Abstract
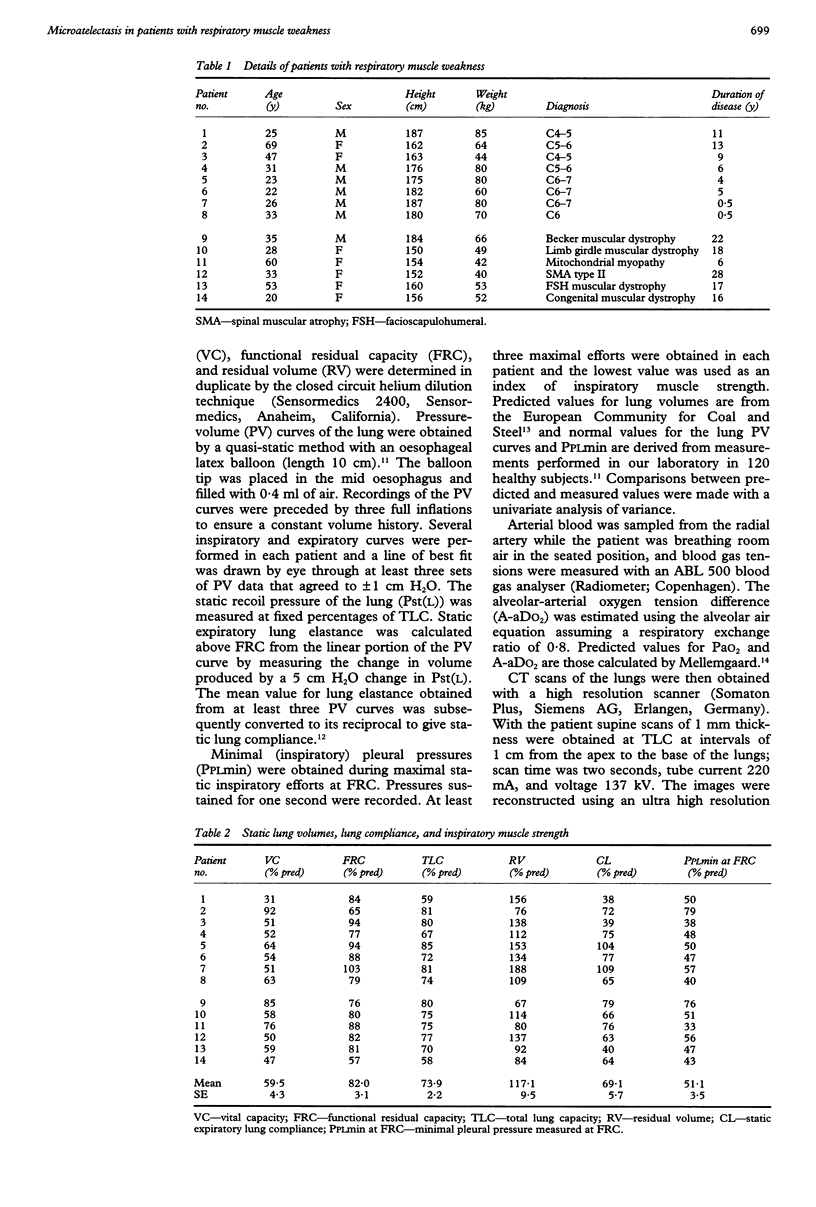
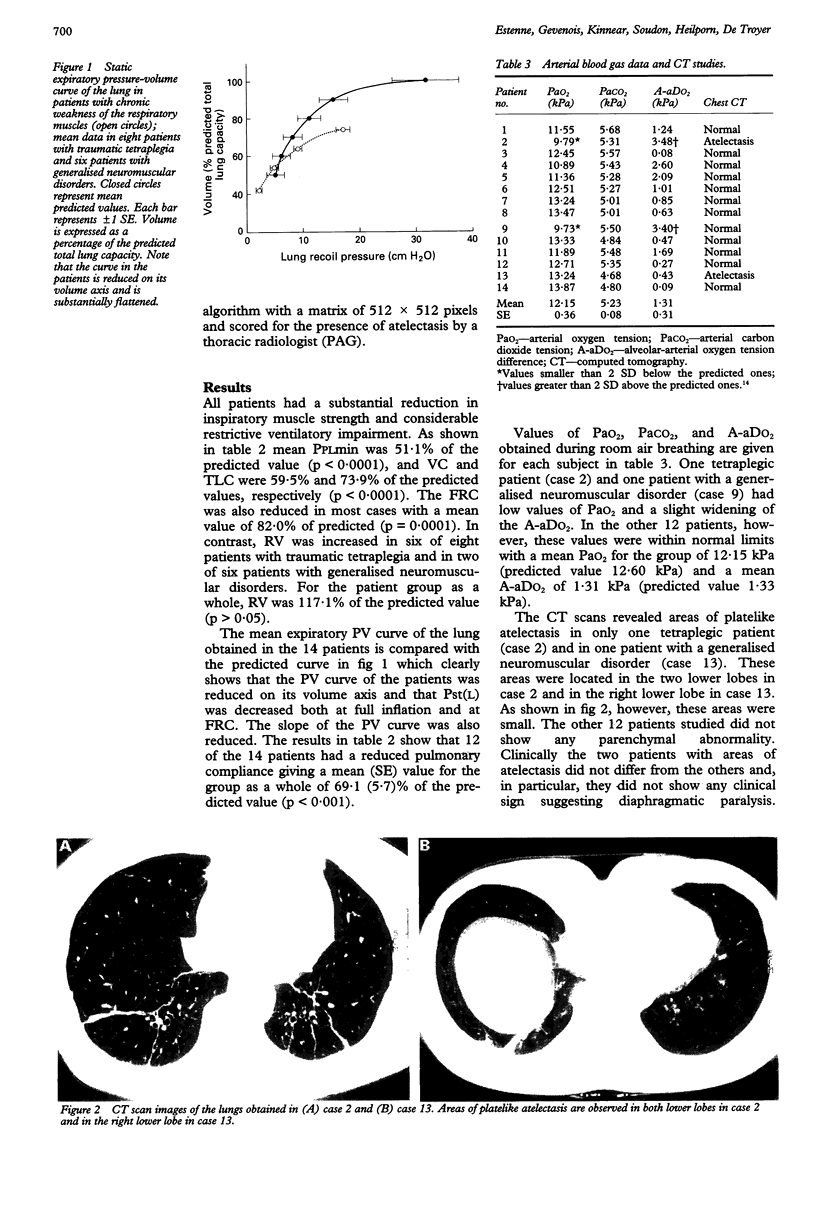
BACKGROUND--It is well established that patients with longstanding weakness of the respiratory muscles have a reduction in lung distensibility. Although this occurs in most patients without any radiographic changes suggesting parenchymal lung disease, it has been attributed to the development of microatelectasis. METHODS--A high resolution computed tomographic (CT) scanner was used in eight patients with traumatic tetraplegia and six patients with generalised neuromuscular disorders to look for areas of atelectasis. With the patient in the supine posture scans of 1 mm thickness were obtained at total lung capacity at intervals of 1 cm from the apex to the base of the lung. RESULTS--Vital capacity, total lung capacity, and inspiratory muscle strength were reduced to a mean of 59.5%, 73.9%, and 51.1% of predicted values, respectively. Static expiratory lung compliance was decreased in 12 of the 14 patients and averaged 69.1% of the predicted value. The CT scans revealed only small areas of atelectasis in one tetraplegic patient and in one patient with a generalised neuromuscular disorder; no parenchymal abnormality was seen in the other 12 patients. CONCLUSIONS--In many patients with chronic weakness of the respiratory muscles the reduced lung distensibility does not appear to be caused by microatelectasis. It might be related to alterations in elasticity of the lung tissue.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOSSOM R. A., AFFELDT J. E. Chronic poliomyelitic respirator deaths. Am J Med. 1956 Jan;20(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J., van de Woestijne K. P. Resistance or conductance? Compliance or elastance? J Appl Physiol. 1971 Mar;30(3):437–439. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Borenstein S., Cordier R. Analysis of lung volume restriction in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Thorax. 1980 Aug;35(8):603–610. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.8.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Deisser P. The effects of intermittent positive pressure breathing on patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Aug;124(2):132–137. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Heilporn A. Respiratory mechanics in quadriplegia. The respiratory function of the intercostal muscles. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):591–600. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estenne M., De Troyer A. The effects of tetraplegia on chest wall statics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):121–124. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estenne M., Heilporn A., Delhez L., Yernault J. C., De Troyer A. Chest wall stiffness in patients with chronic respiratory muscle weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1002–1007. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, MEAD J., WHITTENBERGER J. L., SAXTON G. A., Jr Pulmonary function in convalescent poliomyelitic patients. III. Compliance of the lungs and thorax. N Engl J Med. 1952 Sep 11;247(11):390–393. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195209112471103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, POLLARD D. S. Effect of deep and quiet breathing on pulmonary compliance in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:143–149. doi: 10.1172/JCI104012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Pride N. B., Davis J. N., Loh L. C. Pulmonary mechanics in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):389–395. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo J. R., Webb W. R., Gould R., Stein M. G., Bass I., Gamsu G., Goldberg H. I. High-resolution CT of the lungs: an optimal approach. Radiology. 1987 May;163(2):507–510. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.2.3562834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCool F. D., Mayewski R. F., Shayne D. S., Gibson C. J., Griggs R. C., Hyde R. W. Intermittent positive pressure breathing in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Alterations in total respiratory system compliance. Chest. 1986 Oct;90(4):546–552. doi: 10.1378/chest.90.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellemgaard K. The alveolar-arterial oxygen difference: its size and components in normal man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 May;67(1):10–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon P. D., Loring S. H., Pichurko B. M., McCool F. D., Slutsky A. S., Sarkarati M., Brown R. Respiratory mechanics in acute quadriplegia. Lung and chest wall compliance and dimensional changes during respiratory maneuvers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):615–620. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. V., Tierney D. F., Parker H. R. Surface forces in the lung, atelectasis, and transpulmonary pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):819–827. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Tierney D. F., Clements J. A. Mechanism of compliance change in excised rat lungs at low transpulmonary pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Dec;29(6):780–785. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.6.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Troyer A., Yernault J. C. Inspiratory muscle force in normal subjects and patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1980 Feb;35(2):92–100. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




