Abstract
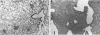
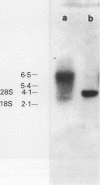
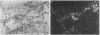
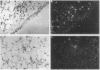
BACKGROUND--Intratracheal instillation of bleomycin into mice leads to deposition of collagen in the lung and fibrosis, but the mechanism for this is poorly understood. Enhanced collagen gene expression, increased collagen synthesis, decreased collagen degradation, and proliferation of fibroblasts have all been proposed as possible contributors. To obtain information on the activity of collagen producing cells at an early stage in the development of pulmonary fibrosis in situ hybridisation was used to detect and localise products of the type III procollagen gene. In addition, assay of type III procollagen gene expression was performed using dot-blot analysis of lung RNA extracts. METHODS--Lung fibrosis was induced in mice by intratracheal instillation of bleomycin sulphate (6 mg/kg body weight) and tissues were examined after three, 10, 21 and 35 days. RNA-RNA hybridisation was accomplished with riboprobes labelled with sulphur-35 which were generated from a 1.7 kb mouse procollagen a1(III) cDNA. In situ hybridisation was performed on sections fixed in paraformaldehyde and embedded in paraffin wax and steady state values of type III procollagen mRNA were assayed by dot-blot analysis of total lung RNA extracted by guanidium isothiocyanate. RESULTS--Data obtained using both techniques suggest that type III procollagen gene expression was enhanced in bleomycin induced fibrosis and that expression was maximal between 10 and 35 days after a single dose of bleomycin. The most active cells were located in interstitial areas around the conducting airways, although these cells were usually seen in areas with no histological evidence of fibrosis. Regions with the most advanced fibrosis, as assessed by histological methods, rarely contained cells with activity above the threshold detectable by this technique. CONCLUSIONS--These results suggest that activation of interstitial fibroblasts, with enhanced type III collagen gene expression, forms at least part of the mechanism leading to increased collagen deposition in bleomycin induced fibrosis and that this occurs before fibrosis is detected by conventional histological staining.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer L. M., Cox K. H., Angerer R. C. Demonstration of tissue-specific gene expression by in situ hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:649–661. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekelmann T. J., Limper A. H., Colby T. V., McDonald J. A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 is present at sites of extracellular matrix gene expression in human pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6642–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. B., Hyde D. M., Giri S. N. Morphometric estimates of infiltrative cellular changes during the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Am J Pathol. 1983 Aug;112(2):170–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Overton J. E., Marino B. A., Uitto J., Starcher B. C. Collagen biosynthesis in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Dec;96(6):943–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Shahzeidi S., Laurent G. Mechanisms of bleomycin-induced lung damage. Arch Toxicol. 1991;65(2):81–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02034932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt D. G., Lazo J. S. Alterations in pulmonary mRNA encoding procollagens, fibronectin and transforming growth factor-beta precede bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordana M., Schulman J., McSharry C., Irving L. B., Newhouse M. T., Jordana G., Gauldie J. Heterogeneous proliferative characteristics of human adult lung fibroblast lines and clonally derived fibroblasts from control and fibrotic tissue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):579–584. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Seyer J. M., Raghow R., Kang A. H. Regulation of extracellular matrix production by chemically synthesized subfragments of type I collagen carboxy propeptide. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7097–7104. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J., Chrin L., Shull S., Rowe D. W., Cutroneo K. R. Bleomycin selectively elevates mRNA levels for procollagen and fibronectin following acute lung injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):836–843. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. M., Da Costa P. E., Turner-Warwick M., Littleton R. J., Laurent G. J. Biochemical evidence for an increased and progressive deposition of collagen in lungs of patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 Jan;70(1):39–45. doi: 10.1042/cs0700039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. M., Heard B. E., Kerr I., Turner-Warwick M., Laurent G. J. Quantitation of types I and III collagen in biopsy lung samples from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Coll Relat Res. 1984 May;4(3):169–182. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., McAnulty R. J., Corrin B., Cockerill P. Biochemical and histological changes in pulmonary fibrosis induced in rabbits with intratracheal bleomycin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;11(6):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb02011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., McAnulty R. J. Protein metabolism during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rabbits. In vivo evidence for collagen accumulation because of increased synthesis and decreased degradation of the newly synthesized collagen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):82–88. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Yamada Y., de Crombrugghe B. Coordinate regulation of the levels of type III and type I collagen mRNA in most but not all mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini A., Gardi C., Corradeschi F., Viti A., Belli C., Calzoni P., Lungarella G. In vivo stimulation of lung collagen synthesis by collagen derived peptides. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;68(1):89–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Kunkel S. L. Lung cytokine production in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 1992 Jan-Mar;18(1):29–43. doi: 10.3109/01902149209020649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Lurie S., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Profiles of steady state levels of messenger RNAs coding for type I procollagen, elastin, and fibronectin in hamster lungs undergoing bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1733–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI112163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahzeidi S., Sarnstrand B., Jeffery P. K., McAnulty R. J., Laurent G. J. Oral N-acetylcysteine reduces bleomycin-induced collagen deposition in the lungs of mice. Eur Respir J. 1991 Jul;4(7):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K. M., Jr, Harris M. J., Mitchell J. J., Cutroneo K. R. Bleomycin treatment of chick fibroblasts causes an increase of polysomal type I procollagen mRNAs. Reversal of the bleomycin effect by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14438–14444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpio B. E., Banes A. J., Link W. G., Johnson G., Jr Enhanced collagen production by smooth muscle cells during repetitive mechanical stretching. Arch Surg. 1988 Oct;123(10):1233–1236. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400340059010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., Champion J. E., McMahon A. P. A molecular analysis of mouse development from 8 to 10 days post coitum detects changes only in embryonic globin expression. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):493–500. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]