Abstract
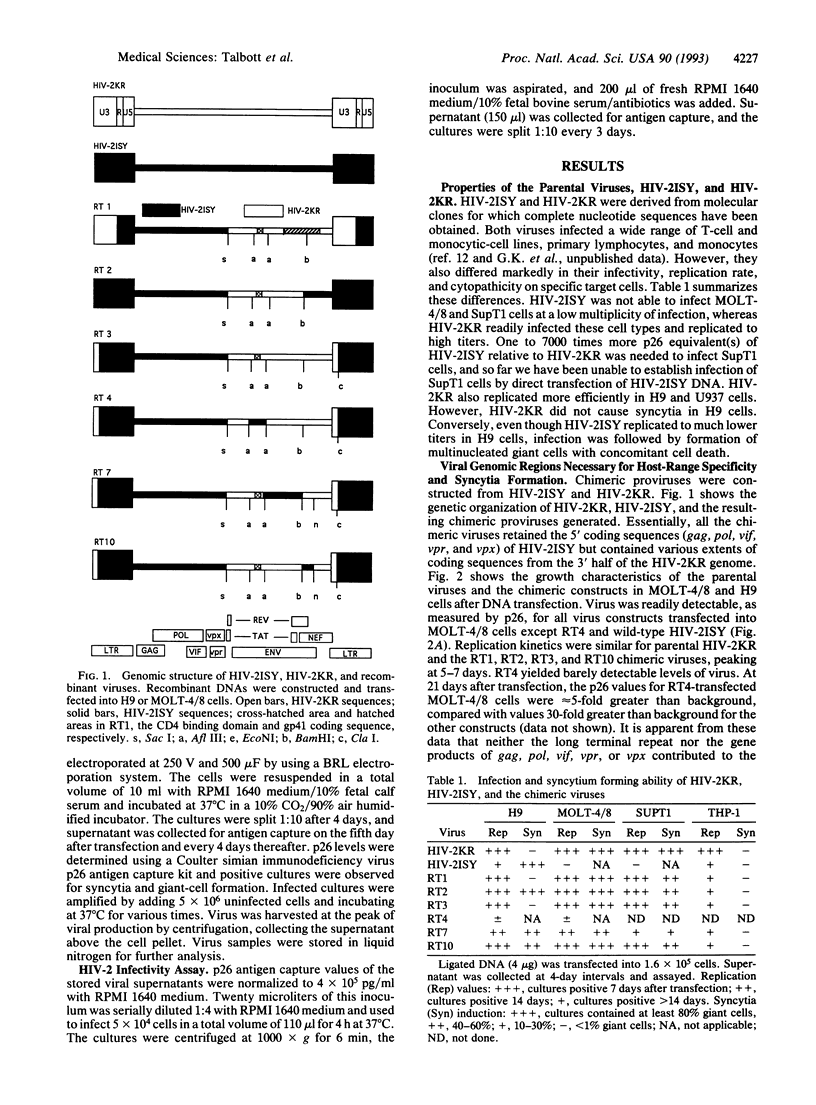
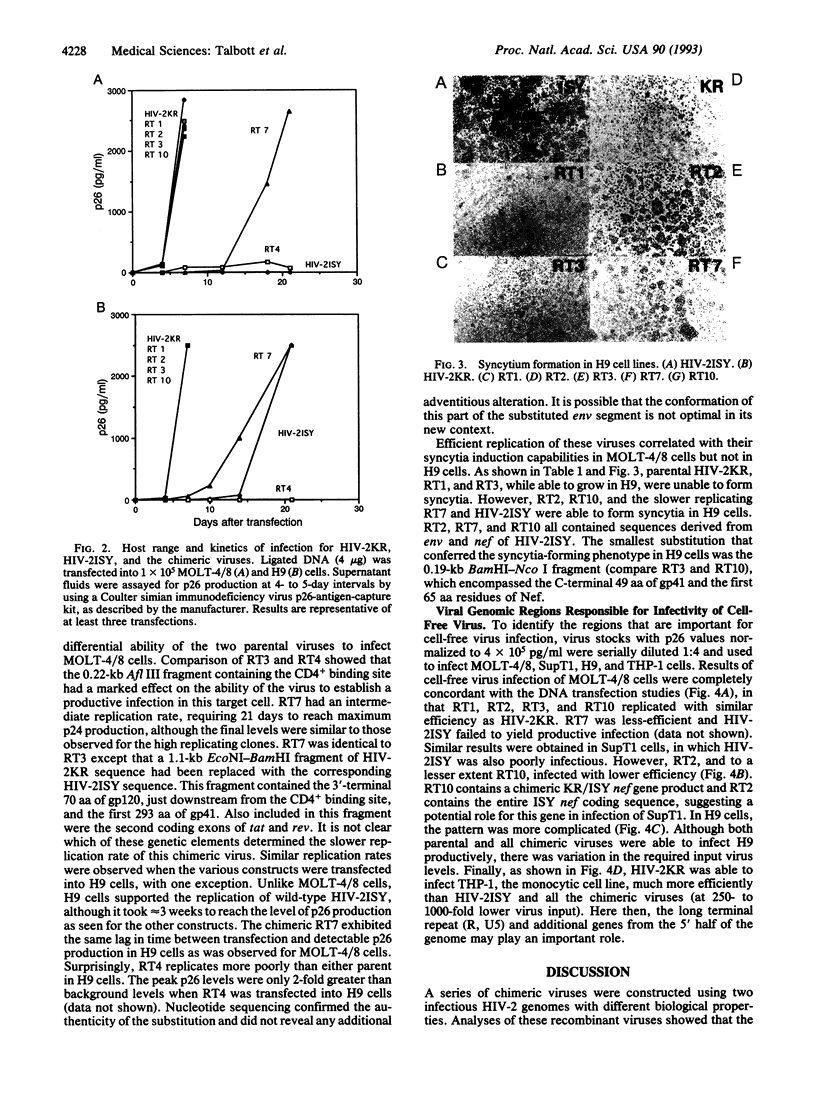
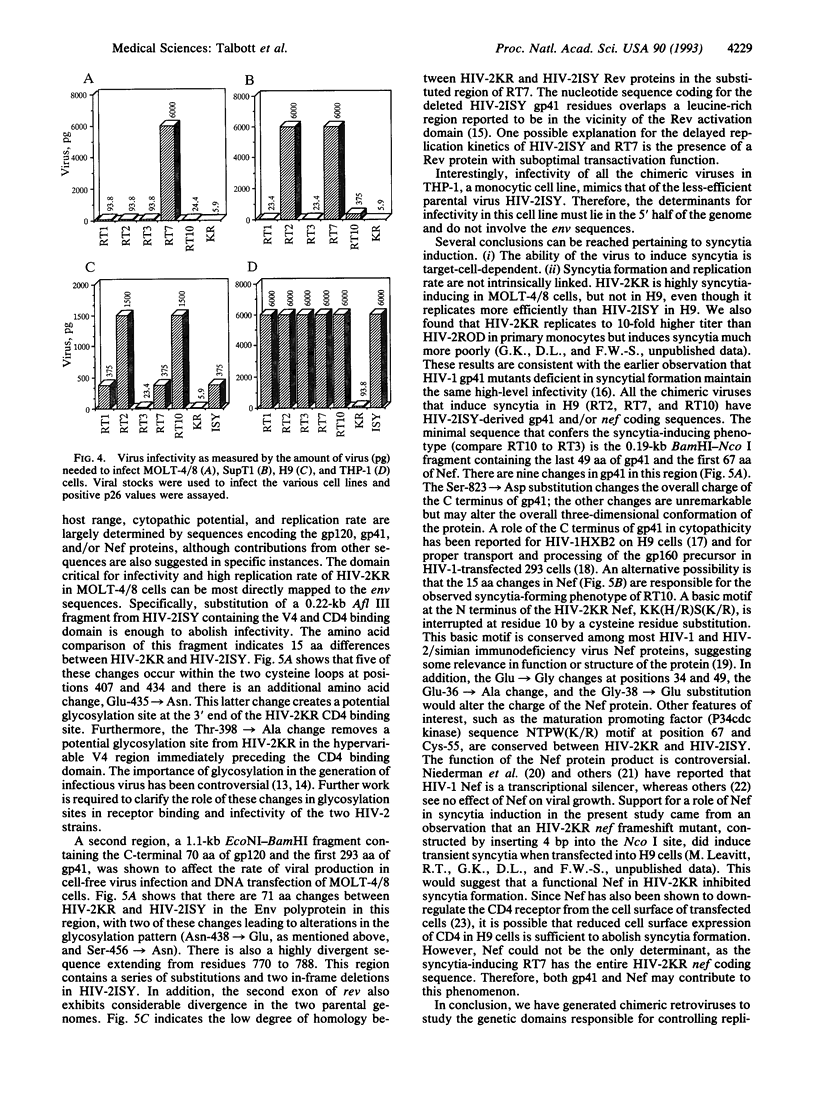
Human immunodeficiency virus 2 (HIV-2) ISY and the newly derived HIV-2KR are infectious molecular clones that yield viruses differing markedly in their abilities to infect and/or induce syncytia in various T- and monocytoid-cell lines. Chimeric viruses were constructed from these two viral genomes to localize the genetic determinants of some of these properties. Envelope sequences, particularly those spanning the CD4 binding site, appear to be critical for the ability of HIV-2KR to infect MOLT-4 clone 8 and SupT1 cells and to efficiently infect the H9 cell line. On the other hand, multiple determinants may contribute to cytopathicity (gp41 and nef) in H9 cells and replication efficiency in monocytic (THP-1) cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Nauclér A., Böttiger B., Broliden P. A., Albino P., Ouattara S. A., Björkegren C., Valentin A., Biberfeld G., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of HIV-2, like HIV-1, correlates with severity of immunodeficiency. AIDS. 1990 Apr;4(4):291–295. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199004000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahraoui E., Benjouad A., Guetard D., Kolbe H., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. Study of the interaction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 envelope glycoproteins with the CD4 receptor and role of N-glycans. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):565–573. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro B. A., Nepomuceno M., Lerche N. W., Eichberg J. W., Levy J. A. Persistent infection of baboons and rhesus monkeys with different strains of HIV-2. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90838-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgnaud V., Lauré F., Fultz P. N., Montagnier L., Bréchot C., Sonigo P. Genetic differences accounting for evolution and pathogenicity of simian immunodeficiency virus from a sooty mangabey monkey after cross-species transmission to a pig-tailed macaque. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):414–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.414-419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. J., Nelbock P., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 Rev protein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.445-449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emilie D., Maillot M. C., Bonnerot C., Devergne O., Delfraissy J. F., Nicolas J. F., Galanaud P. Syncytium induction by fresh HIV isolates: quantitative analysis using a transactivation beta-gal assay. AIDS. 1990 Aug;4(8):791–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Ensoli B., Looney D., Rose A., Gallo R. C., Saag M. S., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H., Wong-Staal F. Biologically diverse molecular variants within a single HIV-1 isolate. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):444–447. doi: 10.1038/334444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Fargnoli K. A., Giombini F., Jagodzinski L., De Rossi A., Bosch M., Biberfeld G., Fenyo E. M., Albert J., Gallo R. C. Molecular and biological characterization of a replication competent human immunodeficiency type 2 (HIV-2) proviral clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2433–2437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Yue L., White A. T., Pappas P. G., Barchue J., Hanson A. P., Greene B. M., Sharp P. M., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Human infection by genetically diverse SIVSM-related HIV-2 in west Africa. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):495–499. doi: 10.1038/358495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Miller A. D. Serine phosphorylation-independent downregulation of cell-surface CD4 by nef. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):508–511. doi: 10.1038/350508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Nakamura G. R., Berman P. W. The carboxy terminus of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp160 limits its proteolytic processing and transport in transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3100–3103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3100-3103.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori N., Michaels F., Fargnoli K., Marcon L., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. The human immunodeficiency virus type 2 vpr gene is essential for productive infection of human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8080–8084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helseth E., Kowalski M., Gabuzda D., Olshevsky U., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Rapid complementation assays measuring replicative potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein mutants. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2416-2420.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Ikeuchi K., Byrn R., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Lack of a negative influence on viral growth by the nef gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9544–9548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi K., Conway B., Cunningham S., Berson A., Evans C., Iversen A. K., Colvin D., Gallo M. V., Coutre S., Shpaer E. G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope gene structure and diversity in vivo and after cocultivation in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):875–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.875-885.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Hu W., Fisher A. G., Looney D. J., Kao V. F., Mitsuya H., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Role of the carboxy-terminal portion of the HIV-1 transmembrane protein in viral transmission and cytopathogenicity. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):441–449. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra R. K., Ahmad N., Holland S. M., Venkatesan S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) provirus expression and LTR transcription are repressed in NEF-expressing cell lines. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):522–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90593-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N. L., Vahey M., Burke D. S., Redfield R. R. Viral DNA and mRNA expression correlate with the stage of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 infection in humans: evidence for viral replication in all stages of HIV disease. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):310–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.310-316.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. J., Ritter G. D., Jr, Chaikin M. A., Yamshchikov G. V., Kumar P., Hahn B. H., Sweet R. W., Compans R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 envelope glycoprotein: differential CD4 interactions of soluble gp120 versus the assembled envelope complex. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90311-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman T. M., Thielan B. J., Ratner L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 negative factor is a transcriptional silencer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel K. P., Hodge D. R., Chen Y. M., Papas T. S. Nef proteins of the human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV-1 and HIV-2) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) are structurally similar to leucine zipper transcriptional activation factors. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Aug;7(8):697–706. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuitemaker H., Koot M., Kootstra N. A., Dercksen M. W., de Goede R. E., van Steenwijk R. P., Lange J. M., Schattenkerk J. K., Miedema F., Tersmette M. Biological phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clones at different stages of infection: progression of disease is associated with a shift from monocytotropic to T-cell-tropic virus population. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1354-1360.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai W. P., Nara P. L., Kung H. F., Oroszlan S. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus infectivity by chloroquine. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Apr;6(4):481–489. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]