In the crystals of the title N-halomethylated quaternary ammonium salts, there are short I⋯I− interactions of 3.564 (4), 3.506 (1) and 3.55781) Å for compounds (I), (II) and (III), respectively. In (I), molecules are linked by C—H⋯I− and C—H⋯π interactions, together with the I⋯I− short contacts, forming ribbons along [100]. In (II), there are only C—H⋯I− interactions, which together with the I⋯I− short contacts, lead to the formation of helices along [010]. In (III), apart from the I⋯I− short contacts, there are no other significant intermolecular interactions present.
Keywords: crystal structure, N-halomethylated quaternary ammonium salts, cation–π interaction, halogen bond, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
In the crystals of the title N-halomethylated quaternary ammonium salts, C19H23IN+·I−, (I) [systematic name: N-(4,4-diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide], C20H25IN+·I−, (II) [systematic name: N-(5,5-diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide], and C21H27IN+·I−, (III) [systematic name: N-(6,6-diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide], there are short I⋯I− interactions of 3.564 (4), 3.506 (1) and 3.557 (1) Å for compounds (I), (II) and (III), respectively. Compound (I) crystallizes in the Sohncke group P21 as an ‘enantiopure’ compound and is therefore a potential material for NLO properties. In the crystal of compound (I), molecules are linked by C—H⋯I− and C—H⋯π interactions which, together with the I⋯I− interactions, lead to the formation of ribbons along [100]. In (II), there are only C—H⋯I− interactions which, together with the I⋯I− interactions, lead to the formation of helices along [010]. In (III), apart from the I⋯I− interactions, there are no significant intermolecular interactions present.
Chemical context and background to halogen bonding and cation–π interactions
Quaternary ammonium salts have been widely studied as anti-cancer (Wang et al., 2012 ▸; Song et al., 2013 ▸), anti-fungal (Ng et al., 2006 ▸), anti-HIV-1 (Shiraishi et al., 2000 ▸), anti-bacterial (Calvani et al., 1998 ▸), anti-malarial (Calas et al., 1997 ▸; Calas et al., 2000 ▸) and anti-leishmanial (Mavromoustakos et al., 2001 ▸) pharmaceuticals. Our research group has been working in the past few years on the activity of quaternary N-halomethyl ammonium salts for likely pharmaceutical purposes, specifically against axenic L. (V) panamensis and L. (L) amazonensis parasites, human pathogenic species that cause cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. The experiments proved that these compounds are very promising anti-leishmanial molecules, and very significant changes in their activity were observed upon a slight modification of the carbon skeleton by only a single methylene unit (Ríos-Vásquez et al., 2015 ▸). A preliminary effort at understanding a structure–activity relationship with three N-iodomethyl quaternary ammonium salts (I), (II) and (III) of the form [ICH2N(CH3)3(CH2)nCH=C(Ph)2]+·I− (with n = 2, 3 and 4, respectively) is currently being carried out. One possible approach to understand the different activities is to establish what kind of interactions are present in compounds (I)–(III), for example whether C—I⋯I− (Desiraju et al., 2013 ▸), C—H⋯I− (Glidewell et al., 1994 ▸), C—H⋯π (Nishio et al., 1998 ▸) or cation–π (Dougherty, 1996 ▸), and if so, how these interactions may affect their structure and biological properties.
As defined by International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC): a halogen bond occurs when there is evidence of a net attractive interaction between an electrophilic region associated with a halogen atom in a molecular entity and a nucleophilic region in another, or the same, molecular entity (Desiraju et al., 2013 ▸). Halogen bonds are characterized by X⋯X distances that are clearly shorter than the van der Waals radii sum (Formigué, 2009 ▸; Awwadi et al.; 2006 ▸); otherwise this interaction is neglected. In a similar way, the existence of C—H⋯X hydrogen bonds (X = F, Cl, Br or I) in neutral organic molecules (Aakeröy & Seddon, 1993 ▸) and even in organic salts has been recognized. On the other hand, a special kind of hydrogen bond, defined as a weak interaction between a soft acid (i.e. an sp
3, sp
2 or sp C—H system) and a soft base (i.e. an aromatic, olefinic or acetilenic p system), with a significant role on diverse chemical and biological phenomena has recently been described (Nishio, 2012 ▸). In particular, this interaction exerts an observable influence on host–guest recognition and crystal packing in the solid state. A related attraction is the cation–π interaction, which is regarded as an electrostatic attraction between a positive charge and the quadrupole moment of an aromatic ring (Dougherty, 1996 ▸). A cation–π interaction between aromatic and ammonium ions is known to play an important role in many biological systems (Ma & Dougherty, 1997 ▸; Dougherty, 2013 ▸; Sussman et al., 1991 ▸; Chen et al., 2011 ▸). Part of our research interest is focused not only in understanding the reactive nature of alpha ammonium distonic radical cations which are generated from N-halomethylated quaternary ammonium salts (Ríos et al., 1996 ▸; Ríos, Bartberger et al., 1997 ▸), but also in trying to understand how these salts behave against Leishmania parasites (Ríos-Vásquez et al., 2015 ▸). The recognition of the occurrence of some supramolecular interactions in these salts may lead to a better understanding of the likely novel biological binding sites, and therefore to new suggestions about biocatalytic mechanisms.
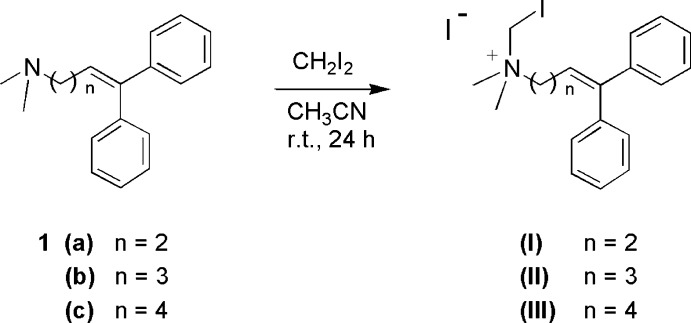
The title N-iodomethyl quaternary ammonium salts, (I)–(III), were synthesized following standard procedures used for other related compounds (Newcomb et al., 1993 ▸; Horner et al., 1995 ▸) and suitable crystals were obtained (Múnera-Orozco, 2014 ▸). This paper reports a comparative crystal structure and supramolecular interactions analysis for the aforementioned compounds.
Structural commentary
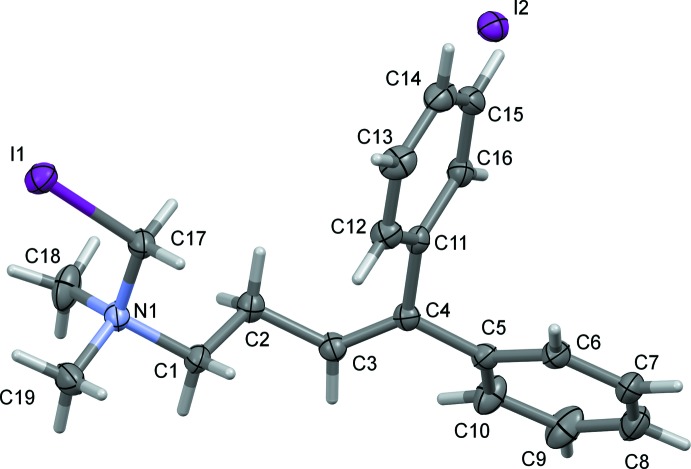
Compound (I), Fig. 1 ▸, crystallizes in the non-centrosymmetric monoclinic space group P21 and is therefore, a potential material for NLO properties. The asymmetric unit consists of an ammonium cation and an iodide anion. In the geminal-substituted diphenylethene unit, the phenyl rings (C5–C10 and C11–C16) are inclined to one another by 74.6 (2)°, and are twisted from the mean plane of the central C=C bond fragment (C2–C5/C11) by 33.2 (2) and 61.4 (2)°, respectively. Co-planarity of the olefin skeleton and the peripheral phenyl rings is prevented because of steric congestion between the associated phenyl rings. The conformation of the side chain reveals an all-trans extended conformation with the iodomethyl moiety on one side of the backbone chain, with bond lengths and angles in the expected ranges.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
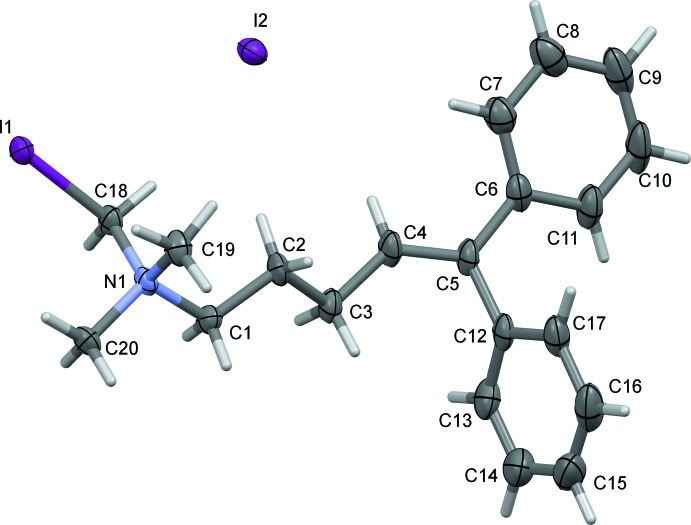
In compound (II), Fig. 2 ▸, the dihedral angles between the mean planes of the C=C double-bond fragment (C3–C6/C12) and the two phenyl rings (C6–C11 and C12–C17) are 31.1 (4) and 58.6 (4)°, respectively, while the phenyl rings are inclined to one another by 76.2 (4)°. The N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethyl-N-propylammonium moiety adopts a fully extended conformation with one methyl group and the iodomethyl unit on opposite sides of the backbone of the side chain (Fig. 2 ▸). This conformation seems to be partially supported by a C—H⋯I− hydrogen bond (Table 2 and Supramolecular features).
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
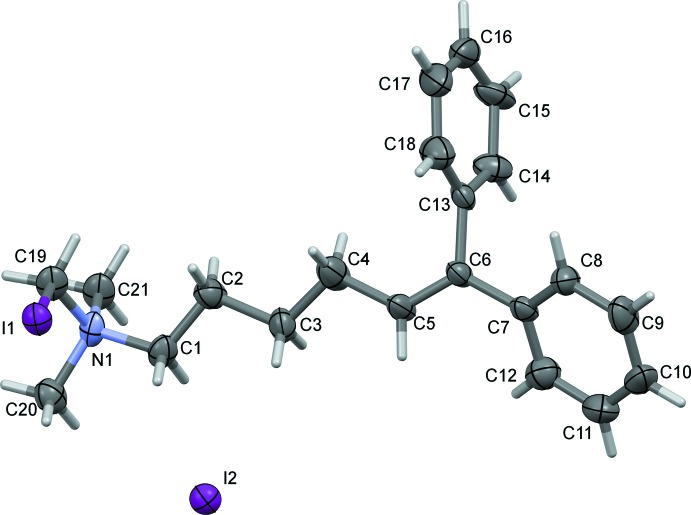
In compound (III), Fig. 3 ▸, the phenyl rings are twisted out of the plane defined by the ethylene moiety (C4–C7/C13), making dihedral angles of 38.7 (4) and 78.7 (6)° for the trans (C7–C12) and cis (C13–C18) phenyl rings, respectively. The phenyl rings are inclined to one another by 78.5 (6)°. The alkylamino side chain is almost fully extended away from the geminal-substituted ethene group.
Figure 3.
The molecular structure of compound (III), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
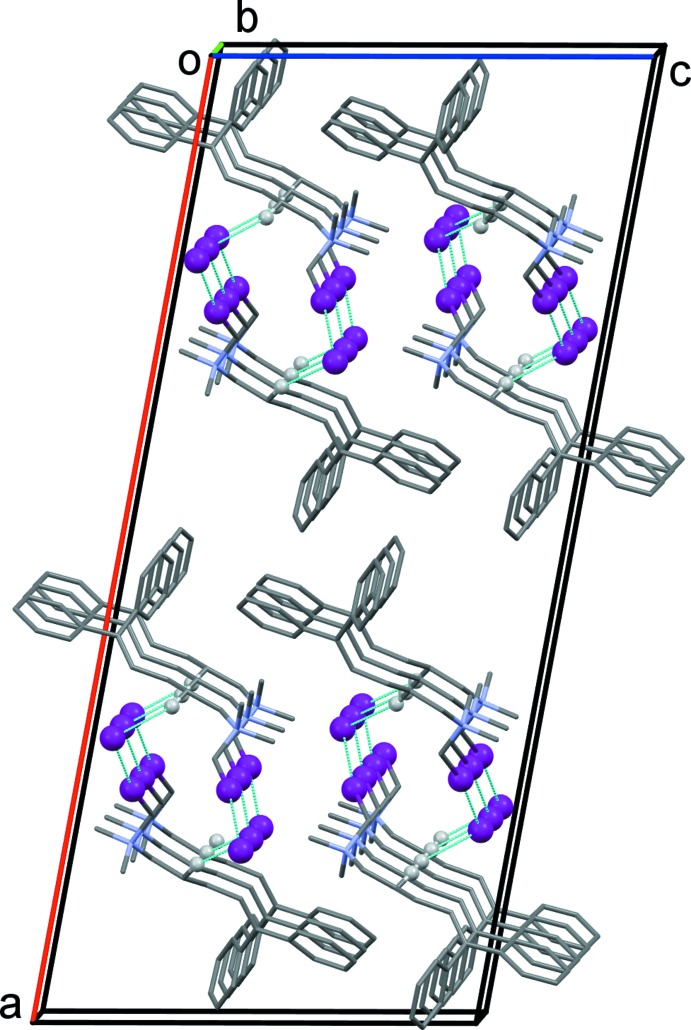
In the crystal of (I), ribbons are formed, by I1⋯I2i contacts [3.564 (4) Å; symmetry code: (i) −x − 1, y −  , −z + 1] and C—H⋯I− hydrogen bonds, along the a-axis direction. The chains are reinforced by C—H⋯π interactions (Fig. 4 ▸ and Table 1 ▸).
, −z + 1] and C—H⋯I− hydrogen bonds, along the a-axis direction. The chains are reinforced by C—H⋯π interactions (Fig. 4 ▸ and Table 1 ▸).
Figure 4.
The crystal packing of compound (I), viewed along the b axis, showing the intermolecular contacts (dashed lines; see Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17B⋯I2i | 0.97 | 3.00 | 3.919 (5) | 159 |
| C7—H7⋯Cg ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.030 (5) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 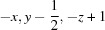 ; (ii)
; (ii) 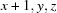 .
.
In the crystal of (II), helical chains along the b-axis direction are formed by molecules linked via C—H⋯I− (Table 2 ▸) and I1⋯I2ii interactions [3.506 (1) Å; symmetry code: (ii) −x +  , y −
, y −  , −z +
, −z +  ]; as shown in Fig. 5 ▸. Here no C—H⋯π interactions are present in the crystal packing. The closest distance between the ammonium substituents and any of the phenyl rings is ca 7.18 Å. These features clearly rule out an intramolecular cation–π interaction for this molecule in the solid state. However, in studies of distonic radical cation (Ríos et al. 1996 ▸; Yates et al., 1986 ▸), evidence is presented that the active conformation of the alkylamino side chain is oriented toward and above the plane of the C=C double bond of the geminal-substituted ethene group. These results confirm that there is considerable freedom of rotation about the bonds separating the basic amino function and the tricyclic system, and thus numerous interconvertible side-chain conformations, differing only slightly in potential energy, may exist.
]; as shown in Fig. 5 ▸. Here no C—H⋯π interactions are present in the crystal packing. The closest distance between the ammonium substituents and any of the phenyl rings is ca 7.18 Å. These features clearly rule out an intramolecular cation–π interaction for this molecule in the solid state. However, in studies of distonic radical cation (Ríos et al. 1996 ▸; Yates et al., 1986 ▸), evidence is presented that the active conformation of the alkylamino side chain is oriented toward and above the plane of the C=C double bond of the geminal-substituted ethene group. These results confirm that there is considerable freedom of rotation about the bonds separating the basic amino function and the tricyclic system, and thus numerous interconvertible side-chain conformations, differing only slightly in potential energy, may exist.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2B⋯I2 | 0.97 | 3.06 | 4.001 (7) | 165 |
Figure 5.
The crystal packing of compound (II), viewed along the b axis, showing the intermolecular contacts (dashed lines; see Table 2 ▸).
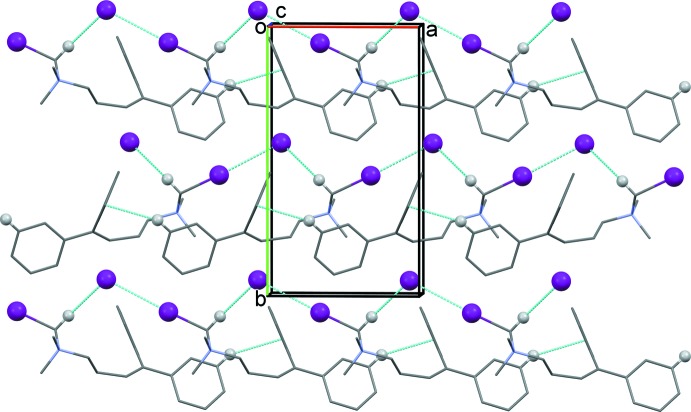
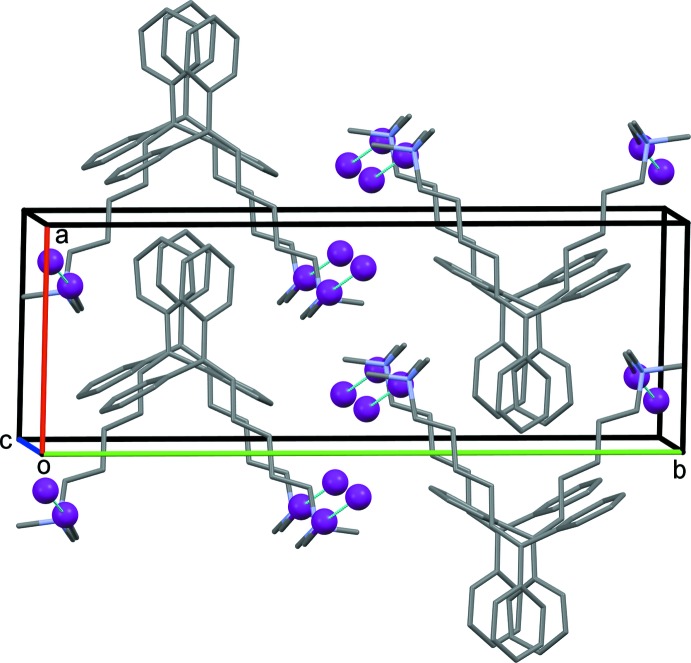
In the crystal of (III), apart from the I1⋯I2iii contact of 3.557 (1) Å [symmetry code: (iii) −x, −y + 1, −z], there are no other significant intermolecular contacts present (Fig. 6 ▸). The only possible conclusion regarding the crystal structure of (III) is that the steric requirements in this molecule outweigh the additional stabilization obtained by an intramolecular cation–π interaction.
Figure 6.
The crystal packing of compound (III), viewed along the b axis.
Synthesis and crystallization
The general procedure for the preparation of the title quaternary ammonium salts is illustrated in Fig. 7 ▸ for compounds (I)–(III). The reactions were carried out following a standard literature method (Ríos et al., 1996 ▸) starting from the appropriate amine [N,N-dimethyl-4,4-diphenylbut-3-en-1-amine 1(a), N,N-dimethyl-5,5-diphenylpent-4-en-1-amine 1(b) and N,N-dimethyl-6,6-diphenylhex-5-en-1-amine 1(c)]. Typically, CH2I2 (4 eq) and 1 eq of the starting tertiary amine [for example, compound 1(a) for the synthesis of (I); as shown in Fig. 7 ▸] were dissolved in acetonitrile. The reactions were allowed to run overnight at room temperature, and the precipitated salts were filtered off and washed several times with diethyl ether, and then recrystallized from a binary mixture water–isopropanol. The desired products were obtained as colourless crystals.
Figure 7.
The general procedure for the preparation of the title quaternary ammonium salts.
Compound (I): The product was obtained as a white solid in 74% yield; m.p. 425–427 K. 1H NMR (DMSO, 300 MHz, δ, p.p.m.): 2.49 (m, 2H), 3.12 (s, 6H), 3.50 (m, 2H), 5.05 (s, 2H), 6.07 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.15–7.58 (m, 10H) p.p.m. 13C NMR (DMSO, 75 MHz,, p.p.m.) 23.70, 31.49, 51.66, 63.58, 121.92, 127.19–129.51, 138.79, 141.62, 145.03 p.p.m. Elemental analysis calculated for C19H23NI2: C, 43.95%; H, 4.46%; N, 2.70%; found, C, 43.48%; H, 4.35%; N, 2.68%. MS–ESI calculated for C19H23NI: 392.09, found: 391.95.
Compound (II): The product was obtained as a white solid in 77% yield; m.p. 430–437 K. 1H NMR (DMSO, 300 MHz, δ, p.p.m.): 1.85 (m, 2H), 2.12 (m, 2H), 2.51 (m, 2H), 3.15 (s, 6H), 5.18 (s, 2H), 6.14 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.11–7.51 (10H). 13C NMR (DMSO, 75 MHz, p.p.m.): 22.30, 25.91, 39.01, 51.19, 63.84, 126.84–141.68. ESI–MS m/z calculated for C20H25NI: 406.10, found: 406.20.
Compound (III): The product was obtained as a white solid in 72% yield; m.p. 429–431 K. 1H NMR (DMSO, 300 MHz, δ, p.p.m.): 1.45 (m, 2H), 1.68 (m, 2H), 2.12 (m, 2H), 2.51 (m, 2H), 3.10 (s, 6H), 5.14 (s, 2H), 6.14 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.06–7.51 (m, 10H) p.p.m. 13C NMR (DMSO, 75 MHz, p.p.m.): 25.07, 28.91, 31.91, 35.35, 54.29, 67.34, 129.89–132.50, 130.19, 142.45, 144.34, 145.02. Elemental analysis calculated for C21H27NI2: C, 46.09%; H, 4.97%; N, 2.56%; found C, 45.91%; H, 4.93%; N, 2.58%. ESI–MS m/z calculated for C21H27NI: 420.12, found: 420.20.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. For all three compounds the C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: C—H = 0.93–0.99 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms. Refining the structure of compound (I) in the non-centrosymmetric space group gives a value of 0.02 (3) for the Flack parameter (Flack & Bernardinelli, 1999 ▸), confirming that the direction of the polar axis has been correctly determined. The studied crystal of compound (III) was a non-merohedral twin with a ratio of two major domains of 0.374 (2):0.626 (2). The two domains are rotated from each other by 180.0° about the reciprocal axis a*, as determined by the CELL NOW program (Sheldrick, 2004 ▸). The final refinement was carried out using the twinned data set.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C19H23IN+·I− | C20H25IN+·I− | C21H27IN+·I− |
| M r | 519.18 | 533.21 | 547.23 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 | Monoclinic, C2/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 298 | 298 | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.9254 (2), 13.6161 (3), 9.4632 (2) | 37.778 (7), 6.6323 (12), 17.021 (3) | 8.9423 (12), 24.058 (3), 10.3749 (13) |
| β (°) | 103.320 (1) | 100.567 (4) | 103.656 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 993.73 (4) | 4192.3 (13) | 2168.9 (5) |
| Z | 2 | 8 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 3.16 | 3.00 | 2.90 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.23 × 0.19 × 0.12 | 0.21 × 0.20 × 0.08 | 0.32 × 0.22 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEX CCD | Bruker SMART APEX CCD | Bruker SMART APEX CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) | Multi-scan (TWINABS; Bruker, 2012 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.624, 0.745 | 0.349, 0.745 | 0.273, 0.429 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 5791, 3085, 3013 | 16925, 3808, 3114 | 3961, 3961, 2941 |
| R int | 0.016 | 0.079 | 0.079 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.017, 0.038, 1.08 | 0.052, 0.145, 1.05 | 0.060, 0.138, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 3085 | 3808 | 3961 |
| No. of parameters | 202 | 210 | 220 |
| No. of restraints | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.27, −0.46 | 1.90, −1.98 | 0.82, −0.80 |
| Absolute structure | Refined as an inversion twin | – | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.02 (3) | – | – |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup3.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIIsup8.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Special thanks are extended to Dr Guillermo Delgado Lamas (Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México) and Dr Eunice Ríos Vásquez [Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and Universidad del Quindío (Colombia)] for assistance with the structural analyses. The authors also acknowledge financial support from the Universidad de Caldas, Colombia, and Illinois State University, USA.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Crystal data
| C19H23IN+·I− | Dx = 1.735 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 519.18 | Melting point = 425–427 K |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.9254 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 4987 reflections |
| b = 13.6161 (3) Å | θ = 2.2–25.3° |
| c = 9.4632 (2) Å | µ = 3.16 mm−1 |
| β = 103.320 (1)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 993.73 (4) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.23 × 0.19 × 0.12 mm |
| F(000) = 500 |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3085 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3013 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.016 |
| Detector resolution: 8.333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.2° |
| ω–scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | k = −16→16 |
| Tmin = 0.624, Tmax = 0.745 | l = −11→11 |
| 5791 measured reflections |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.017 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.038 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0138P)2 + 0.0203P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3085 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 202 parameters | Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Refined as an inversion twin |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.02 (3) |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component inversion twin. |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | −0.65685 (3) | 0.06224 (2) | 0.13054 (3) | 0.04839 (9) | |
| I2 | 0.06519 (4) | 0.44189 (2) | 0.91487 (3) | 0.04368 (9) | |
| N1 | −0.3770 (4) | 0.2023 (3) | 0.0555 (4) | 0.0376 (8) | |
| C1 | −0.1849 (5) | 0.2322 (4) | 0.0948 (5) | 0.0402 (10) | |
| H1A | −0.1144 | 0.1733 | 0.1019 | 0.048* | |
| H1B | −0.1609 | 0.2719 | 0.0166 | 0.048* | |
| C2 | −0.1311 (5) | 0.2891 (3) | 0.2358 (5) | 0.0409 (11) | |
| H2A | −0.1888 | 0.3524 | 0.2249 | 0.049* | |
| H2B | −0.1676 | 0.2536 | 0.3124 | 0.049* | |
| C3 | 0.0613 (6) | 0.3044 (3) | 0.2779 (5) | 0.0382 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.1101 | 0.3408 | 0.2143 | 0.046* | |
| C4 | 0.1686 (5) | 0.2711 (3) | 0.3970 (4) | 0.0329 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.3545 (5) | 0.3021 (3) | 0.4380 (4) | 0.0349 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.4815 (6) | 0.2388 (4) | 0.5116 (5) | 0.0457 (11) | |
| H6 | 0.4514 | 0.1752 | 0.5318 | 0.055* | |
| C7 | 0.6528 (6) | 0.2687 (4) | 0.5557 (5) | 0.0546 (13) | |
| H7 | 0.7362 | 0.2248 | 0.6040 | 0.065* | |
| C8 | 0.7001 (6) | 0.3612 (5) | 0.5292 (6) | 0.0598 (15) | |
| H8 | 0.8148 | 0.3812 | 0.5610 | 0.072* | |
| C9 | 0.5768 (7) | 0.4253 (4) | 0.4549 (7) | 0.0661 (16) | |
| H9 | 0.6087 | 0.4887 | 0.4357 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 0.4056 (6) | 0.3959 (4) | 0.4085 (6) | 0.0532 (13) | |
| H10 | 0.3239 | 0.4395 | 0.3569 | 0.064* | |
| C11 | 0.1128 (5) | 0.2030 (3) | 0.5013 (4) | 0.0326 (9) | |
| C12 | 0.0439 (6) | 0.1106 (3) | 0.4575 (5) | 0.0422 (10) | |
| H12 | 0.0314 | 0.0909 | 0.3616 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | −0.0060 (6) | 0.0480 (3) | 0.5561 (5) | 0.0500 (12) | |
| H13 | −0.0522 | −0.0134 | 0.5258 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0761 (4) | 0.6978 (5) | 0.0523 (13) | |
| H14 | −0.0198 | 0.0334 | 0.7637 | 0.063* | |
| C15 | 0.0784 (6) | 0.1674 (4) | 0.7431 (5) | 0.0467 (12) | |
| H15 | 0.0883 | 0.1871 | 0.8388 | 0.056* | |
| C16 | 0.1298 (5) | 0.2295 (4) | 0.6457 (5) | 0.0403 (10) | |
| H16 | 0.1768 | 0.2905 | 0.6774 | 0.048* | |
| C17 | −0.4036 (5) | 0.1302 (3) | 0.1685 (5) | 0.0411 (10) | |
| H17A | −0.3821 | 0.1637 | 0.2614 | 0.049* | |
| H17B | −0.3174 | 0.0787 | 0.1761 | 0.049* | |
| C18 | −0.4928 (7) | 0.2892 (4) | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0633 (15) | |
| H18A | −0.6106 | 0.2703 | 0.0100 | 0.095* | |
| H18B | −0.4590 | 0.3397 | −0.0076 | 0.095* | |
| H18C | −0.4832 | 0.3135 | 0.1478 | 0.095* | |
| C19 | −0.4089 (7) | 0.1546 (5) | −0.0910 (5) | 0.0596 (14) | |
| H19A | −0.5290 | 0.1369 | −0.1218 | 0.089* | |
| H19B | −0.3385 | 0.0967 | −0.0855 | 0.089* | |
| H19C | −0.3796 | 0.1997 | −0.1596 | 0.089* |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.03965 (16) | 0.05161 (19) | 0.05521 (18) | −0.00709 (15) | 0.01359 (13) | −0.00180 (15) |
| I2 | 0.04705 (17) | 0.03979 (15) | 0.04515 (16) | 0.00372 (15) | 0.01257 (12) | 0.00767 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0317 (17) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0351 (19) | −0.0020 (17) | 0.0010 (15) | 0.0047 (16) |
| C1 | 0.029 (2) | 0.051 (3) | 0.039 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0042 (18) | 0.006 (2) |
| C2 | 0.035 (2) | 0.043 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C3 | 0.038 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.038 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0058 (19) | 0.003 (2) |
| C4 | 0.034 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0022 (18) | 0.0073 (18) | −0.0027 (18) |
| C5 | 0.033 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0087 (18) | −0.0047 (19) |
| C6 | 0.037 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.011 (2) |
| C7 | 0.033 (2) | 0.083 (4) | 0.049 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.009 (3) |
| C8 | 0.034 (3) | 0.080 (4) | 0.065 (4) | −0.009 (3) | 0.011 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| C9 | 0.049 (3) | 0.048 (4) | 0.103 (4) | −0.019 (3) | 0.021 (3) | −0.017 (3) |
| C10 | 0.040 (3) | 0.037 (2) | 0.082 (4) | −0.003 (2) | 0.012 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0266 (19) | 0.035 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0031 (18) | 0.0054 (17) | 0.0010 (18) |
| C12 | 0.043 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.045 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.013 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C13 | 0.054 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.068 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C14 | 0.046 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.019 (2) | 0.023 (3) |
| C15 | 0.043 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.007 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C16 | 0.031 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.040 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0043 (19) | −0.004 (2) |
| C17 | 0.035 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.037 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0035 (18) | 0.005 (2) |
| C18 | 0.041 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.091 (4) | 0.009 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
| C19 | 0.055 (3) | 0.084 (4) | 0.036 (3) | −0.014 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.001 (3) |
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C17 | 2.164 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| I1—I2i | 3.5640 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.386 (7) |
| N1—C18 | 1.492 (6) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C19 | 1.499 (6) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C17 | 1.502 (5) | C11—C16 | 1.390 (6) |
| N1—C1 | 1.536 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.396 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.517 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.387 (6) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.370 (7) |
| C2—C3 | 1.499 (6) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C14—C15 | 1.379 (7) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.326 (6) | C15—C16 | 1.379 (6) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C11 | 1.493 (6) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.495 (6) | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (6) | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C10 | 1.388 (6) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.387 (7) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.353 (8) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.376 (8) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C17—I1—I2i | 176.81 (12) | C9—C10—C5 | 120.8 (5) |
| C18—N1—C19 | 110.2 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C18—N1—C17 | 110.7 (4) | C5—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C19—N1—C17 | 110.7 (4) | C16—C11—C12 | 118.0 (4) |
| C18—N1—C1 | 111.4 (4) | C16—C11—C4 | 120.8 (4) |
| C19—N1—C1 | 106.6 (3) | C12—C11—C4 | 121.2 (4) |
| C17—N1—C1 | 107.1 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 114.2 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 108.7 | C14—C13—C12 | 120.3 (5) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 108.7 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.6 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.2 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 111.6 (4) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.3 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.7 (4) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.3 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.0 | C15—C16—C11 | 121.4 (4) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 126.3 (4) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 116.8 | C11—C16—H16 | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 116.8 | N1—C17—I1 | 116.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C11 | 123.0 (4) | N1—C17—H17A | 108.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.6 (4) | I1—C17—H17A | 108.3 |
| C11—C4—C5 | 115.3 (3) | N1—C17—H17B | 108.3 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 117.5 (4) | I1—C17—H17B | 108.3 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.9 (4) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.4 |
| C10—C5—C4 | 121.6 (4) | N1—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.1 (5) | N1—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.4 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.4 | N1—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.7 (5) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.6 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 | N1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.4 (5) | N1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.3 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.3 | N1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 120.5 (5) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.8 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.8 | ||
| C18—N1—C1—C2 | 55.2 (5) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −1.8 (8) |
| C19—N1—C1—C2 | 175.5 (4) | C4—C5—C10—C9 | 176.1 (5) |
| C17—N1—C1—C2 | −65.9 (5) | C3—C4—C11—C16 | −120.5 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 172.5 (4) | C5—C4—C11—C16 | 57.8 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −117.9 (5) | C3—C4—C11—C12 | 60.2 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C11 | 6.6 (7) | C5—C4—C11—C12 | −121.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −171.6 (4) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −148.1 (5) | C4—C11—C12—C13 | 179.5 (4) |
| C11—C4—C5—C6 | 33.5 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.3 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | 34.0 (6) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.9 (7) |
| C11—C4—C5—C10 | −144.3 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.5 (7) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.9 (7) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 1.5 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.0 (4) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.8 (6) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.7 (7) | C4—C11—C16—C15 | 179.9 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.4 (8) | C18—N1—C17—I1 | 64.6 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.5 (9) | C19—N1—C17—I1 | −57.9 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | 1.1 (9) | C1—N1—C17—I1 | −173.8 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x−1, y−1/2, −z+1.
(I) N-(4,4-Diphenylbut-3-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17B···I2ii | 0.97 | 3.00 | 3.919 (5) | 159 |
| C7—H7···Cgiii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.030 (5) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z.
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Crystal data
| C20H25IN+·I− | Dx = 1.690 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 533.21 | Melting point = 430–431 K |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 37.778 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 4726 reflections |
| b = 6.6323 (12) Å | θ = 2.2–25.3° |
| c = 17.021 (3) Å | µ = 3.00 mm−1 |
| β = 100.567 (4)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 4192.3 (13) Å3 | Platy-prism, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.21 × 0.20 × 0.08 mm |
| F(000) = 2064 |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3808 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3114 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.079 |
| ω–scans | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −45→45 |
| Tmin = 0.349, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −7→7 |
| 16925 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.145 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0918P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3808 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 210 parameters | Δρmax = 1.90 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −1.98 e Å−3 |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.25244 (2) | −0.01229 (6) | 0.13640 (2) | 0.04488 (19) | |
| I2 | 0.30512 (2) | 0.07869 (7) | 0.42246 (3) | 0.04999 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.31227 (12) | 0.3200 (8) | 0.1496 (2) | 0.0383 (11) | |
| C1 | 0.32956 (18) | 0.4989 (9) | 0.1981 (4) | 0.0446 (15) | |
| H1A | 0.3463 | 0.5629 | 0.1690 | 0.053* | |
| H1B | 0.3109 | 0.5965 | 0.2029 | 0.053* | |
| C2 | 0.34941 (19) | 0.4459 (10) | 0.2810 (4) | 0.0503 (16) | |
| H2A | 0.3713 | 0.3736 | 0.2770 | 0.060* | |
| H2B | 0.3345 | 0.3583 | 0.3069 | 0.060* | |
| C3 | 0.35877 (18) | 0.6363 (11) | 0.3312 (4) | 0.0498 (15) | |
| H3A | 0.3769 | 0.7134 | 0.3107 | 0.060* | |
| H3B | 0.3375 | 0.7199 | 0.3284 | 0.060* | |
| C4 | 0.37268 (18) | 0.5764 (12) | 0.4160 (4) | 0.0536 (17) | |
| H4 | 0.3577 | 0.4935 | 0.4394 | 0.064* | |
| C5 | 0.40427 (16) | 0.6276 (11) | 0.4628 (3) | 0.0476 (15) | |
| C6 | 0.41456 (18) | 0.5452 (12) | 0.5446 (4) | 0.0537 (18) | |
| C7 | 0.4042 (2) | 0.3523 (14) | 0.5653 (4) | 0.066 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.3905 | 0.2719 | 0.5265 | 0.080* | |
| C8 | 0.4140 (2) | 0.2791 (17) | 0.6421 (5) | 0.083 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.4068 | 0.1506 | 0.6544 | 0.099* | |
| C9 | 0.4346 (2) | 0.396 (2) | 0.7012 (5) | 0.095 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.4411 | 0.3468 | 0.7530 | 0.114* | |
| C10 | 0.4453 (2) | 0.586 (2) | 0.6822 (5) | 0.098 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.4592 | 0.6652 | 0.7213 | 0.117* | |
| C11 | 0.43528 (19) | 0.6603 (16) | 0.6054 (4) | 0.073 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.4425 | 0.7893 | 0.5937 | 0.088* | |
| C12 | 0.42943 (16) | 0.7710 (12) | 0.4341 (3) | 0.0494 (16) | |
| C13 | 0.4190 (2) | 0.9644 (13) | 0.4097 (5) | 0.067 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.3957 | 1.0067 | 0.4121 | 0.080* | |
| C14 | 0.4417 (3) | 1.0942 (16) | 0.3824 (6) | 0.087 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.4339 | 1.2226 | 0.3655 | 0.104* | |
| C15 | 0.4761 (3) | 1.036 (2) | 0.3796 (7) | 0.097 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.4914 | 1.1257 | 0.3604 | 0.117* | |
| C16 | 0.4882 (2) | 0.849 (2) | 0.4045 (5) | 0.091 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.5118 | 0.8115 | 0.4026 | 0.109* | |
| C17 | 0.46478 (18) | 0.7137 (15) | 0.4330 (4) | 0.067 (2) | |
| H17 | 0.4729 | 0.5865 | 0.4509 | 0.080* | |
| C18 | 0.28176 (16) | 0.2484 (10) | 0.1869 (3) | 0.0425 (14) | |
| H18A | 0.2648 | 0.3587 | 0.1853 | 0.051* | |
| H18B | 0.2911 | 0.2201 | 0.2428 | 0.051* | |
| C19 | 0.33945 (17) | 0.1549 (11) | 0.1464 (4) | 0.0509 (16) | |
| H19A | 0.3288 | 0.0516 | 0.1101 | 0.076* | |
| H19B | 0.3468 | 0.0982 | 0.1988 | 0.076* | |
| H19C | 0.3601 | 0.2098 | 0.1283 | 0.076* | |
| C20 | 0.29821 (18) | 0.3908 (10) | 0.0658 (3) | 0.0495 (16) | |
| H20A | 0.2870 | 0.2801 | 0.0343 | 0.074* | |
| H20B | 0.3178 | 0.4416 | 0.0427 | 0.074* | |
| H20C | 0.2808 | 0.4959 | 0.0668 | 0.074* |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.0501 (3) | 0.0520 (3) | 0.0289 (3) | −0.01023 (17) | −0.00240 (18) | 0.00087 (16) |
| I2 | 0.0512 (3) | 0.0512 (3) | 0.0461 (3) | 0.00415 (19) | 0.0052 (2) | 0.01397 (19) |
| N1 | 0.041 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.021 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.0006 (19) | −0.002 (2) |
| C1 | 0.052 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.033 (3) | −0.013 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C2 | 0.052 (4) | 0.062 (4) | 0.031 (3) | −0.008 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.005 (3) |
| C3 | 0.044 (3) | 0.062 (4) | 0.039 (3) | −0.010 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C4 | 0.047 (4) | 0.082 (5) | 0.028 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C5 | 0.042 (3) | 0.067 (4) | 0.031 (3) | −0.009 (3) | 0.000 (2) | −0.019 (3) |
| C6 | 0.035 (3) | 0.089 (5) | 0.036 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C7 | 0.064 (5) | 0.088 (6) | 0.046 (4) | 0.000 (4) | 0.008 (3) | −0.002 (4) |
| C8 | 0.066 (5) | 0.126 (8) | 0.058 (5) | 0.013 (5) | 0.018 (4) | 0.021 (5) |
| C9 | 0.051 (5) | 0.188 (12) | 0.044 (5) | 0.007 (6) | 0.002 (4) | 0.014 (6) |
| C10 | 0.059 (5) | 0.190 (12) | 0.039 (4) | −0.033 (7) | −0.004 (4) | −0.024 (6) |
| C11 | 0.057 (4) | 0.118 (7) | 0.042 (4) | −0.023 (5) | 0.001 (3) | −0.021 (4) |
| C12 | 0.040 (3) | 0.075 (5) | 0.029 (3) | −0.008 (3) | −0.003 (2) | −0.016 (3) |
| C13 | 0.057 (5) | 0.075 (5) | 0.061 (5) | −0.012 (4) | −0.007 (4) | −0.020 (4) |
| C14 | 0.079 (6) | 0.092 (7) | 0.079 (6) | −0.027 (5) | −0.014 (5) | 0.009 (5) |
| C15 | 0.073 (7) | 0.136 (10) | 0.076 (6) | −0.044 (6) | −0.004 (5) | 0.025 (7) |
| C16 | 0.047 (4) | 0.167 (11) | 0.056 (5) | −0.019 (6) | 0.004 (4) | −0.005 (6) |
| C17 | 0.043 (4) | 0.111 (7) | 0.042 (4) | −0.004 (4) | −0.002 (3) | −0.004 (4) |
| C18 | 0.044 (3) | 0.058 (4) | 0.025 (3) | −0.009 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.004 (3) |
| C19 | 0.048 (4) | 0.058 (4) | 0.044 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.002 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C20 | 0.057 (4) | 0.061 (4) | 0.028 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C18 | 2.146 (6) | C9—C10 | 1.381 (16) |
| I1—I2i | 3.5058 (7) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C18 | 1.492 (7) | C10—C11 | 1.382 (12) |
| N1—C20 | 1.504 (7) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C19 | 1.509 (8) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.522 (8) | C12—C13 | 1.383 (11) |
| C1—C2 | 1.513 (9) | C12—C17 | 1.392 (9) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.357 (12) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.530 (9) | C14—C15 | 1.361 (14) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.363 (16) |
| C3—C4 | 1.496 (9) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C16—C17 | 1.410 (13) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.351 (9) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.480 (10) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C12 | 1.489 (9) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.402 (12) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C11 | 1.404 (10) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.379 (11) | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.390 (14) | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | ||
| C18—I1—I2i | 170.16 (15) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.3 (9) |
| C18—N1—C20 | 109.7 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C18—N1—C19 | 111.6 (5) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C20—N1—C19 | 108.5 (5) | C10—C11—C6 | 121.6 (9) |
| C18—N1—C1 | 107.8 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.2 |
| C20—N1—C1 | 108.2 (5) | C6—C11—H11 | 119.2 |
| C19—N1—C1 | 111.0 (5) | C13—C12—C17 | 118.1 (7) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 114.4 (5) | C13—C12—C5 | 121.8 (6) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.6 | C17—C12—C5 | 120.1 (7) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 108.6 | C14—C13—C12 | 121.8 (8) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.6 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 108.6 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.6 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.0 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 110.7 (6) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.0 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.1 | C15—C16—C17 | 119.3 (9) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 108.9 (6) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.9 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.9 | C12—C17—C16 | 119.7 (9) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.9 | C12—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.9 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.3 | N1—C18—I1 | 117.9 (4) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 128.2 (7) | N1—C18—H18A | 107.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 115.9 | I1—C18—H18A | 107.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 115.9 | N1—C18—H18B | 107.8 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.9 (6) | I1—C18—H18B | 107.8 |
| C4—C5—C12 | 121.0 (6) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.2 |
| C6—C5—C12 | 118.1 (5) | N1—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 117.0 (7) | N1—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 122.5 (6) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C11—C6—C5 | 120.5 (7) | N1—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.4 (8) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.3 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.3 | N1—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.4 (10) | N1—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 | N1—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.3 (8) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 | ||
| C18—N1—C1—C2 | 69.2 (7) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 0.4 (12) |
| C20—N1—C1—C2 | −172.2 (5) | C5—C6—C11—C10 | −179.9 (8) |
| C19—N1—C1—C2 | −53.3 (7) | C4—C5—C12—C13 | 57.8 (9) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −167.8 (5) | C6—C5—C12—C13 | −121.2 (7) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 170.6 (6) | C4—C5—C12—C17 | −123.6 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 124.9 (8) | C6—C5—C12—C17 | 57.4 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −176.7 (7) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | 2.5 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—C12 | 4.3 (12) | C5—C12—C13—C14 | −179.0 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 32.1 (11) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −1.0 (14) |
| C12—C5—C6—C7 | −148.9 (7) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.4 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C11 | −147.5 (7) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.4 (16) |
| C12—C5—C6—C11 | 31.5 (10) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −2.5 (10) |
| C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.0 (11) | C5—C12—C17—C16 | 179.0 (6) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −179.7 (7) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 1.1 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.0 (12) | C20—N1—C18—I1 | 64.9 (6) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.2 (14) | C19—N1—C18—I1 | −55.4 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.6 (15) | C1—N1—C18—I1 | −177.5 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C6 | −0.7 (14) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
(II) N-(5,5-Diphenylpent-4-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2B···I2 | 0.97 | 3.06 | 4.001 (7) | 165 |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Crystal data
| C21H27IN+·I− | Dx = 1.676 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 547.23 | Melting point = 429–431 K |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9423 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 3046 reflections |
| b = 24.058 (3) Å | θ = 2.3–24.4° |
| c = 10.3749 (13) Å | µ = 2.90 mm−1 |
| β = 103.656 (3)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 2168.9 (5) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.22 × 0.04 mm |
| F(000) = 1064 |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3961 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2941 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.079 |
| Detector resolution: 8.333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 1.7° |
| ω–scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (TWINABS; Bruker, 2012) | k = 0→28 |
| Tmin = 0.273, Tmax = 0.429 | l = 0→12 |
| 3961 measured reflections |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.060 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.138 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0515P)2 + 2.9321P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3961 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 220 parameters | Δρmax = 0.82 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.80 e Å−3 |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. The studied crystal was a nonmerohedral twin with a ratio of two major domains of 0.374 (2):0.626 (2). The two domains were rotated from each other by 180.0° about the recipocal axis (1 0 0), which was determined by the CELL NOW program (Sheldrick, 2004). The final refinement was carried out using twinned data set. |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | −0.29957 (8) | 0.44339 (3) | 0.01740 (6) | 0.0597 (2) | |
| I2 | 0.17494 (8) | 0.51476 (3) | 0.26901 (6) | 0.0598 (2) | |
| N1 | −0.3411 (8) | 0.4415 (4) | 0.3070 (7) | 0.056 (2) | |
| C1 | −0.1733 (11) | 0.4319 (4) | 0.3631 (10) | 0.063 (3) | |
| H1A | −0.1159 | 0.4525 | 0.3103 | 0.076* | |
| H1B | −0.1459 | 0.4469 | 0.4524 | 0.076* | |
| C2 | −0.1252 (12) | 0.3731 (4) | 0.3678 (12) | 0.072 (3) | |
| H2A | −0.1407 | 0.3584 | 0.2786 | 0.087* | |
| H2B | −0.1860 | 0.3512 | 0.4153 | 0.087* | |
| C3 | 0.0467 (11) | 0.3699 (4) | 0.4394 (11) | 0.068 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.1029 | 0.3971 | 0.4001 | 0.082* | |
| H3B | 0.0578 | 0.3800 | 0.5317 | 0.082* | |
| C4 | 0.1182 (12) | 0.3134 (4) | 0.4333 (15) | 0.091 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.1013 | 0.3019 | 0.3413 | 0.109* | |
| H4B | 0.0681 | 0.2866 | 0.4789 | 0.109* | |
| C5 | 0.2892 (10) | 0.3135 (4) | 0.4957 (12) | 0.068 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.3381 | 0.3478 | 0.5120 | 0.082* | |
| C6 | 0.3743 (10) | 0.2685 (3) | 0.5287 (10) | 0.055 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.5451 (11) | 0.2703 (3) | 0.5813 (9) | 0.052 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.6398 (11) | 0.2322 (4) | 0.5435 (11) | 0.066 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.5966 | 0.2031 | 0.4881 | 0.080* | |
| C9 | 0.8003 (12) | 0.2359 (5) | 0.5862 (14) | 0.091 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.8636 | 0.2109 | 0.5560 | 0.109* | |
| C10 | 0.8623 (15) | 0.2778 (5) | 0.6747 (14) | 0.097 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.9683 | 0.2798 | 0.7079 | 0.116* | |
| C11 | 0.7701 (16) | 0.3158 (5) | 0.7133 (14) | 0.094 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.8128 | 0.3446 | 0.7699 | 0.113* | |
| C12 | 0.6122 (14) | 0.3116 (5) | 0.6681 (11) | 0.079 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.5495 | 0.3373 | 0.6969 | 0.094* | |
| C13 | 0.3026 (11) | 0.2115 (3) | 0.5086 (10) | 0.055 (2) | |
| C14 | 0.2723 (13) | 0.1847 (4) | 0.6156 (12) | 0.074 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.2993 | 0.2012 | 0.6990 | 0.089* | |
| C15 | 0.2004 (14) | 0.1323 (4) | 0.6000 (16) | 0.088 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.1840 | 0.1135 | 0.6738 | 0.105* | |
| C16 | 0.1551 (14) | 0.1091 (5) | 0.4782 (18) | 0.095 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.1010 | 0.0757 | 0.4681 | 0.114* | |
| C17 | 0.1888 (18) | 0.1347 (6) | 0.3678 (16) | 0.116 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.1614 | 0.1184 | 0.2842 | 0.139* | |
| C18 | 0.2659 (17) | 0.1861 (5) | 0.3880 (12) | 0.091 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.2926 | 0.2034 | 0.3164 | 0.109* | |
| C19 | −0.4077 (11) | 0.4192 (4) | 0.1718 (10) | 0.065 (3) | |
| H19A | −0.5148 | 0.4304 | 0.1460 | 0.078* | |
| H19B | −0.4058 | 0.3789 | 0.1771 | 0.078* | |
| C20 | −0.3648 (13) | 0.5048 (4) | 0.3059 (11) | 0.074 (3) | |
| H20A | −0.4723 | 0.5131 | 0.2740 | 0.111* | |
| H20B | −0.3078 | 0.5218 | 0.2488 | 0.111* | |
| H20C | −0.3294 | 0.5191 | 0.3943 | 0.111* | |
| C21 | −0.4312 (12) | 0.4165 (5) | 0.3995 (10) | 0.071 (3) | |
| H21A | −0.5382 | 0.4256 | 0.3684 | 0.107* | |
| H21B | −0.3936 | 0.4313 | 0.4872 | 0.107* | |
| H21C | −0.4189 | 0.3769 | 0.4015 | 0.107* |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.0559 (4) | 0.0659 (4) | 0.0605 (4) | 0.0039 (3) | 0.0202 (3) | 0.0118 (3) |
| I2 | 0.0586 (4) | 0.0618 (4) | 0.0632 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0228 (3) | 0.0043 (3) |
| N1 | 0.041 (4) | 0.081 (6) | 0.046 (4) | 0.002 (4) | 0.012 (4) | 0.020 (4) |
| C1 | 0.045 (5) | 0.078 (7) | 0.069 (6) | −0.006 (5) | 0.015 (5) | 0.014 (5) |
| C2 | 0.058 (6) | 0.056 (6) | 0.106 (9) | 0.003 (5) | 0.024 (6) | −0.001 (6) |
| C3 | 0.057 (6) | 0.069 (6) | 0.075 (7) | 0.012 (5) | 0.007 (6) | 0.017 (6) |
| C4 | 0.054 (7) | 0.065 (7) | 0.158 (12) | 0.006 (5) | 0.036 (8) | 0.023 (8) |
| C5 | 0.040 (5) | 0.043 (5) | 0.123 (9) | 0.002 (4) | 0.022 (6) | 0.012 (6) |
| C6 | 0.047 (5) | 0.038 (5) | 0.082 (7) | 0.005 (4) | 0.019 (5) | 0.010 (5) |
| C7 | 0.052 (6) | 0.038 (5) | 0.069 (6) | −0.002 (4) | 0.019 (5) | 0.010 (4) |
| C8 | 0.051 (6) | 0.055 (6) | 0.090 (7) | 0.004 (5) | 0.009 (6) | −0.006 (5) |
| C9 | 0.051 (7) | 0.083 (8) | 0.140 (11) | 0.017 (6) | 0.026 (8) | 0.022 (8) |
| C10 | 0.066 (8) | 0.077 (8) | 0.129 (11) | −0.028 (7) | −0.014 (8) | 0.022 (8) |
| C11 | 0.100 (10) | 0.054 (7) | 0.116 (11) | −0.008 (7) | −0.001 (9) | −0.007 (7) |
| C12 | 0.075 (8) | 0.074 (7) | 0.087 (8) | −0.007 (6) | 0.019 (7) | −0.002 (7) |
| C13 | 0.056 (6) | 0.040 (5) | 0.067 (6) | 0.012 (4) | 0.011 (5) | 0.014 (5) |
| C14 | 0.079 (8) | 0.053 (6) | 0.101 (9) | −0.004 (6) | 0.043 (7) | −0.012 (6) |
| C15 | 0.085 (9) | 0.041 (6) | 0.152 (13) | −0.009 (6) | 0.058 (9) | 0.011 (7) |
| C16 | 0.053 (7) | 0.063 (7) | 0.155 (14) | −0.001 (6) | −0.004 (9) | −0.005 (10) |
| C17 | 0.135 (14) | 0.072 (9) | 0.108 (11) | 0.001 (9) | −0.038 (10) | −0.002 (8) |
| C18 | 0.116 (11) | 0.069 (8) | 0.075 (8) | −0.001 (8) | −0.002 (7) | 0.001 (7) |
| C19 | 0.049 (6) | 0.080 (7) | 0.073 (7) | −0.005 (5) | 0.029 (5) | 0.024 (6) |
| C20 | 0.066 (7) | 0.071 (7) | 0.089 (8) | 0.009 (6) | 0.027 (6) | 0.008 (6) |
| C21 | 0.056 (6) | 0.091 (8) | 0.072 (7) | −0.006 (6) | 0.025 (6) | 0.032 (6) |
(III) N-(6,6-Diphenylhex-5-en-1-yl)-N-iodomethyl-N,N-dimethylammonium iodide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C19 | 2.138 (9) | C9—C10 | 1.388 (17) |
| I1—I2i | 3.5565 (9) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C19 | 1.489 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.353 (18) |
| N1—C1 | 1.494 (12) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C21 | 1.515 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (16) |
| N1—C20 | 1.537 (12) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.477 (13) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C13—C18 | 1.360 (14) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.365 (14) |
| C2—C3 | 1.543 (13) | C14—C15 | 1.407 (14) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.353 (18) |
| C3—C4 | 1.510 (14) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C16—C17 | 1.39 (2) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.514 (14) | C17—C18 | 1.409 (17) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.323 (12) | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.497 (12) | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C13 | 1.507 (12) | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.366 (12) | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C12 | 1.379 (14) | C21—H21A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.401 (14) | C21—H21B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C21—H21C | 0.9600 |
| C19—I1—I2i | 171.6 (3) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.6 (11) |
| C19—N1—C1 | 116.9 (8) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C19—N1—C21 | 107.4 (7) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C1—N1—C21 | 109.1 (7) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.7 (12) |
| C19—N1—C20 | 109.1 (7) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C1—N1—C20 | 106.3 (7) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C21—N1—C20 | 107.8 (8) | C7—C12—C11 | 121.7 (12) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 114.8 (8) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.1 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 108.6 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.1 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 108.6 | C18—C13—C14 | 119.1 (9) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 108.6 | C18—C13—C6 | 122.5 (9) |
| N1—C1—H1B | 108.6 | C14—C13—C6 | 118.4 (9) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.5 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.1 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 108.2 (8) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110.1 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110.1 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.4 (12) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110.1 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 110.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.4 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.6 (11) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 114.0 (9) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 108.7 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 108.7 | C16—C17—C18 | 117.3 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 108.7 | C16—C17—H17 | 121.3 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 108.7 | C18—C17—H17 | 121.3 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.6 | C13—C18—C17 | 122.2 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 112.1 (9) | C13—C18—H18 | 118.9 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.2 | C17—C18—H18 | 118.9 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.2 | N1—C19—I1 | 117.2 (6) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.2 | N1—C19—H19A | 108.0 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.2 | I1—C19—H19A | 108.0 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.9 | N1—C19—H19B | 108.0 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 124.8 (9) | I1—C19—H19B | 108.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 117.6 | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 117.6 | N1—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.1 (8) | N1—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C13 | 120.7 (8) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C13 | 116.2 (7) | N1—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 117.9 (10) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.6 (9) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C12—C7—C6 | 120.5 (9) | N1—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.6 (10) | N1—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.2 | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 | N1—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 118.4 (11) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.8 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.8 | ||
| C19—N1—C1—C2 | −55.7 (12) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.8 (16) |
| C21—N1—C1—C2 | 66.3 (12) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −176.9 (10) |
| C20—N1—C1—C2 | −177.7 (9) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −2 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −174.9 (8) | C5—C6—C13—C18 | 78.5 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −171.1 (10) | C7—C6—C13—C18 | −98.8 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 175.7 (10) | C5—C6—C13—C14 | −100.9 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 165.3 (12) | C7—C6—C13—C14 | 81.9 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 175.5 (11) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | −1.6 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C13 | −1.5 (18) | C6—C13—C14—C15 | 177.7 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −140.0 (11) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −2.7 (18) |
| C13—C6—C7—C8 | 37.2 (13) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 4.7 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | 38.6 (15) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −2 (2) |
| C13—C6—C7—C12 | −144.2 (10) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 4.0 (19) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −2.7 (16) | C6—C13—C18—C17 | −175.3 (11) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 175.9 (10) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | −2 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 3.5 (18) | C1—N1—C19—I1 | −54.3 (10) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −3.4 (19) | C21—N1—C19—I1 | −177.2 (7) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 3 (2) | C20—N1—C19—I1 | 66.3 (9) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y+1, −z.
References
- Aakeröy, C. B. & Seddon, K. R. (1993). Z. Naturforsch Teil B, 48, 1023–1025.
- Awwadi, F. F., Willett, R. D., Peterson, K. A. & Twamley, B. (2006). Chem. Eur. J. 12, 8952–8960. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT, SADABS and TWINABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Calas, M., Ancelin, M. L., Cordina, G., Portefaix, P., Piquet, G., Vidal-Sailhan, V. & Vial, H. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 505–516. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Calas, M., Cordina, G., Bompart, J., Ben Bari, M., Jei, T., Ancelin, M. L. & Vial, H. (1997). J. Med. Chem. 40, 3557–3566. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Calvani, M., Critelli, L., Gallo, G., Giorgi, F., Gramiccioli, G., Santaniello, M., Scafetta, N., Tinti, M. O. & De Angelis, F. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 2227–2233. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. C., Hsu, W., Hwang, K. C., Hwu, J. R., Lin, C. C. & Horng, J. (2011). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 508, 46–53. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G. R., Ho, P. S., Kloo, L., Legon, A. C., Marquardt, R., Metrangolo, P., Politzer, P., Resnati, G. & Rissanen, K. (2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 85, 1711–1713.
- Dougherty, D. A. (1996). Science, 271, 163–168. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, D. A. (2013). Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 885–893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. & Bernardinelli, G. (1999). Acta Cryst. A55, 908–915. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Formigué, M. (2009). Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 13, 36–45.
- Glidewell, C., Zakaria, C. M., Ferguson, G. & Gallagher, J. F. (1994). Acta Cryst. C50, 233–238.
- Horner, J. H., Martínez, F. N., Musa, O. M., Newcomb, M. & Shahin, H. E. (1995). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 11124–11133.
- Ma, J. C. & Dougherty, D. A. (1997). Chem. Rev. 97, 1303–1324. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mavromoustakos, T., Calogeropoulou, T., Koufaki, M., Kolocouris, A., Daliani, I., Demetzos, D., Meng, Z., Makriyannis, A., Balzarini, J. & De Clercq, E. (2001). J. Med. Chem. 44, 1702–1709. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Múnera-Orozco, C. (2014). MSc thesis, Universidad de Caldas, Manizales, Colombia.
- Newcomb, M., Horner, J. H. & Shahin, H. (1993). Tetrahedron Lett. 34, 5523–5526.
- Ng, K. L. C., Obando, D., Widmer, F., Wright, L. C., Sorrell, T. C. & Jolliffe, K. A. (2006). J. Med. Chem. 49, 811–816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M. (2012). J. Mol. Struct. 1018, 2–7.
- Nishio, M., Hirota, M. & Umezawa, Y. (1998). In The C—H⋯p Interaction. Evidence, Nature, and Consequences. New York: Wiley–VCH.
- Ríos, L. A., Bartberger, M. D., Dolbier, W. R. & Paredes, R. (1997). Tetrahedron Lett. 38, 7041–7044.
- Ríos, L. A., Dolbier, W. R., Paredes, R., Lusztyk, J., Ingold, K. U. & Jonsson, M. (1996). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 11313–11314.
- Ríos-Vásquez, L. A., Ocampo-Cardona, R., Duque-Benítez, S. M., Cedeño, D. L., Jones, M., Robledo-Restrepo, S. M. & Vélez-Bernal, I. D. (2015). US Patent No. 9,145,352 (September 29, 2015).
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2004). CELL NOW. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shiraishi, M., Aramaki, Y., Seto, M., Imoto, H., Nishikawa, Y., Kanzaki, N., Okamoto, M., Sawada, H., Nishimura, O., Baba, M. & Fujino, M. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 2049–2063. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Song, D., Yang, J. S., Oh, C., Cui, S., Kim, B. K., Won, M., Lee, J. I., Kim, H. M. & Han, G. (2013). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 69, 670–677. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sussman, J. L., Harel, M., Frolow, F., Oefner, C., Goldman, A., Toker, L. & Silman, I. (1991). Science, 253, 872–879. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, W., Bai, Z., Zhang, F., Wang, C., Yuan, Y. & Shao, J. (2012). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 56, 320–331. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Yates, B. F., Bouma, W. J. & Radom, L. (1986). Tetrahedron, 42, 6225–6234.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup3.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179Isup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIsup7.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017181/su5179IIIsup8.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report