Abstract
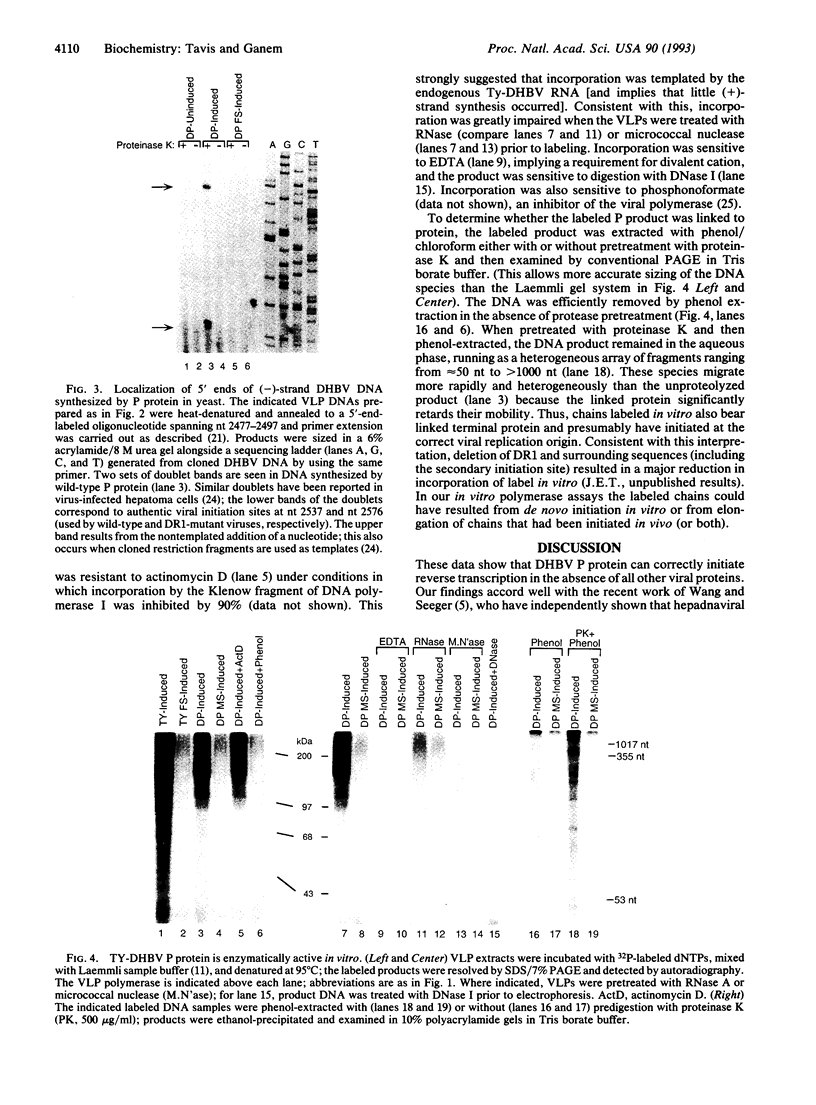
Replication of hepatitis B viruses proceeds by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate, a reaction catalyzed by the virus-encoded polymerase (P protein). The reaction product is a partially duplex DNA whose (-)-strand is covalently linked to the P protein. Efforts to understand the mechanism of the reaction have been severely retarded by an inability to express functional polymerase outside of viral particles. Here we report the successful expression of enzymatically active polymerase in yeast cells, by fusing the P gene to coding sequences of the retrotransposon Ty1. The enzyme initiates correctly on viral RNA in yeast cells in vivo, producing nascent DNA chains covalently linked to protein, exactly as found in virus-infected cells. Replication complexes isolated from these yeast are enzymatically active in vitro, synthesizing DNA in a reaction that is actinomycin D-resistant but sensitive to RNase pretreatment. These results indicate that P protein is the sole viral protein required for the correct priming of reverse transcription and establish a tractable system for the biochemical dissection of the reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Dawson K. M., Gull K., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. The expression of hybrid HIV:Ty virus-like particles in yeast. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):68–70. doi: 10.1038/329068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. E., Mellor J., Gull K., Sim R. B., Tuite M. F., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. The functions and relationships of Ty-VLP proteins in yeast reflect those of mammalian retroviral proteins. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90761-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT3 gene is required for transposition and transpositional recombination of chromosomal Ty elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3575–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Effects of insertional and point mutations on the functions of the duck hepatitis B virus polymerase. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5553–5558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5553-5558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Wu T. T., Aldrich C. E., Delaney M. A., Summers J., Seeger C., Mason W. S. Replication of DHBV genomes with mutations at the sites of initiation of minus- and plus-strand DNA synthesis. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):208–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90751-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel A., Boeke J. D. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a retrotransposon from the trypanosomatid Crithidia fasciculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9794–9798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus contains protein attached to the 5' terminus of its complete DNA strand. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Epitope tagging and protein surveillance. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:508–519. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94038-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Initiation and termination of duck hepatitis B virus DNA synthesis during virus maturation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3832–3840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3832-3840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D. Sequence-independent RNA cleavages generate the primers for plus strand DNA synthesis in hepatitis B viruses: implications for other reverse transcribing elements. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3533–3540. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natsoulis G., Boeke J. D. New antiviral strategy using capsid-nuclease fusion proteins. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):632–635. doi: 10.1038/352632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Zentgraf H., Schaller H., Bosch V. The duck hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase is tightly associated with the viral core structure and unable to switch to an exogenous template. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S., Loeb D. D., Ganem D. Mutations affecting hepadnavirus plus-strand DNA synthesis dissociate primer cleavage from translocation and reveal the origin of linear viral DNA. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1255-1262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W., Malim M. H., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Expression strategies of the yeast retrotransposon Ty: a short sequence directs ribosomal frameshifting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7001–7016. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngren S. D., Boeke J. D., Sanders N. J., Garfinkel D. J. Functional organization of the retrotransposon Ty from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Ty protease is required for transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1421–1431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]