Abstract
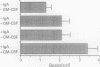
BACKGROUND--IgA is the major antibody class in mucosal secretions, yet its biological functions remain poorly understood and its role as an opsonin for neutrophils has been the subject of controversy. It has been reported that treatment of neutrophils with granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) induces the cells to phagocytose particles opsonised with IgA. A study was performed to investigate the effects of GM-CSF and IgA opsonisation on the ability of human neutrophils to recognise and phagocytose latex beads coated with the P6 outer membrane protein of Haemophilus influenzae. METHODS--Human neutrophils with and without preincubation with 100 pmol/l GM-CSF, were incubated with non-opsonised P6-coated latex beads or beads opsonised with IgA purified from the blood of a bronchiectatic patient with high titres of IgA anti-P6. Phagocytosis was measured by counting internalised beads during microscopic examination. RESULTS--The phagocytosis of IgA opsonised beads by untreated neutrophils (mean (SE) 2.1 (0.43) beads/cell) was significantly greater than that of non-opsonised beads (mean (SE) 1.3 (0.30) beads/cell). Treatment of neutrophils with GM-CSF resulted in increased phagocytosis of non-opsonised beads (mean (SE) 2.1 (0.39) beads/cell) but opsonisation with IgA increased this further (mean (SE) 3.4 (0.53) beads/cell). CONCLUSIONS--Human neutrophils recognise and phagocytose non-opsonised particles coated with bacterial antigen. Antibodies of the IgA isotype opsonise for neutrophil phagocytosis of particles coated with bacterial antigen but this behaviour is enhanced, in an additive fashion, by treatment of the cells with GM-CSF. The results suggest that IgA and GM-CSF are important cofactors for neutrophil recognition and elimination of bacterial pathogens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrechtsen M., Yeaman G. R., Kerr M. A. Characterization of the IgA receptor from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):201–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., deVos S., Gruss H. J., Herrmann F. Prolongation of survival of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is caused by inhibition of programmed cell death. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2920–2924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Hill S. L., Bradwell A. R., Stockley R. A. IgA subclasses in sputum from patients with bronchiectasis. Respir Med. 1990 Mar;84(2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamba A., Afford S. C., Stockley R. A., Burnett D. Extracellular proteolysis of fibronectin by neutrophils: characterization and the effects of recombinant cytokines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;4(4):330–337. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.4.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Goldstine S. N., Shen L. Cytofluorographic analysis of receptors for IgA on human polymorphonuclear cells and monocytes and the correlation of receptor expression with phagocytosis. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1019–1027. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Shen L., Pugh J., Bernier G. M. Subpopulations of human peripheral granulocyes and monocytes express receptors for IgA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., Eijk P. P., van Alphen L., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Haemophilus influenzae infections in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease despite specific antibodies in serum and sputum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 May;141(5 Pt 1):1316–1321. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.5_Pt_1.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. The leukocyte integrins. Immunol Today. 1989 Apr;10(4):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90238-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh A., Yamaguchi E., Kuzumaki N., Okazaki N., Furuya K., Abe S., Kawakami Y. Expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA by inflammatory cells in the sarcoid lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Sep;3(3):245–249. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen L. V., Skottun T. A rapid one-step method for the isolation of human granulocytes from whole blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 May;42(3):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Dalmasso A. P., Woodson M. Complement-dependent opsonization of incompatible erythrocytes by human secretory IgA. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):275–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Olchowski J. J., Reynolds H. Y. Immunoglobulin G subclass proteins in serum and lavage fluid of normal subjects. Quantitation and comparison with immunoglobulins A and E. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):584–587. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Rice P. A., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Apicella M. A. Identification of a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein on nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a target for human serum bactericidal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Somatic antigens of Haemophilus influenzae as vaccine components. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S66–S68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Sethi S. Bacterial infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Oct;146(4):1067–1083. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.4.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Goree A., Baughn R. E., Birdsall H. H. Immunoglobulin A from bronchopulmonary secretions blocks bactericidal and opsonizing effects of antibody to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):36–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.36-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Kubitschek K. R., Crennan J., Baughn R. E. Pneumonia and acute febrile tracheobronchitis due to haemophilus influenzae. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):444–450. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naids F. L., Belisle B., Lee N., Rest R. F. Interactions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils: studies with purified PII (Opa) outer membrane proteins and synthetic Opa peptides. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4628–4635. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4628-4635.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A., Murphy T. F., Vankeulen H., Spotila L. D., Rekosh D. Cloning and sequencing of Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane protein P6. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.128-134.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. B., Munson R. S., Jr, Apicella M. A., Sikkema D. J., Molleston J. P., Murphy T. F. Molecular conservation of the P6 outer membrane protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae: analysis of antigenic determinants, gene sequences, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2658–2663. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2658-2663.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Sharon N. Lectinophagocytosis: a molecular mechanism of recognition between cell surface sugars and lectins in the phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):539–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.539-547.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Phagocytosis in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Localization of the primary opsonic site to Fc fragment. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):553–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P. Serum factors capable of opsonizing Shigella for phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Immunology. 1975 Jun;28(6):1051–1059. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Lee D. K., Lacy J., Coleman D. L. Rat tracheal epithelial cells produce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):59–68. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vancheri C., Gauldie J., Bienenstock J., Cox G., Scicchitano R., Stanisz A., Jordana M. Human lung fibroblast-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) mediates eosinophil survival in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Oct;1(4):289–295. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Kacena A., Schuh A., Golde D. W. GM-CSF induces human neutrophil IgA-mediated phagocytosis by an IgA Fc receptor activation mechanism. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):647–648. doi: 10.1038/332647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. D. Studies on the opsonic activity of human secretory IgA using an in vitro phagocytosis system. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman G. R., Kerr M. A. Opsonization of yeast by human serum IgA anti-mannan antibodies and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):200–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky A., Brown E. J., Bienenstock J. Lack of opsonization potential of 11S human secretory A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):181–184. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]