Abstract
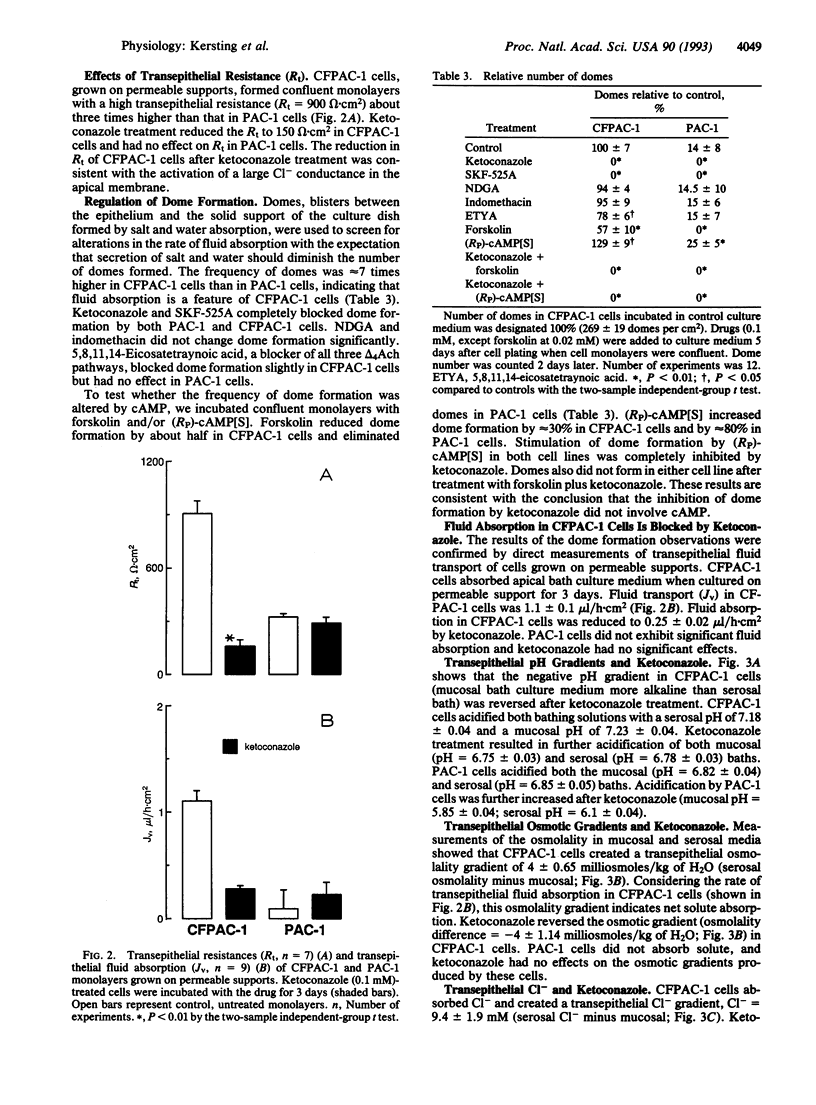
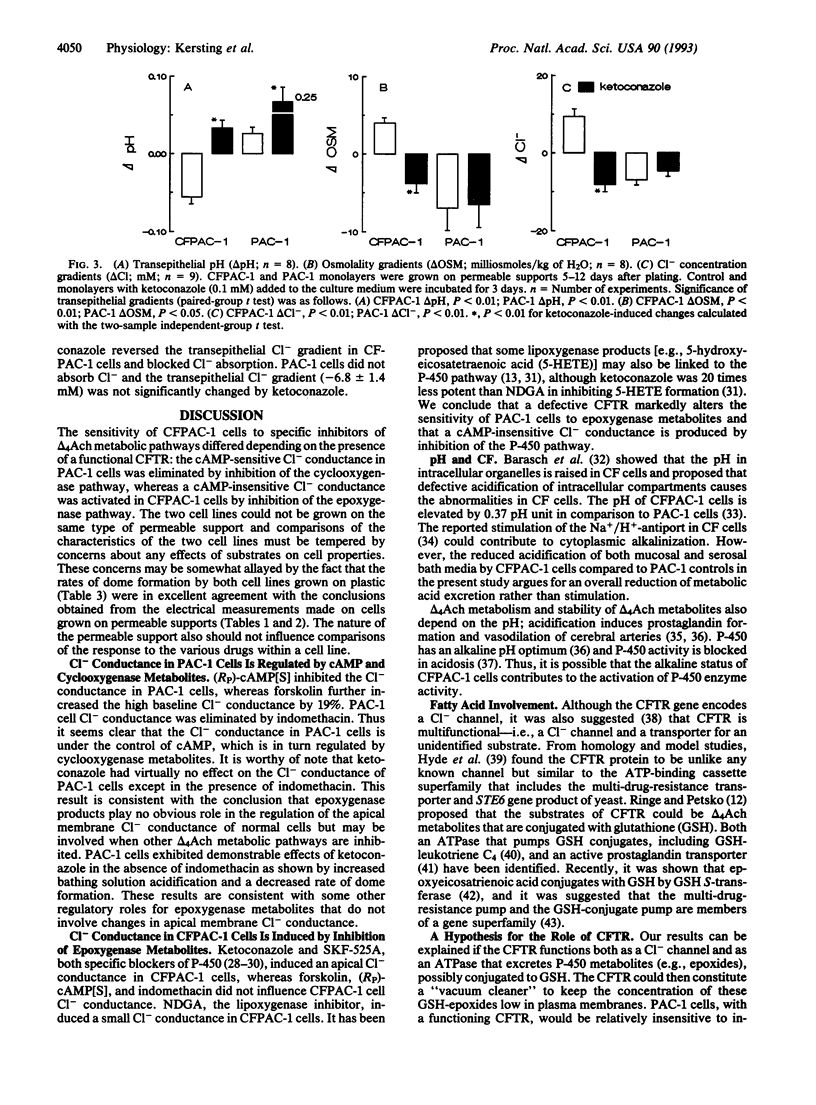
The role of arachidonic acid metabolites in the regulation of apical cell membrane Cl- conductance and transepithelial transport of fluid and Cl- by cultured pancreatic cells from cystic fibrosis (CFPAC-1) and corrected (PAC-1) cell lines was evaluated by the use of inhibitors. CFPAC-1 cells did not exhibit an apical membrane Cl- conductance, absorbed Cl- and fluid, and did not respond to stimulation or inhibition of cAMP action. PAC-1 cells exhibited a cAMP-responsive apical Cl- conductance, which was blocked by indomethacin, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor. Ketoconazole, an epoxygenase inhibitor, had virtually no effects on PAC-1 cell Cl- conductance but caused CFPAC-1 cells to develop a cAMP-insensitive Cl- conductance, blocked Cl- and fluid absorption, and reduced transepithelial electrical resistance. Ketoconazole treatment effectively reversed the cystic fibrosis defect in these cultured cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barasch J., Kiss B., Prince A., Saiman L., Gruenert D., al-Awqati Q. Defective acidification of intracellular organelles in cystic fibrosis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):70–73. doi: 10.1038/352070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beetens J. R., Loots W., Somers Y., Coene M. C., De Clerck F. Ketoconazole inhibits the biosynthesis of leukotrienes in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):883–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitch B. R., Beitch I., Zadunaisky J. A. The stimulation of chloride transport by prostaglandins and their interaction with epinephrine, theophylline, and cyclic AMP in the corneal epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(4):381–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01869987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z. Absorptive transport of prostaglandins from intraocular fluids to blood: a review of recent findings. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Aug 10;16(4):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. Renal tubular arachidonic acid metabolism. Kidney Int. 1991 Mar;39(3):438–449. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cheng E. H., Paradiso A. M., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Earp H. S. Chloride secretory response of cystic fibrosis human airway epithelia. Preservation of calcium but not protein kinase C- and A-dependent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1424–1431. doi: 10.1172/JCI114316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderaro V., Giovane A., De Simone B., Camussi G., Rossiello R., Quagliuolo L., Servillo L., Taccone W., Giordano C., Balestrieri C. Arachidonic acid metabolites and chloride secretion in rabbit distal colonic mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):G443–G450. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.3.G443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Gil L., Orellana M., Marnett L. J., Mason J. I., Yadagiri P., Falck J. R. Inhibitors of cytochrome P-450-dependent arachidonic acid metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Mar;261(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Parkhill L., Chacos N., Okita R., Masters B. S., Estabrook R. W. The oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid by purified cytochromes P-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 31;101(4):1357–1363. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91597-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J., Brönnegård M., Strandvik B. Pathological regulation of arachidonic acid release in cystic fibrosis: the putative basic defect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9202–9206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. A., Sala A., Dunn C. E., McGiff J. C., Murphy R. C. Structural identification of cytochrome P450-dependent arachidonate metabolites formed by rabbit medullary thick ascending limb cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12306–12312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. P., Dupont J. Abnormal levels of prostaglandins and fatty acids in blood of children with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1978 Jul 29;2(8083):236–238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm M. L., Pope H. A., Cliff W. H., Rommens J. M., Marvin S. A., Tsui L. C., Collins F. S., Frizzell R. A., Wilson J. M. Correction of the cystic fibrosis defect in vitro by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan M., Flotte T., Afione S., Solow R., Zeitlin P. L., Carter B. J., Guggino W. B. Defective regulation of outwardly rectifying Cl- channels by protein kinase A corrected by insertion of CFTR. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):581–584. doi: 10.1038/358581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman O., Guay-Broder C., van Galen P. J., Jacobson K. A., Fox C., Turner R. J., Cabantchik Z. I., Pollard H. B. A1 adenosine-receptor antagonists activate chloride efflux from cystic fibrosis cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5562–5566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgavish A. High intracellular pH in CFPAC: a pancreas cell line from a patient with cystic fibrosis is lowered by retrovirus-mediated CFTR gene transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):342–348. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eling T. E., Danilowicz R. M., Henke D. C., Sivarajah K., Yankaskas J. R., Boucher R. C. Arachidonic acid metabolism by canine tracheal epithelial cells. Product formation and relationship to chloride secretion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12841–12849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante B., Erlij D., Falck J. R., McGiff J. C. Effect of cytochrome P450 arachidonate metabolites on ion transport in rabbit kidney loop of Henle. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):799–802. doi: 10.1126/science.1846705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick F. A., Murphy R. C. Cytochrome P-450 metabolism of arachidonic acid: formation and biological actions of "epoxygenase"-derived eicosanoids. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):229–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. M., Benos D. J. CFTR! Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C267–C286. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong T. J., Moriyama T., Spring K. R. Activation of osmolyte efflux from cultured renal papillary epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Sep;123(3):269–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01870410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper T. B., Chase H. P., Henson J., Henson P. M. Essential fatty acid deficiency in the rabbit as a model of nutritional impairment in cystic fibrosis. In vitro and in vivo effects on lung defense mechanisms. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):540–547. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hyde S. C. Cystic fibrosis. Channelling our thoughts. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):194–195. doi: 10.1038/352194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. Cystic fibrosis. Chloride channels revisited. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):536–536. doi: 10.1038/358536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. C., Emsley P., Hartshorn M. J., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Gill D. R., Hubbard R. E., Higgins C. F. Structural model of ATP-binding proteins associated with cystic fibrosis, multidrug resistance and bacterial transport. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):362–365. doi: 10.1038/346362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T. ATP/Mg2+-dependent cardiac transport system for glutathione S-conjugates. A study using rat heart sarcolemma vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17343–17348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta Y., Kusunose E., Okumoto T., Kubota I., Kusunose M. Purification and characterization of two forms of cytochrome P-450 with omega-hydroxylase activities toward prostaglandin A and fatty acids from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biochem. 1990 Feb;107(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. D., Bubien J. K., Drumm M. L., Zheng T., Peiper S. C., Collins F. S., Kirk K. L., Frizzell R. A., Rado T. A. Transfection of wild-type CFTR into cystic fibrosis lymphocytes restores chloride conductance at G1 of the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):875–883. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler C. W., Busija D. W. Prostanoids in cortical subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid and pial arterial diameter in newborn pigs. Circ Res. 1985 Nov;57(5):689–694. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.5.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikauf G. D., Ueki I. F., Widdicombe J. H., Nadel J. A. Alteration of chloride secretion across canine tracheal epithelium by lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F47–F53. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marom Z., Shelhamer J. H., Sun F., Kaliner M. Human airway monohydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid generation and mucus release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):122–127. doi: 10.1172/JCI110949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton P. M. Cystic fibrosis: a disease in electrolyte transport. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2709–2717. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2197151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringe D., Petsko G. A. Cystic fibrosis. A transport problem? Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):312–313. doi: 10.1038/346312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogiers V., Dab I., Michotte Y., Vercruysse A., Crokaert R., Vis H. L. Abnormal fatty acid turnover in the phospholipids of the red blood cell membranes of cystic fibrosis patients (in vitro study). Pediatr Res. 1984 Aug;18(8):704–709. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198408000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer B. E., Zadunaisky J. A. Leukotriene modulation of chloride transport in frog cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jun;27(6):898–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer B. E., Zadunaisky J. A. Stimulation of chloride transport by fatty acids in corneal epithelium and relation to changes in membrane fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 4;556(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoumacher R. A., Ram J., Iannuzzi M. C., Bradbury N. A., Wallace R. W., Hon C. T., Kelly D. R., Schmid S. M., Gelder F. B., Rado T. A. A cystic fibrosis pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman M. L., Balazy M., Masferrer J., Abraham N. G., McGiff J. C., Murphy R. C. 12(R)-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid: a cytochrome-P450-dependent arachidonate metabolite that inhibits Na+,K+-ATPase in the cornea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8125–8129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevanian A., Muakkassah-Kelly S. F., Montestruque S. The influence of phospholipase A2 and glutathione peroxidase on the elimination of membrane lipid peroxides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevanian A., Stein R. A., Mead J. F. Metabolism of epoxidized phosphatidylcholine by phospholipase A2 and epoxide hydrolase. Lipids. 1981 Nov;16(11):781–789. doi: 10.1007/BF02535029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. L., Smith Q. T., Warick W. J. Serum glutathione reductase and cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1975 Dec;9(12):885–888. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197512000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L. The eicosanoids and their biochemical mechanisms of action. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):315–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2590315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spearman M. E., Prough R. A., Estabrook R. W., Falck J. R., Manna S., Leibman K. C., Murphy R. C., Capdevila J. Novel glutathione conjugates formed from epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90496-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Marichal P., Lauwers W. Hypothesis on the molecular basis of the antifungal activity of N-substituted imidazoles and triazoles. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):665–667. doi: 10.1042/bst0110665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagerle L. C., Mishra O. P. Mechanism of CO2 response in cerebral arteries of the newborn pig: role of phospholipase, cyclooxygenase, and lipoxygenase pathways. Circ Res. 1988 May;62(5):1019–1026. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.5.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Abnormal regulation of ion channels in cystic fibrosis epithelia. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2718–2725. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.1695593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Liedtke C. M. Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):467–470. doi: 10.1038/322467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C. What determines the substrate specificity of the multi-drug-resistance pump? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Feb;15(2):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Boucher R. C. Activation of an apical Cl- conductance by Ca2+ ionophores in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C226–C233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Boucher R. C. Transcellular sodium transport in cultured cystic fibrosis human nasal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C332–C341. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


