Abstract
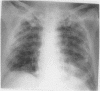
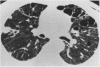
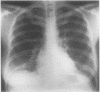
A 54 year old man with a staphylococcal sepsis developed staphylococcal pneumonia complicated by multiple pneumatoceles and bilateral tension pneumothoraces caused by bronchopleural fistulae. Excessive enlargement of the right sided pneumatoceles and a tension pneumothorax not improved by drainage led to mediastinal shift and compression of the right lung. Reversal of the mediastinal shift and closure of the bronchopleural fistulae was achieved by assisted independent lung ventilation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop M. J., Benson M. S., Sato P., Pierson D. J. Comparison of high-frequency jet ventilation with conventional mechanical ventilation for bronchopleural fistula. Anesth Analg. 1987 Sep;66(9):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlon G. C., Ray C., Jr, Klein R., Goldiner P. L., Miodownik S. Criteria for selective positive end-expiratory pressure and independent synchronized ventilation of each lung. Chest. 1978 Nov;74(5):501–507. doi: 10.1378/chest.74.5.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A. C., Creach M., Cameron I. R. Staphylococcal pneumonia, pneumatoceles, and the toxic shock syndrome. Thorax. 1990 Aug;45(8):639–640. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.8.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. D., Tonnesen A. S., Gabel J. C., Arens J. F. Therapy of unilateral pulmonary insufficiency with a double lumen endotracheal tube. Crit Care Med. 1976 Nov-Dec;4(6):323–326. doi: 10.1097/00003246-197611000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Eykyn S. J., Phillips I. Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: 400 episodes in St Thomas's Hospital. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jan 28;288(6413):300–303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6413.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton P. P., Onayemi A., Smyth J. A., Gillan J. E., Cutz E., Froese A. B., Bryan A. C. Comparison of conventional and high-frequency ventilation: oxygenation and lung pathology. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jul;55(1 Pt 1):131–138. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highman J. H. Staphylococcal pneumonia and empyema in childhood. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1969 May;106(1):103–108. doi: 10.2214/ajr.106.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powner D. J., Eross B., Grenvik A. Differential lung ventilation with PEEP in the treatment of unilateral pneumonia. Crit Care Med. 1977 Jul-Aug;5(4):170–172. doi: 10.1097/00003246-197707000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley M. J., Fraser R. S. Pulmonary pneumatocele: pathology and pathogenesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Jun;150(6):1275–1277. doi: 10.2214/ajr.150.6.1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Bacteremic Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(6):623–627. doi: 10.3109/00365548709117196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead M. A., Radvan J., Macfarlane J. T. Adult community-acquired staphylococcal pneumonia in the antibiotic era: a review of 61 cases. Q J Med. 1987 Sep;64(245):783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates S. P., Morcos S. K. Delayed tension pneumothorax complicating staphylococcal pneumonia. Postgrad Med J. 1988 Oct;64(756):796–798. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.64.756.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]