Abstract
The title compound, [RuCl(C10H14)(C11H10N4)]Cl is an RuII complex in which an η6-p-cymene ligand, two N atoms of 3-amino-2-(phenylazo)pyridine and one Cl ion form a piano-stool coordination environment around the metal ion. In the crystal structure, N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds play an important role in the formation of the supramolecular zigzag chain along the a-axis direction. Disorder is observed for the isopropyl group with site-occupancy factors refined to 0.78 (5) and 0.22 (5).
Keywords: crystal structure, 3-amino-2-(phenylazo)pyridine, ruthenium complex, N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds
Related literature
For anticancer activity of organometallic ruthenium complexes, see: Almodares et al. (2014 ▸); Stepanenko et al. (2011 ▸). For the use of a similar azopyridine ligand to stabilize ruthenium complexes, see: Velders et al. (2000 ▸). For related η6-p-cymene ruthenium complexes, see: Singh et al. (2002 ▸), Kumar et al. (2008 ▸). For the crystal structure of an η6-p-cymene ruthenium complex with an azopyridine ligand, see: Dougan et al. (2006 ▸).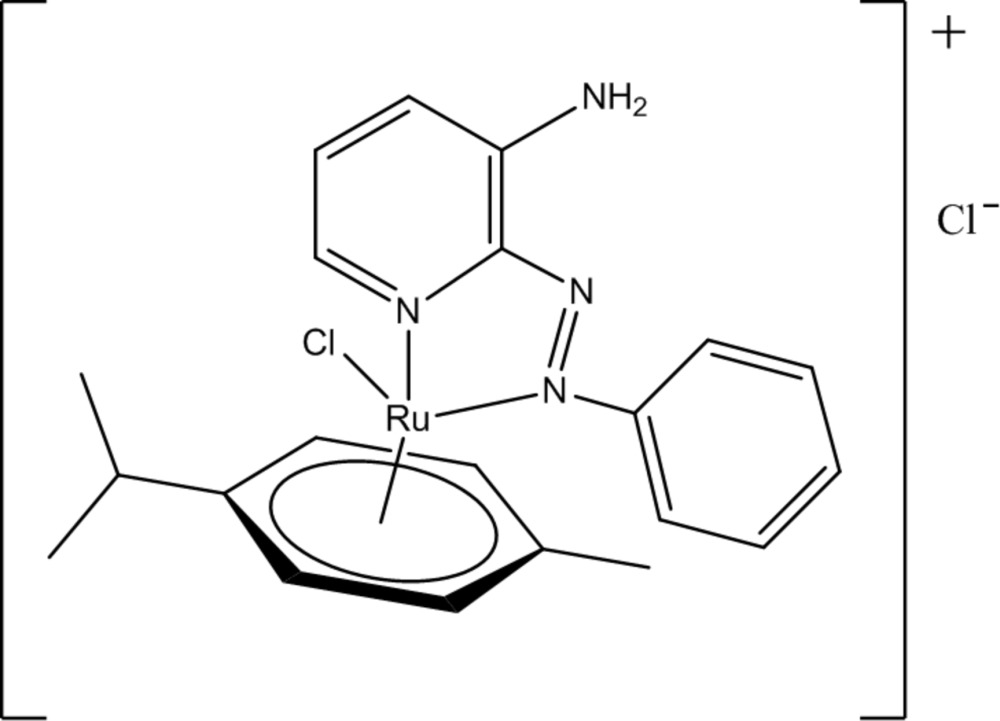
Experimental
Crystal data
[RuCl(C10H14)(C11H10N4)]Cl
M r = 504.41
Orthorhombic,

a = 8.9642 (8) Å
b = 17.6283 (16) Å
c = 26.976 (3) Å
V = 4262.8 (7) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.00 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.44 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD Diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2003 ▸) T min = 0.693, T max = 1.000
40186 measured reflections
5127 independent reflections
4242 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.069
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.074
wR(F 2) = 0.136
S = 1.12
5127 reflections
265 parameters
15 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.71 e Å−3
Δρmin = −1.61 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2003 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2012 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸) and SHELXLE (Hübschle et al., 2011 ▸); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound showing the N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds along the a axis.
CCDC reference: 1425731
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4H4ACl2 | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.200(5) | 176 |
| N4H4BCl2i | 0.86 | 2.37 | 3.152(5) | 151 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Center of Excellence for Innovation of Chemistry (PERCH–CIC), Office of the Higher Education Commission, Ministry of Education, Department of Chemistry, and Graduate School, Prince of Songkla University are gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
S0.1. Synthesis and crystallization
3-amino-2-(phenylazo)pyridine (3aazpy) was prepared by condensation of 2,3-diamino-pyridine (14 mg, 2 mmol) with nitrosobenzene (217 mg, 2.1 mmol) in a mixture of 30 M NaOH (3 mL) and 35 mL of benzene solution. The reaction mixture was stirred and heated under reflux for 14 h. The product was extracted many times with benzene to obtain the brown solution. Then the volume was reduced to 3 mL. The residue was purified by column chromatography. The red-orange band was collected and evaporated to dryness (yield : 37%).
The title compound was obtained by the following procedure: [(η6-p-cym)RuCl2]2 (0.05 mmol) was added to a THF solution of 3aazpy (0.1 mmol); the solution color change from red to purple. The solution was stirred at ambient temperature for 2 h. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with a small amount of THF. Monocrystals were obtained by diffusion of ether into a dichloromethane solution of the complex (yield: 82%).
S0.2. Refinement
H atoms bonded to C and N atoms were included in calculated positions and were refined with a riding model using distances of 0.93 Å (aryl H), and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C); 0.98 Å (CH) and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C); 0.96 Å (CH3) and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C); 0.86 Å (NH2), and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). A disorder is observed for the isopropyl group with site-occupancy factors refined to 0.78 (5) and 0.22 (5).
S1. Results and discussion
Organometallic ruthenium complexes have gained much interest due to promising anticancer activity (Almodares et al., 2014; Stepanenko et al., 2011). These arene complexes consist of a chelating ligand and one chloride ion. In this work, a new ruthenium(II) complex of this type is reported.
The title complex exists as a half sandwich complex with the neutral arene ring bonded to the ruthenium center along with two N atoms from 3-amino-2-(phenylazo)pyridine (3aazpy) and one chloride ion (Fig. 1). The 3aazpy ligand contains the –N=N—C=N linkage which is similar to 2-(phenylazo)pyridine (azpy). Azo ligands of this type can stabilize metals in their lower oxidation states (Velders et al., 2000). The ruthenium atom is π-bonded to the p-cymene ligand with an average Ru—C bond length of 2.215 (6) Å (range 2.185 (6) - 2.243 (5) Å) similar to those observed in related η6-p-cymene ruthenium complexes (Singh et al., 2002, Kumar et al., 2008). The p-cymene ring is almost planar and the C—C bond lengths within the ring are in the range 1.376 – 1.435 Å. The ruthenium center is also coordinated to N1 (azo moiety, 2.078 (4) Å) and to N3 (pyridine, 2.077 (4) Å) of 3aazpy. These Ru—N bond lengths are longer than those in [(η6-p-cymene)Ru(azpy)Cl](PF6) (Dougan et al., 2006). It indicates that azpy is a better ligand to stabilize the ruthenium(II) center than 3aazpy. Meanwhile, the bite angle of 75.6 (2)° of the chelate ligand and the Ru—Cl bond distance of 2.3938 (15) Å are comparable to those in [(η6-p-cym)Ru(azpy)Cl](PF6). In the crystal structure, chloride ions are linked with the complex molecule through N4—H4A···Cl2i and N4—H4B···Cl2 hydrogen bonds leading to the formation of a 1-D zigzag chain along the a-axis (see Table 1 and Fig. 2). A disorder is observed for the isopropyl group with site-occupancy factors refined to 0.78 (5) and 0.22 (5).
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.

Crystal packing of the title compound showing the N—H···Cl hydrogen bonds along the a axis.
Crystal data
| [RuCl(C10H14)(C11H10N4)]Cl | Dx = 1.572 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 504.41 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 7302 reflections |
| a = 8.9642 (8) Å | θ = 2.3–27.9° |
| b = 17.6283 (16) Å | µ = 1.00 mm−1 |
| c = 26.976 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 4262.8 (7) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.44 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm |
| F(000) = 2048 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD Diffractometer | 4242 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | Rint = 0.069 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2003) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.693, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −23→23 |
| 40186 measured reflections | l = −35→35 |
| 5127 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.074 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.136 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0276P)2 + 25.095P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5127 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 265 parameters | Δρmax = 0.71 e Å−3 |
| 15 restraints | Δρmin = −1.61 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Ru1 | 0.62601 (5) | 0.03668 (2) | 0.38760 (2) | 0.03006 (13) | |
| Cl1 | 0.73313 (19) | −0.03312 (8) | 0.45488 (5) | 0.0473 (4) | |
| Cl2 | 0.98928 (17) | −0.30554 (8) | 0.21404 (6) | 0.0434 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.5259 (5) | −0.0663 (2) | 0.37034 (16) | 0.0298 (9) | |
| N2 | 0.5993 (5) | −0.1133 (2) | 0.34347 (16) | 0.0310 (10) | |
| N3 | 0.7791 (5) | −0.0169 (2) | 0.34159 (16) | 0.0283 (9) | |
| N4 | 0.7774 (5) | −0.2032 (3) | 0.28221 (19) | 0.0450 (13) | |
| H4A | 0.8322 | −0.2296 | 0.2625 | 0.054* | |
| H4B | 0.6955 | −0.2218 | 0.2935 | 0.054* | |
| C1 | 0.3803 (6) | −0.0944 (3) | 0.3838 (2) | 0.0352 (12) | |
| C2 | 0.3052 (7) | −0.0609 (3) | 0.4228 (2) | 0.0410 (14) | |
| H2 | 0.3527 | −0.0249 | 0.4423 | 0.049* | |
| C3 | 0.1594 (7) | −0.0812 (4) | 0.4325 (3) | 0.0511 (17) | |
| H3 | 0.1065 | −0.0564 | 0.4574 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 0.0923 (8) | −0.1376 (4) | 0.4057 (3) | 0.0571 (19) | |
| H4 | −0.0057 | −0.1514 | 0.4125 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 0.1712 (8) | −0.1743 (4) | 0.3684 (3) | 0.0542 (18) | |
| H5 | 0.1273 | −0.2140 | 0.3510 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.3139 (7) | −0.1520 (3) | 0.3573 (2) | 0.0413 (14) | |
| H6 | 0.3658 | −0.1757 | 0.3318 | 0.050* | |
| C7 | 0.7341 (6) | −0.0871 (3) | 0.32750 (18) | 0.0270 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.8194 (6) | −0.1338 (3) | 0.2952 (2) | 0.0311 (11) | |
| C9 | 0.9527 (6) | −0.1018 (3) | 0.2774 (2) | 0.0389 (13) | |
| H9 | 1.0131 | −0.1291 | 0.2558 | 0.047* | |
| C10 | 0.9932 (7) | −0.0306 (3) | 0.2921 (2) | 0.0477 (15) | |
| H10 | 1.0801 | −0.0090 | 0.2796 | 0.057* | |
| C11 | 0.9061 (6) | 0.0096 (3) | 0.3252 (2) | 0.0396 (14) | |
| H11 | 0.9388 | 0.0568 | 0.3361 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | 0.6938 (7) | 0.1496 (3) | 0.4186 (2) | 0.0374 (13) | |
| C13 | 0.5524 (8) | 0.1272 (3) | 0.4388 (3) | 0.0495 (17) | |
| H13 | 0.5459 | 0.1158 | 0.4743 | 0.059* | |
| C14 | 0.4329 (8) | 0.1095 (3) | 0.4089 (3) | 0.0565 (19) | |
| H14 | 0.3456 | 0.0853 | 0.4240 | 0.068* | |
| C15 | 0.4465 (8) | 0.1082 (3) | 0.3565 (3) | 0.0549 (18) | |
| C16 | 0.5835 (7) | 0.1301 (3) | 0.3363 (2) | 0.0447 (15) | |
| H16 | 0.6012 | 0.1223 | 0.3008 | 0.054* | |
| C17 | 0.7038 (7) | 0.1516 (3) | 0.3669 (2) | 0.0382 (13) | |
| H17 | 0.8028 | 0.1568 | 0.3518 | 0.046* | |
| C18 | 0.3198 (8) | 0.0843 (5) | 0.3244 (3) | 0.081 (3) | |
| H18A | 0.3575 | 0.0676 | 0.2929 | 0.121* | |
| H18B | 0.2536 | 0.1264 | 0.3195 | 0.121* | |
| H18C | 0.2667 | 0.0436 | 0.3401 | 0.121* | |
| C19 | 0.8212 (9) | 0.1721 (4) | 0.4513 (3) | 0.0580 (19) | 0.78 (5) |
| H19 | 0.7999 | 0.1522 | 0.4845 | 0.070* | 0.78 (5) |
| C20 | 0.9735 (12) | 0.1408 (13) | 0.4358 (7) | 0.066 (4) | 0.78 (5) |
| H20A | 0.9682 | 0.0865 | 0.4335 | 0.099* | 0.78 (5) |
| H20B | 1.0471 | 0.1547 | 0.4600 | 0.099* | 0.78 (5) |
| H20C | 1.0006 | 0.1614 | 0.4041 | 0.099* | 0.78 (5) |
| C21 | 0.824 (3) | 0.2586 (7) | 0.4555 (12) | 0.111 (8) | 0.78 (5) |
| H21A | 0.9016 | 0.2735 | 0.4781 | 0.167* | 0.78 (5) |
| H21B | 0.7298 | 0.2763 | 0.4675 | 0.167* | 0.78 (5) |
| H21C | 0.8437 | 0.2802 | 0.4234 | 0.167* | 0.78 (5) |
| C19B | 0.8212 (9) | 0.1721 (4) | 0.4513 (3) | 0.0580 (19) | 0.22 (5) |
| H19B | 0.8245 | 0.1339 | 0.4777 | 0.070* | 0.22 (5) |
| C20B | 0.974 (4) | 0.169 (4) | 0.426 (2) | 0.066 (4) | 0.22 (5) |
| H20D | 0.9845 | 0.1215 | 0.4094 | 0.099* | 0.22 (5) |
| H20E | 1.0504 | 0.1738 | 0.4510 | 0.099* | 0.22 (5) |
| H20F | 0.9819 | 0.2098 | 0.4030 | 0.099* | 0.22 (5) |
| C21B | 0.791 (9) | 0.247 (3) | 0.477 (3) | 0.111 (8) | 0.22 (5) |
| H21D | 0.8799 | 0.2637 | 0.4939 | 0.167* | 0.22 (5) |
| H21E | 0.7125 | 0.2405 | 0.5011 | 0.167* | 0.22 (5) |
| H21F | 0.7618 | 0.2844 | 0.4533 | 0.167* | 0.22 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ru1 | 0.0334 (2) | 0.02129 (19) | 0.0355 (2) | 0.00223 (18) | 0.00250 (19) | −0.00160 (17) |
| Cl1 | 0.0641 (10) | 0.0363 (7) | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0089 (7) | −0.0093 (7) | 0.0017 (6) |
| Cl2 | 0.0424 (8) | 0.0322 (7) | 0.0558 (9) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0150 (7) | −0.0051 (6) |
| N1 | 0.033 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0030 (19) | 0.0057 (19) | −0.0007 (17) |
| N2 | 0.030 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0006 (18) | 0.0072 (19) | −0.0019 (18) |
| N3 | 0.028 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.036 (2) | −0.0013 (17) | −0.0003 (19) | −0.0040 (17) |
| N4 | 0.039 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.065 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.011 (2) |
| C1 | 0.032 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.041 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.009 (3) | 0.006 (2) |
| C2 | 0.043 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.011 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C3 | 0.049 (4) | 0.050 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.009 (3) |
| C4 | 0.036 (4) | 0.069 (5) | 0.066 (5) | −0.005 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.020 (4) |
| C5 | 0.047 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.069 (5) | −0.016 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C6 | 0.038 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.049 (4) | −0.008 (3) | 0.009 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C7 | 0.025 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.032 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C8 | 0.034 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C9 | 0.031 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.010 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C10 | 0.036 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.062 (4) | −0.011 (3) | 0.014 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C11 | 0.032 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.053 (4) | −0.004 (2) | 0.010 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C12 | 0.060 (4) | 0.015 (2) | 0.037 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.004 (3) | 0.002 (2) |
| C13 | 0.076 (5) | 0.021 (3) | 0.052 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.020 (4) | −0.004 (3) |
| C14 | 0.050 (4) | 0.026 (3) | 0.093 (6) | 0.011 (3) | 0.019 (4) | −0.005 (3) |
| C15 | 0.048 (4) | 0.030 (3) | 0.087 (5) | 0.011 (3) | −0.014 (4) | 0.002 (3) |
| C16 | 0.055 (4) | 0.031 (3) | 0.049 (4) | 0.010 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| C17 | 0.045 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.006 (2) |
| C18 | 0.053 (5) | 0.064 (5) | 0.126 (8) | 0.007 (4) | −0.038 (5) | 0.020 (5) |
| C19 | 0.089 (6) | 0.036 (3) | 0.049 (4) | −0.013 (4) | −0.013 (4) | −0.012 (3) |
| C20 | 0.066 (6) | 0.064 (10) | 0.068 (8) | −0.018 (6) | −0.016 (5) | −0.002 (7) |
| C21 | 0.147 (15) | 0.048 (6) | 0.14 (2) | −0.010 (8) | −0.054 (14) | −0.032 (9) |
| C19B | 0.089 (6) | 0.036 (3) | 0.049 (4) | −0.013 (4) | −0.013 (4) | −0.012 (3) |
| C20B | 0.066 (6) | 0.064 (10) | 0.068 (8) | −0.018 (6) | −0.016 (5) | −0.002 (7) |
| C21B | 0.147 (15) | 0.048 (6) | 0.14 (2) | −0.010 (8) | −0.054 (14) | −0.032 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ru1—N3 | 2.077 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| Ru1—N1 | 2.078 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| Ru1—C16 | 2.185 (6) | C12—C17 | 1.398 (8) |
| Ru1—C15 | 2.210 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.435 (9) |
| Ru1—C13 | 2.211 (6) | C12—C19 | 1.498 (9) |
| Ru1—C17 | 2.215 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.376 (10) |
| Ru1—C14 | 2.231 (6) | C13—H13 | 0.9800 |
| Ru1—C12 | 2.243 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.419 (10) |
| Ru1—Cl1 | 2.3938 (15) | C14—H14 | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.283 (6) | C15—C16 | 1.398 (9) |
| N1—C1 | 1.442 (7) | C15—C18 | 1.489 (10) |
| N2—C7 | 1.363 (6) | C16—C17 | 1.411 (8) |
| N3—C11 | 1.307 (7) | C16—H16 | 0.9800 |
| N3—C7 | 1.356 (6) | C17—H17 | 0.9800 |
| N4—C8 | 1.327 (7) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| N4—H4A | 0.8600 | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| N4—H4B | 0.8600 | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.376 (8) | C19—C21 | 1.529 (12) |
| C1—C2 | 1.381 (8) | C19—C20 | 1.531 (12) |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (8) | C19—H19 | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.368 (10) | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.389 (10) | C21—H21A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C21—H21B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (8) | C21—H21C | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C20B—H20D | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C20B—H20E | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.422 (7) | C20B—H20F | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.406 (8) | C21B—H21D | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.365 (8) | C21B—H21E | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C21B—H21F | 0.9600 |
| C10—C11 | 1.382 (8) | ||
| N3—Ru1—N1 | 75.80 (16) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.6 (5) |
| N3—Ru1—C16 | 94.5 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| N1—Ru1—C16 | 116.2 (2) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| N3—Ru1—C15 | 120.9 (2) | N3—C11—C10 | 121.8 (5) |
| N1—Ru1—C15 | 95.7 (2) | N3—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C16—Ru1—C15 | 37.1 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| N3—Ru1—C13 | 153.9 (2) | C17—C12—C13 | 116.3 (6) |
| N1—Ru1—C13 | 129.9 (2) | C17—C12—C19 | 122.2 (6) |
| C16—Ru1—C13 | 78.4 (2) | C13—C12—C19 | 121.5 (6) |
| C15—Ru1—C13 | 66.9 (3) | C17—C12—Ru1 | 70.6 (3) |
| N3—Ru1—C17 | 93.25 (19) | C13—C12—Ru1 | 70.0 (3) |
| N1—Ru1—C17 | 151.50 (19) | C19—C12—Ru1 | 131.4 (4) |
| C16—Ru1—C17 | 37.4 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 121.9 (6) |
| C15—Ru1—C17 | 67.1 (2) | C14—C13—Ru1 | 72.7 (4) |
| C13—Ru1—C17 | 65.9 (2) | C12—C13—Ru1 | 72.4 (3) |
| N3—Ru1—C14 | 158.2 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 118.6 |
| N1—Ru1—C14 | 103.0 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 118.6 |
| C16—Ru1—C14 | 66.1 (3) | Ru1—C13—H13 | 118.6 |
| C15—Ru1—C14 | 37.3 (3) | C13—C14—C15 | 121.3 (7) |
| C13—Ru1—C14 | 36.1 (3) | C13—C14—Ru1 | 71.2 (4) |
| C17—Ru1—C14 | 77.5 (2) | C15—C14—Ru1 | 70.6 (4) |
| N3—Ru1—C12 | 116.54 (19) | C13—C14—H14 | 118.5 |
| N1—Ru1—C12 | 167.39 (19) | C15—C14—H14 | 118.5 |
| C16—Ru1—C12 | 67.3 (2) | Ru1—C14—H14 | 118.5 |
| C15—Ru1—C12 | 80.3 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 117.4 (7) |
| C13—Ru1—C12 | 37.6 (2) | C16—C15—C18 | 121.3 (7) |
| C17—Ru1—C12 | 36.5 (2) | C14—C15—C18 | 121.2 (7) |
| C14—Ru1—C12 | 66.6 (2) | C16—C15—Ru1 | 70.5 (3) |
| N3—Ru1—Cl1 | 87.39 (12) | C14—C15—Ru1 | 72.2 (4) |
| N1—Ru1—Cl1 | 83.92 (13) | C18—C15—Ru1 | 127.9 (5) |
| C16—Ru1—Cl1 | 159.70 (18) | C15—C16—C17 | 121.1 (6) |
| C15—Ru1—Cl1 | 150.8 (2) | C15—C16—Ru1 | 72.4 (4) |
| C13—Ru1—Cl1 | 91.00 (19) | C17—C16—Ru1 | 72.5 (3) |
| C17—Ru1—Cl1 | 122.36 (16) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.1 |
| C14—Ru1—Cl1 | 114.3 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.1 |
| C12—Ru1—Cl1 | 93.73 (15) | Ru1—C16—H16 | 119.1 |
| N2—N1—C1 | 112.6 (4) | C12—C17—C16 | 121.9 (6) |
| N2—N1—Ru1 | 118.0 (3) | C12—C17—Ru1 | 72.8 (3) |
| C1—N1—Ru1 | 129.4 (3) | C16—C17—Ru1 | 70.1 (3) |
| N1—N2—C7 | 114.5 (4) | C12—C17—H17 | 118.3 |
| C11—N3—C7 | 119.4 (4) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.3 |
| C11—N3—Ru1 | 128.0 (4) | Ru1—C17—H17 | 118.3 |
| C7—N3—Ru1 | 112.7 (3) | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C8—N4—H4A | 120.0 | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C8—N4—H4B | 120.0 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| H4A—N4—H4B | 120.0 | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.0 (5) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 120.9 (5) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.0 (5) | C12—C19—C21 | 108.7 (9) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.8 (6) | C12—C19—C20 | 115.0 (7) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C21—C19—C20 | 111.3 (10) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C12—C19—H19 | 107.2 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.2 (6) | C21—C19—H19 | 107.2 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C20—C19—H19 | 107.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C19—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (6) | C19—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C19—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.0 (7) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C19—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.0 (6) | C19—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C19—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—N2 | 119.0 (4) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 122.7 (5) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| N2—C7—C8 | 118.2 (4) | H20D—C20B—H20E | 109.5 |
| N4—C8—C9 | 121.4 (5) | H20D—C20B—H20F | 109.5 |
| N4—C8—C7 | 123.0 (5) | H20E—C20B—H20F | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 115.7 (5) | H21D—C21B—H21E | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.8 (5) | H21D—C21B—H21F | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.1 | H21E—C21B—H21F | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.1 | ||
| C1—N1—N2—C7 | 176.3 (4) | C19—C12—C13—C14 | 177.3 (6) |
| Ru1—N1—N2—C7 | −3.0 (6) | Ru1—C12—C13—C14 | −55.7 (5) |
| N2—N1—C1—C6 | −19.8 (7) | C17—C12—C13—Ru1 | 55.0 (4) |
| Ru1—N1—C1—C6 | 159.5 (4) | C19—C12—C13—Ru1 | −127.0 (5) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | 162.6 (5) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 3.7 (9) |
| Ru1—N1—C1—C2 | −18.2 (7) | Ru1—C13—C14—C15 | −51.8 (5) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −5.1 (9) | C12—C13—C14—Ru1 | 55.5 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 172.7 (5) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −3.7 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 4.1 (10) | Ru1—C14—C15—C16 | −55.8 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.3 (10) | C13—C14—C15—C18 | 176.1 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.5 (11) | Ru1—C14—C15—C18 | 124.0 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.5 (10) | C13—C14—C15—Ru1 | 52.1 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.3 (9) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.7 (9) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −175.4 (6) | C18—C15—C16—C17 | −179.1 (6) |
| C11—N3—C7—N2 | −177.9 (5) | Ru1—C15—C16—C17 | −55.9 (5) |
| Ru1—N3—C7—N2 | 1.0 (6) | C14—C15—C16—Ru1 | 56.6 (5) |
| C11—N3—C7—C8 | −0.1 (8) | C18—C15—C16—Ru1 | −123.2 (6) |
| Ru1—N3—C7—C8 | 178.8 (4) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −2.3 (8) |
| N1—N2—C7—N3 | 1.3 (7) | C19—C12—C17—C16 | 179.7 (5) |
| N1—N2—C7—C8 | −176.6 (4) | Ru1—C12—C17—C16 | 52.4 (5) |
| N3—C7—C8—N4 | 178.4 (5) | C13—C12—C17—Ru1 | −54.7 (4) |
| N2—C7—C8—N4 | −3.8 (8) | C19—C12—C17—Ru1 | 127.4 (5) |
| N3—C7—C8—C9 | −1.8 (7) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 2.3 (9) |
| N2—C7—C8—C9 | 176.0 (5) | Ru1—C16—C17—C12 | −53.6 (5) |
| N4—C8—C9—C10 | −179.2 (6) | C15—C16—C17—Ru1 | 55.9 (5) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.9 (8) | C17—C12—C19—C21 | 81.0 (17) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.6 (10) | C13—C12—C19—C21 | −96.8 (16) |
| C7—N3—C11—C10 | 2.9 (9) | Ru1—C12—C19—C21 | 172.9 (15) |
| Ru1—N3—C11—C10 | −175.8 (5) | C17—C12—C19—C20 | −44.5 (14) |
| C9—C10—C11—N3 | −3.7 (10) | C13—C12—C19—C20 | 137.7 (12) |
| C17—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (8) | Ru1—C12—C19—C20 | 47.4 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H4A···Cl2 | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.200 (5) | 176 |
| N4—H4B···Cl2i | 0.86 | 2.37 | 3.152 (5) | 151 |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, y, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZQ2235).
References
- Almodares, Z., Lucas, S. J., Crossley, B. D., Basri, A. M., Pask, C. M., Hebden, A. J., Phillips, R. M. & McGowan, P. C. (2014). Inorg. Chem. 53, 727–736. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (1998). SMART. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2003). SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dougan, S. J., Melchart, M., Habtemariam, A., Parsons, S. & Sadler, P. J. (2006). Inorg. Chem. 45, 10882–10894. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K. N., Venkatachalam, G., Ramesh, R. & Liu, Y. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 157–166.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Singh, A., Singh, N. & Pandey, D. S. (2002). J. Organomet. Chem. 642, 48–57.
- Stepanenko, I. N., Novak, M. S., Mühlgassner, M., Roller, A., Hejl, M., Arion, V. B., Jakupec, M. A. & Keppler, B. K. (2011). Inorg. Chem. 50, 11715–11728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Velders, A. H., Kooijman, H., Spek, A. L., Haasnoot, J. G., de Vos, D. & Reedijk, J. (2000). Inorg. Chem. 39, 2966–2967. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015017466/zq2235fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound showing the N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds along the a axis.
CCDC reference: 1425731
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


