCCACGCAC | ||||
| Indel-004_F | GCCTGTAACTGCCTCAAAGC | [0038] | LTP | 18 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-004_R | CATACAAAGACTACAAGAGGARAGG | ||||
| Indel-005_F | CAAGCCAGGCTATTGACTCC | [0041] | Isoprene synthase | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-005_R | TCGTGAAATGACCATCATTG | ||||
| Indel-006_F | AGCTTAACGGCATCCTCTCA | [0055] | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 10 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-006_R | GCTTAACAAGTGTAGTGGTAATAGTAG | ||||
| Indel-007_F | ACCGTGCTGTGACAAATTCA | [0047] | Hyoscyamine-6-dioxygenase | 22 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-007_R | GCACCTCTACATGAAGGTGAAC | ||||
| Indel-008_F | ACGTCTGACCCATGAAATCC | [0061] | Catalase | 30 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-008_R | CGTACACGCGGACAGATTTAG | ||||
| Indel-009_F | GCCTTATCAACYCTTTCACCCTC | [0057] | Gibberellin 2-oxidase | 15 bp | 5′ coding |
| Indel-009_R | AGCGGCAAGGAGAAGAATTT | ||||
| Indel-010_F | AGAGCATTAAGGAGAAAGCTGC | [0100] | LEA 4 | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-010_R | ATGTTGTCCGGTTGTGGAAT | ||||
| Indel-011_F | CTGCAAATTCGACAAGAGCA | [0059] | Cysteine proteinase | 5 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-011_R | GCAGAACATTTCACAGCATACATG | ||||
| Indel-012_F | CACATAGTGGGGCCTGATCT | [0113] | 1-Cys peroxiredoxin | 3 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-012_R | AACCATATTTAGATTTGTGAGATAGC | ||||
| Indel-013_F | CCACCCCCAGAGTACATCAC | [0110] | Vacuolar processing enzyme | 69 bp | Coding |
| Indel-013_R | GATGGATGCAGGATCGAAGC | ||||
| Indel-014_F | GGCACAGAGCAAAGTGAACA | [0115] | F-box protein | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-014_R | TTCTCAGAACCCCACAAAGG | ||||
| Indel-015_F | AGAGAAGCTGTGGGATGACG | [0276] | Auxin repressed protein | 2 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-015_R | CCACAGACCAAACAAGCAGA | ||||
| Indel-016_F | TCCTCATCAGGAACTGGGATA | [0160] | Alkaline alpha galactosidase | 19 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-016_R | TGCAGCAATAGGACTTCTGG | ||||
| Indel-017_F | GTGGAGGAGTGTACGGAGGA | [0137] | Drought induced protein | 7 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-017_R | CACACAAGAATGAAAGTGTAAAACC | ||||
| Indel-018_F | AGCTGGAAAGCAAGAGCAAG | [0177] | Arachin Ahy-3 | 12 bp | Coding |
| Indel-018_R | GCTGTTTGCGTTCATGTTGT | ||||
| Indel-019_F | CACCGACAACCTAGGCGTAT | [0285] | Lipid binding protein | 26 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-019_R | GAGCAATAGTGACCTTGCATTG | ||||
| Indel-020_F | CATTTTCAAACATTACACTCACTCATC | [0294] | Plant lipid transfer protein | 5 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-020_R | CAACACATGCAATGCAACAA | ||||
| Indel-021_F | CCGATTCCTTCAGATAGCAC | [0296] | 40S ribosomal protein | 2 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-021_R | GAGAAAATTGAAATTCAACTTCATC | ||||
| Indel-022_F | GCGGTGAAATCAACTCATCA | [0315] | Cell wall N rich protein | 6 bp | Coding |
| Indel-022_R | CTTTGTTGAAGCCACCGTTG | ||||
| Indel-023_F | CATCCGACATGTTACAATACTGAG | [0326] | bZip Transcription factor | 26 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-023_R | CCATTGATAGAGTGATTACAATTTCTC | ||||
| Indel-024_F | GTTGTGTTGATCCTTTCATTCGG | [0421] | Glutamate binding | 12 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-024_R | AGACGGTGATGGAGGATACG | ||||
| Indel-025_F | GACTCCATAATCGGAATCCAAG | [0495] | Vesicle membrane protein | 18 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-025_R | GCTTGAGCGCTGGAAGTAAC | ||||
| Indel-026_F | TCGGCTTACTCTCCCCTGAAC | [0500] | Plastic protein | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-026_R | GTCAATCTCGCACCCAAATC | ||||
| Indel-027_F | GGCTATTGCAGGTGGAACAC | [0518] | Wound induced protein | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-027_R | GACCCCACGTGCTCAAATAC | ||||
| Indel-028_F | ACCAATGCATGTGGATCATGC | [0534] | Lipid binding protein | 3 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-028_R | GCAGTGCACAAACAAAGTGC | ||||
| Indel-029_F | TTCCTTTGCTTTCCACCATT | [1556] | Protease inhibitor | 5 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-029_R | GCATGATGAGGATTAAAAGATGATAG | ||||
| Indel-030_F | TTGAAGGCAGAGGAGGTAGC | [0522] | Remorin | 11 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-030_R | GAAAGGAACATTGAACTAAATTTTGC | ||||
| Indel-031_F | CGTCATATCCATCACCACCA | [0581] | Proline rich cell wall protein | 12 bp | Coding |
| Indel-031_R | GGAGGAGTCATGCCACAAGT | ||||
| Indel-032_F | AGGAGCAACCGGACACATAC | [0628] | Electron transporter/metal ion | 7 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-032_R | TGCACCTCATCAACCTCTCA | ||||
| Indel-033_F | CCTTTAGGCCCAAGGATTTC | [3275] | Salt tolerance protein | 3 bp | Coding |
| Indel-033_R | TGCCTCTAAGTCCCTTCTTATTG | ||||
| Indel-034_F | TGCAGCACGTAAGGATCAAG | [0898] | Unknown | 3 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-034_R | TTTGTAACGCAACCTTGCAC | ||||
| Indel-035_F | CGTGGGAGGGACAGAGATTA | [1457] | Arginine/serine splicing factor | 3 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-035_R | AGATCGTCCATCACGGCTAC | ||||
| Indel-036_F | ATTGGCTTGTGAAGCATTCC | [2962] | ATARLA, GTP binding | 3 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-036_R | CAGCTACATCAACAATGACATGA | ||||
| Indel-037_F | CACCCCAAGTTTGGAAAATG | [3189] | Unknown | 7 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-037_R | CACTTGATTGCAAGCTTGTACAAAT | ||||
| Indel-038_F | TGAAGTCAGTGACAGTGGTGAA | [3291] | Glycine dehydrogenase | 1 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-038_R | GCAGTCAAAGCACAAGACAAG | ||||
| Indel-039_F | ACTTCCAATTCCCAGCACAG | [3482] | Unknown | 6 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-039_R | CCCAATGAAAGCTTGAAGGA | ||||
| Indel-040_F | CTTAATAATTTGGATGAAGGATCATC | [3624] | Unknown | 6 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-040_R | CGGTGGTTCCAAAAAGAAGA | ||||
| Indel-041_F | AAGCTGCTGAGAGGGAAAGAC | [3694] | Unknown | 18 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-041_R | GCCCACACATGCATAGACAG | ||||
| Indel-042_F | GGGATTGAGCATGAACGATT | [3863] | Dihydroxy-acid dehydratase | 2 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-042_R | GATAACAAATGGGGGCAAGA | ||||
| Indel-043_F | GATATAGCACCAGCAGCATAGTTTC | [1258] | Unknown | 9 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-043_R | TTTTCAGTCAAATGATGGAAGC | ||||
| Indel-044_F | TTGAGGCCCTAAGAATGAGC | [2367] | Cyclin-dependent protein kinase | 12 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-044_R | TTTTTGTCCTCATGAAGAACTACG | ||||
| Indel-045_F | GAGGAGGCCAAGAAGGAGTT | [3274] | Frutose-bisphosphate aldolase | 2 bp | 3′ non-coding |
| Indel-045_R | TGGCTCCTAACTTATGGCAAA | ||||
| Indel-046_F | TGAACTCGAGCGAACATCAC | [1585] | Ran GTPase binding | 24 bp | Coding |
| Indel-046_R | TTTGTGCTTTGGCACCATTA | ||||
| Indel-047_F | GCGCCTTTCTTTCACAACTC | [1596] | YABBy-like transcription factor | 18 bp | 5′ non-coding |
| Indel-047_R | AACAAAGCTGTTCGGAAGGA | ||||
| Indel-048_F | CTCCACATTCTTATCCTCAGATCTG | [3076] | Omega-3 fatty acid desaturase | 9 bp | Coding |
| Indel-048_R | CTCATTGACCTCCATGGATCC |
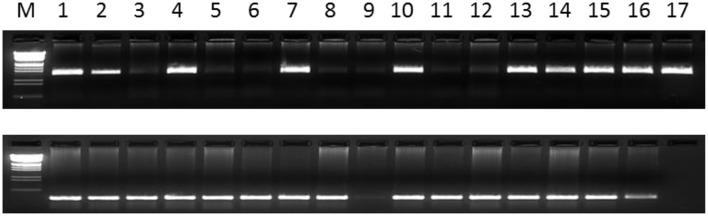
Figure 2.
The fragments amplified by InDel-016 (above) and Indel-042 (bottom). The sequences (5′–3′) of Indel-016 primer are TCCTCATCAGGAACTGGGATA(F) and TGCAGCAATAGGACTTCTGG(R). For Indel-042 primer, the sequences (5′–3′) are GGGATTGAGCATGAACGATT(F) and GATAACAAATGGGGGCAAGA(R). 1-PI 152146; 2-PI 155107; 3-PI 157542; 4-PI 158854; 5-PI 159786; 6-PI 162655; 7-PI 162857; 8-PI 196622; 9-PI 196635; 10-PI 200441; 11-PI 240560; 12-PI 259617; 13-PI 259658; 14-PI 259836; 15-PI 259851; 16-PI 262038; 17-PI 268586.
Table 3.
Polymorphic information of 16 InDel markers among six botanical types of cultivated peanut.
| Markers | Distribution of polymorphic InDels marker | PCR product | PIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fastigiata | hypogaea | vulgaris | peruviana | hirsuta | aequatoriana | |||
| InDel-03 | √ | 440 | 0.0169 | |||||
| InDel-04 | √ | √ | √ | 310 | 0.0830 | |||
| InDel-05 | √ | √ | √ | 420 | 0.0666 | |||
| InDel-07 | √ | 430 | 0.0169 | |||||
| InDel-011 | √ | 470 | 0.0169 | |||||
| InDel-016 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 320 | 0.5288 | |
| InDel-017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 320 | 0.1151 | ||
| InDel-018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 470 | 0.5960 | |
| InDel-020 | √ | √ | 390 | 0.0336 | ||||
| InDel-029 | √ | √ | 300 | 0.0336 | ||||
| InDel-030 | √ | √ | √ | 240 | 0.0502 | |||
| InDel-032 | √ | √ | 400 | 0.2232 | ||||
| InDel-033 | √ | √ | 300 | 0.0336 | ||||
| InDel-039 | √ | √ | 200 | 0.0666 | ||||
| InDel-042 | √ | √ | 250 | 0.1467 | ||||
| InDel-046 | √ | √ | √ | 300 | 0.1310 | |||
| Total | 7 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 9 | ||
Table 4.
Number of alleles, PIC of different botanical types based on the InDel markers.
| Botanical type | No. of accessions | Alleles | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| fastigiata | 34 | 7 | 0.1763 |
| hypogaea | 55 | 9 | 0.1809 |
| vulgaris | 12 | 2 | 0.3056 |
| peruviana | 3 | 2 | 0.5556 |
| hirsuta | 7 | 12 | 0.6597 |
| aequatoriana | 7 | 9 | 0.5341 |
| Total | 118 | 16 | 0.1457 |
The genetic relationships revealed by InDel markers among 6 botanical varieties
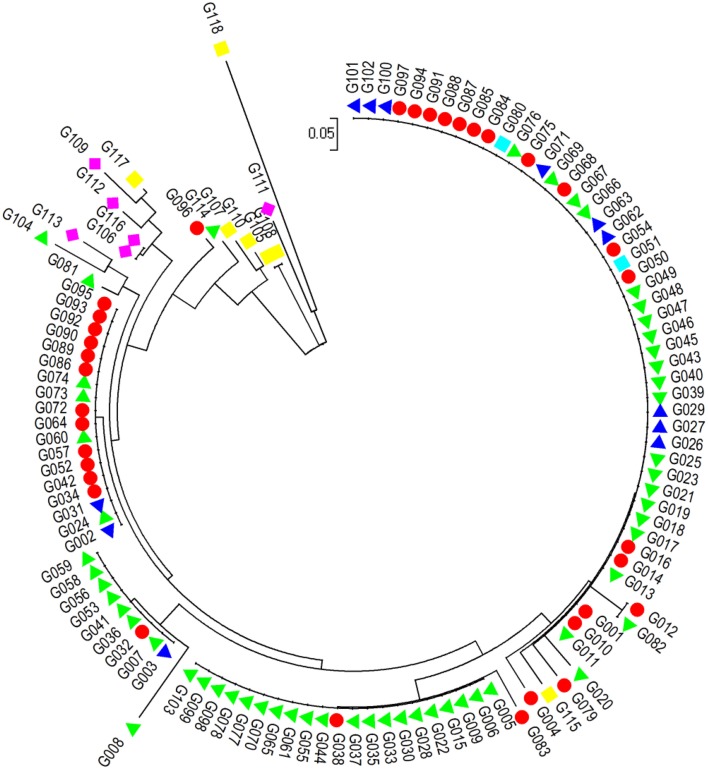
A neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm method assigned the 118 accessions into four major basic groups and some small clusters. Cluster 1 consists of 51 accessions from G101 to G004 (Figure 3). This is a complex cluster, in which var. fastigiata; var. vulgaris; var. hypogaea var. peruviana were included. Cluster 2 has all 20 var. hypogaea accessions (from G005 to G103) plus two var. fastigiata G038 and G083. In cluster 3, eight of 10 accessions are var. hypogaea (G008 to G059). Cluster 4 contains 12 var. fastigiata accessions, 4 var. hypogaea accessions (G024, G060, G073, and G074), and 2 var. vulgaris accessions (G002 and G031). The rest of 15 accessions formed small clusters. They are mainly var. aequatoriana lines and var. hirsuta lines and have longest genetic distances to other 4 botanical varieties. The results from this analysis are consistent with the PIC values among different botanical varieties.
Figure 3.
Dengrogram of 118 accessions of six botanical varieties of cultivated peanuts based on 16 polymorphism Indel makers with a neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm method.  - var. fastigiata,
- var. fastigiata,  - var. vulgaris,
- var. vulgaris,  -var. hypogaea,
-var. hypogaea,  - var. aequatoriana,
- var. aequatoriana,  - var. hirsuta,
- var. hirsuta,  - var. peruviana.
- var. peruviana.
Marker–trait correlation
Five markers, InDel-016, InDel-018, InDel-032, InDel-042, and InDel-046, were identified by single marker analysis to be significantly correlated to tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) and leaf spot resistance. Among them, three markers (InDel-032, InDel-042, and InDel-046) were associated to both TSWV and leaf spot resistance, but InDel-018 and 046 were only for leaf spot (Table 4). These markers were designed from conserved sequences of functional genes that were associated with alkaline alpha galactosidase, arachin Ahy-3, electron transporter/metal ion, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase, and ran GTPase binding, respectively. InDel-018 and InDel-046 were from the coding region, while InDel-016, InDel-032, and InDel-042 were from non-coding region (Table 2).
In general, the accessions carrying the alleles of the markers had a low leaf spot rate or low percentages of TSWV incidents (Table 5). For example, 43 accessions with InDel-018 alleles had an average of 2.9 leaf spot rate while 75 accessions without the alleles had an average of 4.1 (Table 5). Similar results were observed for TSWV, in which the accessions carrying the alleles of InDel-032 showed a low disease incident (10.7%) compared to the accessions that are lacking of the alleles (46.1%) (Table 5).
Table 5.
Significance (P-value) of associations between the InDel makers and the targeted traits.
| Marker | Leaf spot | TSWV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-value | Mean of rate | Number of lines | Genotype | P-value | Mean of rate | Number of lines | Genotype | |
| InDel-016 | 0.0099 | 3.9 | 81 | + | − | − | − | − |
| 3.1 | 37 | − | − | − | − | |||
| InDel-018 | < 0.0001 | 4.1 | 75 | + | − | − | − | − |
| 2.9 | 43 | − | − | − | − | |||
| InDel-032 | < 0.0001 | 4.1 | 104 | + | < 0.0001 | 46.1% | 104 | + |
| 0.28 | 14 | − | 10.7% | 14 | − | |||
| InDel-042 | < 0.0001 | 4.0 | 109 | + | < 0.0001 | 44.5% | 109 | + |
| 0 | 9 | − | 11.1% | 9 | − | |||
| InDel-046 | < 0.0001 | 3.9 | 110 | + | 0.0053 | 43.5% | 110 | + |
| 0.7 | 8 | − | 20% | 8 | − | |||
Discussion
Difference in genetic pattern or polymorphism is a main criterion to evaluate the potential functionality of DNA molecular markers. In the present study, the polymorphism of the InDel markers was 33.3%, which was higher than some markers that have been previously reported as to RAPD marker (6.6%) by Subramanian et al. (2000); AFLP marker (3.6%) by He and Prakash (1997); EST-SSR marker (10.4%) by Liang et al. (2009); SSR marker (14.5%) by Zhao et al. (2012) but was lower than Start Codon Targeted polymorphism (SCoT) marker (38.2%) as reported by Xiong et al. (2011) (Table 6). Among the reports, the numbers of accessions evaluated were much less than the 118 accessions used in this study. In general, the larger the number of accessions with diverse genetic background the higher the accuracy of estimated polymorphism associated with a particular trait. Therefore, our reported polymorphism for the InDel markers in this study can be useful in peanut breeding programs.
Table 6.
Comparisons of the polymorphism of various molecular markers developed in the previous reports.
| Marker | No. of markers tested | Polymorphic markers | Polymorphism rate (%) | No. of accessions tested | No. of botanical types | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RADP | 408 | 27 | 6.6 | 70 | 4 | Subramanian et al., 2000 |
| AFLP | 111 | 4 | 3.6 | 6 | 3 | He and Prakash, 1997 |
| EST-SSR | 251 | 26 | 10.4 | 22 | 4 | Liang et al., 2009 |
| SSR | 9274 | 1343 | 14.5 | 8 | Var. | Zhao et al., 2012 |
| ScoT | 157 | 60 | 38.2 | 20 | 4 | Xiong et al., 2011 |
| InDel | 48 | 16 | 33.3 | 118 | 6 | Present study |
Germplasm resources provide fundamental materials for peanut genetic improvement, and the study of genetic diversity on cultivated peanut will enhance the utilization of peanut genetic resources. Genetic diversity of six botanical types of cultivated peanuts has been extensively investigated using molecular markers. Based on SSR markers, Jiang et al. (2010) demonstrated that the accessions of fastigiata and hypogaea were more diversified than other botanical types. The genetic diversity of 72 accessions of the U.S. mini core was estimated using 67 SSR primer pairs and the results indicated that the PIC of SSR markers ranged from 0.063 to 0.918 and the gene diversity ranged from 0.027 to 0.50 (Kottapalli et al., 2007). In the present study, PICs varied from 0.176 for fastigiata var. to 0.660 for hirsuta var., and hirsuta var., peruviana var., and aequatoriana var. have higher genetic diversity than the other types, indicating that, like other molecular markers, InDel markers can be used for evaluation of genetic diversity for peanuts. Cluster analysis showed that hirsuta var. and aequatoriana var. have longest genetic distances from the other four types, indicating that hirsuta var. and aequatoriana var. have higher genetic diversity than the other types.
Unlike the QTL that using biparental RIL (Recombinant Inbred Lines) mapping populations to link markers with target traits, the identified marker trait association in present cannot validated in different backgrounds, but in our another apparel association mapping study we have extensively evaluated leaf spot and TSWV resistances for the U.S. mini-core collection and mapped three SSR markers named “pPGPseq2D12B,” “pPGSseq19B1,” and “TC04F12,” to be associated both with leaf spot and TSWV resistances. The marker “TC20B05” can explain 15% phenotypical variation of leaf spot resistance.
Regarding application of MAS in peanut, there are only two molecular markers currently being utilized in breeding programs: nematode resistance and high oleic seed chemistry. Chu et al. (2011) demonstrated that a tremendous reduction in the amount of time (at least 3-fold) for plant selection was achieved with MAS to pyramid nematode resistance with high oleic trait in peanut. This recent success is only possible due to the initial discovery of the genetic markers and the development of breeding lines. For example, the identification of high oleic marker was achieved by utilizing different genes in fatty acid biosynthesis for high oleic chemistry in other oil seed crops enabling a straightforward characterization in peanut and discovery of similar functional mutations in breeding populations (Jung et al., 2000; Lopez et al., 2002). Nematode resistance was introgressed from wild species (Simpson and Starr, 2001), and resistant plants were selected based on the availability of molecular markers at the time (Nagy et al., 2010). High Oleic trait resulted from the expression of two recessive genes (Lopez et al., 2001) while nematode resistance was determined to result from the expression of two dominant genes (Garcia et al., 1996). For other traits such as disease resistance or drought tolerance, complex interaction between genetic and environment poses daunting challenge to breeders to select resistant plants. Since InDel markers were developed from sequences of functional genes, they will lay the groundwork for the identification of genes related to superior agronomic traits, provide information on population genetic variations, and identify homologous genes for functional studies. Since InDel markers were found to be associated with leaf spot and TSWV resistance with a higher level of DNA polymorphism compared to other molecular markers, they provide a very useful type of molecular marker to identify other agronomical important traits in peanut.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Brian Gamble and Larry Wells for devoted assistance with management of field experiment research plots at the Wiregrass Research and Extension Center, Auburn University, Headland, Alabama. The contributions and assistances of Sam Hilton, Joseph Powell, Kathy Gray, Lori Riles, Dan Todd, Robin Barfield, Staci Ingram, and Bill Edwards from the USDA-ARS National Peanut Research Laboratory are gratefully acknowledged. The author, LL was sponsored by Grant of 948 project (2013-Z65) and The Excellent Going Abroad Experts Training Program in Hebei, China to conduct this research in Auburn University.
References
- Belamkar V., Selvaraj M. G., Ayers J. L., Payton P. R., Puppala N., Burow M. D., et al. (2011). A first insight into population structure and linkage disequilibrium in the US peanut minicore collection. Genetica 139, 411–429. 10.1007/s10709-011-9556-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burow M. D., Simpson C. E., Faries M. W., Starr J. L., Paterson A. H. (2009). Molecular biogeographic study of recently described B- and A-genome Arachis species, also providing new insights into the origins of cultivated peanut. Genome 52, 107–119. 10.1139/G08-094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burow M. D., Simpson C. E., Paterson A. H., Starr J. L. (1996). Identification of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) RAPD markers diagnostic of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal) Chitwood) resistance. Mol. Breeding 2, 369–319. 10.1007/BF00437915 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Barkley N. A., Wang M. L., Holbrook C. C., Dang P. M. (2014). Registration of purified accessions for the U.S. peanut mini-core germplasm collection. J. Plant Reg. 8, 77–85. 10.3198/jpr2013.01.0003crg [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chiteka Z. A., Gorbet D. W., Knauft D. A., Shokes F. M., Kucharek T. A. (1988). Components of resistance to late leaf spot in peanut. Peanut Sci. 15, 76–81. 10.3146/i0095-3679-15-2-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chu Y., Wu C. L., Holbrook C. C., Tillman B. L., Person G., Ozias-Akins P. (2011). Marker-assisted selection to pyramid nematode resistance and the high oleic trait in peanut. Plant Genome 4, 110–117. 10.3835/plantgenome2011.01.0001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cuc L. M., Mace E. S., Crouch J. H., Quang V. D., Long T. D., Varshney R. K. (2008). Isolation and characterization of novel microsatellite markers and their application for diversity assessment in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea). BMC Plant Biol. 8:55. 10.1186/1471-2229-8-55 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang P. M., Chen C. Y. (2013). Modified method for combined DNA and RNA isolation from peanut and other oil seeds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 40, 1563–1568. 10.1007/s11033-012-2204-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Wang X., Zhang X., Dang P. M., Holbrook C. C., Culbreath A. K., et al. (2012). Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) expressed sequence tag project: progress and application. Comp. Funct. Genomics 2012:373768. 10.1155/2012/373768 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia G. M., Stalker H. T., Shroeder E., Kochert G. (1996). Identification of RAPD, SCAR and RFLP markers tightly linked to nematode resistance genes introgressed from Arachis cardenasii to A. hypogaea. Genome 39, 836–845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautami B., Foncéka D., Pandey M. K., Moretzsohn M. C., Sujay V., Qin H., et al. (2012). An international reference consensus genetic map with 897 marker loci based on 11 mapping populations for tetraploid groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PLoS ONE 7:e41213. 10.1371/journal.pone.0041213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo B., Chen X., Hong Y., Liang X., Dang P., Brenneman T., et al. (2009). Analysis of gene expression profiles in leaf tissues of cultivated peanuts and development of EST- SSR markers and gene discovery. Int. J. Plant Genomics 2009:715605. 10.1155/2009/715605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He G. H., Prakash C. S. (1997). Identification of polymorphic DNA markers in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Euphytica 97, 143–149. 10.1023/A:1002949813052 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hong Y., Chen X., Liang X., Liu H., Zhou G., Li S., et al. (2010). A SSR-based composite genetic linkage map for the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genome. BMC Plant Biol. 10:17. 10.1186/1471-2229-10-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. C., Stam P. (1994). High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics 136, 1447–1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H. F., Ren X. P., Zhang X. J., Huang J. Q., Lei Y., Yan L. Y., et al. (2010). Comparison of genetic diversity between peanut mini core collections from China and ICRISAT by SSR markers. Acta Agr. Sin. 36, 1084-1091. 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2010.01084 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Huang L., Ren X., Chen Y., Zhou X., Xia Y., et al. (2014). Diversity characterization and association analysis of agronomic traits in a Chinese peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) mini-core collection. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 56, 159–169. 10.1111/jipb.12132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Swift D., Sengoku E., Patel M., Teule F., Powell G., et al. (2000). The high oleate trait in the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Isolation and characterization of two genes encoding microsomal oleoyl-PC desaturases. Mol. Gen. Genet. 263, 796–805. 10.1007/s004380000244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koilkonda P., Sato S., Tabata S., Shirasawa K., Hirakawa H., Sakai H., et al. (2012). Large-scale development of expressed sequence tag-derived simple sequence repeat markers and diversity analysis in Arachis spp. Mol. Breeding 30, 125–138. 10.1007/s11032-011-9604-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottapalli K. R., Burow M. D., Burow G., Burke J., Puppala N. (2007). Molecular characterization of the US peanut mini core collection using microsatellite markers. Crop Sci. 47, 1718–1727. 10.2135/cropsci2006.06.0407 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Chen X., Hong Y., Liu H., Zhou G., Li S., et al. (2009). Utility of EST-derived SSR in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and Arachis wild species. BMC Plant Biol. 9:35. 10.1186/1471-2229-9-35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Wang Y., Zhai W., Deng J., Wang H., Cui Y., et al. (2013). Development of InDel markers for Brassica rapa based on whole-genome re-sequencing. Theor. Appl. Genet. 126, 231–239. 10.1007/s00122-012-1976-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Y., Nadaf H. L., Smith O. D., Simpson C. E., Fritz A. K. (2002). Expressed variants of Delta(12)-fatty acid desaturase for the high oleate trait in spanish market-type peanut lines. Mol. Breeding 9, 183–190. 10.1023/A:1019767825486 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Y., Smith O. D., Senseman S. A., Rooney W. L. (2001). Genetic factors influencing high oleic acid content in Spanish market-type peanut cultivars. Crop Sci. 41, 51–56. 10.2135/cropsci2001.41151x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lv H. H., Yang L. M., Kang J. G., Wang Q. B., Wang X. W., Fang Z. Y., et al. (2013). Development of InDel markers linked to Fusarium wilt resistance in cabbage. Mol. Breeding 32, 961–967. 10.1007/s11032-013-9925-x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moretzsohn M. C., Gouvea E. G., Inglis P. W., Leal-Bertioli S. C., Valls J. F., Bertioli D. J. (2013). A study of the relationships of cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea) and its most closely related wild species using intron sequences and microsatellite markers. Ann. Bot. 111, 113–126. 10.1093/aob/mcs237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukri G., Nadaf H. L., Bhat R. S., Gowda M. V. C., Upadhyaya H. D., Sujay V. (2012). Phenotypic and molecular dissection of ICRISAT mini core collection of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) for high oleic acid. Plant Breeding 131, 418–422. 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2012.01970.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy E. D., Chu Y., Guo Y., Khanal S., Tang S., Li Y., et al. (2010). Recombination is suppressed in an alien introgression in peanut harboring Rma, a dominant root-knot nematode resistance gene. Mol. Breed. 26, 357–370. 10.1007/s11032-010-9430-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy E. D., Guo Y., Tang S., Bowers J. E., Okashah R. A., Taylor C. A., et al. (2012). A high-density genetic map of Arachis duranensis, a diploid ancestor of cultivated peanut. BMC Genomics 13:469. 10.1186/1471-2164-13-469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin H. D., Feng S. P., Chen C., Guo Y., Knapp S., Culbreath A., et al. (2012). An integrate genetic linkage map of cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) constructed from two RIL populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 124, 653–664. 10.1007/s00122-011-1737-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina S. N., Rani V., Kojima T., Ogihara Y., Singh K. P., Devarumath R. M. (2001). RAPD and ISSR fingerprints as useful genetic markers for analysis of genetic diversity, varietal identification, and phylogenetic relationships in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) cultivars and wild species. Genome 44, 763–772. 10.1139/gen-44-5-763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravi K., Vadez V., Isobe S., Mir R. R., Guo Y., Nigam S. N., et al. (2011). Identification of several small main-effect QTLs and a large number of epistatic QTLs for drought tolerance related traits in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 122, 1119–1132. 10.1007/s00122-010-1517-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren X. P., Zhang X. J., Liao B. S., Lei Y., Huang J. Q., Chen Y. N., et al. (2010). Analysis of genetic diversity in ICRISAT mini core collection of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by SSR markers. Sci. Agr. Sin. 43, 2848–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Rockah-Shmuel L., Tóth-Petróczy Á., Sela A., Wurtzel O., Sorek R., Tawfik D. S. (2013). Correlated occurrence and bypass of frame-shifting insertion-deletions (InDels) to give functional proteins. PLoS Genet 9:e1003882. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute (2009). SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 9.2. Cary, NC: SAS Inst. [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa K., Bertioli D. J., Varshney R. K., Moretzsohn M. C., Leal-Bertioli S. C., Thudi M., et al. (2013). Integrated consensus map of cultivated peanut and wild relatives reveals structures of the A and B genomes of Arachis and divergence of the legume genomes. DNA Res. 20, 173–184. 10.1093/dnares/dss042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson C. E., Starr J. L. (2001). Registration of ‘COAN’ peanut. Crop Sci. 41, 918 10.2135/cropsci2001.413918x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian V., Gurtu S., Nageswara Rao R. C., Nigam S. N. (2000). Identification of DNA polymorphism in cultivated groundnut using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay. Genome 43, 656–660. 10.1139/g00-034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sujay V., Gowda M. V., Pandey M. K., Bhat R. S., Khedikar Y. P., Nadaf H. L., et al. (2012). Quantitative trait locus analysis and construction of consensus genetic map for foliar disease resistance based on two recombinant inbred line populations in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol. Breeding 30, 773–788. 10.1007/s11032-011-9661-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Dudley J., Nei M., Kumar S. (2007). MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599. 10.1093/molbev/msm092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D. (1989). Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 6463–6471. 10.1093/nar/17.16.6463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillman B. L., Gorbet D. W., Andersen P. C. (2007). Influence of planting date on yield and tomato spotted wilt of runner market type peanut. Peanut Sci. 34, 79–84. 10.3146/0095-3679(2007)34[79:IOPDOY]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya H. D., Mukri G., Nadaf H. L., Singh S. (2012). Variability and stability analysis for nutritional traits in the mini core collection of peanut. Crop Sci. 52, 168–178. 10.2135/cropsci2011.05.0248 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney R. K., Bertioli D. J., Moretzsohn M. C., Vadez V., Krishnamurthy L., Aruna R., et al. (2009). The first SSR-based genetic linkage map for cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 118, 729–739. 10.1007/s00122-008-0933-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Hogers R., Bleeker M., Reijans M., van de Lee T., Hornes M., et al. (1995). AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl. Acids Res. 23, 4407–4414. 10.1093/nar/23.21.4407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Penmetsa R. V., Yuan M., Gong L., Zhao Y., Guo B., et al. (2012). Development and characterization of BAC-end sequence derived SSRs, and their incorporation into a new higher density genetic map for cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol. 12:10. 10.1186/1471-2229-12-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Chen C. Y., Tonnis B., Barkley N. A., Pinnow D. L., Pittman R. N., et al. (2013). Oil, fatty acid, flavonoid, and resveratrol content variability and FAD2A functional SNP genotypes in the U.S. peanut mini-core collection. J. Agr. Food Chem. 61, 2875–2882. 10.1021/jf305208e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Sukumaran S., Barkley N. A., Chen Z., Chen C. Y., Guo B., et al. (2011). Population structure and marker-trait association analysis of the US peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) mini-core collection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 123, 1307–1317. 10.1007/s00122-011-1668-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. (1990). DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6531–6535. 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K., Yang M., Liu H., Tao Y., Mei J., Zhao Y. (2014). Genetic analysis and molecular characterization of Chinese sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cultivars using insertion-deletion (InDel) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. BMC Genet 15:35. 10.1186/1471-2156-15-35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong F., Zhong R., Han Z., Jiang J., He L., Zhuang W., et al. (2011). Start codon targeted polymorphism for evaluation of functional genetic variation and relationships in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38, 3487–3494. 10.1007/s11033-010-0459-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaki S., Ohyanagi H., Yamasaki M., Eiguchi M., Miyabayashi T., Kubo T., et al. (2013). Development of INDEL markers to discriminate all genome types rapidly in the genus Oryza. Breeding Sci. 63, 246–254. 10.1270/jsbbs.63.246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Liang S., Duan J., Wang J., Chen S., Cheng Z., et al. (2012). De novo assembly and characterization of the transcriptome during seed development, and generation of genic-SSR markers in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Genomics 13:90. 10.1186/1471-2164-13-90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y. L., Prakash C. S., He G. (2012). Characterization and compilation of polymorphic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers of peanut from public database. BMC Res. Notes 5, 362–369. 10.1186/1756-0500-5-362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zietkiewicz E., Rafalski A., Labuda D. (1994). Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20, 176–183. 10.1006/geno.1994.1151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]