Abstract
The title compound, C6H12O6, was crystallized from an aqueous solution of equimolar mixture of d- and l-fructose (1,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexan-2-one, arabino-hexulose or levulose), and it was confirmed that d-fructose (or l-fructose) formed β-pyranose with a 2 C 5 (or 5 C 2) conformation. In the crystal, two O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the hydroxy groups at the C-1 and C-3 positions, and at the C-4 and C-5 positions connect homochiral molecules into a column along the a axis. The columns are linked by other O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between d- and l-fructose molecules, forming a three-dimensional network.
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bonding, racemic compound, rare sugar
Related literature
For crystal structures of chiral β-d-fructose, racemic β-d,l-allose and racemic β-d,l-psicose, see: Kanters et al. (1977 ▸); Ishii, Senoo et al. (2015 ▸); Ishii, Sakane et al. (2015 ▸), respectively. For the synthesis of chiral l-fructose, see: Itoh & Izumori (1996 ▸).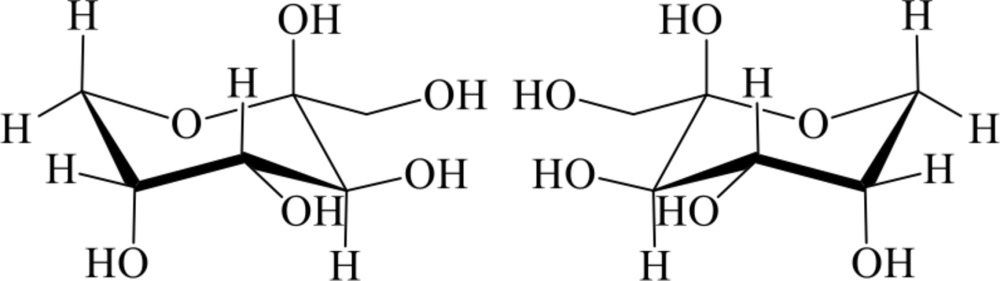
Experimental
Crystal data
C6H12O6
M r = 180.16
Triclinic,
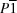
a = 5.43124 (19) Å
b = 7.2727 (3) Å
c = 10.1342 (4) Å
α = 69.120 (2)°
β = 83.907 (2)°
γ = 78.381 (2)°
V = 366.09 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.30 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.10 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995 ▸) T min = 0.729, T max = 0.878
6710 measured reflections
1329 independent reflections
1211 reflections with F 2 > 2.0σ(F 2)
R int = 0.079
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.095
S = 1.08
1329 reflections
115 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku, 2009 ▸); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: RAPID-AUTO; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2011 (Burla et al., 2012 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2013 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: CrystalStructure (Rigaku, 2014 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: CrystalStructure.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416Isup3.cml
ORTEP . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig1.tif
ORTEP view of the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme. The thermal ellipsoids of all non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
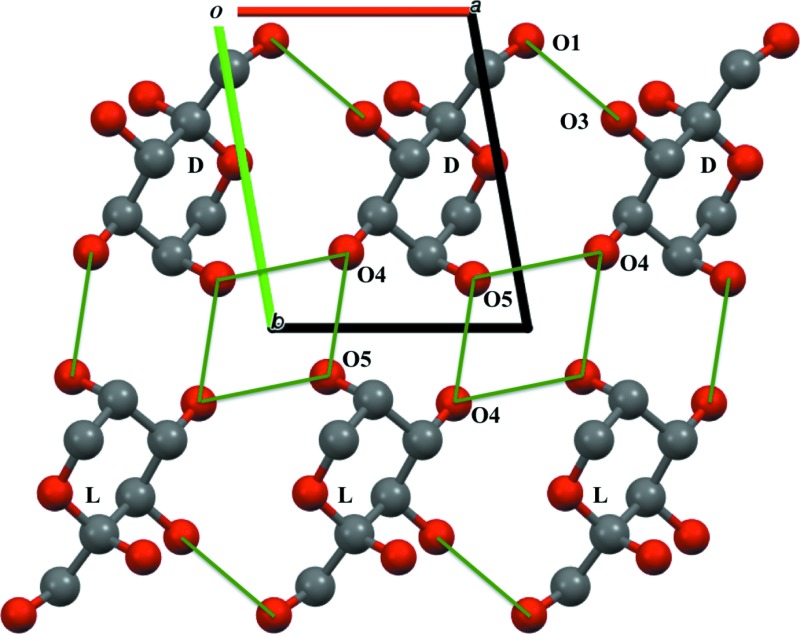
c . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig2.tif
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the c-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
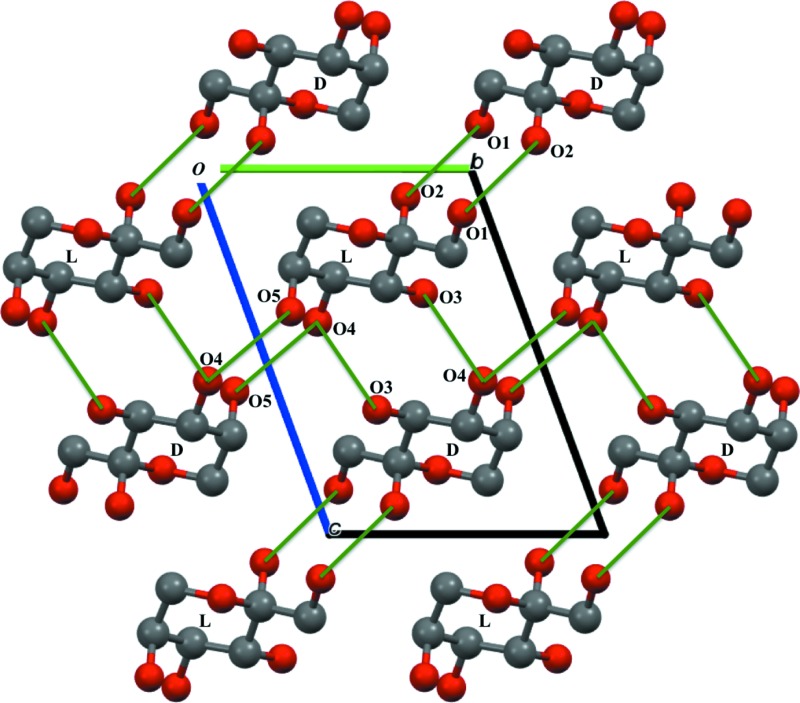
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig3.tif
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the a-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
CCDC reference: 1422317
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1H1AO3i | 0.82 | 2.28 | 2.9202(14) | 135 |
| O2H2AO1ii | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.7224(13) | 161 |
| O3H3AO4iii | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.7831(18) | 177 |
| O4H4AO5iv | 0.82 | 2.01 | 2.7893(13) | 158 |
| O5H5AO4v | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.8431(12) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 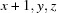 ; (ii)
; (ii) 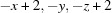 ; (iii)
; (iii) 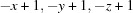 ; (iv)
; (iv) 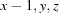 ; (v)
; (v) 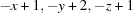 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Grants-in-Aid for Rare Sugar Research of Kagawa University.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Fructose, especially in D-fructose, is one of the most famous, fundamental and important monosaccharides in sugar family, and has been under intense investigation. On the other hand, L-fructose is classified into a rare sugar, and hardly exists in nature. In this study we investigate to create a novel racemic single-crystal including these D- and L-fructoses together with the ratio of 1: 1. The space group is triclinic P1 (Z = 2), which is significantly different from our previous reports of the racemic β-D,L-allose (monoclinic P21/c, Z = 4; Ishii, Senoo et al., 2015) and psicose (orthorhombic Pna21, Z = 4; Ishii, Sakane et al., 2015). In the unit cell, the D- and L-molecules are located with the heterochiral hydrogen bonding networks (O3—H3A···O4). As shown in Fig. 2, two homochiral hydrogen bonding networks (O1—H1A···O3 and O4—H4A···O5) have also been observed along to the a-axis. Additional two heterochiral hydrogen bonds (O2—H2A···O1 and O5—H5A···O4) are also confirmed (Fig. 3).
S2. Experimental
D-Fructose was purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries. L-Fructose was prepared from L-psicose by enzymatic epimerization using D-tagatose 3-epimerase (Itoh & Izumori, 1996). D-Fructose and L-fructose were mixed in equal amount and dissolved in hot water to give a 70 wt% solution. And these samples were kept at room temperature. After one day, small single crystals were obtained in a hermetically sealed test tube.
S3. Refinement
H atoms bounded to methine-type C (H3B, H4B, H5B) and methylene-type C (H1B, H1C, H6A, H6B) were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.98 and 0.97 Å, respectively, and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). H atoms bounded to O (H1A, H2A, H3A, H4A, H5A) were positioned geometrically (O—H = 0.82 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(O), allowing for free rotation of the OH groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
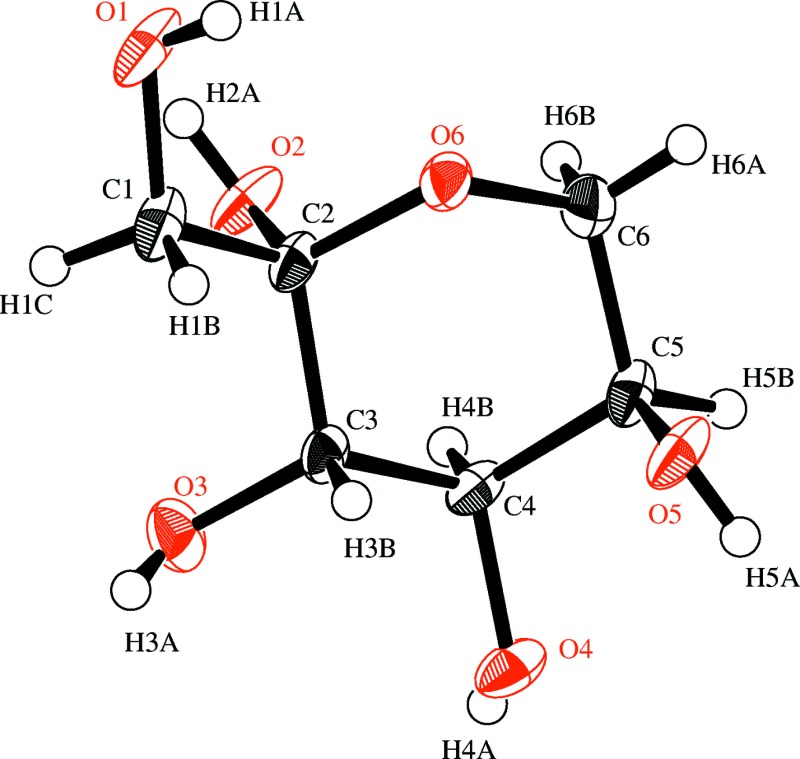
ORTEP view of the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme. The thermal ellipsoids of all non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the c-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
Fig. 3.
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the a-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
Crystal data
| C6H12O6 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 180.16 | F(000) = 192.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.634 Mg m−3 |
| a = 5.43124 (19) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54187 Å |
| b = 7.2727 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 4534 reflections |
| c = 10.1342 (4) Å | θ = 4.7–68.4° |
| α = 69.120 (2)° | µ = 1.30 mm−1 |
| β = 83.907 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 78.381 (2)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 366.09 (2) Å3 | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 1211 reflections with F2 > 2.0σ(F2) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.079 |
| ω scans | θmax = 68.2°, θmin = 4.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.729, Tmax = 0.878 | k = −8→8 |
| 6710 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
| 1329 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0374P)2 + 0.1404P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1329 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 115 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2013 (Sheldrick, 2015) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.125 (6) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.19555 (19) | 0.09152 (15) | 0.87814 (12) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.66671 (18) | 0.27440 (15) | 0.92243 (11) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.50386 (19) | 0.33842 (16) | 0.65941 (12) | 0.0294 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.34223 (18) | 0.76120 (15) | 0.58108 (11) | 0.0264 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.81908 (18) | 0.84537 (14) | 0.60893 (12) | 0.0290 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.96847 (17) | 0.47716 (14) | 0.82413 (11) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| C1 | 1.0136 (3) | 0.1818 (2) | 0.77318 (17) | 0.0265 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.8236 (2) | 0.34747 (19) | 0.80373 (15) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.6557 (2) | 0.46432 (19) | 0.67791 (15) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.4906 (3) | 0.6455 (2) | 0.70256 (15) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.6558 (3) | 0.77295 (19) | 0.72899 (16) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.8182 (3) | 0.6457 (2) | 0.85210 (16) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| H1A | 1.30779 | 0.15812 | 0.86062 | 0.0390* | |
| H1C | 0.92594 | 0.08085 | 0.76811 | 0.0318* | |
| H1B | 1.0976 | 0.23653 | 0.68208 | 0.0318* | |
| H2A | 0.74136 | 0.16995 | 0.97716 | 0.0345* | |
| H3A | 0.55367 | 0.31042 | 0.58847 | 0.0353* | |
| H3B | 0.76216 | 0.5097 | 0.59244 | 0.0227* | |
| H4A | 0.19353 | 0.75392 | 0.60178 | 0.0317* | |
| H4B | 0.37832 | 0.60041 | 0.78545 | 0.0240* | |
| H5A | 0.74552 | 0.94902 | 0.55285 | 0.0348* | |
| H5B | 0.55062 | 0.8858 | 0.75058 | 0.0268* | |
| H6A | 0.92669 | 0.72507 | 0.86923 | 0.0305* | |
| H6B | 0.71231 | 0.59981 | 0.93633 | 0.0305* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0465 (8) | −0.0003 (4) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0066 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0251 (6) | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0265 (6) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0074 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0280 (6) | 0.0361 (7) | −0.0153 (5) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0118 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0160 (5) | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0298 (6) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0051 (4) | 0.0019 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0385 (7) | −0.0035 (4) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0060 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0164 (5) | 0.0309 (6) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0061 (4) | −0.0071 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0223 (7) | 0.0144 (7) | 0.0389 (9) | −0.0022 (6) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0054 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0176 (7) | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0242 (8) | −0.0039 (5) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0140 (7) | 0.0233 (8) | −0.0070 (5) | −0.0006 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0213 (8) | −0.0018 (5) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0131 (7) | 0.0315 (9) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0060 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0304 (8) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0044 (6) | −0.0107 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.4153 (19) | O1—H1A | 0.820 |
| O2—C2 | 1.4017 (16) | O2—H2A | 0.820 |
| O3—C3 | 1.419 (2) | O3—H3A | 0.820 |
| O4—C4 | 1.4395 (16) | O4—H4A | 0.820 |
| O5—C5 | 1.4305 (17) | O5—H5A | 0.820 |
| O6—C2 | 1.423 (2) | C1—H1C | 0.970 |
| O6—C6 | 1.4298 (19) | C1—H1B | 0.970 |
| C1—C2 | 1.520 (2) | C3—H3B | 0.980 |
| C2—C3 | 1.5304 (19) | C4—H4B | 0.980 |
| C3—C4 | 1.521 (2) | C5—H5B | 0.980 |
| C4—C5 | 1.517 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.970 |
| C5—C6 | 1.5075 (19) | C6—H6B | 0.970 |
| C2—O6—C6 | 113.25 (10) | C4—O4—H4A | 109.467 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 111.97 (14) | C5—O5—H5A | 109.473 |
| O2—C2—O6 | 111.23 (13) | O1—C1—H1C | 109.215 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 112.44 (10) | O1—C1—H1B | 109.220 |
| O2—C2—C3 | 107.69 (10) | C2—C1—H1C | 109.218 |
| O6—C2—C1 | 105.55 (11) | C2—C1—H1B | 109.221 |
| O6—C2—C3 | 109.06 (10) | H1C—C1—H1B | 107.907 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 110.86 (13) | O3—C3—H3B | 109.026 |
| O3—C3—C2 | 109.62 (10) | C2—C3—H3B | 109.028 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 110.08 (11) | C4—C3—H3B | 109.024 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 110.04 (13) | O4—C4—H4B | 109.255 |
| O4—C4—C3 | 110.05 (13) | C3—C4—H4B | 109.253 |
| O4—C4—C5 | 109.74 (10) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.254 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 109.27 (11) | O5—C5—H5B | 109.808 |
| O5—C5—C4 | 110.97 (14) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.810 |
| O5—C5—C6 | 107.71 (11) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.807 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 108.69 (11) | O6—C6—H6A | 109.512 |
| O6—C6—C5 | 110.67 (14) | O6—C6—H6B | 109.511 |
| C1—O1—H1A | 109.469 | C5—C6—H6A | 109.511 |
| C2—O2—H2A | 109.478 | C5—C6—H6B | 109.513 |
| C3—O3—H3A | 109.476 | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.082 |
| C2—O6—C6—C5 | −61.73 (13) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −172.62 (10) |
| C6—O6—C2—O2 | −58.74 (12) | O3—C3—C4—O4 | −62.10 (13) |
| C6—O6—C2—C1 | 179.03 (9) | O3—C3—C4—C5 | 177.33 (9) |
| C6—O6—C2—C3 | 59.88 (13) | C2—C3—C4—O4 | 176.97 (10) |
| O1—C1—C2—O2 | −68.49 (15) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 56.41 (12) |
| O1—C1—C2—O6 | 52.95 (13) | O4—C4—C5—O5 | −58.98 (13) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 170.90 (9) | O4—C4—C5—C6 | −177.25 (10) |
| O2—C2—C3—O3 | −57.21 (15) | C3—C4—C5—O5 | 61.77 (12) |
| O2—C2—C3—C4 | 63.99 (14) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −56.50 (14) |
| O6—C2—C3—O3 | −178.02 (10) | O5—C5—C6—O6 | −61.97 (15) |
| O6—C2—C3—C4 | −56.82 (13) | C4—C5—C6—O6 | 58.34 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | 66.18 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···O3i | 0.82 | 2.28 | 2.9202 (14) | 135 |
| O2—H2A···O1 | 0.82 | 2.60 | 2.9721 (14) | 110 |
| O2—H2A···O1ii | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.7224 (13) | 161 |
| O3—H3A···O4iii | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.7831 (18) | 177 |
| O4—H4A···O5iv | 0.82 | 2.01 | 2.7893 (13) | 158 |
| O5—H5A···O4v | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.8431 (12) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+2; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x−1, y, z; (v) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS5416).
References
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Mallamo, M., Mazzone, A., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 357–361.
- Ishii, T., Sakane, G., Yoshihara, A., Fukada, K. & Senoo, T. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o289–o290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T., Senoo, T., Kozakai, T., Fukada, K. & Sakane, G. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Itoh, H. & Izumori, K. (1996). J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81, 351–353.
- Kanters, J. A., Roelofsen, G., Alblas, B. P. & Meinders, I. (1977). Acta Cryst. B33, 665–672.
- Rigaku (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2009). RAPID-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2014). CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416Isup3.cml
ORTEP . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig1.tif
ORTEP view of the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme. The thermal ellipsoids of all non-hydrogen atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
c . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig2.tif
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the c-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015016503/is5416fig3.tif
Part of the packing diagram of the title compound viewed down the a-axis, showing the hydrogen-bonding network (green solid lines).
CCDC reference: 1422317
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


