Abstract
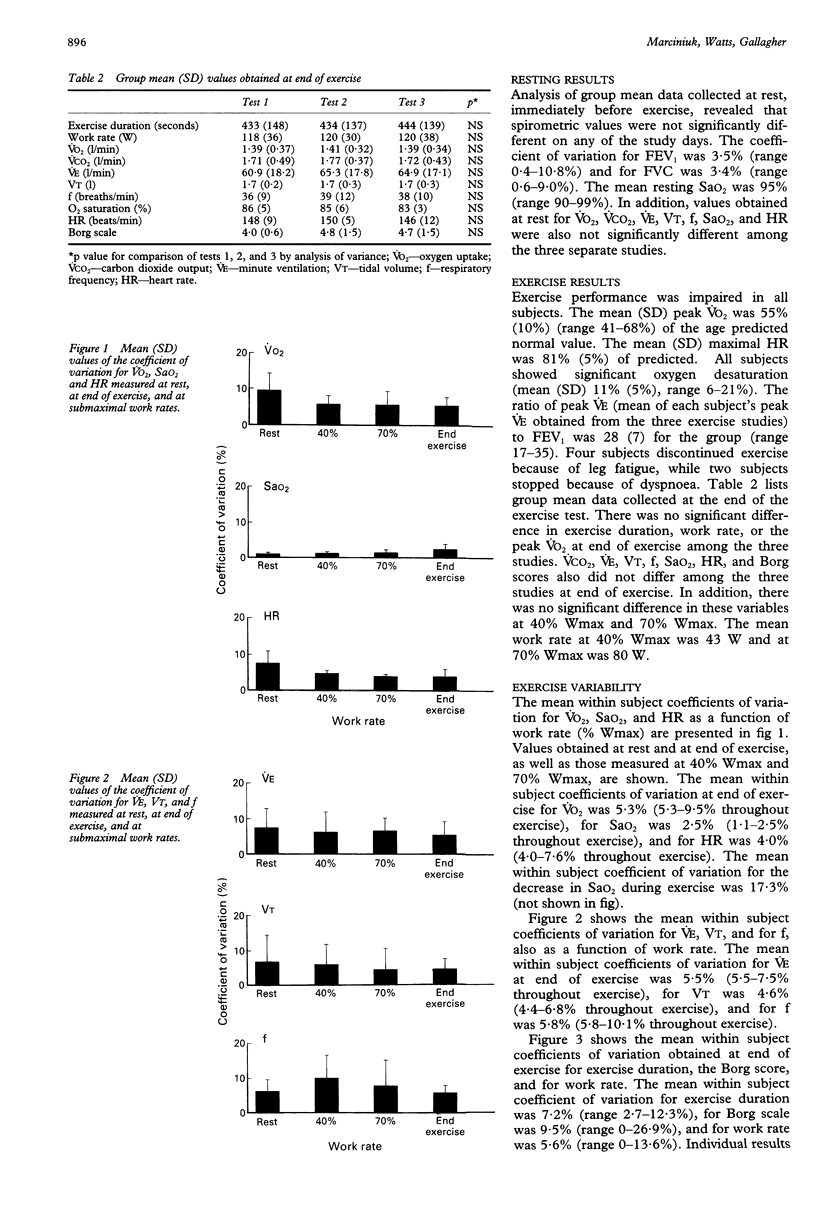
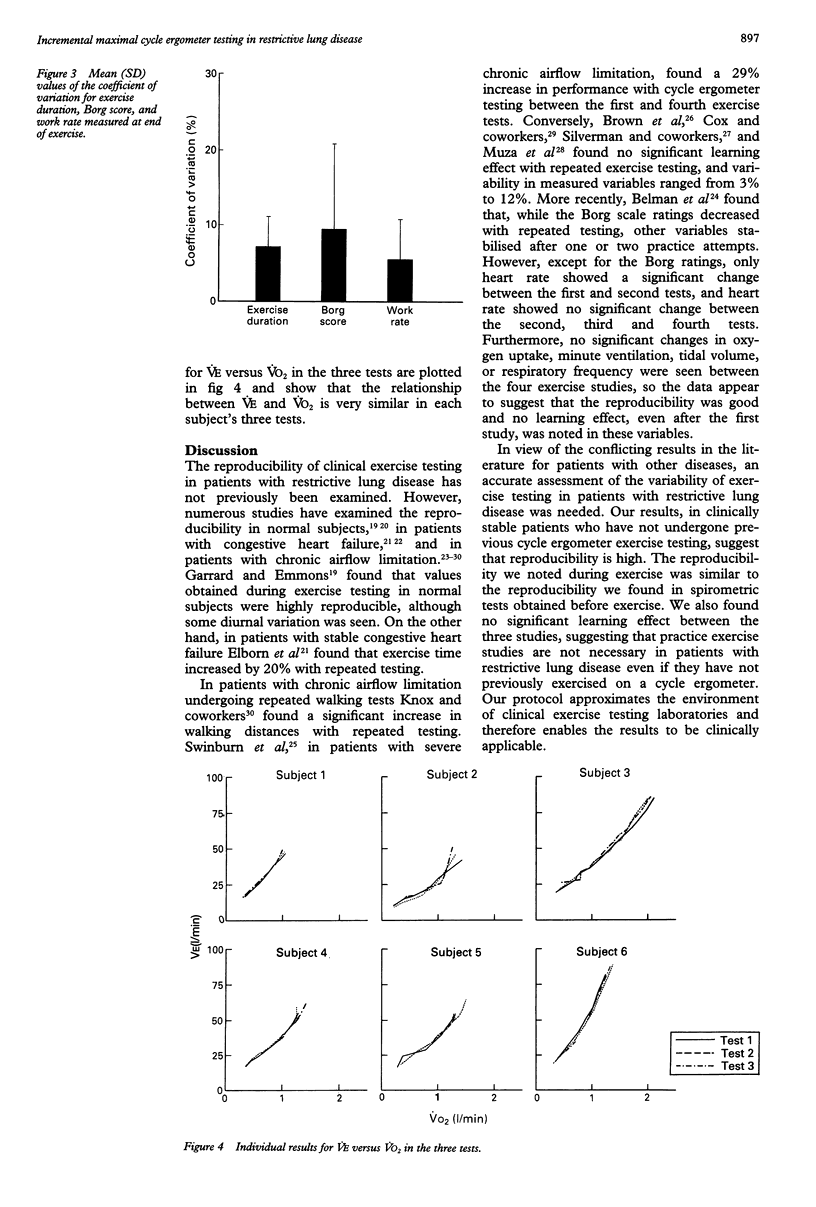
BACKGROUND--Exercise testing has become an important tool in the diagnosis and treatment of restrictive lung disease. The reproducibility of variables measured during exercise testing was examined in subjects with stable restrictive lung disease. METHODS--Six subjects, who had never previously undergone exercise testing, each underwent three maximal incremental exercise studies on a bicycle ergometer conducted during a 28 day period. RESULTS--Data collected at rest, before exercise, were not significantly different during the three study days. Comparison of results at the end of the exercise tests from the three studies also revealed no evidence of a significant learning effect. Reproducibility of exercise performance by subjects was assessed by the coefficient of variation. The mean within subject coefficient of variation at the end of the exercise tests was 5.6% for work rate, 7.9% for exercise duration, and 9.5% for dyspnoea. The mean within subject coefficient of variation obtained at the end of the exercise tests was 5.3% for oxygen uptake (VO2), 2.5% for oxygen saturation (SaO2), 4.0% for heart rate (HR), 5.5% for minute ventilation (VE), 5.8% for respiratory frequency (f), and 4.6% for tidal volume (VT). The mean within subject coefficient of variation at 40% and 70% of maximal work rates for VO2 was 5.7% and 5.6% respectively, for SaO2 1.3% and 1.5%, for HR 4.8% and 4.0%, for VE 6.3% and 6.6%, for f 10.1% and 7.8%, and for VT 6.0% and 4.5%. CONCLUSIONS--Variables measured during clinical exercise testing in subjects with restrictive lung disease are highly reproducible. No significant learning effect was found on repeated testing in subjects who had never previously undergone exercise testing.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS B., KASIK J. E., NIDEN A. H., BARCLAY W. R. Clinical usefulness of the single-breath pulmonucy diffusing capacity test. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:789–806. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belman M. J., Brooks L. R., Ross D. J., Mohsenifar Z. Variability of breathlessness measurement in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1991 Mar;99(3):566–571. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.3.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G. A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(5):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. E., Fischer C. E., Stansbury D. W., Light R. W. Reproducibility of VO2max in patients with chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):435–438. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon J. G., Killian K. J., Jones N. L. Pattern of breathing during exercise in patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1983 Oct;38(10):778–784. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.10.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bye P. T., Anderson S. D., Woolcock A. J., Young I. H., Alison J. A. Bicycle endurance performance of patients with interstitial lung disease breathing air and oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1005–1012. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. J., Hendriks J. C., Binkhorst R. A., Folgering H. T., van Herwaarden C. L. Reproducibility of incremental maximal cycle ergometer tests in patients with mild to moderate obstructive lung diseases. Lung. 1989;167(2):129–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02714939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborn J. S., Stanford C. F., Nicholls D. P. Reproducibility of cardiopulmonary parameters during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. The need for a preliminary test. Eur Heart J. 1990 Jan;11(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epler G. R., Saber F. A., Gaensler E. A. Determination of severe impairment (disability) in interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Apr;121(4):647–659. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard C. S., Emmons C. The reproducibility of the respiratory responses to maximum exercise. Respiration. 1986;49(2):94–100. doi: 10.1159/000194865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda K., Zintel T., McParland C., Orchard R., Gallagher C. G. Diagnostic value of maximal exercise tidal volume. Chest. 1990 Dec;98(6):1351–1354. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.6.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicki J. S., Gupta S., Ferris S. T., McElroy P. A. Long-term reproducibility of respiratory gas exchange measurements during exercise in patients with stable cardiac failure. Chest. 1990 Jan;97(1):12–17. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. L., Rebuck A. S. Tidal volume during exercise in patients with diffuse fibrosing alveolitis. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1979 Mar-Apr;15(2):321–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. A., Daniele R. P. Exercise testing in interstitial lung disease. Clin Chest Med. 1984 Mar;5(1):145–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Lakatos E., Price D., Crystal R. G. Importance of the lower respiratory tract in oxygen transfer. Exercise testing in patients with interstitial and destructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2 Pt 2):S76–S80. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.2P2.S76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox A. J., Morrison J. F., Muers M. F. Reproducibility of walking test results in chronic obstructive airways disease. Thorax. 1988 May;43(5):388–392. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.5.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Koski A., Johnson L. C. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jan;103(1):57–67. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muza S. R., Silverman M. T., Gilmore G. C., Hellerstein H. K., Kelsen S. G. Comparison of scales used to quantitate the sense of effort to breathe in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):909–913. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens M. W., Kinasewitz G. T., Strain D. S. Evaluating the effects of chronic therapy in patients with irreversible air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;134(5):935–937. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Barry J., Hellerstein H., Janos J., Kelsen S. Variability of the perceived sense of effort in breathing during exercise in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):206–209. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.1.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S. G., Dowdeswell I. R., Clark T. J. An analysis of submaximal exercise responses in patients with sarcoidosis and fibrosing alveolitis. Br J Dis Chest. 1981 Apr;75(2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(81)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standardization of spirometry--1987 update. Statement of the American Thoracic Society. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1285–1298. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn C. R., Wakefield J. M., Jones P. W. Performance, ventilation, and oxygen consumption in three different types of exercise test in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):581–586. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. C., Jones P. W. Long-term reproducibility of Borg scale estimates of breathlessness during exercise. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Apr;80(4):309–312. doi: 10.1042/cs0800309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



