FIGURE 2.
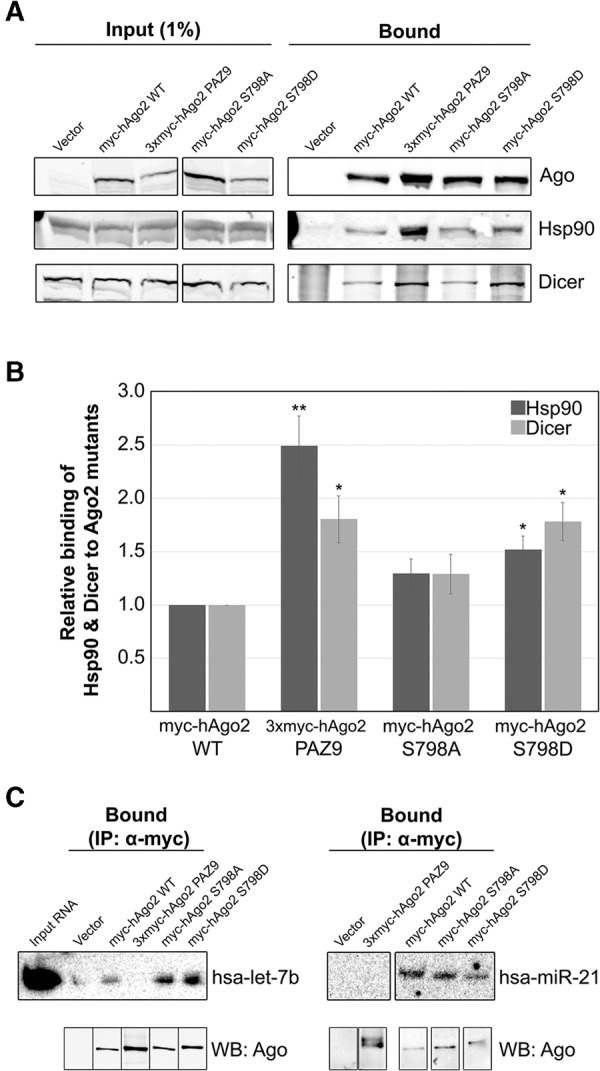
Interaction of myc-hAgo2 S798D with components of the RISC-loading complex and small RNAs. (A) HeLa cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type or mutant Ago2 were lysed 16 h post-transfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation using sepharose beads coated with anti-myc antibodies. Total cell lysate (Input) and bound fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for Ago2, Hsp90, and Dicer as indicated. (B) Signal intensities for Hsp90 and Dicer were quantitated and normalized to level of immunoprecipitated Ago2. The bar graph indicates the fold change in the amount of each coimmunoprecipitated Ago2-binding partner relative to the amount associated with wild-type Ago2. Paired Student's two-tailed t-test was used to compare amounts of coimmunoprecipitated Hsp90 and Dicer to amounts bound to wild-type Ago2, (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01. Error bars indicate SE. (C) HeLa cells transiently transfected with plasmids expressing wild-type or mutant Ago2 were lysed 16 h post-transfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation using sepharose beads coated with monoclonal anti-myc antibodies. RNA was extracted from the bound fractions (IP α-myc) and subjected to UREA-PAGE. Cells transfected with empty vector were used as the negative control for immunoprecipitation (labeled “Vector”). Loading of RNA was normalized to level of bound Ago2 (immunoblot of 3% of immunoprecipitated protein shown below). MiRNAs detected by Northern blotting using 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes. Total RNA isolated from cell lysate included as a control (Input RNA).
