Abstract
BACKGROUND: Impedance measurements by the forced pseudo random noise oscillation technique can be used to study the mechanical characteristics of the respiratory system. The objective of this study was to analyse the changes in impedance to a cold air provocation test in patients with asthma, and to correlate these changes with those in the forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). METHODS: The response to isocapnic hyperventilation with cold air was assessed by respiratory impedance measurements and spirometry in 60 patients with bronchial asthma in whom the provocative dose of histamine resulting in a 20% fall in FEV1 (PD20) was < or = 8 mumol. RESULTS: Cold air provocation resulted in a mean(SD) fall in FEV1 from 3.75(0.85) litres to 3.10(0.90) litres. The mean(SD) decrease in FEV1 as a percentage of predicted was 15.4(3.8)%. The oscillatory resistance at 8 Hz increased from a mean(SD) of 0.367(0.108) kPa/l/s to 0.613(0.213) kPa/l/s and at 28 Hz the resistance increased from 0.348(0.089) to 0.403(0.099) kPa/l/s. Frequency dependence of resistance became significantly more negative. The reactance at 8 Hz decreased from a mean(SD) of -0.035 (0.041) kPa/l/s to -0.234(0.199) kPa/l/s, and the resonant frequency increased from 12.5(4.9) Hz to 25.7(9.1) Hz. Significant correlations were calculated between the decrease in FEV1 and changes in the various impedance parameters, especially between the decrease in FEV1 and the increase in resistance at 8 Hz (r = -0.66), and the decrease in FEV1 and the increase in the resonant frequency (r = -0.63). CONCLUSION: Cold air provocation in asthmatic subjects results in changes in the impedance of the respiratory system that correlate well with the changes in FEV1. These changes in impedance reflect ventilatory inhomogeneities in the peripheral compartment of the bronchial tree. These observations show the value of this technique in the evaluation of induced bronchoconstriction, as both a quantitative and a qualitative analysis of the response is possible.
Full text
PDF
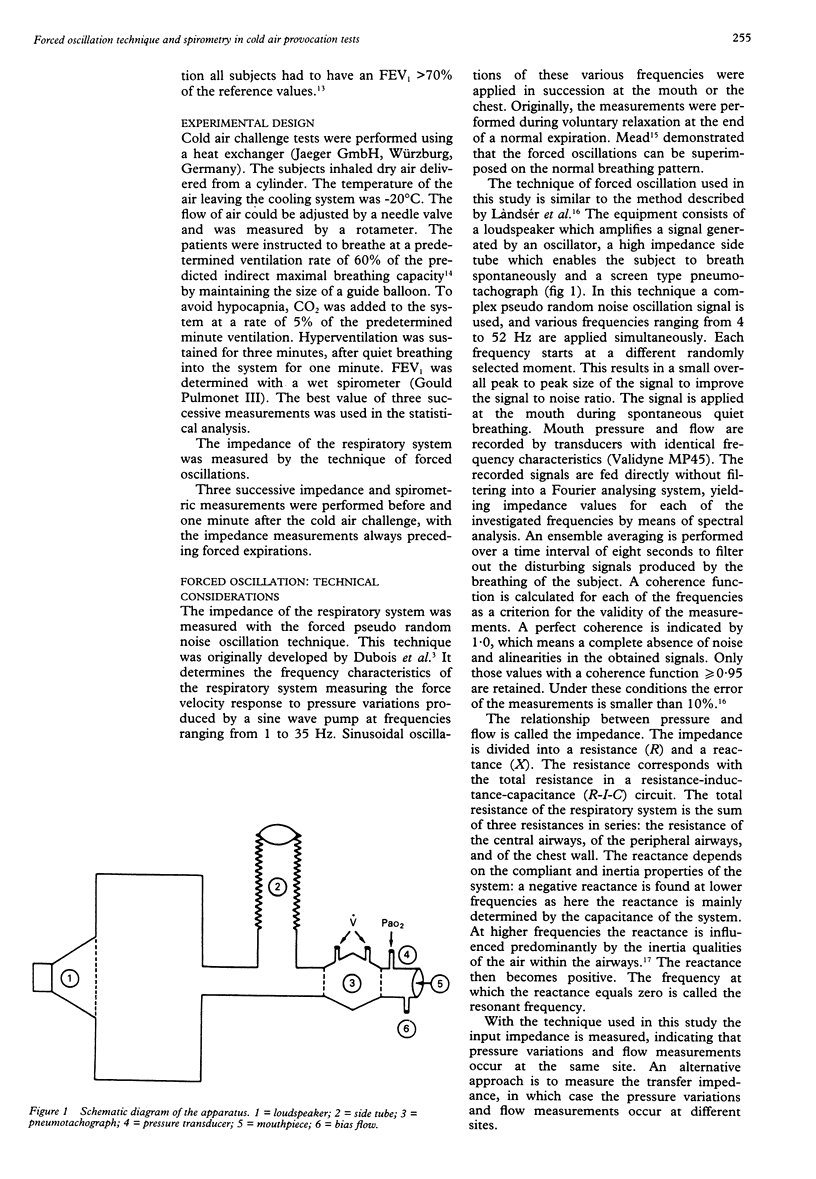

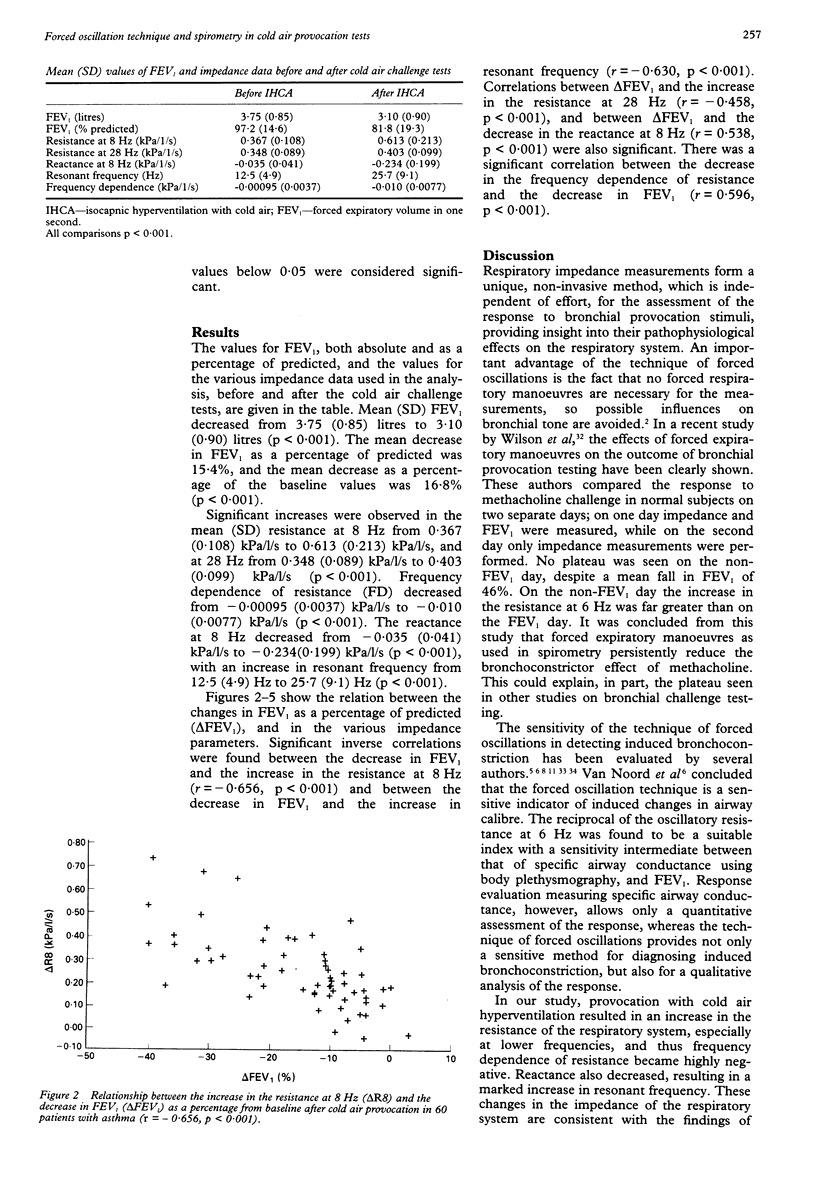
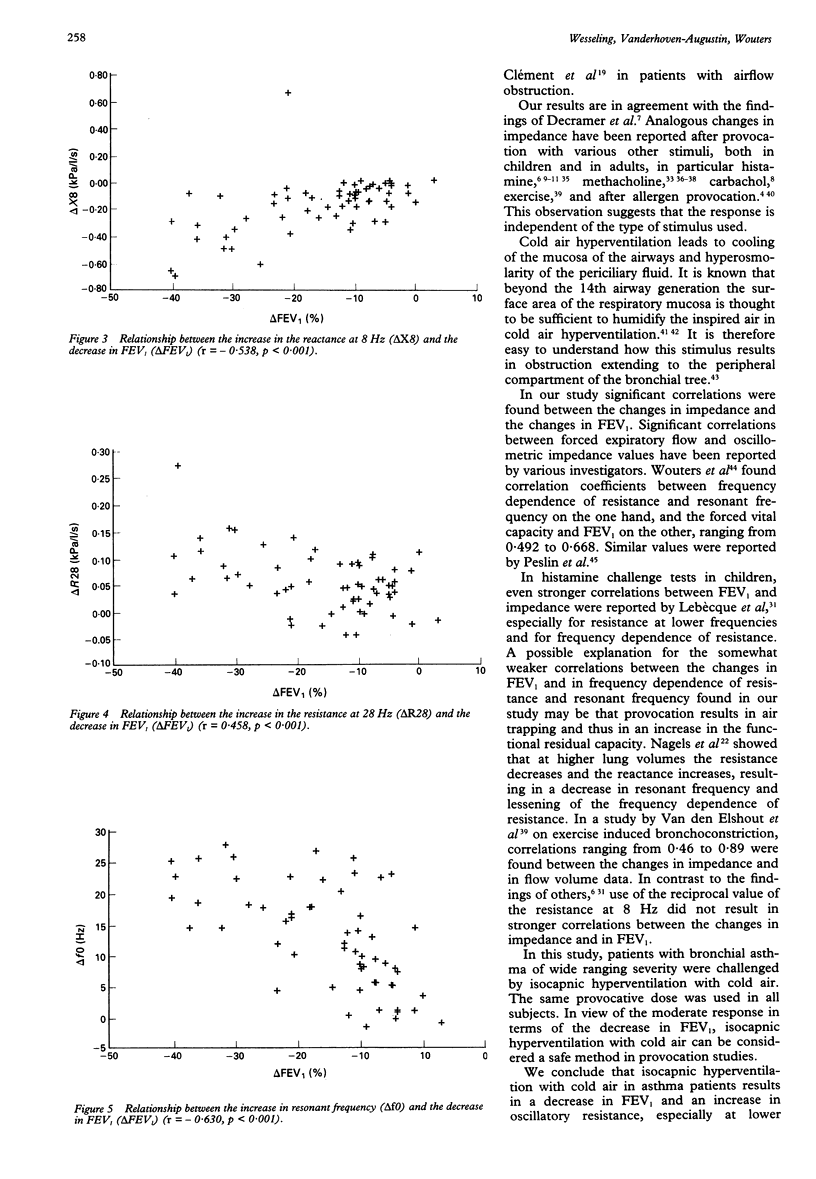

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoufi B. K., Dally M. B., Newman-Taylor A. J., Denison D. M. Cold air test: a simplified standard method for airway reactivity. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Jul-Aug;22(4):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates J. H., Decramer M., Zin W. A., Harf A., Milic-Emili J., Chang H. K. Respiratory resistance with histamine challenge by single-breath and forced oscillation methods. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Sep;61(3):873–880. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brochard L., Pelle G., de Palmas J., Brochard P., Carre A., Lorino H., Harf A. Density and frequency dependence of resistance in early airway obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):579–584. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauberghs M., Van de Woestijne K. P. Effect of upper airway shunt and series properties on respiratory impedance measurements. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 May;66(5):2274–2279. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.5.2274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinet T., Pelle G., Macquin-Mavier I., Lorino H., Harf A. Comparison of the dose-response curves obtained by forced oscillation and plethysmography during carbachol inhalation. Eur Respir J. 1988 Jul;1(7):600–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J., Làndsér F. J., Van de Woestijne K. P. Total resistance and reactance in patients with respiratory complaints with and without airways obstruction. Chest. 1983 Feb;83(2):215–220. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BRODY A. W., LEWIS D. H., BURGESS B. F., Jr Oscillation mechanics of lungs and chest in man. J Appl Physiol. 1956 May;8(6):587–594. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.8.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decramer M., Demedts M., van de Woestijne K. P. Isocapnic hyperventilation with cold air in healthy non-smokers, smokers and asthmatic subjects. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1984 May-Jun;20(3):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duiverman E. J., Neijens H. J., Van der Snee-van Smaalen M., Kerrebijn K. F. Comparison of forced oscillometry and forced expirations for measuring dose-related responses to inhaled methacholine in asthmatic children. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Sep-Oct;22(5):433–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duiverman E. J., Neijens H. J., van Strik R., van der Snee-van Smaalen M., Kerrebijn K. F. Bronchial responsiveness in asthmatic children aged 3 to 8 years measured by forced pseudo-random noise oscillometry. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Jan-Feb;22(1):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feihl F., Badan M., Depeursinge F., Depeursinge C., Leuenberger P., Pécoud A., Perret C. Respiratory acoustical impedance: a new technique to measure airway response during bronchial inhalation challenges. Ann Allergy. 1988 Oct;61(4):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed A. N., Kelly L. J., Menkes H. A. Airflow-induced bronchospasm. Imbalance between airway cooling and airway drying? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):595–599. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayrard P., Orehek J., Grimaud C., CHarpin J. Bronchoconstrictor effects of a deep inspiration in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):433–439. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimby G., Takishima T., Graham W., Macklem P., Mead J. Frequency dependence of flow resistance in patients with obstructive lung disease. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1455–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI105837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for standardization of bronchial challenges with (nonspecific) bronchoconstricting agents. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Sep-Oct;19(5):495–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harf A., Decramer M., Zin W., Milic-Emili J., Chang H. K. Respiratory resistance in dogs by the single-breath and the forced oscillation methods. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Jul;59(1):262–265. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.1.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebecque P., Spier S., Lapierre J. G., Lamarre A., Zinman R., Coates A. L. Histamine challenge test in children using forced oscillation to measure total respiratory resistance. Chest. 1987 Aug;92(2):313–318. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lándsér F. J., Nagles J., Demedts M., Billiet L., van de Woestijne K. P. A new method to determine frequency characteristics of the respiratory system. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Jul;41(1):101–106. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manço J. C., Hyatt R. E., Rodarte J. R. Respiratory impedance in normal humans: effects of bronchodilatation and bronchoconstriction. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987 Jun;62(6):487–497. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65475-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Lenner K. A., Strohl K. P. Postexertional airway rewarming and thermally induced asthma. New insights into pathophysiology and possible pathogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):18–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI112549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. Contribution of compliance of airways to frequency-dependent behavior of lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1969 May;26(5):670–673. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.5.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson E. D., Grassman E. D., Peters W. R. Pulmonary mechanics by spectral analysis of forced random noise. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1210–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI108198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. K., 3rd, Pimmel R. L. Standard errors on respiratory mechanical parameters obtained by forced random excitation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1983 Dec;30(12):826–832. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1983.325085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagels J., Làndsér F. J., van der Linden L., Clément J., Van de Woestijne K. P. Mechanical properties of lungs and chest wall during spontaneous breathing. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Sep;49(3):408–416. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neild J. E., Twort C. H., Chinn S., McCormack S., Jones T. D., Burney P. G., Cameron I. R. The repeatability and validity of respiratory resistance measured by the forced oscillation technique. Respir Med. 1989 Mar;83(2):111–118. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(89)80224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peslin R., Duvivier C., Gallina C., Cervantes P. Upper airway artifact in respiratory impedance measurements. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):712–714. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimmel R. L., Fullton J. M., Ginsberg J. F., Hazucha M. J., Haak E. D., McDonnell W. F., Bromberg P. A. Correlation of airway resistance with forced random noise resistance parameters. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jul;51(1):33–39. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotger M., Peslin R., Navajas D., Gallina C., Duvivier C. Density dependence of respiratory input impedance re-evaluated with a head generator minimizing upper airway shunt. Eur Respir J. 1988 May;1(5):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snashall P. D., Parker S., Ten Haave P., Simmons D., Noble M. I. Use of an impedance meter for measuring airways responsiveness to histamine. Chest. 1991 May;99(5):1183–1185. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.5.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solymar L., Aronsson P. H., Engström I., Bake B., Bjure J. Forced oscillation technique and maximum expiratory flows in bronchial provocation tests in children. Eur J Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;65(7):486–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjwa M. K., Smeets J. J., Jansen L. P., Maesen F. P. Measurement of the non-specific threshold stimulus for the bronchial tree by continuous monitoring of respiratory resistance using the oscillation method. Respiration. 1985;48(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000194792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N. M., Phagoo S. B., Silverman M. Use of transcutaneous oxygen tension, arterial oxygen saturation, and respiratory resistance to assess the response to inhaled methacholine in asthmatic children and normal adults. Thorax. 1991 Jun;46(6):433–437. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.6.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters E. F., Mostert R., Polko A. H., Visser B. F. Forced expiratory flow and oscillometric impedance measurement in evaluating airway obstruction. Respir Med. 1990 May;84(3):205–209. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters E. F., Polko A. H., Schouten H. J., Visser B. F. Contribution of impedance measurement of the respiratory system to bronchial challenge tests. J Asthma. 1988;25(5):259–267. doi: 10.3109/02770908809073211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters E. F., Polko A. H., Visser B. F. Response localization of the pharmacological agents histamine and salbutamol along the respiratory system by forced oscillations in asthmatic subjects. J Asthma. 1989;26(3):185–193. doi: 10.3109/02770908909070989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters E. F. Total respiratory impedance measurement by forced oscillations: a noninvasive method to assess bronchial response in occupational medicine. Exp Lung Res. 1990 Jan;16(1):25–40. doi: 10.3109/01902149009064697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying Y., Peslin R., Duvivier C., Gallina C., Felicio da Silva J. Respiratory input and transfer mechanical impedances in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 1990 Nov;3(10):1186–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Noord J. A., Clement J., van de Woestijne K. P., Demedts M. Total respiratory resistance and reactance as a measurement of response to bronchial challenge with histamine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Apr;139(4):921–926. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.4.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


