Abstract
BACKGROUND--Open lung biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis in patients with suspected fibrosing alveolitis. The superior sensitivity and specificity of high resolution computed tomography (CT) over chest radiography in various diffuse lung diseases suggest that the characteristic appearance of fibrosing alveolitis on high resolution CT might render biopsy confirmation unnecessary. METHODS--The chest radiographs and high resolution CT scans of 86 patients (41 with fibrosing alveolitis and 45 with various other diffuse lung diseases) were examined individually and independently by two observers. No clinical information was given and the observers gave a level of confidence when the diagnosis was thought to be fibrosing alveolitis. RESULTS--The observers correctly and confidently discriminated between fibrosing alveolitis and other diffuse lung diseases on high resolution CT with an accuracy of 88% and on chest radiography with an accuracy of 76%. The false negative rate for fibrosing alveolitis diminished from 29% on chest radiography to 11% on high resolution CT. The false positive rate on chest radiography was 19% and on high resolution CT 13%; the false positive diagnoses on CT were the result of a few conditions (extrinsic allergic alveolitis, sarcoidosis, cryptogenic organising pneumonia, and pulmonary eosinophilia) which mimicked some of the CT features of fibrosing alveolitis. The superficial similarity of the CT patterns of these conditions are discussed. CONCLUSIONS--High resolution CT is superior to chest radiography in establishing the diagnosis of fibrosing alveolitis and the typical CT appearances are virtually pathognomonic. The diagnostic advantages of CT over chest radiography should further reduce the need for open lung biopsy in this condition.
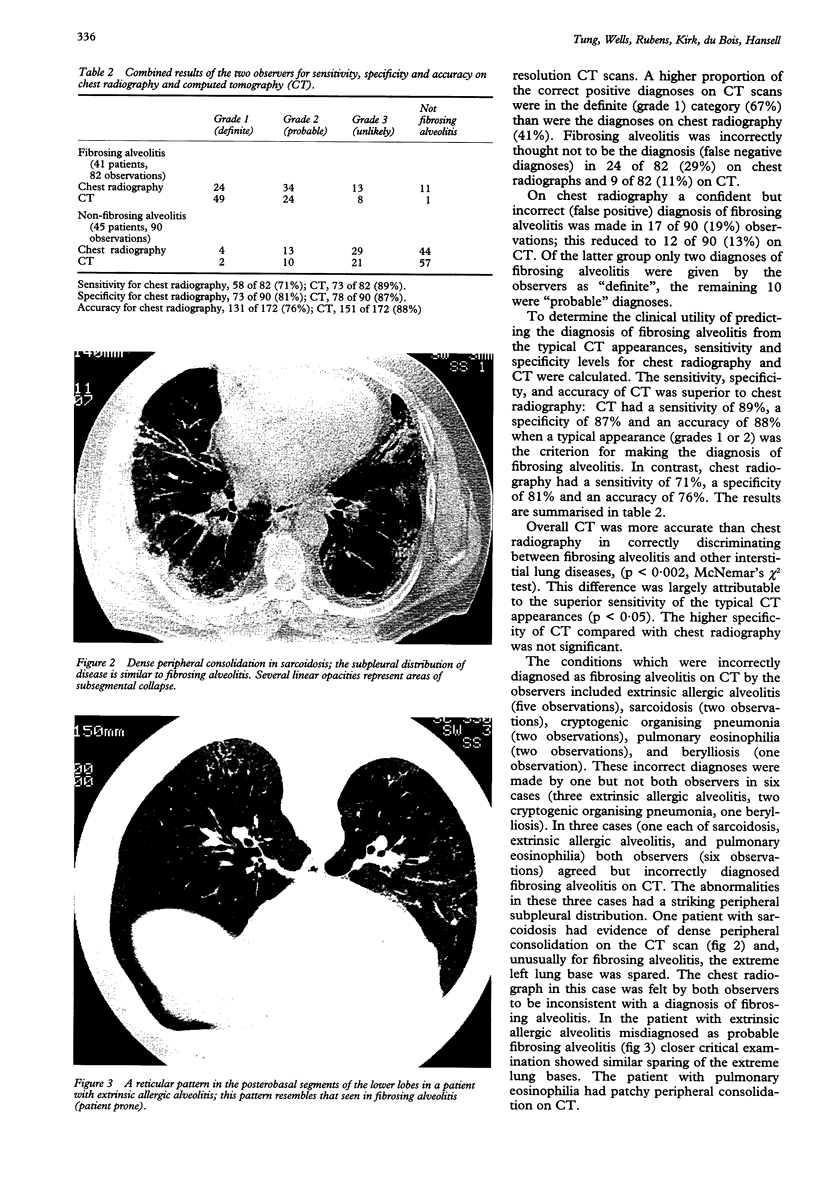
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergin C. J., Coblentz C. L., Chiles C., Bell D. Y., Castellino R. A. Chronic lung diseases: specific diagnosis by using CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 Jun;152(6):1183–1188. doi: 10.2214/ajr.152.6.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A., Coutu R. E., FitzGerald M. X., Gupta R. G. Natural history and treated course of usual and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 13;298(15):801–809. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804132981501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Carrington C. B. Open biopsy for chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease: clinical, roentgenographic, and physiological correlations in 502 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1980 Nov;30(5):411–426. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)61291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer H. S., Levitt R. G., Shackelford G. D. Peripheral pulmonary infiltrates in sarcoidosis. Chest. 1984 Nov;86(5):741–744. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.5.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier P., Valeyre D., Cluzel P., Brauner M. W., Lenoir S., Chastang C. Chronic diffuse interstitial lung disease: diagnostic value of chest radiography and high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1991 Apr;179(1):123–132. doi: 10.1148/radiology.179.1.2006262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansell D. M., Coleman R., du Bois R. M., Carr D. H., Goodman L. R., Kerr I. H., Pearson M. C., Rubens M. B. Advanced multiple beam equalization radiography (AMBER) in the detection of diffuse lung disease. Clin Radiol. 1991 Oct;44(4):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(05)80184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansell D. M., Coleman R., du Bois R. M., Carr D. H., Goodman L. R., Kerr I. H., Pearson M. C., Rubens M. B. Advanced multiple beam equalization radiography (AMBER) in the detection of diffuse lung disease. Clin Radiol. 1991 Oct;44(4):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(05)80184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban R. H., Meziane M. A., Zerhouni E. A., Khouri N. F., Fishman E. K., Wheeler P. S., Dumler J. S., Hutchins G. M. High resolution computed tomography of inflation-fixed lungs. Pathologic-radiologic correlation of centrilobular emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4):935–940. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L. K. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Chest Med. 1982 Sep;3(3):579–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. E., Jr Diagnostic advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1991 Jul;100(1):238–241. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.1.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieson J. R., Mayo J. R., Staples C. A., Müller N. L. Chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease: comparison of diagnostic accuracy of CT and chest radiography. Radiology. 1989 Apr;171(1):111–116. doi: 10.1148/radiology.171.1.2928513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo J. R., Müller N. L., Road J., Sisler J., Lillington G. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia: CT findings in six cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 Oct;153(4):727–730. doi: 10.2214/ajr.153.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L. Clinical value of high-resolution CT in chronic diffuse lung disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991 Dec;157(6):1163–1170. doi: 10.2214/ajr.157.6.1950859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L., Miller R. R. Computed tomography of chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease. Part 1. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1206–1215. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L., Miller R. R., Webb W. R., Evans K. G., Ostrow D. N. Fibrosing alveolitis: CT-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1986 Sep;160(3):585–588. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.3.3737898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N. L., Staples C. A., Miller R. R. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: CT features in 14 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990 May;154(5):983–987. doi: 10.2214/ajr.154.5.2108572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland B., Strickland N. H. The value of high definition, narrow section computed tomography in fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Radiol. 1988 Nov;39(6):589–594. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(88)80056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Burrows B., Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax. 1980 Mar;35(3):171–180. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb W. R., Stein M. G., Finkbeiner W. E., Im J. G., Lynch D., Gamsu G. Normal and diseased isolated lungs: high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1988 Jan;166(1 Pt 1):81–87. doi: 10.1148/radiology.166.1.3336706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. H., Heard B. E., Steel S. J., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: assessment by graded trephine lung biopsy histology compared with clinical, radiographic, and physiological features. Br J Dis Chest. 1981 Jan;75(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(81)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






