Background: Characterization of a Nonconsensus xenobiotic response element (NC-XRE), a novel AhR binding site.
Results: AhR binding to the NC-XRE in response to TCDD results in the recruitment of CPS1 and concomitant homocitrullination of histone H1.
Conclusion: CPS1-mediated homocitrullination of histone H1 on lysine 34 is a novel epigenetic mark.
Significance: Homocitrulline (hcit) is a novel epigenetic histone mark involved in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional activation.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) (AHR), chromatin modification, dioxin, gene regulation, hepatocyte
Abstract
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a regulator of xenobiotic toxicity, is a member of the eukaryotic Per-Arnt-Sim domain protein family of transcription factors. Recent evidence identified a novel AhR DNA recognition sequence called the nonconsensus xenobiotic response element (NC-XRE). AhR binding to the NC-XRE in response to activation by the canonical ligand 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin resulted in concomitant recruitment of carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) to the NC-XRE. Studies presented here demonstrate that CPS1 is a bona fide nuclear protein involved in homocitrullination (hcit), including a key lysine residue on histone H1 (H1K34hcit). H1K34hcit represents a hitherto unknown epigenetic mark implicated in enhanced gene expression of the peptidylarginine deiminase 2 gene, itself a chromatin-modifying protein. Collectively, our data suggest that AhR activation promotes CPS1 recruitment to DNA enhancer sites in the genome, resulting in a specific enzyme-independent post-translational modification of the linker histone H1 protein (H1K34hcit), pivotal in altering local chromatin structure and transcriptional activation.
Introduction
Since its discovery in 1980s, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)2 has been a major focus of study in the field of toxicology because it mediates the effects of environmental pollutants such as dioxins. The AhR is a ligand-mediated basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor in the Per/Arnt/Sim domain protein family (1). It regulates adaptive and toxic responses to a variety of chemical pollutants, most notably 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) (2). In the canonical pathway, the cytoplasmic AhR translocates to the nucleus upon ligand binding and forms a heterodimer with the Arnt (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator). The AhR-Arnt heterodimer binds to the xenobiotic response element flanking numerous AhR target genes. The XRE is present in the promoter regions for many detoxification genes, which code for the phase I and II xenobiotic metabolic enzymes including the cytochrome P450 superfamily (CYP) (3–5). Assessment of the epigenetic mechanisms regulating CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 genes revealed that TCDD induction triggered several core histone modifications associated with recruitment of the histone acetylase coactivators p300, steroid receptor coactivator 1, steroid receptor coactivator 2, and the p300/CBP-associated factor (6, 7).
Recent studies identified a novel DNA sequence referred to as nonconsensus xenobiotic response element (NC-XRE) capable of binding the AhR independently of the Arnt protein (8). Subsequent experiments demonstrated that AhR binding to the NC-XRE depended instead on an interaction with Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) (9). Using the NC-XRE as a DNA affinity reagent to purify the TCDD-inducible complex in mouse liver, we identified carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1) as a component of the AhR-KLF6 complex by mass spectrometry sequencing. CPS1 is a ≈160-kDa multidomain protein that catalyzes the irreversible reaction (2ATP + HCO3− + NH3 → 2ADP + Pi + carbamoyl-phosphate) (10, 11). CPS1 is ordinarily considered a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the detoxification of ammonia by producing urea through the urea cycle (12). In this study we demonstrate that CPS1 is also a nuclear protein recruited by the AhR to NC-XRE sites in the hepatocyte genome and is responsible for carbamylation (homocitrullination) of a functionally important histone H1 lysine residue (H1K34) implicated in transcriptional regulation. The homocitrulline (hcit) constitutes a novel epigenetic mark envisioned to promote chromatin remodeling into a more accessible transcriptionally active conformation.
Experimental Procedures
Animals and Primary Hepatocyte Isolation
C57BL/6 mice (8–10-week-old females) were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME). AhRfl/fl (AhR floxed) and AhRfl/fl/CreAlb mice (AhR CKO, a hepatocyte-specific conditional AhR knock-out using Cre-loxP recombination system) are maintained as in-house colonies. All experimental procedures were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. AhR floxed and AhR CKO primary hepatocytes were isolated using a collagenase perfusion method as previously described by us (13). TCDD (Cerilliant, Round Rock, TX) was dissolved in anisol and diluted to 2 μg/ml in peanut oil (vehicle) for in vivo use or to 200 nm in DMSO (vehicle) for use in cell culture. Mice were gavaged with either 100 μl of vehicle or 20 μg/kg TCDD (100 μl) for 2 h before sacrifice. For cell culture, primary hepatocytes were treated vehicle or 6 nm TCDD for 24 h.
Nuclear Extract Preparation
Nuclear extracts from liver tissues and isolated hepatocytes from C57BL6, AhRfl/fl (AhR floxed), and AhRfl/fl/CreAlb AhR CKO were prepared using sucrose cushion as described previously (9).
Affinity Pulldown with NC-XRE-Biotin
Nuclear extracts from vehicle or TCDD (20 μg/kg for 2 h) treated C57BL/6 mice were prepared and incubated with beads binding buffer (20 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mm MgCl2, 1 mm DTT, 10% glycerol, 0.01 μg/μl poly(dI-dC), 1 mm NaF, 1 mm Na2VO4, 1 mm PMSF, 5 μl/ml protease inhibitor mixture (Sigma-Aldrich), 0.1% BSA. In a separate tube, prewashed Dynal streptavidin M280 beads (Life Technologies, Inc.) were mixed with 100 ng/μl of annealed NC-XRE-Biotin primers (forward, biotin-GTCCCAGCAAGTCACTGGGAGGGAGGGAGGGAGGGGGAG; reverse, CTCCCCCTCCCTCCCTCCCTCCCAGTGACTTGCTGGGAC). Nuclear extracts were added to the streptavidin beads containing NC-XRE-biotin and incubated for 30 min. Magnetic beads were washed three times with beads wash buffer (20 mm NaCl, 20 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 1 mm MgCl2, 0.5 mm DTT, 0.01 μg/μl poly(dI-dC), 1 mm NaF, 1 mm Na2VO4, 1 mm PMSF, 5 μl/ml protease inhibitor mixture (Sigma-Aldrich), 0.1% BSA). Samples were eluted and stored at −80 °C.
Two-dimensional Difference Gel Electrophoresis (2D-DIGE)
Affinity pulldown nuclear proteins were cleaned using the Ettan 2-D cleanup kit (GE Healthcare), protein pellets were resuspended in ice-cold DIGE-specific lysis buffer (30 mm Tris, 8 m urea, 2% CHAPS, pH 8.5 buffer) and labeled with Cy dyes (Cy3 for vehicle-treated, Cy5 for TCDD-treated), and Cy2 for internal standard composed of pooled aliquots comprising equal amounts of the vehicle and TCDD samples. 400 pm of dye was used for 50 μg of protein. Labeling was stopped with 10 mm lysine, and 2× sample buffer containing 8 m urea and 2% CHAPS was added. After adding 100 μl of rehydration buffer (Destreak rehydration buffer containing 0.5% IPG buffer 3-11 NL) samples were loaded on a 3-11 nonlinear IPG strip. After equilibration with DTT and iodoacetamide equilibration solutions, strip was loaded onto second dimension 4–15% Tris-HCl gradient gels. DeCyder version 7.0 was used to analyze the 2D-DIGE images as described in the Ettan DIGE user manual (GE Healthcare). Spots with p < 0.05, filtered based on an average volume ratio >2-fold between vehicle- and TCDD-treated, were selected for picking.
Mass Spectrometry
For spot picking and identification, preparative IEF/2D-PAGE was performed using 500 μg of protein by pooling equal amounts of vehicle- and TCDD-treated affinity-purified nuclear extracts. Preparative gels were stained with Sypro Ruby for 3–4 h at room temperature and destained for 1 h or until the spots were clearly visible. The MASCOT search results for CPS1 are available in the supplemental materials. hcit PTMs (carbamyl lysines) in the TCDD-treated nuclear extracts were detected using nanoLC-MS/MS (LTQ Orbitrap Velos (Thermo Scientific, West Palm Beach, FL). Data files were processed using Proteome Discoverer (Thermo Scientific) and searched against a combined Uniprot Rat-Mouse database using MASCOT (Matrix Sciences) with carbamidomethyl cysteine as fixed modification and methionine oxidation and hcit as variable modifications.
Western Blotting and Coimmunoprecipitation
Nuclear extracts were mixed with TGH buffer (50 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, 150 mm NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1.5 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EGTA, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mm PMSF, 10 mm NaF, 1 mm Na3VO4, 5 μl/ml protease inhibitor mixture, and 1 μg/ml BSA) and with either anti-AhR (Enzo Life Sciences, Farmingdale, NY) or anti-CPS1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX). Precipitation was carried out using protein A/G Plus-agarose beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Samples were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE gels, transferred to PVDF membranes, and probed with goat anti-CPS1 or rabbit anti-AhR antibodies respectively. Images were captured using Typhoon Trio variable mode imager (GE Healthcare). Homocitrullination was detected using goat anti-carbamyl-lysine polyclonal antibody (Cell Biolabs, San Diego, CA). Rabbit polyclonal anti-CYP1A1 antibody and anti-histone H1 antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were also used.
Immunocytochemistry and Confocal Imaging
Primary hepatocytes from C57BL6 mice were treated with either DMSO or TCDD (6 nm) for 24 h. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at 4 °C, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100, and blocked for 1 h with 5% BSA. Cells were incubated with anti-CPS1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 1:100) overnight at 4 °C and treated with Alexa Fluor 488 anti-goat secondary antibody (Life Technologies, Inc.; 1:200). Nuclei were stained with SlowFade Gold with DAPI (Life Technologies, Inc.). Cells were imaged with Nikon D-Eclipse C1 inverted confocal microscope (60× oil immersion). Data analysis such as line scan was carried out using the digital image analysis software AxioVision (Zeiss, Thornwood, NY).
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
ChIP assays were performed on whole livers from AhR floxed mice treated with vehicle or TCDD (20 μg/kg) as described previously (9). Antibodies against the AhR (Abcam, Cambridge, MA), CPS1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), KLF6 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), H3 (positive control), and IgG (negative control) were used to immunoprecipitate the target proteins. Immunoprecipitated and input DNA were PCR-amplified using primers specific to the XRE in CYP1A1 and NC-XRE in the PAI-1 and PADI2 promoters. PCR products were fractionated on a 5% polyacrylamide gel, stained with SYBR Green (Life Technologies, Inc.), and imaged on a Typhoon Trio, and the band intensities were quantified using ImageQuant (GE Healthcare). Quantitative PCR on ChIP samples was performed by the Molecular Genomics Core at the University of Texas Medical Branch. The primers used for PCR were CYP1A1 (forward, 5′-CTATCTCTTAAACCCCACCCCAA-3′; reverse, 5′-CTAAGTATGGTGGAGGAAAGGGTG-3′) and PAI1 promoters (forward, 5′-GTCCCAGCAAGTCACTGGGAGG-3′; reverse, 5′-CTGGAGGCGGGTGTGCGGCG-3′). The NC-XRE in PADI2 was amplified using primers 5′-TCCATCGTTCCTCTG-3′ (forward) and 5′ CGATGATGACAGCACAACA-3′ (reverse).
Amino Acid Analysis
Nuclear extracts isolated from AhR floxed and AhR CKO mice treated with vehicle or TCDD were subjected to amino acid analysis to detect hcit. 100 μg of protein was precipitated using the two-dimensional cleanup kit (GE Healthcare) to remove salts and detergents from samples. The protein pellet was hydrolyzed using 6 n HCl. Amino acid analysis was performed using Hitachi L-8800 amino acid analyzer. The EZChrom Elite was used to monitor the height and area of the amino acid peak and calculate estimated concentration of amino acid in nmol. Mole percentage for homocitrulline was calculated as [(nmol of homocitrulline)/(total nmol of all amino acids in the sample)] * 100.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
EMSAs were performed using crude nuclear extracts or extracts immunodepleted for the AhR, KLF6, or CPS1 isolated from vehicle- and TCDD-treated (20 μg/kg for 2 h) mouse livers. Immunoprecipitations were carried out using protein A/G Plus-agarose beads. Nuclear extracts (10 μg) were used in EMSA with 300 ng of 32P-NC-XRE ([32P]ATP end-labeled double stranded DNA probe, 3000 mCi/mmol) as described previously (9, 14).
Pulse-Chase Experiment
Primary hepatocytes isolated from AhR floxed mice were starved in methionine-free DMEM + 5% FBS for 30 min. [35S]Methionine (100 μCi) was added to the medium, and the cells were incubated for 14 h at 37 °C. Radioactive medium was carefully removed, cells were washed with PBS, and DMEM containing 5% FBS was added. Hepatocytes were treated with 10 μm β-naphthoflavone (βNF) for 2, 24 and 48 h. Cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-histone H1 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and homocitrullination was detected using an anti-carbamyl lysine antibody. Autoradiography was performed using storage phosphor screens (GE Healthcare) and imaged on Typhoon Trio variable mode imager (GE Healthcare).
Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as means ± S.E. The data were analyzed by applying t test using Sigma Stat software (Systat Software). Differences between the groups were considered significant only if the p value is <0.05.
Results
Identification of CPS1 as an Integral Component of the NC-XRE-bound AhR Complex
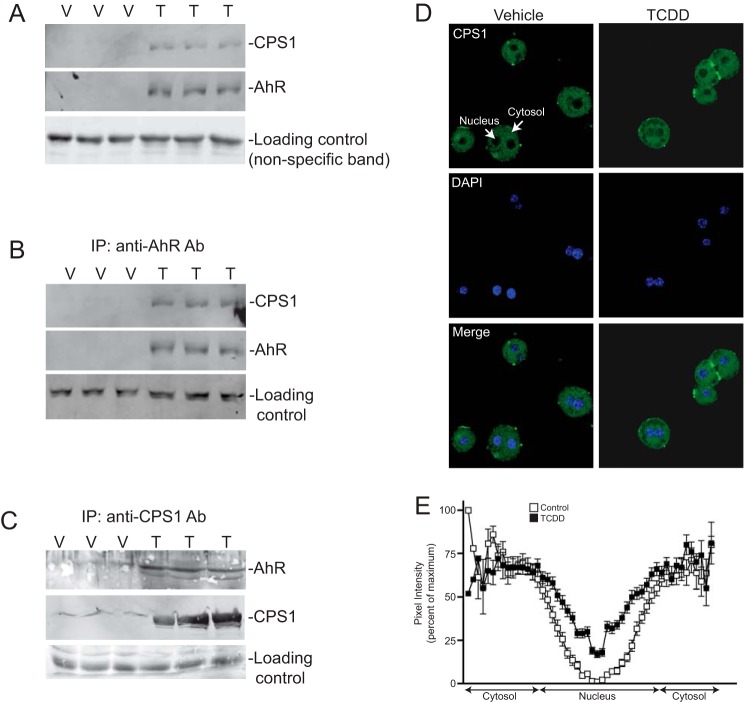
Given the recruitment of established chromatin modifying coactivator proteins to the XRE, we wished to identify the AhR coactivators recruited to the newly identified NC-XRE. Nuclear extracts isolated from vehicle- and TCDD-treated mouse liver nuclei with a biotinylated NC-XRE oligonucleotide (bound to streptavidin-conjugated magnetic beads) as an affinity reagent to capture and enrich the AhR complex from TCDD-treated mouse liver nuclei. 2D-DIGE was performed on Cy3 (vehicle control) and Cy5 (TCDD) labeled proteins to identify protein spots enriched (>2-fold) in the TCDD-treated extracts (Fig. 1). Protein spots picked from a preparative gel were subjected to trypsin digestion and Nano-LC/MS/MS (Thermo Finnigan LTQ Orbitrap Velos). CPS1 was identified by MS sequencing as one of several novel proteins increased as a function of TCDD treatment. Western blotting on independently isolated replicate murine liver nuclear extracts confirmed that CPS1 is enriched in TCDD-treated nuclei concomitant with AhR activation and nuclear translocation (Fig. 2). Moreover, CPS1 coimmunoprecipitated with the AhR in a TCDD-dependent manner (Fig. 2B), and reciprocal coimmunoprecipitation experiments confirmed the association (Fig. 2C). The ability to detect some CPS1 protein in vehicle-treated nuclei (Fig. 2C), suggested that a trace amount of CPS1 may be constitutively present in nuclei and is rendered detectable following immunological enrichment. Further evidence for CPS1 nuclear compartmentalization was obtained using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy (Fig. 2D). Cultured C57BL6 mouse primary hepatocytes treated with DMSO (vehicle) or 6 nm TCDD for 2 h were immunologically probed for CPS1 and staining analyzed by confocal microscopy. DAPI staining identified the nuclei. Quantitation of nuclear staining and the surrounding cytosol revealed that nuclear CPS1 levels are markedly increased in TCDD-treated cells (Fig. 2E). The result shows that only a small fraction of the total cellular CPS1 protein enters the nuclei.
FIGURE 1.
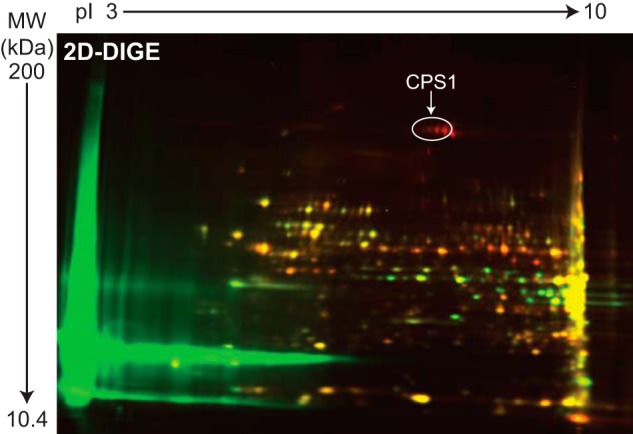
CPS1 recruitment to the NC-XRE. Nuclear extracts from C57BL/6 mice treated with vehicle (peanut oil) or 20 μg/kg TCDD for 2 h were subjected to affinity purification using the NC-XRE sequence. Affinity-purified proteins from vehicle-treated (Cy3, green) and TCDD-treated (Cy5, red) extracts were fractionated by 2D-DIGE. Nano-LC-MS/MS identified CPS1 (see annotation) as one of several proteins enriched in the TCDD-treated samples.
FIGURE 2.
AhR interaction and nuclear translocation of CPS1. A, whole liver nuclear extracts (50 μg) isolated from C57BL/6 mice treated with 20 μg/kg TCDD (T) or vehicle (V) for 2 h were subjected to immunoblotting. The results are for independent animals. B, vehicle- (V) and TCDD-treated (T) mouse liver nuclear protein (1 mg) was immunoprecipitated (IP) with an antibody against AhR and immunoblotted for the AhR and CPS1 as independent animals in triplicate. C, reciprocal immunoprecipitation using a CPS1 antibody followed by immunoblotting as described for B. D, indirect immunofluorescence confocal microscopy on vehicle (DMSO) and TCDD-treated primary hepatocytes stained for CPS1 (green) and DAPI (blue). E, densitometric quantitation across individual hepatocytes was performed to measure nuclear and cytosolic CPS1 staining and plotted as percentages of pixel intensity. The data represent n = 47 cells for vehicle controls and n = 46 for TCDD-treated cultures (in 12 random fields from two independent experiments).
CPS1 and AhR Are Recruited to the PAI-1 Promoter in Vivo in Response to TCDD
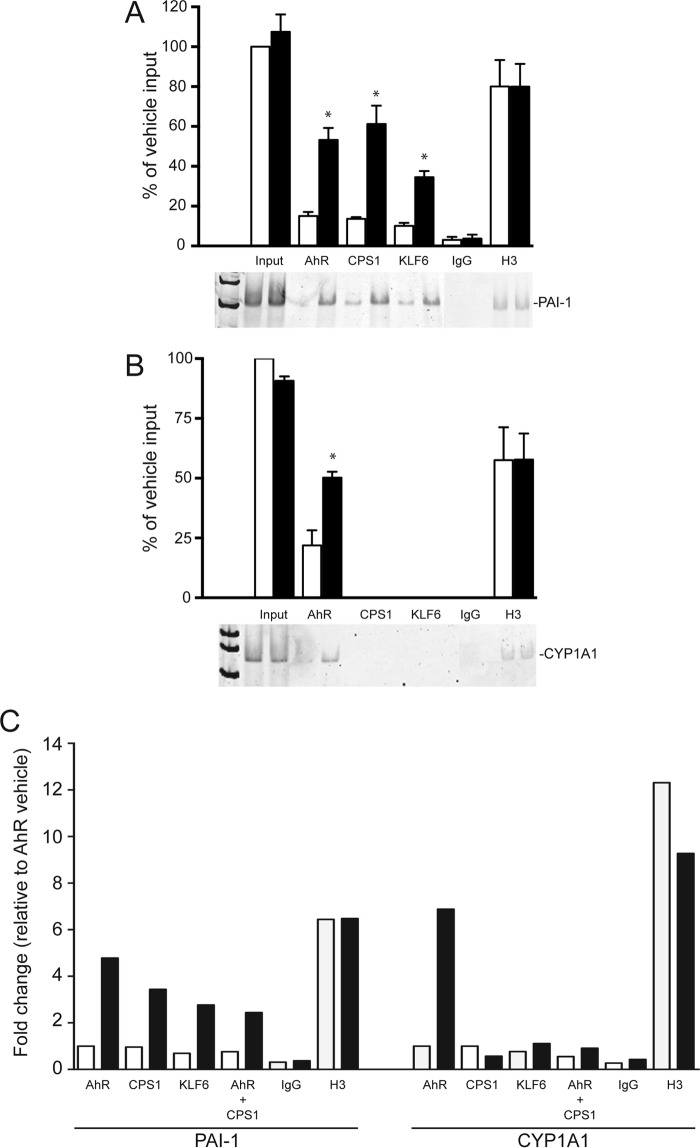
We recently showed that the AhR-KLF6 complex is recruited to an upstream PAI-1 gene regulatory region containing a functional NC-XRE (8, 9). In vivo ChIP assays were performed on whole liver tissue targeting the PAI-1 and CYP1A1 promoter regions harboring the NC-XRE and XREs, respectively (Fig. 3). ChIP on the PAI-1 promoter revealed that the AhR, KLF6, and CPS1 each exhibited TCDD-dependent DNA binding, whereas binding to the CYP1A1 promoter was restricted to the AhR. Quantitative re-ChIP experiments confirmed that the AhR and CPS1 are simultaneously bound to the same PAI-1 promoter sequence (Fig. 3C). Immunological evaluation of the protein-DNA complex using mouse liver nuclear extracts and the NC-XRE oligonucleotide established the presence of each protein in the complex (Fig. 4). Because the antibodies against the AhR, CPS1, and KLF6 did not generate a “supershift” product in the EMSA (data not shown), we used immunodepleted nuclear extracts to establish involvement of each protein in complex formation. Fig. 4A confirms successful immunodepletion of the extracts for AhR, CPS1, and KLF6 with the specific antibodies, whereas use of a nonspecific IgG preserved the proteins. EMSA was performed using AhR-, CPS1-, and KLF6-depleted nuclear extracts (Fig. 4B). Although a pronounced TCDD-inducible protein-DNA complex was readily detectable with the IgG-treated nuclear extract, the absence of a gel shift product using immunodepleted extracts demonstrated that AhR, CPS1, and KLF6 all contribute to the formation of a single multisubunit complex at the NC-XRE.
FIGURE 3.
TCDD-dependent AhR and CPS1 binding to the PAI-1 promoter. ChIP assays were performed on liver tissue isolated from vehicle-treated (open bars) and TCDD-treated (solid bars) floxed mice (20 μg/kg for 2 h). Antibodies against AhR, CPS1, KLF6, H3 (positive control), and IgG (negative control) were used to immunoprecipitate target proteins. PCR primers against the PAI-1 and CYP1A1 promoters flanking NC-XRE and XRE sites, respectively, were used to amplify genomic DNA. PCR products were electrophoretically fractionated and stained with SYBR green. A and B, quantitation of PCR products against the PAI-1 promoter (A) and CYP1A1 promoter (B) from vehicle (open bars) and TCDD-treated mice is presented as a percentage of vehicle input DNA (n = 3, average ± S.E.). *, p < 0.05. C, quantitative PCR was performed on DNA isolated from vehicle- and TCDD-treated mouse livers in a sequential re-ChIP experiment using antibodies against the AhR, followed by CPS1.
FIGURE 4.
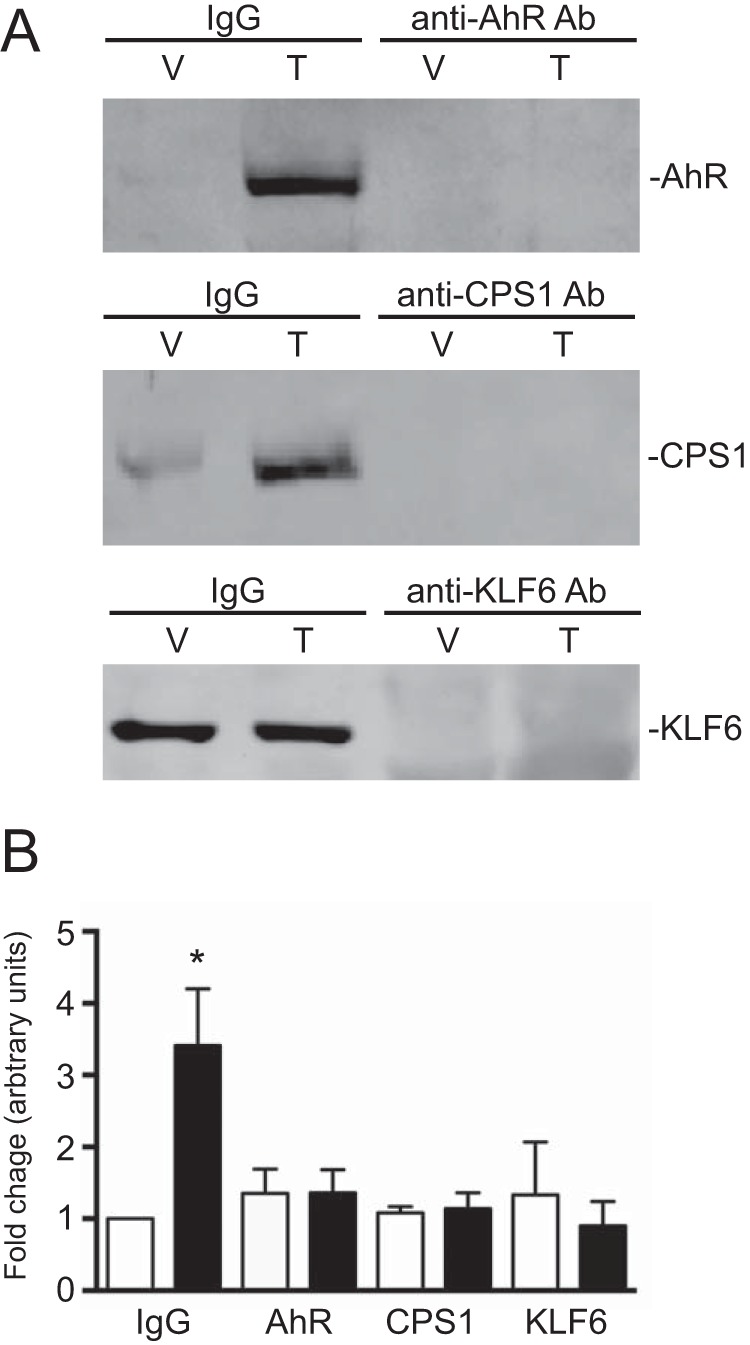
The AhR, KLF6, and CPS1 are required for NC-XRE complex formation. A, nuclear extracts were prepared from vehicle-treated (V) and TCDD-treated (T) mouse livers. Extracts were incubated with antibodies against the AhR, CPS1, and KLF6 to immunodeplete the nuclear extracts. A nonspecific IgG antibody was used as a control in both vehicle- and TCDD-treated extracts. B, EMSAs were performed with vehicle-treated (open bars) and TCDD-treated (solid bars) immunodepleted nuclear extracts (10 μg per reaction) using a 32P-radiolabeled NC-XRE probe. EMSA complexes were quantified using ImageQuant TL8.1 software (n = 3). *, p < 0.05.
In Vivo Carbamylation of Lysine Residues upon TCDD Treatment
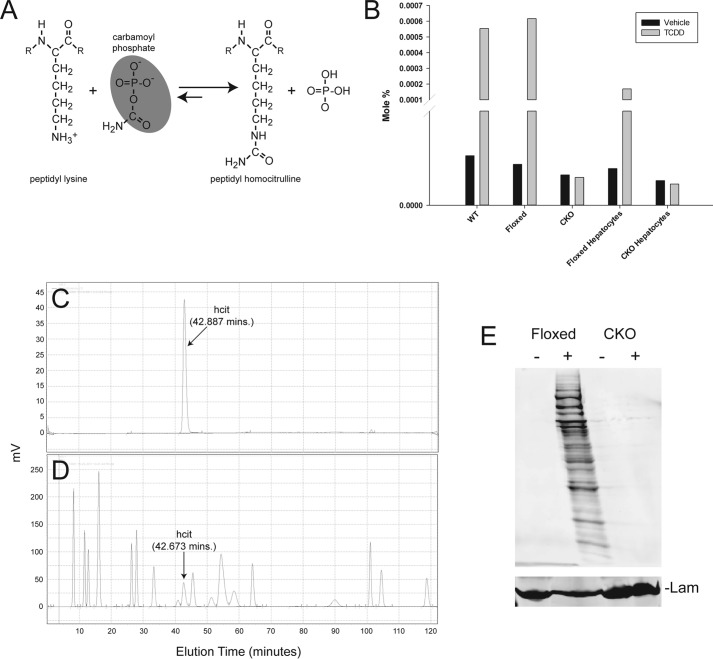
Carbamoyl phosphate, the product of CPS1 catalysis, can carbamylate lysine-rich histones in vitro to produce hcit through a nonenzymatic mechanism (15). Evidence for enzyme-independent covalent PTMs in cells has been documented previously (16–19). Identification of CPS1 as a nuclear protein recruited to the NC-XRE suggested that its DNA association could promote homocitrullination of nearby chromatin proteins. Because reactive metabolites readily interact with nucleophilic protein residues, we envision a mechanism where the highly electrophilic acylphosphate group on carbamoyl phosphate is subject to nucleophilic attack (Fig. 5A). This process was recently demonstrated for 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, which formed a specific, functionally important PTM on glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by a nonenzymatic process (17). To establish that AhR activation promotes homocitrullination of nuclear proteins, liver nuclear extracts prepared from vehicle- and TCDD-treated wild-type and AhR CKO mouse livers or primary hepatocytes were initially subjected to amino acid analysis (Fig. 5B). Amino acid analysis detected hcit only in nuclear extracts from TCDD-treated AhR-expressing cells. hcit detection by HPLC—eluting at 42–43 min—was confirmed using both pure hcit as a standard (Fig. 5C) and by monitoring hcit elution of potassium cyanate-treated pure bovine serum albumin under conditions that carbamylate 78% of the lysine residues (20) (Fig. 5D). Formation of hcit was independently confirmed by Western blotting using an anti-hcit polyclonal antibody to probe liver nuclear extracts from vehicle- and TCDD-treated AhR floxed and AhR CKO mice (Fig. 5E). The evidence also revealed that numerous nuclear proteins are targets for homocitrullination.
FIGURE 5.
The AhR is required for homocitrullination. A, peptidyl homocitrulline formed by reaction of a lysine ϵ-amine with the acylphosphate functionality in carmamoyl phosphate (shaded). B, amino acid analysis was performed on nuclear extracts from C57BL/6 (WT), AhR floxed, and hepatocyte-specific AhR CKO mice treated with vehicle (solid bars) or 20 μg/kg of TCDD for 2 h (shaded bars) or nuclear extracts from primary hepatocytes isolated from AhR floxed and AhR CKO mice and treated with vehicle or 6 nm TCDD for 24 h (n = 1). hcit eluted from the HPLC as a peak at ∼43 min and is expressed as a mole percentage. C and D, amino acid analysis on pure homocitrulline as a standard (C) and potassium cyanate-treated BSA (D) is shown. E, nuclear protein from vehicle-treated (−) and TCDD-treated (+) AhR floxed and CKO mouse liver tissue was analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-carbamyl-lysine (anti-hcit) polyclonal antibody (n = 2). Lamin B (Lam) was used as a loading control.
CPS1 Is Required for Nuclear Protein Homocitrullination
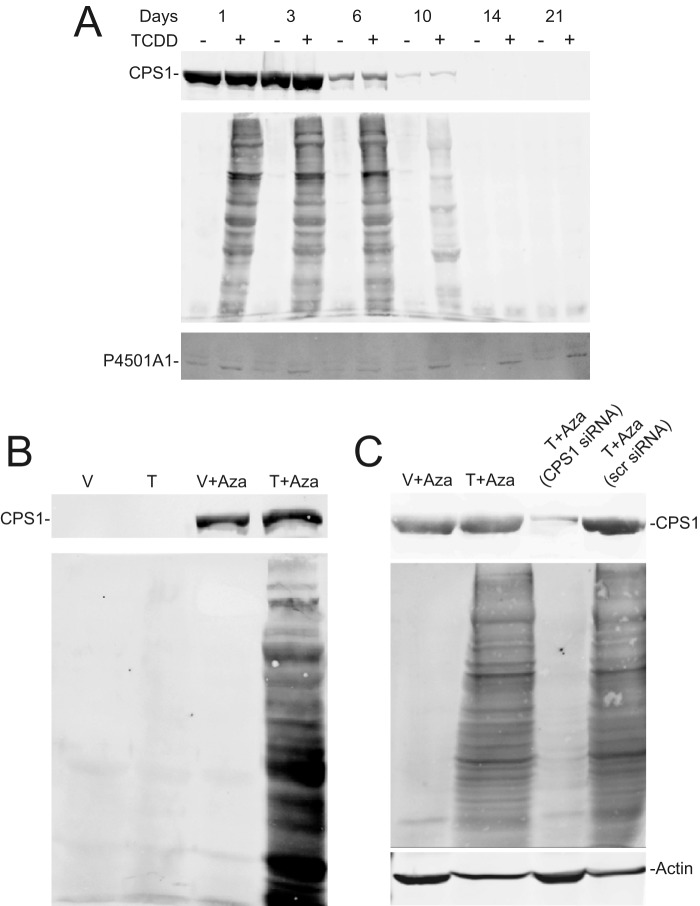
Studies using primary hepatocytes and AML12 cells—a differentiated nontransformed mouse hepatocyte line (21)—confirmed that CPS1 is necessary for homocitrullination of nuclear proteins. Although CPS1 is a long-lived protein refractory to RNA interference-based knockdown strategies (22, 23), cultured primary hepatocytes spontaneously suppress CPS1 expression (Fig. 6A). Taking advantage of this observation, we observed that TCDD-dependent homocitrullination of nuclear proteins diminished in lock step with loss of CPS1 expression. However, P4501A1 inducibility, which does not rely on CPS1, confirmed that AhR functionality persisted over the 3-week culture period. In complementary studies, CPS1 expression was re-established in AML12 cells using 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine (5-Aza) to hypomethylate the CPS1 promoter (24). TCDD-inducible hcit formation only occurred in the 5-Aza-treated CPS1-positive cells (Fig. 6B). Using siRNA, we were able to specifically suppress nascent CPS1 expression in AML12 cells grown in the presence of 5-Aza (Fig. 6C) and demonstrate that homocitrullination is absolutely dependent on CPS1.
FIGURE 6.
CPS1 is required for homocitrullination. A, primary hepatocytes isolated from C57BL/6 mice were plated on Matrigel. Hepatocytes were treated with vehicle (−) or 6 nm TCDD for 24 h prior to harvesting at the indicated times. Total cell lysates (top and bottom panels) and nuclear extracts (middle panel) were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting for CPS1 (top panel), hcit (middle panel), and P4501A1 (bottom panel). B, AML12 cells were cultured in the absence or presence of 10 μm 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine (Aza) for 3 consecutive days. Cells were treated with vehicle (V) or 6 nm TCDD (T) for the final 24 h. Nuclear extracts and total cell lysates were prepared for immunoblotting against hcit and CPS1, respectively. The data are representative of three independent experiments. C, AML12 cells were treated with 10 μm 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine for 2 days in the absence of siRNA or the presence of a CPS1 specific siRNA or a nonspecific scrambled siRNA (scr siRNA), delivered by transient transfection. Cells were treated with vehicle (V) or 6 nm TCDD (T) for the final 24 h. Nuclear extracts and total lysates were prepared for detection of hcit and CPS1 respectively (n = 2). Actin was used as a loading control.
Next, nuclear proteins were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and processed for mass spectrometry to identify the hcit-modified proteins. Tryptic peptides were analyzed by nanoLC-MS/MS using a LTQ Orbitrap Velos. Data files were processed using Proteome Discoverer and searched against the Uniprot-Mouse database using Mascot with carbamidomethyl cysteine as a fixed modification and variable modifications of methionine oxidation, lysine carbamylation, and peptide N-terminal carbamylation. For trials 1 and 2, MS/MS spectra were acquired in the ion trap. To confirm the identity and site localization for carbamylated peptides, the top four ions were chosen for fragmentation in the ion trap with detection in the Orbitrap at 7500 resolution. In three independent experiments, numerous nuclear proteins were reproducibly identified with one or more homocitrullinated peptides, including histone H1. Homocitrullination specifically targeted a single lysine residue at position 34 (H1K34) on histone H1.2/1.3 (Fig. 7). Mass accuracy of the parent ion in the mass scan is illustrated in Fig. 7A. Carbamylated peptides for histone H1.2/1.3 were manually verified by comparing observed fragment m/z values to theoretical values obtained from the MS-Product utility within Protein Prospector. All fragment ions whose measured mass error fell within 2× standard deviation from the mean error value were accepted as being correct. Table 1 denotes mass accuracy for all fragment ions in the MS/MS spectrum. It is noteworthy that Lys-34 in histone H1.2/1.3—the peptide KASGPPVSELITK being common to both histone variants—is also subject to acetylation, monomethylation, and formylation (25). Interestingly, the same lysine residue is also acetylated in histone variant H1.4 (H1.4K34Ac), a modification recently shown to be associated with transcriptional activation (26).
FIGURE 7.
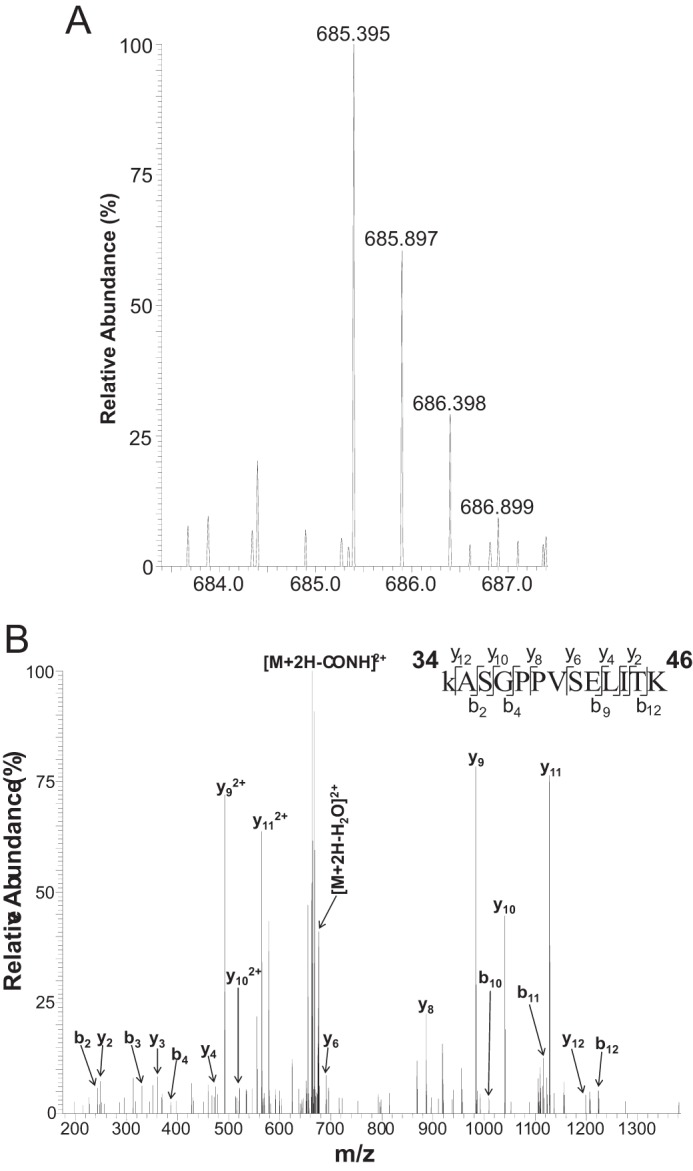
Lysine 34 on histone H1 is homocitrullinated. A, high resolution MS spectrum of (hcit-K)ASGPPVSELITK (theoretical [M+2H]2+ = 685.388; observed = 685.395; error = 10.2 ppm). The mass of the parent ion is shifted from the mass of the unmodified form of the peptide (theoretical [M+2H]2+ = 663.885) by 43.006 Da, corresponding to the addition of a carbamyl group. B, high resolution MS/MS spectrum of (hcit-K)ASGPPVSELITK (Mascot ion score 47), encompassing residues 34–46 in the histone variants 1.2 and 1.3. The mass accuracy of the parent ion in the mass scan is shown. Detailed information regarding observed and theoretical m/z values for fragment ions can be found in Table 1 and the supplemental materials.
TABLE 1.
Detailed information regarding observed and theoretical m/z values for the fragment ions detected in the MS/MS spectrum of (hcit-K) ASGPPVSELITK
| Observed m/z | Theoretical m/z | Mass error | Ion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Da | |||
| 243.15 | 243.15 | 0.00 | b2 |
| 248.16 | 248.16 | 0.00 | y2 |
| 330.18 | 330.18 | 0.00 | b3 |
| 361.25 | 361.24 | 0.01 | y3 |
| 387.2 | 387.20 | 0.00 | b4 |
| 474.33 | 474.33 | 0.00 | y4 |
| 492.3 | 492.29 | 0.01 | y9+2 |
| 520.81 | 520.80 | 0.01 | y10+2 |
| 564.33 | 564.32 | 0.01 | y11+2 |
| 599.85 | 599.84 | 0.01 | y12+2 |
| 663.89 | 663.89 | 0.00 | [M + 2H-CONH2]+ 2 |
| 676.39 | 676.38 | 0.01 | [M + 2H-H2O]+ 2 |
| 690.41 | 690.40 | 0.01 | y6 |
| 886.53 | 886.52 | 0.01 | y8 |
| 896.45 | 896.45 | 0.00 | b9 |
| 983.59 | 983.58 | 0.01 | y9 |
| 1009.54 | 1009.53 | 0.01 | b10 |
| 1040.61 | 1040.60 | 0.01 | y10 |
| 1122.62 | 1122.62 | 0.00 | b11 |
| 1127.64 | 1127.63 | 0.01 | y11 |
| 1198.68 | 1198.67 | 0.01 | y12 |
| 1223.68 | 1223.66 | 0.02 | b12 |
CPS1 Is Required for AhR-mediated PADI2 Induction
Peptidylarginine deiminase (PADI) enzymes convert arginine and methylarginine residues to citrulline via a hydrolytic process called citrullination or deimination (27). PADI2 has been shown to citrullinate histone H3 and H4, respectively (28). In silico analysis of the murine PADI2 promoter and upstream flanking region revealed the presence of multiple putative NC-XRE sites (Fig. 8A). Quantitative RT-PCR results confirmed that PADI2 is a TCDD-responsive gene in AML12 cells, but only when CPS1 is expressed (Fig. 8B). Moreover, quantitative ChIP and re-ChIP assays confirmed that the AhR and CPS1 simultaneously bind to a NC-XRE containing region between 3850 and 3550 bp upstream of the PADI2 transcription start site (Fig. 8C). The AhR-mediated induction of PADI2 expression has important implications for histone epigenetics affecting chromatin structure and function.
FIGURE 8.
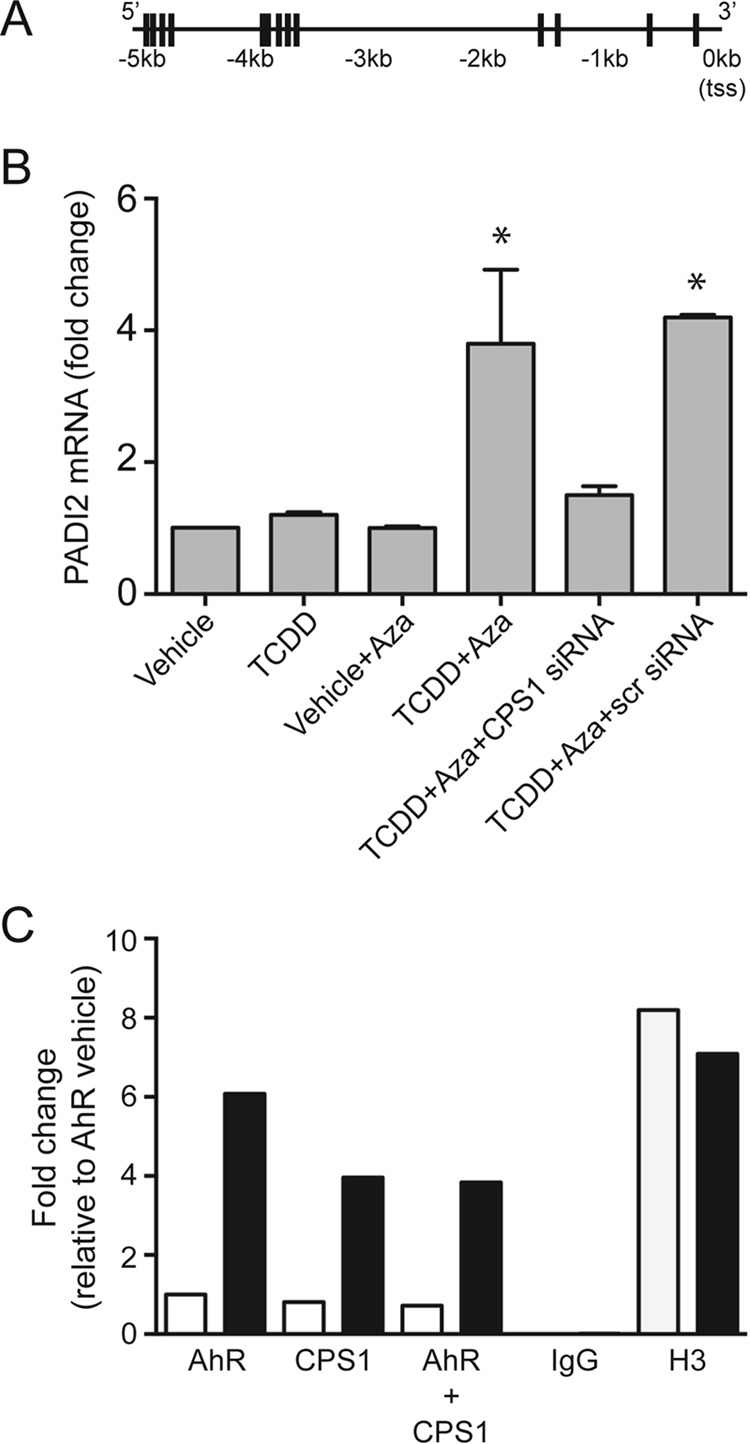
CPS1 is necessary for AhR-mediated PADI2 induction. A, schematic depicting the location of NC-XRE sequences (vertical lines) within a 5-kb region upstream of the PADI2 gene transcription start site. B, AML12 cells were grown in the presence and absence of 10 μm 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine (Aza) and transfected with siRNAs as described in the Fig. 6 legend. For final 24 h, AML12 cells were treated with either vehicle or 6 nm TCDD. Quantitative RT-PCR for PADI2 on isolated total RNA is shown. *, p < 0.05 (n = 3). C, in vivo ChIP and re-ChIP assays for the AhR, CPS1, H3 (positive control), and IgG (negative control) in mouse liver treated with vehicle or TCDD (20 μg/kg for 2 h). Quantitative PCR-amplified the NC-XRE cluster between −3850 and −3550 bp in the PADI2 upstream region.
Histone H1 Homocitrullination Is Reversible
Because histone H1 turnover is slow (29), dynamic physiologically meaningful PTMs ought to be reversible. Accordingly, evidence of transient (i.e. reversible) hcit formation is a prerequisite for ascribing functional significance to the hcit PTM. We used the rapidly metabolized AhR agonist, β-naphthoflavone (βNF) (30) in lieu of long-lived TCDD to transiently activate the receptor (Fig. 9). Transient, changes in nuclear protein homocitrullination mirrored AhR activity, which was monitored using P4501A1 protein expression over a 48-h period, suggesting that hcit formation is indeed reversible. Furthermore, pulse-chase experiments measuring 35S-labeled histone H1 protein turnover revealed that although H1 is stable over a 48-h period, H1 homocitrullinaltion following βNF treatment was fleeting, peaking at 24 h coincident with maximal AhR-mediated transcriptional activity (Fig. 9B). These data clearly show that histone H1 homocitrullination is reversible, in keeping with a dynamic, regulable epigenetic mechanism. The enzymatic process responsible for hcit removal remains elusive, however.
FIGURE 9.
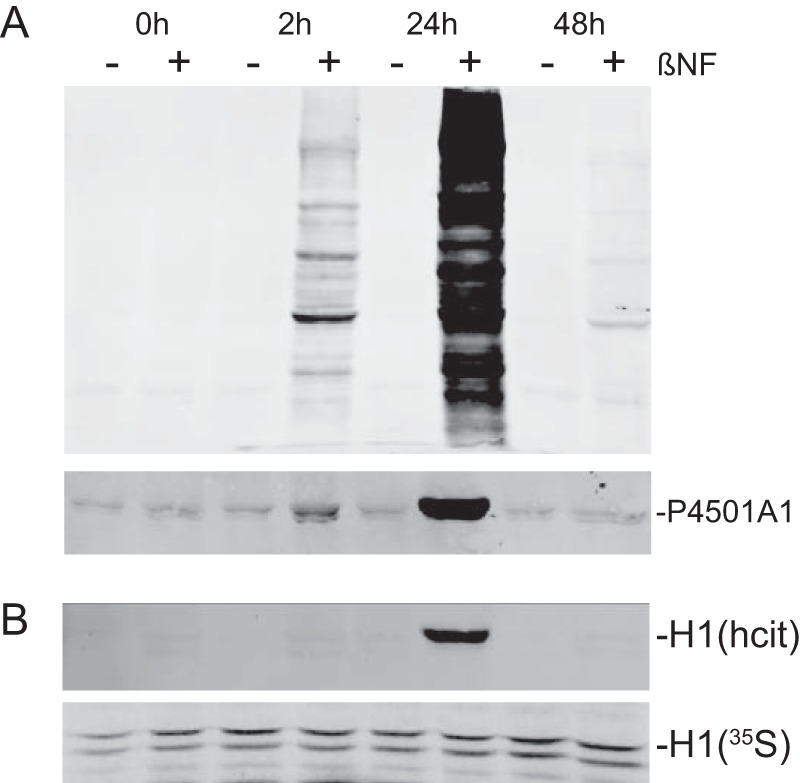
Homocitrullination is reversible. A, primary hepatocytes isolated from C57BL6 mice were treated with vehicle (−βNF) or 10 μm β-naphthoflavone (+βNF) for the indicated time. Nuclear extracts (20 μg) and total cell lysates (50 μg) were probed for hcit (top panel) and P4501A1, respectively, by immunoblotting. B, pulse-chase experiment using primary hepatocytes labeled with [35S]methionine (12 h) followed by cold methionine chase for up to 48 h. Cells were treated with 10 μm βNF for the indicated time followed by immunoprecipitation of the histone H1. Histone H1 was probed by Western blot for hcit and autoradiographed for 35S labeling.
Discussion
Identifying the NC-XRE as a novel AhR binding site served as the catalyst in the discovery of CPS1 as a component in the AhR-KLF6 complex. 2D-DIGE and MS sequencing identified CPS1 as one of several proteins enriched in NC-XRE-bound nuclear extracts from TCDD-treated mouse liver. The findings presented here demonstrate that CPS1 is a bona fide nuclear protein involved in an epigenetic process involving a hitherto unknown histone mark (H1K34hcit) that functionally regulates the expression of PADI2. Increased PADI2 expression is projected to enhance histone H3 citrullination (H3R26cit) at target promoters, resulting in chromatin decondensation and transcriptional activation (27). The implication is that CPS1 and PADI2 function in concert to modify histones H1 and H3, respectively, altering the epigenome in response to AhR activation. The precise repertoire of target genes regulated through this mechanism, and the physiological ramifications will be examined in future studies.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthase activity is catalyzed by three isoforms. The predominant isoforms are CPS1 and CPS2 (also known as CAD; carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 1, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase), which are responsible for urea and pyrimidine biosynthesis, respectively (31). Whereas CPS2 is a cytosolic enzyme, CPS1 is ostensibly a mitochondrial protein, yet it is CPS1 that is recruited to the NC-XRE. Both MS sequencing and Western blotting using isoform-specific antibodies confirmed CPS1 rather than CPS2 as a component of the NC-XRE complex. It is unclear at this time whether the CPS1 protein translocated into nuclei relies on CPS1 protein released from the mitochondrial compartment or draws upon a reservoir of cytosolic CPS1 not formerly identified. Cellular fractionation studies to date are inconclusive (data not shown) and will require further follow-up. Mitochondrial CPS1 is composed of six distinct domains, and the entire multidomain protein is required for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate (32). Although CPS1 is detected predominantly in the liver, biochemical studies in sheep demonstrated that CSP1 is also expressed—albeit at low levels—in several extrahepatic tissues including the intestinal epithelium, heart, kidney, lung, and spleen, suggesting that its expression is widespread (33). Hence, it is conceivable that the functional consequence of homocitrullination is not limited to the liver. It is also noteworthy that we detected multiple CPS1 species with different isoelectric points by 2D-DIGE (Fig. 1), suggesting that CPS1 is also post-translationally modified even though the nature of these modifications and their functional significance is currently unknown.
Homocitrullination (the carbamylation of lysines) is a known PTM arising from a nonenzymatic reaction of urea-driven cyanate with free amino groups on lysines to yield hcit unrelated to CPS 1 activity (34). It was also demonstrated that carbamoyl phosphate, the product of CPS1 catalysis, can react with lysines in histones to yield hcit in an enzyme-independent manner (15). The proposed mechanism depends on the highly electrophilic acylphosphate group on carbamoyl phosphate undergoing nucleophilic attack (Fig. 5A). We envision that the AhR-mediated recruitment of CPS1 to NC-XRE-containing promoters results in spontaneous homocitrullination of specific proximal chromatin proteins including histone H1 through an enzyme-independent mechanism (Fig. 10). Histones are evolutionarily conserved chromatin proteins responsible for condensation, organization, and regulation of DNA within the eukaryotic nucleus. Aside from the nucleosomal core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), higher order chromatin structure depends on binding by the linker histone, H1 (35, 36). Linker histones consist of three domains, a conserved globular core, and two intrinsically disordered N- and C-terminal domains. Despite the high degree of functional redundancy among histone H1 variants, the essential role of histone H1 in mammals was elegantly demonstrated by the Skoultchi laboratory, using a triple knock-out mouse for histones H1.2, H1.3, and H1.4, in which a 50% reduction of H1 expression resulted in embryonic lethality at day 11.5 (37, 38). Both the human and mouse genomes code for 11 distinct histone H1 variants (39). Five somatic variants (H1.1, H1.2, H1.3, H1.4, and H1.5) are ubiquitously expressed. Although the majority of the H1 histones are believed to be bound to the nucleosome at any given time, individual H1 histone interactions with chromatin are transient attesting to a dynamic process (40, 41). These transient interactions are influenced by H1 PTMs and competition for chromatin binding by other nuclear factors.
FIGURE 10.
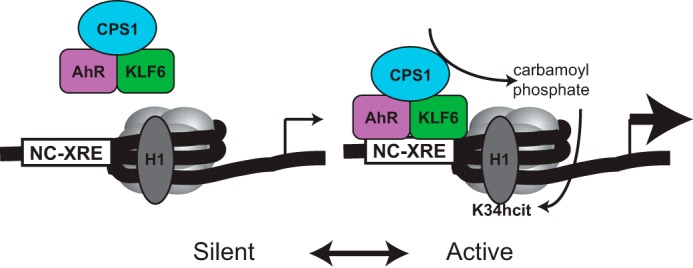
The model depicts transcriptionally silent chromatin with unmodified histone H1 in the absence of AhR-KLF6 binding to the NC-XRE. AhR-KLF6 DNA binding and CPS1 recruitment results in localized synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate and histone H1 homocitrullination (H1K34hcit) through a nonenzymatic process, shifting chromatin into an active conformation.
Sixteen classes of histone modifications have been identified to date (42), and this diversity imparts enormous complexity to transcriptional control. Homocitrullination constitutes a novel epigenetic mark that adds to the range of PTMs identified on histone H1. Other histone H1 PTMs include phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, formylation, and ubiquitination (25). Although much is known about the role of histone H1 phosphorylation, the functional relevance of the other PTMs is only recently beginning to be appreciated. Of particular note is acetylation of a conserved lysine at position 34 on histone H1.4 (H1.4K34Ac), which is associated with increased H1 mobility and transcriptional activation (26). Compared with the core histones, which remain in place for several hours, H1 proteins are substantially more mobile with a mean residence time at any one binding site estimated to be ∼3 min (43), albeit less mobile than transcription factors that boast mean residence times of 5–25 s (44). It is tempting to speculate that akin to H1.4K34Ac, the H1.2/1.3K34hcit PTM may also reduce the mean residence time, resulting in a more open chromatin conformation conducive to increased transcription. Alternatively, H1K34hcit may constitute a distinctive PTM in the “histone code” read by regulatory proteins to promote transcription.
Finally, the studies using βNF confirm the existence of a mechanism that can remove hcit (Fig. 9); however, the results do not shed light on how homocitrullination is reversed. Nevertheless, the evidence of reversibility is considered a prerequisite for homocitrullination to be considered a dynamic physiologically relevant epigenetic event. Because there are no reports in the literature describing enzymatic activity consistent with decarbamylation of lysine residues, future studies designed to identify the protein responsible will probably require protein purification and a detailed biochemical analysis. To date we have identified plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (8), p21Cip1 (45), and, in this report, PADI2 as NC-XRE-driven target genes. Future global gene expression profile analyses using experimental models lacking CPS1 will presumably identify a host of other CPS1-dependent target genes. It is conceivable that the expression of certain genes will rely on CPS1 recruitment by transcription factors other than the AhR, consistent with a more general role for homocitrullination as an epigenetic mark.
Author Contributions
A. D. J. designed the research, performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; M. G. M. performed 2D-DIGE experiments and analyzed the data; C. F. L. performed MS experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; and C. J. E. designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Samples were analyzed in the Mass Spectrometry Core of the Biomolecular Resource Facility and by the Molecular Genomics Core at University of Texas Medical Branch. We thank Dwayne Carter for valuable help in primary hepatocyte isolations.
This work was supported by the NIEHS, National Institutes of Health Grants R01ES007800, R21ES024607 and P30ES006676 (to C. J. E.). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.

This article contains supplemental materials.
- AhR
- aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- CPS1
- carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1
- NC-XRE
- nonconsensus xenobiotic response element
- hcit
- homocitrulline
- PTM
- post-translational modification
- TCDD
- 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- 2D-DIGE
- two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis
- KLF
- Kruppel-like factor
- CKO
- conditional knock-out
- 5-Aza
- 5-aza-2′-deoxycitidine
- PADI
- peptidylarginine deiminase
- βNF
- β-naphthoflavone.
References
- 1.Fukunaga B. N., and Hankinson O. (1996) Identification of a novel domain in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor required for DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 3743–3749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Denison M. S., and Nagy S. R. (2003) Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 43, 309–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fernandez-Salguero P. M., Hilbert D. M., Rudikoff S., Ward J. M., and Gonzalez F. J. (1996) Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 140, 173–179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nebert D. W., Puga A., and Vasiliou V. (1993) Role of the Ah receptor and the dioxin-inducible [Ah] gene battery in toxicity, cancer, and signal transduction. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 685, 624–640 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Poland A., and Knutson J. C. (1982) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 22, 517–554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beedanagari S. R., Taylor R. T., Bui P., Wang F., Nickerson D. W., and Hankinson O. (2010) Role of epigenetic mechanisms in differential regulation of the dioxin-inducible human CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 genes. Mol. Pharmacol. 78, 608–616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taylor R. T., Wang F., Hsu E. L., and Hankinson O. (2009) Roles of coactivator proteins in dioxin induction of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in human breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Sci. 107, 1–8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huang G., and Elferink C. J. (2012) A novel nonconsensus xenobiotic response element capable of mediating aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent gene expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 81, 338–347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wilson S. R., Joshi A. D., and Elferink C. J. (2013) The tumor suppressor Kruppel-like factor 6 is a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor DNA binding partner. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 345, 419–429 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Metzenberg R. L., Marshall M., and Cohen P. P. (1958) Carbamyl phosphate synthetase: studies on the mechanism of action. J. Biol. Chem. 233, 1560–1564 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Metzenberg R. L., Marshall M., and Cohen P. P. (1958) Purification of carbamyl phosphate synthetase from frog liver. J. Biol. Chem. 233, 102–105 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Martínez A. I., Pérez-Arellano I., Pekkala S., Barcelona B., and Cervera J. (2010) Genetic, structural and biochemical basis of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 101, 311–323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harper T. A. Jr., Joshi A. D., and Elferink C. J. (2013) Identification of stanniocalcin 2 as a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor target gene. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 344, 579–588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shen E. S., Elferink C. J., and Whitlock J. P. Jr. (1991) Use of gel retardation to analyze protein-DNA interactions upstream of CYPIA1 gene. Methods Enzymol. 206, 403–408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ramponi G., Leaver J. L., and Grisolia S. (1971) Homocitrulline formation following carbamylation of histones with carbamyl phosphate. FEBS Lett. 16, 311–314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Christophorou M. A., Castelo-Branco G., Halley-Stott R. P., Oliveira C. S., Loos R., Radzisheuskaya A., Mowen K. A., Bertone P., Silva J. C., Zernicka-Goetz M., Nielsen M. L., Gurdon J. B., and Kouzarides T. (2014) Citrullination regulates pluripotency and histone H1 binding to chromatin. Nature 507, 104–108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moellering R. E., and Cravatt B. F. (2013) Functional lysine modification by an intrinsically reactive primary glycolytic metabolite. Science 341, 549–553 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Paulsen C. E., Truong T. H., Garcia F. J., Homann A., Gupta V., Leonard S. E., and Carroll K. S. (2012) Peroxide-dependent sulfenylation of the EGFR catalytic site enhances kinase activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 8, 57–64 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saiardi A., Bhandari R., Resnick A. C., Snowman A. M., and Snyder S. H. (2004) Phosphorylation of proteins by inositol pyrophosphates. Science 306, 2101–2105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mydel P., Wang Z., Brisslert M., Hellvard A., Dahlberg L. E., Hazen S. L., and Bokarewa M. (2010) Carbamylation-dependent activation of T cells: a novel mechanism in the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis. J. Immunol. 184, 6882–6890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wu J. C., Merlino G., and Fausto N. (1994) Establishment and characterization of differentiated, nontransformed hepatocyte cell lines derived from mice transgenic for transforming growth factor α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 674–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nicoletti M., Guerri C., and Grisolia S. (1977) Turnover of carbamyl-phosphate synthase, of other mitochondrial enzymes and of rat tissues. Effect of diet and of thyroidectomy. Eur. J. Biochem. 75, 583–592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vargas J. L., Roche E., Knecht E., and Grisolía S. (1987) Differences in the half-lives of some mitochondrial rat liver enzymes may derive partially from hepatocyte heterogeneity. FEBS Lett. 224, 182–186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu H., Dong H., Robertson K., and Liu C. (2011) DNA methylation suppresses expression of the urea cycle enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 178, 652–661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wisniewski J. R., Zougman A., Krüger S., and Mann M. (2007) Mass spectrometric mapping of linker histone H1 variants reveals multiple acetylations, methylations, and phosphorylation as well as differences between cell culture and tissue. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 72–87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kamieniarz K., Izzo A., Dundr M., Tropberger P., Ozretic L., Kirfel J., Scheer E., Tropel P., Wisniewski J. R., Tora L., Viville S., Buettner R., and Schneider R. (2012) A dual role of linker histone H1.4 Lys 34 acetylation in transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 26, 797–802 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Klose R. J., and Zhang Y. (2007) Regulation of histone methylation by demethylimination and demethylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 307–318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang X., Bolt M., Guertin M. J., Chen W., Zhang S., Cherrington B. D., Slade D. J., Dreyton C. J., Subramanian V., Bicker K. L., Thompson P. R., Mancini M. A., Lis J. T., and Coonrod S. A. (2012) Peptidylarginine deiminase 2-catalyzed histone H3 arginine 26 citrullination facilitates estrogen receptor α target gene activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 13331–13336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ghidelli S., Claus P., Thies G., and Wiśniewski J. R. (1997) High mobility group proteins cHMG1a, cHMG1b, and cHMGI are distinctly distributed in chromosomes and differentially expressed during ecdysone dependent cell differentiation. Chromosoma 105, 369–379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sugihara K., Okayama T., Kitamura S., Yamashita K., Yasuda M., Miyairi S., Minobe Y., and Ohta S. (2008) Comparative study of aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand activities of six chemicals in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 82, 5–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simmer J. P., Kelly R. E., Rinker A. G. Jr., Scully J. L., and Evans D. R. (1990) Mammalian carbamyl phosphate synthetase (CPS): DNA sequence and evolution of the CPS domain of the Syrian hamster multifunctional protein CAD. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 10395–10402 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pekkala S., Martínez A. I., Barcelona B., Yefimenko I., Finckh U., Rubio V., and Cervera J. (2010) Understanding carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) deficiency by using expression studies and structure-based analysis. Hum. Mutat. 31, 801–808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Emmanuel B. (1980) Urea cycle enzymes in tissues (liver, rumen epithelium, heart, kidney, lung and spleen) of sheep (Ovis aries). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 65B, 693–697 [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sirpal S. (2009) Myeloperoxidase-mediated lipoprotein carbamylation as a mechanistic pathway for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 116, 681–695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Biterge B., Richter F., Mittler G., and Schneider R. (2014) Methylation of histone H4 at aspartate 24 by protein l-isoaspartate O-methyltransferase (PCMT1) links histone modifications with protein homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 4, 6674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Over R. S., and Michaels S. D. (2014) Open and closed: the roles of linker histones in plants and animals. Mol. Plant 7, 481–491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fan Y., Nikitina T., Morin-Kensicki E. M., Zhao J., Magnuson T. R., Woodcock C. L., and Skoultchi A. I. (2003) H1 linker histones are essential for mouse development and affect nucleosome spacing in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 4559–4572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fan Y., Sirotkin A., Russell R. G., Ayala J., and Skoultchi A. I. (2001) Individual somatic H1 subtypes are dispensable for mouse development even in mice lacking the H1(0) replacement subtype. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 7933–7943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Izzo A., Kamieniarz K., and Schneider R. (2008) The histone H1 family: specific members, specific functions? Biol. Chem. 389, 333–343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lever M. A., Th'ng J. P., Sun X., and Hendzel M. J. (2000) Rapid exchange of histone H1.1 on chromatin in living human cells. Nature 408, 873–876 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Misteli T., Gunjan A., Hock R., Bustin M., and Brown D. T. (2000) Dynamic binding of histone H1 to chromatin in living cells. Nature 408, 877–881 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dawson M. A., and Kouzarides T. (2012) Cancer epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy. Cell 150, 12–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brown D. T., Izard T., and Misteli T. (2006) Mapping the interaction surface of linker histone H1(0) with the nucleosome of native chromatin in vivo. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 250–255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Phair R. D., Gorski S. A., and Misteli T. (2004) Measurement of dynamic protein binding to chomatin in vivo, using photobleaching microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 375, 393–414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jackson D. P., Li H., Mitchell K. A., Joshi A. D., and Elferink C. J. (2014) Ah receptor-mediated suppression of liver regeneration through NC-XRE-driven p21Cip1 expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 85, 533–541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.