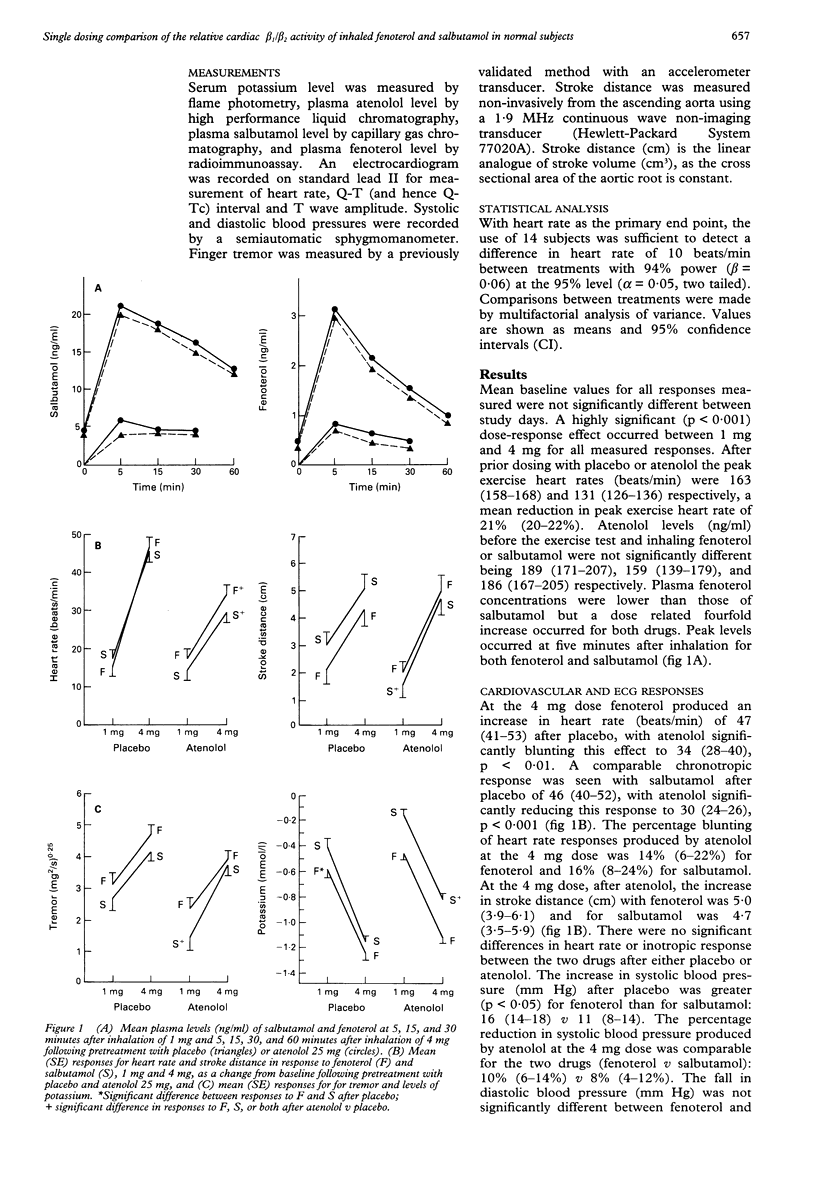
Abstract
BACKGROUND--The aim of the present study was to compare the dose related effects of fenoterol and salbutamol on cardiac beta 1 and beta 2 receptors using the beta 1 selective antagonist atenolol, in order to dissect out relative beta 1/beta 2 mediated responses. METHODS--Fourteen normal volunteers were randomised to receive pretreatment with either atenolol 25 mg or placebo, followed by inhaled fenoterol or salbutamol in equal doses by weight (cumulative doses of 1 mg and 4 mg). Measurements were made 30 minutes after inhaling each dose of beta 2 agonist. Values (mean and 95% CI) were expressed as a change from baseline. RESULTS--At 4 mg fenoterol produced equivalent falls in serum potassium and increases in tremor to salbutamol. The mean (95% CI) increase in heart rate (beats/min) with fenoterol at 4 mg after placebo was 47 (41-53) and after atenolol was 34 (28-40), with values for salbutamol being 46 (40-52) after placebo and 30 (24-36) after atenolol. The inotropic response (stroke distance) after atenolol at the 4 mg dose was 5.0 (3.9-6.1) cm for fenoterol and 4.7 (3.5-5.9) cm for salbutamol. There were no significant differences in heart rate or stroke distance response between the two drugs after either placebo or atenolol. Furthermore, ECG effects (Q-Tc and T wave) of fenoterol and salbutamol were comparable at both doses. CONCLUSIONS--These results show that there is no difference in the respective chronotropic or inotropic activities of fenoterol and salbutamol on cardiac beta 1 or beta 2 receptors when given at higher than conventional doses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crane J., Burgess C., Beasley R. Cardiovascular and hypokalaemic effects of inhaled salbutamol, fenoterol, and isoprenaline. Thorax. 1989 Feb;44(2):136–140. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. A., Petch M. C., Brown M. J. Intracoronary injections of salbutamol demonstrate the presence of functional beta 2-adrenoceptors in the human heart. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):546–553. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz A., Schwartz J., Velly J. Beta-adrenoceptors of the human myocardium: determination of beta 1 and beta 2 subtypes by radioligand binding. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):711–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipworth B. J., Brown R. A., McDevitt D. G. Assessment of airways, tremor and chronotropic responses to inhaled salbutamol in the quantification of beta 2-adrenoceptor blockade. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;28(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipworth B. J., Irvine N. A., McDevitt D. G. A dose-ranging study to evaluate the beta 1-adrenoceptor selectivity of bisoprolol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;40(2):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00280067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipworth B. J., Tregaskis B. F., McDevitt D. G. Comparison of hypokalaemic, electrocardiographic and haemodynamic responses to inhaled isoprenaline and salbutamol in young and elderly subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;40(3):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00315205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Lincoln C. Beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human, rat, guinea pig, and rabbit atria. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):1216–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windom H. H., Burgess C. D., Siebers R. W., Purdie G., Pearce N., Crane J., Beasley R. The pulmonary and extrapulmonary effects of inhaled beta-agonists in patients with asthma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Sep;48(3):296–301. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1990.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. S., Pavord I. D., Williams J., Britton J. R., Tattersfield A. E. Bronchodilator, cardiovascular, and hypokalaemic effects of fenoterol, salbutamol, and terbutaline in asthma. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1396–1399. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93099-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



