Abstract
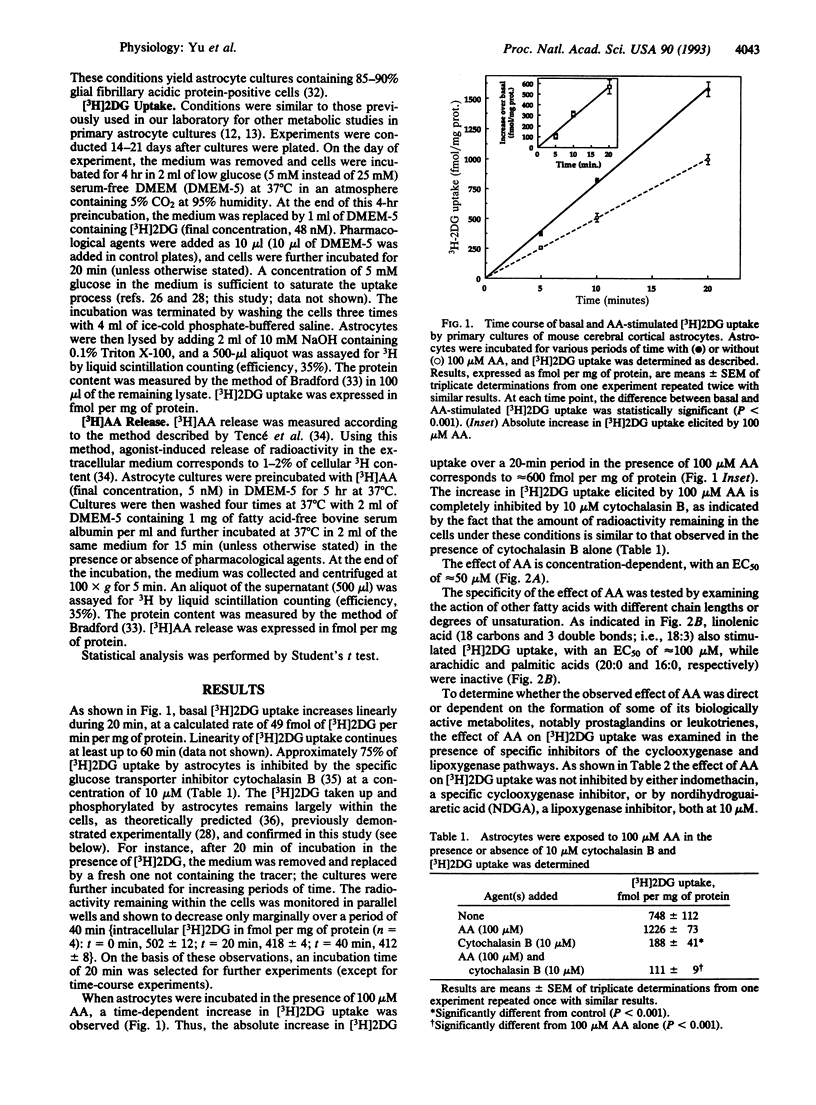
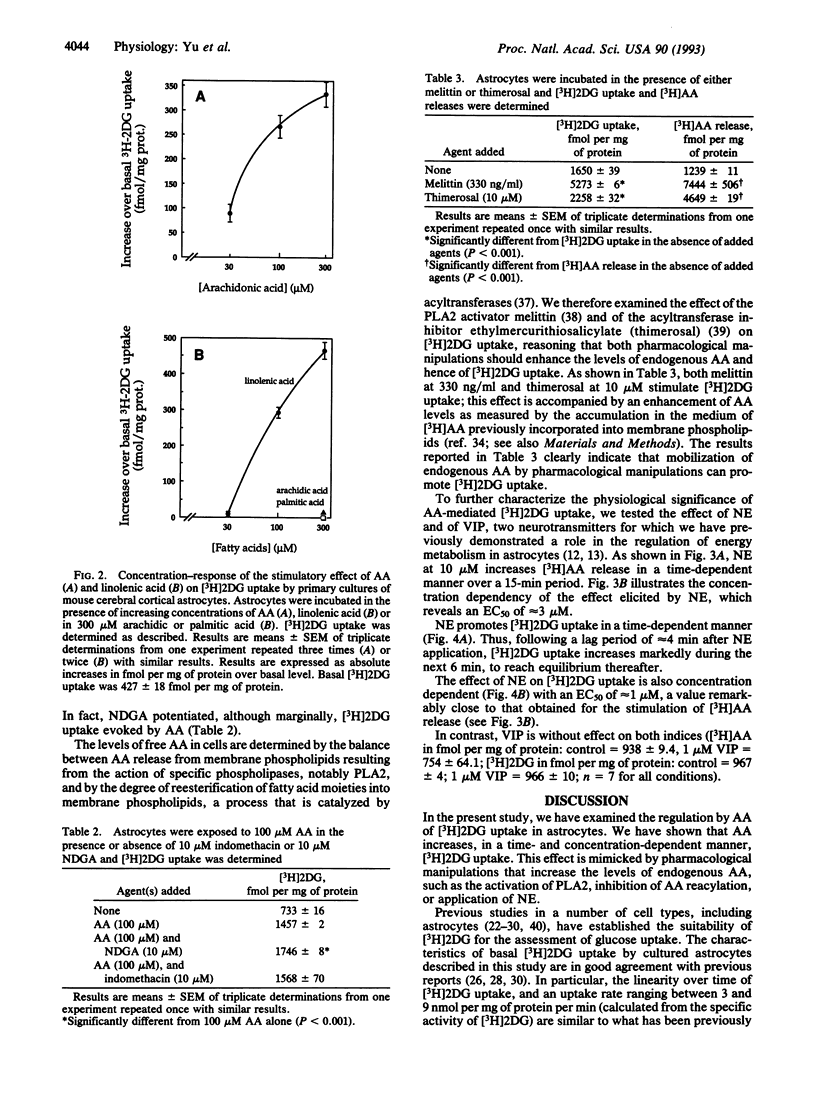
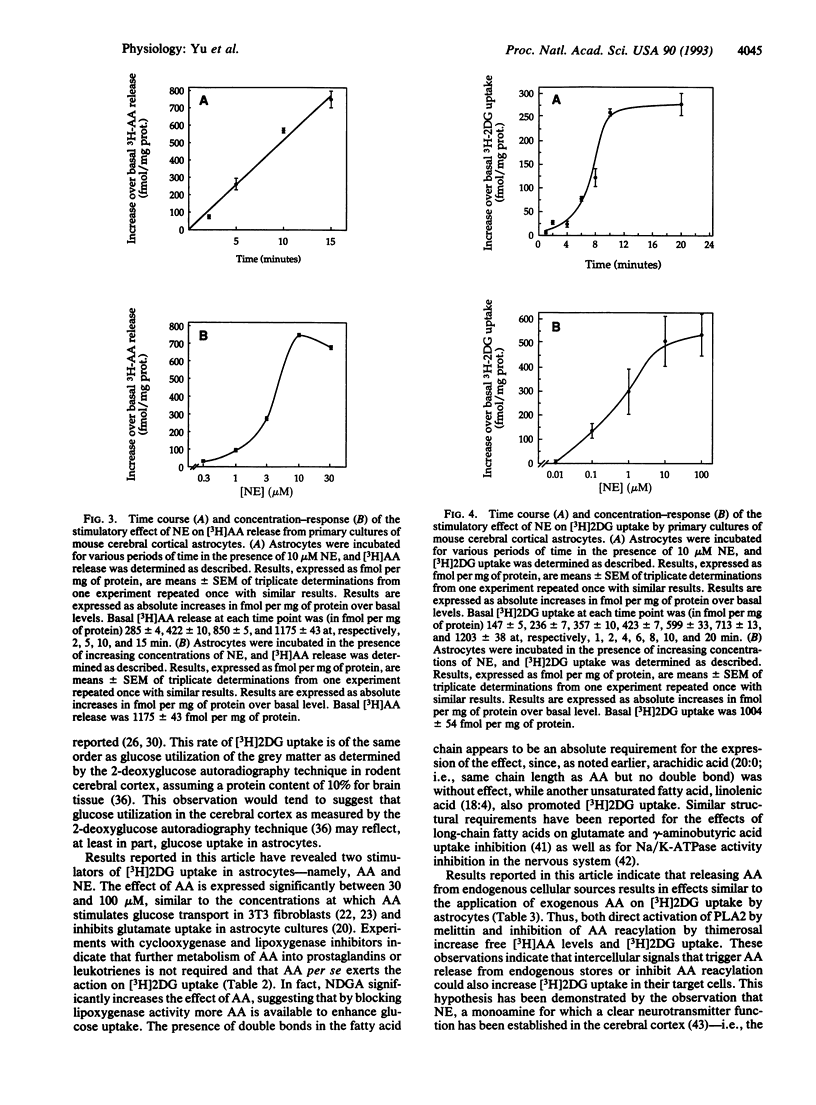
Arachidonic acid (AA) has recently been shown to influence various cellular functions in the central nervous system. Here we report that AA increases, in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, 2-deoxy-D-[1-3H]glucose ([3H]2DG) uptake in primary cultures of astrocytes prepared from the cerebral cortex of neonatal mice. This effect is mimicked by an unsaturated fatty acid such as linolenic acid, while palmitic and arachidic acids, two saturated fatty acids, are inactive. Pharmacological agents that increase the endogenous levels of AA by stimulating AA release (melittin) or by inhibiting its reacylation (thimerosal) also promote [3H]2DG uptake by astrocytes. We also report that norepinephrine (NE) stimulates the release of [3H]AA from membrane phospholipids, with an EC50 of 3 microM; this effect is accompanied, with a temporal delay of approximately 4 min, by the stimulation of [3H]2DG uptake, for which the EC50 of NE is 1 microM. Since the cerebral cortex, the brain region from which astrocytes used in this study were prepared, receives a massive noradrenergic innervation, originating from the locus coeruleus, the effects of NE reported here further stress the notion that certain neurotransmitters may play a role in the regulation of energy metabolism in the cerebral cortex and point at astrocytes as the likely targets of such metabolic effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aston-Jones G., Bloom F. E. Norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats exhibit pronounced responses to non-noxious environmental stimuli. J Neurosci. 1981 Aug;1(8):887–900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-08-00887.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan N. G., Birkle D. L., Tang W., Reddy T. S. The accumulation of free arachidonic acid, diacylglycerols, prostaglandins, and lipoxygenase reaction products in the brain during experimental epilepsy. Adv Neurol. 1986;44:879–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. C., Samih A., Franks S. Uptake, distribution and release of 3H-arachidonic acid from human endometrium. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1990 Feb;39(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(90)90019-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes N., Yarowsky P. J. Determinants of deoxyglucose uptake in cultured astrocytes: the role of the sodium pump. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Kerlan R., Fishman R. A. Reductions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate uptake and (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity in brain slices and synaptosomes by arachidonic acid. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. W., Boyd F. T., Jr, Kappy M. S., Raizada M. K. Insulin binds to specific receptors and stimulates 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in cultured glial cells from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11672–11675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins C. J., Glover R. A., Sellinger O. Z. Astroglial uptake is modulated by extracellular K+. J Neurochem. 1979 Sep;33(3):779–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazeli M. S. Synaptic plasticity: on the trail of the retrograde messenger. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Apr;15(4):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90350-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. L., Bloom F. E., Aston-Jones G. Nucleus locus ceruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jul;63(3):844–914. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.3.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. L., Morrison J. H. Extrathalamic modulation of cortical function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:67–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin A. R. A study of the mechanisms by which potassium moves through brain tissue in the rat. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:353–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouras P. Identification of cone mechanisms in monkey ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):533–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. F., Rampal A. L., Jung C. Y. Inhibition of glucose transport in human erythrocytes by cytochalasins: A model based on diffraction studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3759–3763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki Y., Morita I., Murota S. Arachidonic acid metabolism in cultured astrocytes from rat embryo and in C6 glioma cells. Brain Res. 1989 Aug 7;494(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti J., Dettori C., Meldolesi J. Glucose transport stimulation by bradykinin in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism operates without involvement of arachidonic acid and cyclic AMP. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jan;192(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90158-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J., Morrison J. H., Shoemaker W. J., Sapin V., Bloom F. E. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide induces glycogenolysis in mouse cortical slices: a possible regulatory mechanism for the local control of energy metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6535–6539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J. VIP neurons in the cerebral cortex. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Pearce B. Functional receptors for neurotransmitters on astroglial cells. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce B., Cambray-Deakin M., Murphy S. Astrocyte opioid receptors: activation modifies the noradrenaline-evoked increase in 2-[14C]deoxyglucose incorporation into glycogen. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Apr 9;55(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poitry-Yamate C. L., Tsacopoulos M. Glucose metabolism in freshly isolated Müller glial cells from a mammalian retina. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Jun 8;320(2):257–266. doi: 10.1002/cne.903200209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. E., Kaplan M. A., Peterson N. A., Raghupathy E. Effects of free fatty acids on synaptosomal amino acid uptake systems. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1255–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder L. M., Williams I. B., Tildon J. T. Glucose transport in astrocytes: regulation by thyroid hormone. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1653–1657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T. Activation of high levels of endogenous phospholipase A2 in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Wolfe L. S. Arachidonic acid cascade and signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorg O., Magistretti P. J. Characterization of the glycogenolysis elicited by vasoactive intestinal peptide, noradrenaline and adenosine in primary cultures of mouse cerebral cortical astrocytes. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 1;563(1-2):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91538-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorg O., Magistretti P. J. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and noradrenaline exert long-term control on glycogen levels in astrocytes: blockade by protein synthesis inhibition. J Neurosci. 1992 Dec;12(12):4923–4931. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-12-04923.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa N., Takuwa Y., Rasmussen H. Stimulation of mitogenesis and glucose transport by 1-monooleoylglycerol in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9738–9745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tencé Martine, Cordier Jocelyne, Glowinski Jacques, Prémont Joël. Endothelin-evoked Release of Arachidonic Acid from Mouse Astrocytes in Primary Culture. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(10):993–999. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxinger R. R., Marshall S. Suitability of 2-deoxyglucose for measuring initial rates of glucose uptake in isolated adipocytes. Biochem Int. 1990 Nov;22(4):607–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volterra A., Trotti D., Cassutti P., Tromba C., Salvaggio A., Melcangi R. C., Racagni G. High sensitivity of glutamate uptake to extracellular free arachidonic acid levels in rat cortical synaptosomes and astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1992 Aug;59(2):600–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz W., Hertz L. Ouabain-sensitive and ouabain-resistant net uptake of potassium into astrocytes and neurons in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):70–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarowsky P., Boyne A. F., Wierwille R., Brookes N. Effect of monensin on deoxyglucose uptake in cultured astrocytes: energy metabolism is coupled to sodium entry. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):859–866. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00859.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. C., Chan P. H., Fishman R. A. Effects of arachidonic acid on glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake in primary cultures of rat cerebral cortical astrocytes and neurons. J Neurochem. 1986 Oct;47(4):1181–1189. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



