Abstract
In the title compound, C9H11NO5S, the O=S=O plane of the sulfonyl group is twisted at a dihedral angle of 52.54 (16)° with respect to the benzene ring. The dihedral angle between the carboxylic acid group and the benzene ring is 49.91 (16)°. In the crystal, C—H⋯O, N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into (001) sheets.
Keywords: crystal structure, benzenesulfonamido, propanoic acid, sulfonyl group, O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds
Related literature
For related structures, see: Aguilar-Castro et al. (2004 ▸); Arshad et al. (2009 ▸, 2012 ▸); Zolotarev et al. (2014 ▸).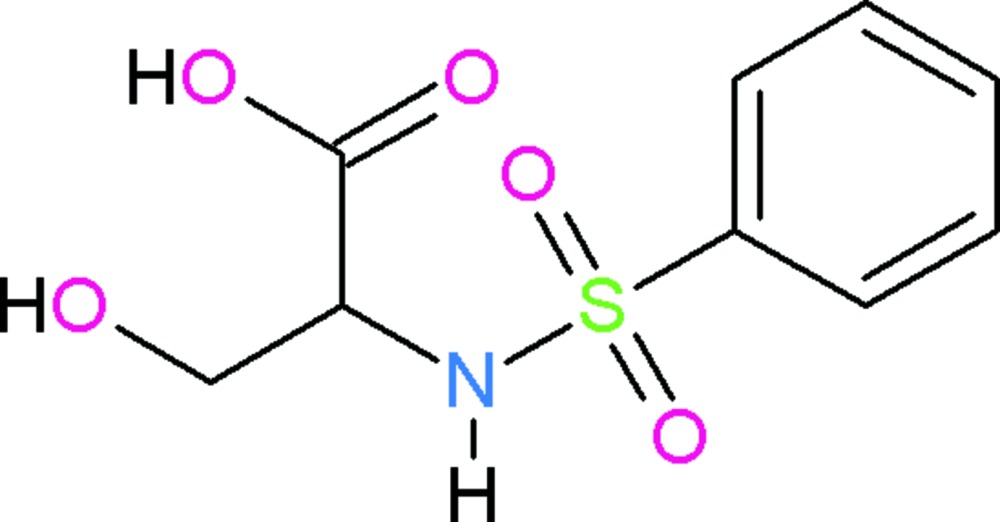
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H11NO5S
M r = 245.25
Orthorhombic,

a = 5.0464 (4) Å
b = 9.9752 (8) Å
c = 21.4701 (17) Å
V = 1080.78 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.31 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.40 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▸) T min = 0.890, T max = 0.950
5013 measured reflections
2354 independent reflections
1978 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.03
2354 reflections
149 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 919 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.05 (5)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▸); data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▸); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▸) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▸) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530fig1.tif
View of the asymmetric unit of title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
PLATON . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530fig2.tif
The partial packing (PLATON; Spek, 2009), which shows that molecules form two dimensional polymeric network.
CCDC reference: 1433189
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1H1O3i | 0.84(5) | 1.81(5) | 2.621(4) | 164(5) |
| O3H3O5i | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.754(3) | 164 |
| N1H1AO4ii | 0.86 | 2.39 | 3.066(4) | 136 |
| C2H2O2iii | 0.98 | 2.48 | 3.425(5) | 162 |
| C6H6O5iv | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.342(5) | 148 |
| C7H7O2v | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.347(5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the provision of funds for the purchase of a diffractometer and encouragement by Dr Muhammad Akram Chaudhary, Ex-Vice Chancellor, University of Sargodha, Pakistan.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
The title compound (I), (Fig. 1) has been synthesized for complexation and other studius.
The crystal structures of N-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)serine (Zolotarev et al., 2014), N(S)-(p-toluenesulfonyl)-L-alanine (Aguilar-Castro et al., 2004), 2-benzenesulfonamido-3-methylbutyric acid (Arshad et al., 2012) and (2R)-2-benzenesulfonamido-2- phenylethanoic acid (Arshad et al., 2009) have been reported which are related to the title compound.
The aminoacetic acid moiety B (C1/C2/N1/O1/O2) is roughly planar with r.m.s. deviation of 0.0588 Å. The dihedral angle between the benzene ring and B is 52.96 (14)°. The sulfonyl group C (S1/O4/O5) is oriented at a dihedral angle of 52.54 (16)° with the parent benzene ring. In the crystal, the molecules are linked into a two-dimensional polymeric network (Table 2, Fig. 2) due to H-bondings of C–H···O, N–H···O and O–H···O types with base vectors [100], [010] and in the plane (001).
S2. Experimental
The title compound was prepared by using equimolar ratio of L-serine and benzenesulfonyl chloride in 40 ml water. The benzenesulfonyl chloride disolved in distilled water was added pinch by pinch in the L-serine already disolved in distilled water and stirred at 296–298 K, while keeping the pH of the reaction mixture was maintained at 8–9 by adding 1.0 M sodium bicarbonate solution. The 1.0 M HCl solution was added after an hour which resulted in the form of white precipitates. The precipitates obtained were filtered and dried from which colourless needles of (I) were obtained after recrystallization from ethanol solution after 48 h. Yield: 68% Melting point: 493 K.
S3. Refinement
The coordinates of H-atom of carboxyl group were refined. The other H-atoms were positioned geometrically (O—H = 0.82, N—H = 0.86, C–H = 0.93—0.98 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C, N, O), where x = 1.5 for hydroxy and x = 1.2 for all other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.

View of the asymmetric unit of title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

The partial packing (PLATON; Spek, 2009), which shows that molecules form two dimensional polymeric network.
Crystal data
| C9H11NO5S | Dx = 1.507 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 245.25 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 1978 reflections |
| a = 5.0464 (4) Å | θ = 2.8–27.1° |
| b = 9.9752 (8) Å | µ = 0.31 mm−1 |
| c = 21.4701 (17) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 1080.78 (15) Å3 | Needle, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| F(000) = 512 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2354 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1978 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.025 |
| Detector resolution: 7.80 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.1°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −6→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −9→12 |
| Tmin = 0.890, Tmax = 0.950 | l = −27→27 |
| 5013 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0432P)2 + 0.1053P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2354 reflections | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 149 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 919 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.05 (5) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.68841 (17) | 0.37500 (8) | 0.12794 (3) | 0.0362 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.7864 (6) | 0.8154 (3) | 0.20233 (14) | 0.0624 (8) | |
| H1 | 0.871 (11) | 0.885 (5) | 0.194 (2) | 0.094* | |
| O2 | 1.1199 (6) | 0.6949 (3) | 0.16402 (14) | 0.0651 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.9705 (7) | 0.5474 (2) | 0.30216 (11) | 0.0583 (8) | |
| H3 | 1.0059 | 0.6065 | 0.3274 | 0.087* | |
| O4 | 0.4135 (5) | 0.3816 (3) | 0.14371 (11) | 0.0504 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.8178 (6) | 0.2474 (2) | 0.12476 (11) | 0.0502 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.8462 (6) | 0.4600 (2) | 0.17945 (11) | 0.0368 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.9985 | 0.4323 | 0.1920 | 0.044* | |
| C1 | 0.9047 (8) | 0.7029 (3) | 0.18768 (14) | 0.0406 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.7369 (7) | 0.5833 (3) | 0.20543 (14) | 0.0384 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.5583 | 0.5962 | 0.1886 | 0.046* | |
| C3 | 0.7171 (9) | 0.5712 (4) | 0.27649 (16) | 0.0530 (10) | |
| H3A | 0.6444 | 0.6533 | 0.2936 | 0.064* | |
| H3B | 0.5990 | 0.4981 | 0.2873 | 0.064* | |
| C4 | 0.7318 (7) | 0.4526 (3) | 0.05482 (14) | 0.0365 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.9275 (9) | 0.4077 (4) | 0.01556 (16) | 0.0542 (10) | |
| H5 | 1.0338 | 0.3355 | 0.0269 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.9645 (11) | 0.4717 (4) | −0.04132 (17) | 0.0653 (12) | |
| H6 | 1.0988 | 0.4436 | −0.0679 | 0.078* | |
| C7 | 0.8028 (10) | 0.5765 (4) | −0.05829 (16) | 0.0609 (11) | |
| H7 | 0.8250 | 0.6180 | −0.0967 | 0.073* | |
| C8 | 0.6103 (9) | 0.6193 (4) | −0.01864 (17) | 0.0618 (12) | |
| H8 | 0.5028 | 0.6909 | −0.0301 | 0.074* | |
| C9 | 0.5718 (9) | 0.5581 (4) | 0.03840 (17) | 0.0512 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.4395 | 0.5879 | 0.0652 | 0.061* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0337 (4) | 0.0291 (3) | 0.0459 (4) | −0.0024 (4) | −0.0051 (4) | 0.0017 (3) |
| O1 | 0.061 (2) | 0.0327 (13) | 0.0933 (19) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0105 (17) | −0.0028 (13) |
| O2 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0283 (17) | 0.0134 (14) |
| O3 | 0.089 (2) | 0.0342 (13) | 0.0514 (14) | 0.0014 (15) | −0.0182 (15) | −0.0063 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0350 (13) | 0.0529 (14) | 0.0634 (14) | −0.0087 (13) | −0.0019 (13) | 0.0046 (12) |
| O5 | 0.0590 (17) | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0635 (14) | 0.0039 (11) | −0.0118 (16) | 0.0015 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0325 (16) | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0428 (12) | 0.0059 (13) | −0.0089 (14) | −0.0030 (11) |
| C1 | 0.042 (2) | 0.0349 (17) | 0.0444 (17) | 0.0068 (17) | −0.0013 (18) | 0.0026 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0300 (19) | 0.0357 (16) | 0.0496 (16) | 0.0040 (14) | −0.0014 (16) | −0.0043 (13) |
| C3 | 0.059 (3) | 0.0427 (19) | 0.0569 (19) | −0.005 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0085 (15) |
| C4 | 0.036 (2) | 0.0331 (15) | 0.0405 (14) | −0.0015 (16) | −0.0064 (16) | −0.0051 (12) |
| C5 | 0.059 (3) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0528 (19) | 0.018 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.0045 (16) |
| C6 | 0.081 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.0457 (19) | 0.011 (3) | 0.014 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C7 | 0.080 (3) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0400 (16) | 0.000 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.0020 (16) |
| C8 | 0.071 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.011 (2) | 0.0106 (19) |
| C9 | 0.048 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0560 (19) | 0.0159 (19) | 0.003 (2) | 0.0046 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O4 | 1.429 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9700 |
| S1—O5 | 1.432 (2) | C3—H3B | 0.9700 |
| S1—N1 | 1.605 (3) | C4—C9 | 1.373 (5) |
| S1—C4 | 1.764 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.374 (5) |
| O1—C1 | 1.310 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.391 (5) |
| O1—H1 | 0.84 (5) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C1 | 1.201 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.375 (6) |
| O3—C3 | 1.413 (5) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C7—C8 | 1.360 (6) |
| N1—C2 | 1.458 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C8—C9 | 1.382 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.512 (5) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.534 (5) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9800 | ||
| O4—S1—O5 | 119.67 (16) | C2—C3—H3A | 109.7 |
| O4—S1—N1 | 107.09 (15) | O3—C3—H3B | 109.7 |
| O5—S1—N1 | 106.03 (14) | C2—C3—H3B | 109.7 |
| O4—S1—C4 | 108.12 (15) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.2 |
| O5—S1—C4 | 106.92 (15) | C9—C4—C5 | 121.0 (3) |
| N1—S1—C4 | 108.64 (14) | C9—C4—S1 | 119.5 (3) |
| C1—O1—H1 | 115 (4) | C5—C4—S1 | 119.5 (3) |
| C3—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C4—C5—C6 | 119.1 (4) |
| C2—N1—S1 | 121.4 (2) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| C2—N1—H1A | 119.3 | C6—C5—H5 | 120.5 |
| S1—N1—H1A | 119.3 | C7—C6—C5 | 120.1 (4) |
| O2—C1—O1 | 124.8 (4) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 124.1 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 111.1 (3) | C8—C7—C6 | 119.7 (4) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 110.9 (3) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 109.8 (3) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 110.4 (3) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.1 (4) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 108.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.4 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 108.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.4 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 108.5 | C4—C9—C8 | 118.9 (4) |
| O3—C3—C2 | 110.0 (3) | C4—C9—H9 | 120.6 |
| O3—C3—H3A | 109.7 | C8—C9—H9 | 120.6 |
| O4—S1—N1—C2 | −37.2 (3) | N1—S1—C4—C9 | −83.5 (3) |
| O5—S1—N1—C2 | −166.0 (2) | O4—S1—C4—C5 | −148.5 (3) |
| C4—S1—N1—C2 | 79.4 (3) | O5—S1—C4—C5 | −18.4 (3) |
| S1—N1—C2—C1 | −114.8 (3) | N1—S1—C4—C5 | 95.6 (3) |
| S1—N1—C2—C3 | 122.8 (3) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | 0.7 (6) |
| O2—C1—C2—N1 | −11.0 (5) | S1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.4 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—N1 | 170.0 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.4 (6) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 111.1 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.4 (7) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −68.0 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.8 (7) |
| N1—C2—C3—O3 | 59.3 (4) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | −0.1 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | −63.3 (4) | S1—C4—C9—C8 | 179.1 (3) |
| O4—S1—C4—C9 | 32.4 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.1 (7) |
| O5—S1—C4—C9 | 162.5 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O3i | 0.84 (5) | 1.81 (5) | 2.621 (4) | 164 (5) |
| O3—H3···O5i | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.754 (3) | 164 |
| N1—H1A···O4ii | 0.86 | 2.39 | 3.066 (4) | 136 |
| C2—H2···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.48 | 3.425 (5) | 162 |
| C6—H6···O5iv | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.342 (5) | 148 |
| C7—H7···O2v | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.347 (5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z; (v) x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7530).
References
- Aguilar-Castro, L., Tlahuextl, M., Tapia-Benavides, A. R. & Alvarado-Rodríguez, J. G. (2004). Struct. Chem. 15, 215–221.
- Arshad, M. N., Danish, M., Tahir, M. N., Aabideen, Z. U. & Asiri, A. M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Shafiq, M. & Ahmad, S. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2005). SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zolotarev, P. N., Arshad, M. N., Asiri, A. M., Al-amshany, Z. M. & Blatov, V. A. (2014). Cryst. Growth Des. 14, 1938–1949.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530fig1.tif
View of the asymmetric unit of title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
PLATON . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020149/hb7530fig2.tif
The partial packing (PLATON; Spek, 2009), which shows that molecules form two dimensional polymeric network.
CCDC reference: 1433189
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


