Abstract
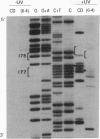
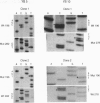
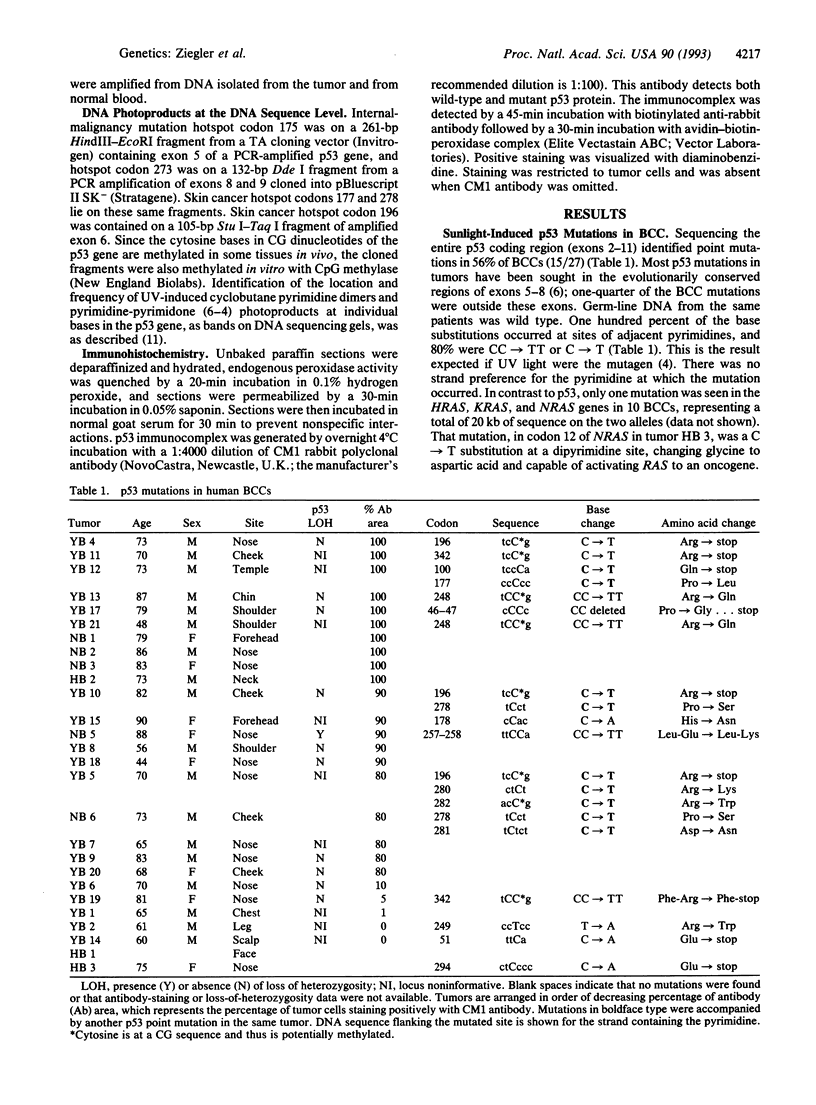
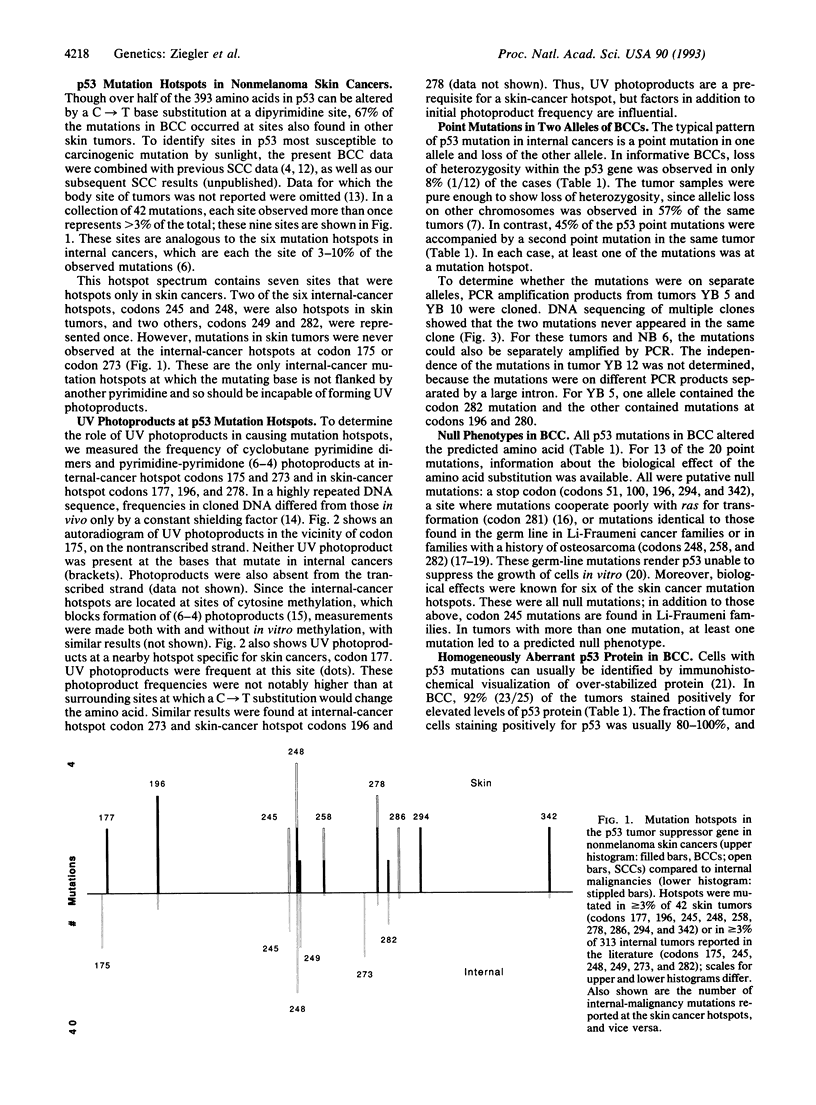
To identify the sites in the p53 tumor suppressor gene most susceptible to carcinogenic mutation by sunlight, the entire coding region of 27 basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) of the skin was sequenced. Fifty-six percent of tumors contained mutations, and these were UV-like: primarily CC-->TT or C-->T changes at dipyrimidine sites. Such mutations can alter more than half of the 393 amino acids in p53, but two-thirds occurred at nine sites at which mutations were seen more than once in BCC or in 27 previously studied squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. Seven of these mutation hotspots were specific to skin cancers. Internal-cancer hotspots not located at dipyrimidine sites were not mutated in skin cancers; moreover, UV photoproducts were absent at these nucleotides. The existence of hotspots altered the process of inactivating p53 in BCC compared to other cancers: allelic loss was rare, but 45% of the point mutations were accompanied by a second point mutation on the other allele. At least one of each pair was located at a hotspot. Sunlight, acting at mutation hotspots, appears to cause mutations so frequently that it is often responsible for two genetic events in BCC development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Paraskeva C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Hamilton S., Vogelstein B. p53 gene mutations occur in combination with 17p allelic deletions as late events in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 1;50(23):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Rudolph J. A., Simon J. A., Lin A., McKenna G. J., Baden H. P., Halperin A. J., Pontén J. A role for sunlight in skin cancer: UV-induced p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10124–10128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff A. M., Humphrey P. A., Iglehart J. D., Marks J. R. Genetic basis for p53 overexpression in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frebourg T., Kassel J., Lam K. T., Gryka M. A., Barbier N., Andersen T. I., Børresen A. L., Friend S. H. Germ-line mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in patients with high risk for cancer inactivate the p53 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailani M. R., Bale S. J., Leffell D. J., DiGiovanna J. J., Peck G. L., Poliak S., Drum M. A., Pastakia B., McBride O. W., Kase R. Developmental defects in Gorlin syndrome related to a putative tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 9. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90122-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman B. W., Schaaper R. M., Haseltine W. A., Dunn R. L., Brash D. E. The C-C (6-4) UV photoproduct is mutagenic in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6945–6949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.2218501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. B. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Profile of genetic and environmental factors in oncogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 Jul;11(1):98–104. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)70141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Lee M. M., Scotto J. DNA repair protects against cutaneous and internal neoplasia: evidence from xeroderma pigmentosum. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Apr;5(4):511–514. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricker A., Armstrong B. K., English D. R., Heenan P. J. Pigmentary and cutaneous risk factors for non-melanocytic skin cancer--a case-control study. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jul 9;48(5):650–662. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunala S., Brash D. E. Excision repair at individual bases of the Escherichia coli lacI gene: relation to mutation hot spots and transcription coupling activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11031–11035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. A., Bennett W. P., Metcalf R. A., Welsh J. A., Ecker J., Modali R. V., Ullrich S., Romano J. W., Appella E., Testa J. R. p53 mutations, ras mutations, and p53-heat shock 70 protein complexes in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4090–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. D., Groopman J. D., Lim S. E., Seidman M. M., Kraemer K. H. Sequence specificity of aflatoxin B1-induced mutations in a plasmid replicated in xeroderma pigmentosum and DNA repair proficient human cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 15;52(20):5668–5673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Heat-induced deamination of cytosine residues in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3405–3410. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippke J. A., Gordon L. K., Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. Distribution of UV light-induced damage in a defined sequence of human DNA: detection of alkaline-sensitive lesions at pyrimidine nucleoside-cytidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Jolly K. W., Barbier N., Look A. T., Friend S. H., Gebhardt M. C., Andersen T. I., Børresen A. L., Li F. P., Garber J. Germline mutations of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene in children and young adults with second malignant neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 14;326(20):1309–1315. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205143262002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor W. G., Chen R. H., Lukash L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Cell cycle-dependent strand bias for UV-induced mutations in the transcribed strand of excision repair-proficient human fibroblasts but not in repair-deficient cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1927–1934. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer S. J., Yin J., Huang Y., McDaniel T. K., Newkirk C., Iseri O., Vogelstein B., Resau J. H. Reduction to homozygosity involving p53 in esophageal cancers demonstrated by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. G., Ledbetter D. H., Rich D. C., Seizinger B. R., Rouleau G. A., Michels V. F., Schmidt M. A., Dewald G., DallaTorre C. M., Haines J. L. Characterization of a translocation within the von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis region of chromosome 17. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. J. Biology of basal cell carcinoma (Part II). J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Feb;24(2 Pt 1):161–175. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70022-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolgavkar S. H., Knudson A. G., Jr Mutation and cancer: a model for human carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Jun;66(6):1037–1052. doi: 10.1093/jnci/66.6.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto A., Sameshima Y., Yokoyama S., Terashima Y., Sugimura T., Terada M., Yokota J. Frequent allelic losses and mutations of the p53 gene in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5171–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierceall W. E., Mukhopadhyay T., Goldberg L. H., Ananthaswamy H. N. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(6):445–449. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rady P., Scinicariello F., Wagner R. F., Jr, Tyring S. K. p53 mutations in basal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3804–3806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid T. M., Loeb L. A. Mutagenic specificity of oxygen radicals produced by human leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1082–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Carrier W. L. Pyrimidine dimers in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA's. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea C. R., McNutt N. S., Volkenandt M., Lugo J., Prioleau P. G., Albino A. P. Overexpression of p53 protein in basal cell carcinomas of human skin. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):25–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky D., Von Eschenbach A., Tsai Y. C., Jones P., Summerhayes I., Marshall F., Paul M., Green P., Hamilton S. R., Frost P. Identification of p53 gene mutations in bladder cancers and urine samples. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):706–709. doi: 10.1126/science.2024123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. L., Elpern D. J., Reizner G., Farmer E. R., Scotto J., Pabo R. Incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer in Kauai during 1983. Hawaii Med J. 1986 Aug;45(8):281-2, 285-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toguchida J., Yamaguchi T., Dayton S. H., Beauchamp R. L., Herrera G. E., Ishizaki K., Yamamuro T., Meyers P. A., Little J. B., Sasaki M. S. Prevalence and spectrum of germline mutations of the p53 gene among patients with sarcoma. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 14;326(20):1301–1308. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205143262001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore A. S. Quantitative theories of oncogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:55–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60930-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Calle-Martín O., Fabregat V., Romero M., Soler J., Vives J., Yagüe J. AccII polymorphism of the p53 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4963–4963. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Calle-Martín O., Romero M., Fabregat V., Ercilla G., Vives J., Yagüe J. MspI polymorphism of the human p53 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4963–4963. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]