Abstract
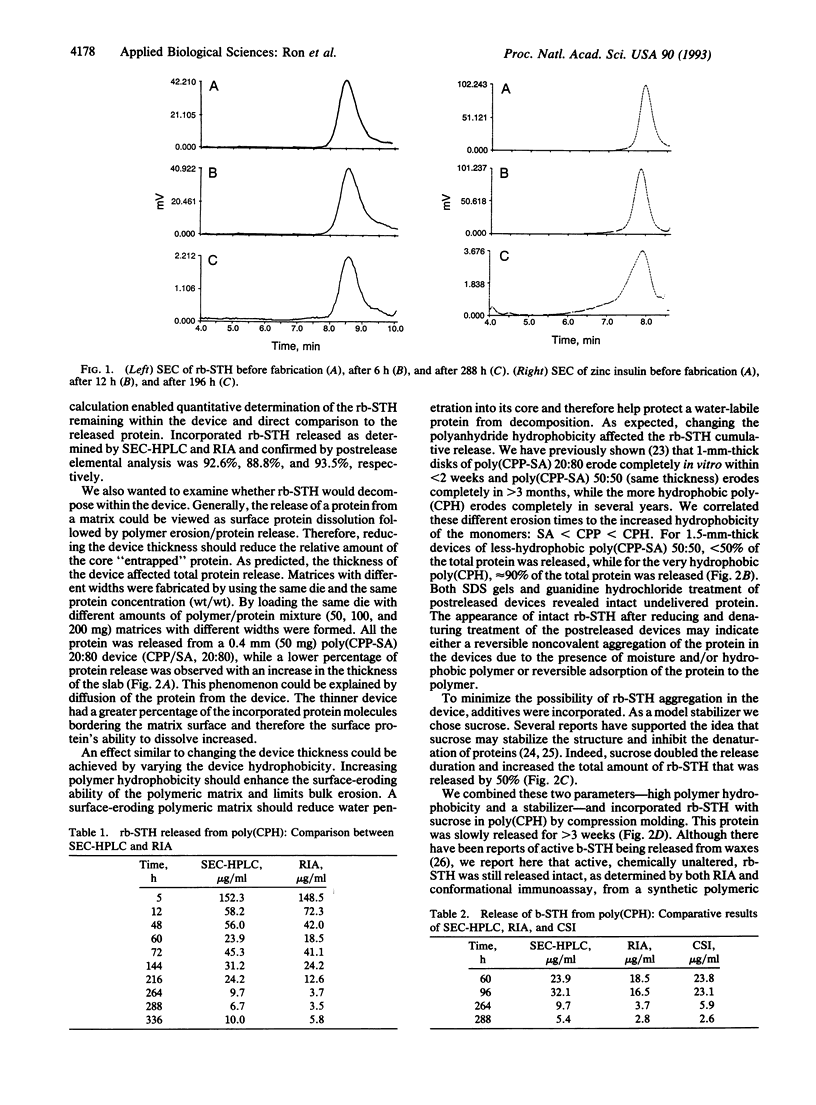
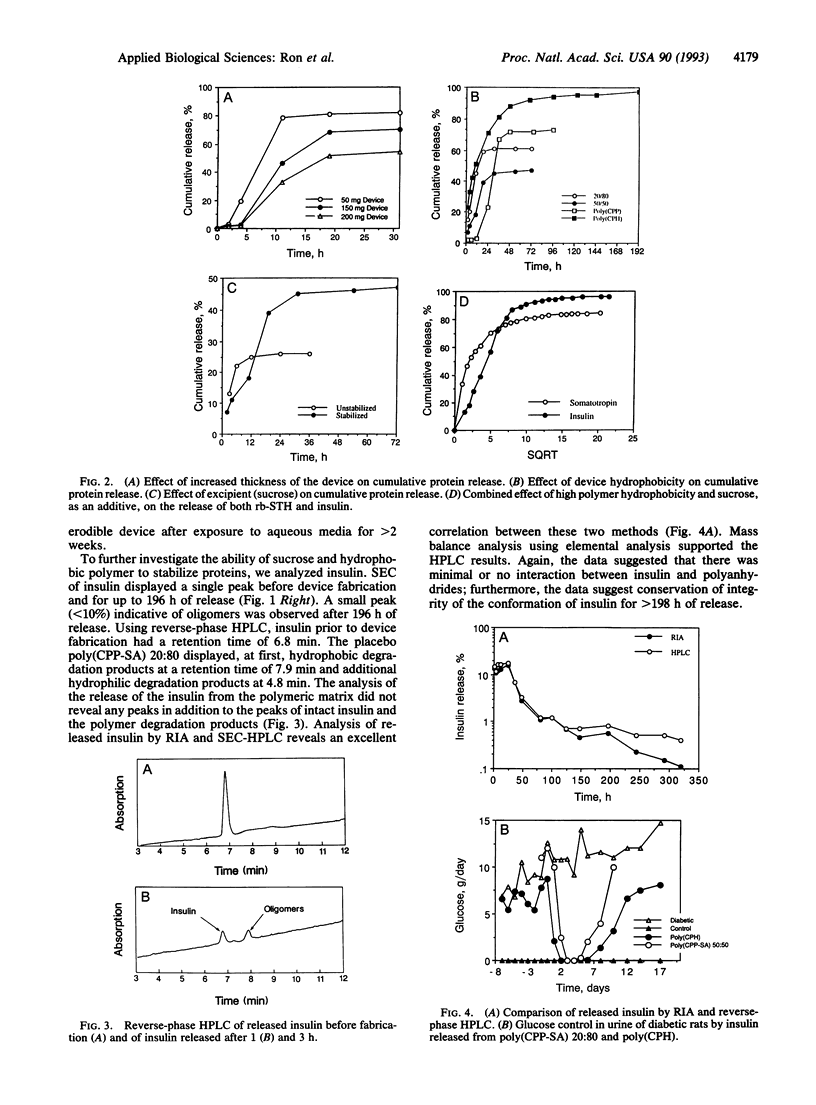
The effects of both polymer hydrophobicity and addition of stabilizers on the release and integrity of polymer-encapsulated proteins were studied. By using very hydrophobic poly[1,3-bis(p-carboxyhydroxy)hexane anhydride] with sucrose as an excipient, both recombinant bovine somatotropin and zinc insulin were released intact over 3 weeks. The released proteins appeared to maintain their integrity as judged by acidic reverse-phase HPLC, size-exclusion HPLC, radioimmunoassay, and conformation-sensitive immunoassays. Our results also suggest how polymer hydrophobicity can be used to enhance protein stability.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back J. F., Oakenfull D., Smith M. B. Increased thermal stability of proteins in the presence of sugars and polyols. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5191–5196. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem H., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Vick N. A., Black K. L., Schold S. C., Jr, Burger P. C., Friedman A. H., Ciric I. S., Eller T. W., Cozzens J. W. Interstitial chemotherapy with drug polymer implants for the treatment of recurrent gliomas. J Neurosurg. 1991 Mar;74(3):441–446. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.74.3.0441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L., Munoz C., Siemer L., Edelman E., Langer R. Controlled release of insulin from polymer matrices. Control of diabetes in rats. Diabetes. 1986 Jun;35(6):692–697. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.6.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori R., Komada F., Okumura K. Pharmaceutical approach to subcutaneous dosage forms of insulin. J Pharm Sci. 1983 Apr;72(4):435–439. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600720428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain A., Faraj J., Aramaki Y., Truelove J. E. Hydrolysis of leucine enkephalin in the nasal cavity of the rat--a possible factor in the low bioavailability of nasally administered peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):923–928. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurencin C., Domb A., Morris C., Brown V., Chasin M., McConnell R., Lange N., Langer R. Poly(anhydride) administration in high doses in vivo: studies of biocompatibility and toxicology. J Biomed Mater Res. 1990 Nov;24(11):1463–1481. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820241105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Timasheff S. N. The stabilization of proteins by sucrose. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7193–7201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K. W., Brott B. C., Langer R. Bioerodible polyanhydrides as drug-carrier matrices. I: Characterization, degradation, and release characteristics. J Biomed Mater Res. 1985 Oct;19(8):941–955. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820190806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K. W., D'Amore P. D., Marletta M., Langer R. Bioerodible polyanhydrides as drug-carrier matrices. II. Biocompatibility and chemical reactivity. J Biomed Mater Res. 1986 Jan;20(1):51–64. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley W. M., Krabill L. F., Olsen R. F. Effect of bovine growth hormone administered in various patterns on nitrogen metabolism in the Holstein steer. J Anim Sci. 1982 Nov;55(5):1062–1070. doi: 10.2527/jas1982.5551062x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. B., Brown L., Langer R., Klagsburn M. A micro sustained release system for epidermal growth factor. In Vitro. 1983 Oct;19(10):743–748. doi: 10.1007/BF02618093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswender G. D., Reichert L. E., Jr, Midgley A. R., Jr, Nalbandov A. V. Radioimmunoassay for bovine and ovine luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1969 May;84(5):1166–1173. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-5-1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Okada H., Yamamoto M., Shimamoto T. In vivo release profiles of leuprolide acetate from microcapsules prepared with polylactic acids or copoly(lactic/glycolic) acids and in vivo degradation of these polymers. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1988 Jul;36(7):2576–2581. doi: 10.1248/cpb.36.2576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Yamamoto M., Okada H., Yashiki T., Shimamoto T. A new technique to efficiently entrap leuprolide acetate into microcapsules of polylactic acid or copoly(lactic/glycolic) acid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1988 Mar;36(3):1095–1103. doi: 10.1248/cpb.36.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Yamamoto M., Takada S., Okada H., Shimamoto T. Controlled-release of leuprolide acetate from polylactic acid or copoly(lactic/glycolic) acid microcapsules: influence of molecular weight and copolymer ratio of polymer. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1988 Apr;36(4):1502–1507. doi: 10.1248/cpb.36.1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Heya T., Ogawa Y., Shimamoto T. One-month release injectable microcapsules of a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist (leuprolide acetate) for treating experimental endometriosis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfund W. P., Bourdage J. S. The conformation-sensitive immunoassay: a membrane based ELISA system for identifying antibodies sensitive to alterations of protein conformation. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jun;27(6):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90068-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santomé J. A., Dellacha J. M., Paladini A. C., Peña C., Biscoglio M. J., Daurat S. T., Poskus E., Wolfenstein C. E. Primary structure of bovine growth hormone. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):164–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis M. The primary structure of bovine growth hormone. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



