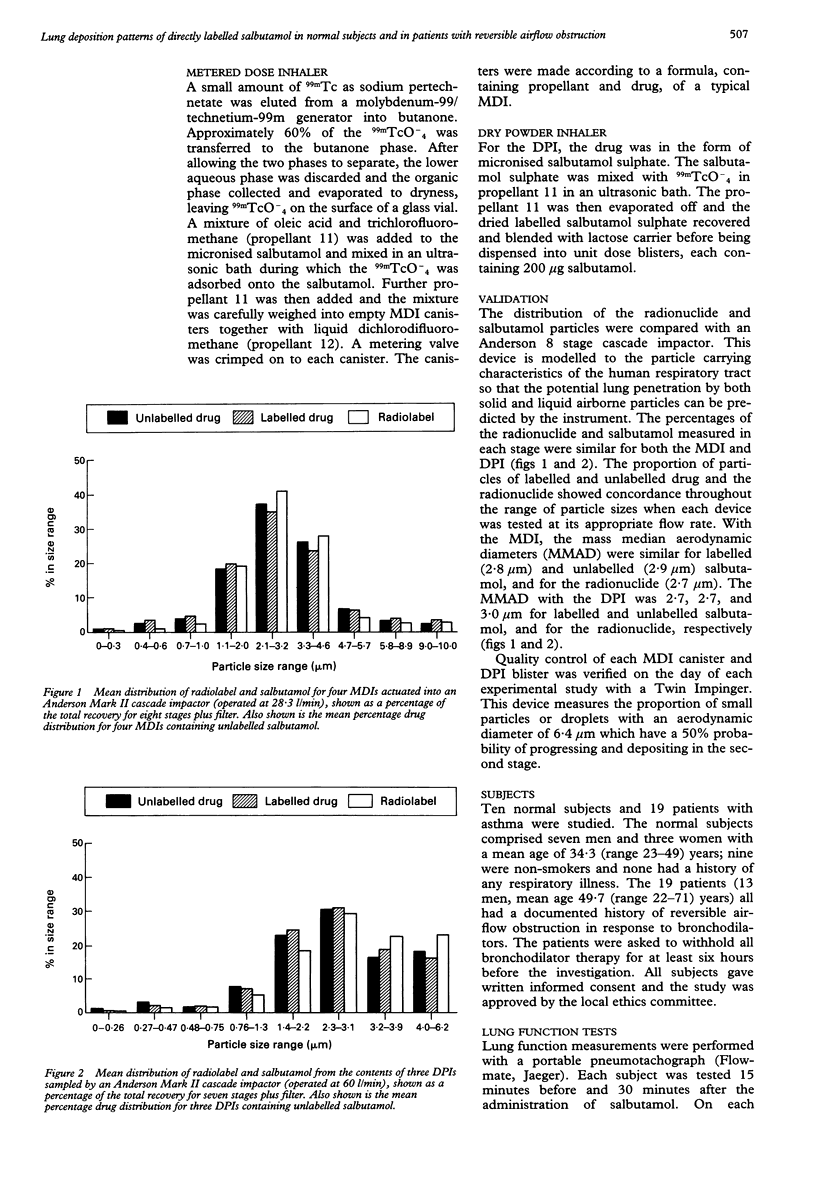
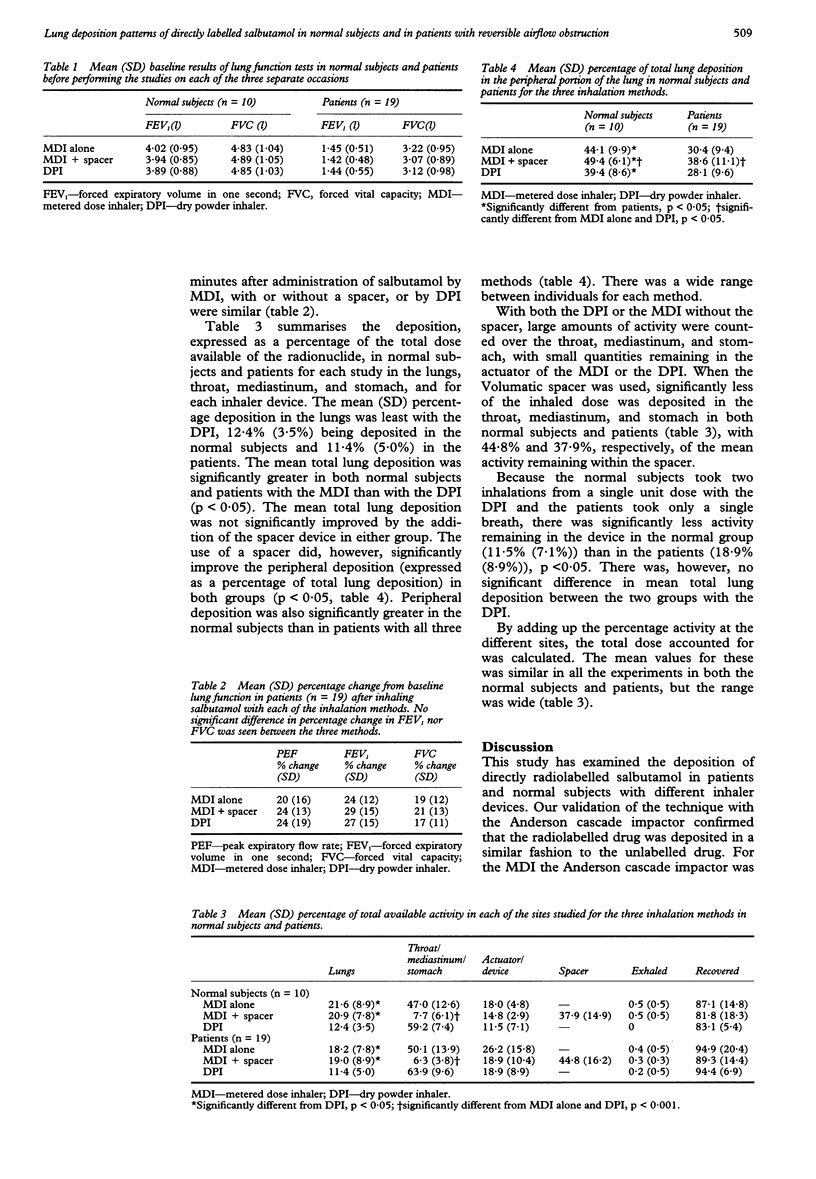
Abstract
BACKGROUND--Earlier studies of aerosol deposition in the lungs have relied on indirect labelling of Teflon spheres of a similar size distribution to the drug in question and have assumed similar aerodynamic properties. Using a modification of a new technique for directly labelling salbutamol, the deposition of salbutamol within the lungs of normal subjects and patients with asthma has been studied with the use of a metered dose inhaler (MDI) alone, an MDI with a spacer device, and a dry powder inhaler (DPI). METHOD--Salbutamol was directly labelled with technetium-99m and placed in an MDI or DPI. Ten normal subjects and 19 patients with asthma inhaled 200 micrograms of salbutamol by means of the MDI alone, the MDI with a spacer device attached, and by DPI on separate days. Deposition was assessed by a dual headed gamma camera after inhalation of the drug. RESULTS--The total mean (SD) percentage deposition of the drug in the normal subjects was 21.6% (8.9%) with the MDI alone, 20.9% (7.8%) with the MDI with spacer, and 12.4% (3.5%) with the DPI. For the patients, the mean percentage deposition was 18.2% (7.8%) with the MDI alone, 19.0% (8.9%) with the MDI and spacer, and 11.4% (5.0%) with the DPI. Bronchodilatation achieved by the patients was similar with all three techniques. Mean peripheral lung deposition was significantly greater with a spacer device than when the MDI was used alone in both normal subjects (49.4% (6.1%) v 44.1% (9.9%)) and patients (38.6% (11.1%) v 30.4% (9.4%)). CONCLUSIONS--The deposition of directly labelled salbutamol from an MDI is greater than previously estimated by indirect labelling techniques. The deposition of labelled salbutamol from a DPI, however, is little different from that measured by indirect techniques.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth H. L., Wilson C. G., Sims E. E., Wotton P. K., Hardy J. G. Delivery of propellant soluble drug from a metered dose inhaler. Thorax. 1991 Apr;46(4):245–247. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.4.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. W. Inhaler therapy. Q J Med. 1988 May;67(253):355–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich M., Ruffin R. E., Roberts R., Newhouse M. T. Optimal delivery of aerosols from metered dose inhalers. Chest. 1981 Dec;80(6 Suppl):911–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler D., Fleischer W., Matthys H. New method for easy labeling of beta-2-agonists in the metered dose inhaler with technetium 99m. Respiration. 1988;53(2):65–73. doi: 10.1159/000195399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. P., Clark A. R., Talaee N., Clarke S. W. Pressurised aerosol deposition in the human lung with and without an "open" spacer device. Thorax. 1989 Sep;44(9):706–710. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.9.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. P., Weisz A. W., Talaee N., Clarke S. W. Improvement of drug delivery with a breath actuated pressurised aerosol for patients with poor inhaler technique. Thorax. 1991 Oct;46(10):712–716. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.10.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J. Asthma without airway hyperreactivity: fact or artifact? Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;63(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. D., Singh C. A., Few J. D., Studdy P. R., Heaf P. J., Spiro S. G. The labelling and monitoring of lung deposition of an inhaled synthetic anticholinergic bronchodilating agent. Chest. 1981 Dec;80(6 Suppl):918–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zainudin B. M., Biddiscombe M., Tolfree S. E., Short M., Spiro S. G. Comparison of bronchodilator responses and deposition patterns of salbutamol inhaled from a pressurised metered dose inhaler, as a dry powder, and as a nebulised solution. Thorax. 1990 Jun;45(6):469–473. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.6.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



