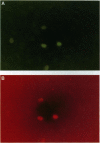
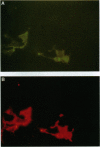
Abstract
Conventional antibody generation usually requires active immunization with antigen immediately prior to the preparation procedure. Combinatorial antibody library technology offers the possibility of cloning a range of antibody specificities at a single point in time and then accessing these specificities at will. Here we show that human monoclonal antibody Fab fragments against a plethora of infectious agents can be readily derived from a single library. Further examination of a number of libraries shows that whenever antibody against a pathogen can be detected in the serum of the donor, then specific antibodies can be derived from the corresponding library. We describe the generation of human Fab fragments against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, human cytomegalovirus, varicella zoster virus, rubella, human immunodeficiency virus type 1, and respiratory syncytial virus. The antibodies are shown to be highly specific and a number are effective in neutralizing virus in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amadori A., Chieco-Bianchi L. B cell activation and HIV infection: protective or potentially detrimental response? Int Rev Immunol. 1992;9(1):15–24. doi: 10.3109/08830189209061780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balfour H. H., Jr Varicella zoster virus infections in immunocompromised hosts. A review of the natural history and management. Am J Med. 1988 Aug 29;85(2A):68–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Björling E., Chiodi F., Dunlop N., Cababa D., Jones T. M., Zebedee S. L., Persson M. A., Nara P. L., Norrby E. Recombinant human Fab fragments neutralize human type 1 immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9339–9343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Crowe J. E., Jr, Cababa D., Jones T. M., Zebedee S. L., Murphy B. R., Chanock R. M., Burton D. R. Human monoclonal Fab fragments derived from a combinatorial library bind to respiratory syncytial virus F glycoprotein and neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10164–10168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Kang A. S., Lerner R. A., Benkovic S. J. Assembly of combinatorial antibody libraries on phage surfaces: the gene III site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7978–7982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Stevens C. E., Lin C. C., Hsieh F. J., Wang K. Y., Sun T. S., Szmuness W. Efficacy of hepatitis B immune globulin for prevention of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus carrier state: final report of a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):135–141. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Barbas C. F., 3rd Antibodies from libraries. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):782–783. doi: 10.1038/359782b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Barbas C. F., 3rd, Persson M. A., Koenig S., Chanock R. M., Lerner R. A. A large array of human monoclonal antibodies to type 1 human immunodeficiency virus from combinatorial libraries of asymptomatic seropositive individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10134–10137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. Probing the human B-cell repertoire with EBV: polyreactive antibodies and CD5+ B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:513–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clackson T., Hoogenboom H. R., Griffiths A. D., Winter G. Making antibody fragments using phage display libraries. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):624–628. doi: 10.1038/352624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collet T. A., Roben P., O'Kennedy R., Barbas C. F., 3rd, Burton D. R., Lerner R. A. A binary plasmid system for shuffling combinatorial antibody libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10026–10030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler K. B., Stagno S., Pass R. F., Britt W. J., Boll T. J., Alford C. A. The outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in relation to maternal antibody status. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 5;326(10):663–667. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S. Effect of human immune serum globulin on infectivity of hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):70–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Hardwick J. M., Trapp B. D., Crawford T. O., Bollinger R. C., Griffin D. E. Antibody-mediated clearance of alphavirus infection from neurons. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):856–860. doi: 10.1126/science.1658936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty J., Griffiths A. D., Winter G., Chiswell D. J. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):552–554. doi: 10.1038/348552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed M. D., Gordon J., Ley S. J., Edgar D., Hughes-Jones N. C. Senescence of a human lymphoblastoid clone producing anti-Rhesus(D). Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):742–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Leszczynski J., Zaia J. A., Flournoy N., Newton B., Snydman D. R., Wright G. G., Levin M. J., Thomas E. D. Prevention of cytomegalovirus infection by cytomegalovirus immune globulin after marrow transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):442–446. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie M. M., Vathenen A. S., Radford M., Codd J., Key S. Maternal antibody and respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. J Med Virol. 1981;7(4):263–271. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle P. A., Palladino G., Gerhard W. Mice can recover from pulmonary influenza virus infection in the absence of class I-restricted cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Werner B. G., Heinze-Lacey B., Berardi V. P., Tilney N. L., Kirkman R. L., Milford E. L., Cho S. I., Bush H. L., Jr, Levey A. S. Use of cytomegalovirus immune globulin to prevent cytomegalovirus disease in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 22;317(17):1049–1054. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710223171703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Werner B. G., Tilney N. L., Kirkman R. L., Milford E. L., Cho S. I., Bush H. L., Jr, Levey A. S., Strom T. B., Carpenter C. B. Final analysis of primary cytomegalovirus disease prevention in renal transplant recipients with a cytomegalovirus-immune globulin: comparison of the randomized and open-label trials. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 2):1357–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura Y., Yokoyama K., Nishida M., Suyama T. Immunoglobulin preparation: safe from virus transmission? Vox Sang. 1989;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1989.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. E., Yap P. L., Gillon J., Crawford R. J., Urbaniak S. J., Galea G. Transmission of non-A, non-B hepatitis by pH4-treated intravenous immunoglobulin. Vox Sang. 1989;57(1):15–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1989.tb04977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Levin M. J., Preblud S. R., Leszczynski J., Wright G. G., Ellis R. J., Curtis A. C., Valerio M. A., LeGore J. Evaluation of varicella-zoster immune globulin: protection of immunosuppressed children after household exposure to varicella. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):737–743. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Barbas C. F., 3rd, Hom Y. L., Caothien R. H., Graff R., DeGraw J., Pyati J., LaPolla R., Burton D. R., Lerner R. A. Human combinatorial antibody libraries to hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3175–3179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]