Abstract
Background:
Generalized rash is amongst the most common conditions presented to practicing General Practitioners and common differentials include contact dermatitis, atopic eczema, sun-induced damage, drug eruption and general manifestations of systemic diseases or infections.
Materials and Methods:
We illustrate with differential diagnoses our clinical case of a generalized rash in a 55-year-old man with pathognomonic signs of a diagnosis, which has received increasing global concern.
Conclusion:
Despite the array of available laboratory tests, a detailed history and physical examination is still of paramount importance to arrive at the most likely diagnosis for any patient with a generalized skin rash.
Keywords: Generalized rash, secondary syphilis, public health
Case Report
Mr. B is a 55-year-old man with Parkinson's disease who lives in a local long term care facility. He initially presented with 1 month's history of multiple red spots affecting his arms and legs that would not resolve. He described the rash as non-tender and non-pruritic. He denied any systematic symptoms such as weight loss, fever, night sweating or loss of appetite. He also denied any contact with soil, plants or any flowers. On examination, Mr. B had a generalized copper-red maculopapular eruption with lesions scattered over the flexor and extensor aspect of the upper and lower limbs [Figures 1 and 2]. The lesions were pleomorphic in shape and with sizes up to 3 mm in diameter. Margins were well-defined with no scaling or blanching upon pressure. Closer inspection confirmed the presence of lesions on the palm [Figure 3].
Figure 1.
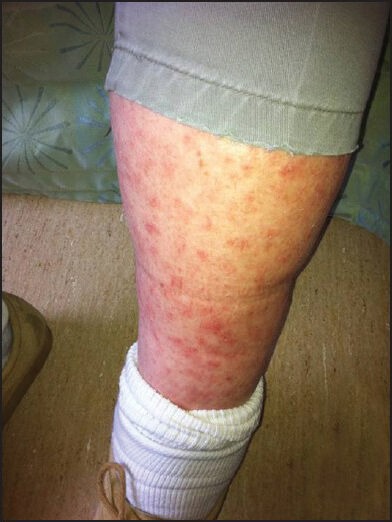
Generalized copper-color maculo-papular rash on the thigh
Figure 2.
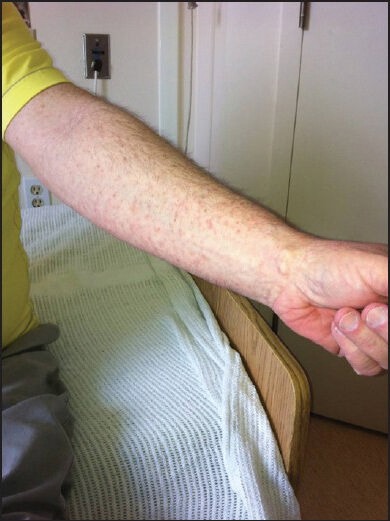
Generalized copper-color maculo-papular rash as seen on the arm
Figure 3.
Presence of rash on the palm
Differential Diagnosis and Investigations
In view of the generalized morphology and non-pruritic nature of the lesions and their color, systematic causes such as psoriasis, mycosis fungoides, zinc deficiency and secondary syphilis are likely diagnoses. Mycosis fungoides is a cutaneous form of T-cell lymphoma of unknown etiology. Early stage of mycosis fungoides exhibits fine scaly erythematous papules over the limbs and trunk, which may coalesce to copper-red plaques as the disease advances. Zinc deficiency can happen in adult as an acquired condition and gives rise to generalized eczema like eruption on the body and face, which is non-pruritic. Finally, secondary syphilis can manifest with a deeply erythematous, maculopapular rash that involves the whole body including the palms and soles. Necessary investigations include blood tests for zinc levels, venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) ± Treponemal Pallidum Agglutination (TPA) tests and skin biopsy to exclude mycosis fungoides.
Unfortunately, patient was seen a few days before the long Christmas holidays and in-view of the relative lack of symptoms, the attending physician postponed further investigations and prescribed 0.1% betamethasone cream. However, the rash did not improve and extend to the groin and axillary areas, for which the same attending doctor added in antifungal cream. Over the next 2 weeks, the axillary and groin rash subsided, but the lesions over the hands and feet persisted. The attending physician switched to a higher potency steroid cream (0.05% Clobetasol), again with no improvement. The resident then went back to the patient for a more detailed sexual history. Patient later admitted that he recently started a relationship with another male without engaging any genital or anal sex; yet he remembered his partner had an oral ulcer, which he noticed on kissing him. At the same time, the VDRL and TPA antigen tests came back as strongly positive and suggestive of a recent syphilis infection. The diagnosis of the rash was hence confirmed to be secondary syphilis. Patient was commenced on daily intramuscular procaine penicillin G, 2.4 million units to be given for 14 days.
Syphilis
Background
The origin of syphilis has been debated for over the last 600 years. While biblical scholars of the old testament would claim that the term “leprosy” and the plagues that struck Egypt and Moab were clear accounts of syphilis,[1] recent thinking basing on deoxyribonucleic acid and skeletal analysis of archeological specimens insists that syphilis was due to a new contagion brought from the New World by Columbus in 15th Century.[2] A recent appraisal of all published reports of so-called syphilis in the pre-Columbus era all lack diagnostic concordance and certainty.[3] The widely acclaimed pre-Columbian existence of syphilis in Europe was also proven to be solely speculative, originating in fact from popular television documentaries.[4] The causative pathogen of syphilis is Treponema pallidum, a spirochete bacteria, which succumbs easily to environmental adversities and hence violates Münch and Robert Koch's 2nd postulate in being unable to be grown in pure culture.[5] Nevertheless, the bacteria is highly infectious due to its unique paucity of integral proteins in its outer membrane[6] and the constant antigenic variation of the TprK surface protein,[7] both enabling the spirochetes to evade the host's immunological surveillance.[6]
The comeback
In the last two decades, there seem to be a global rise in incidence of syphilis infection as evidenced in Australasia,[8,9] Europe,[10,11,12] USA[13,14] and China.[15,16] At present, syphilis has the highest prevalence in Latin American and Caribbean countries especially among men who have sex with men and also in the transgender populations.[17] Furthermore, co-infection rate of syphilis with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in men who have sex with men is reported to be disproportionately high in USA,[18] Norway[19] and China,[20] up to a 140-fold increase in risks.[21] Possible explanations include the painless genital ulcers from syphilis enhances HIV transmission,[22] and in reverse, HIV infection suppress the CD4+/CD8+ T-cell mediation immune responses, which are essential in clearing treponemal bacteria in the blood.[23]
Diagnosis and screening
As a result, serological tests remain to be the methods of choice for screening or diagnosis of syphilis: The non-treponemal tests like rapid plasma reagin or the VDRL; and the treponemal specific tests like the fluorescent treponemal antibody, T. pallidum particle agglutination and enzyme immunoassay.[24] When used alone, neither of these tests is sufficient for an accurate diagnosis; so, it is customary for laboratories to use non-treponemal tests for screening and then proceed to treponemal specific tests for diagnostic confirmation.[24,25] However, such diagnostic workflow entails an initial screening test which is non-specific for treponemal antigen and is time-consuming due to manual operation. This leads to recent advocacy of a reverse screening algorithm, which uses treponemal-specific tests for initial screening to be followed by non-treponemal specific tests. The advantages of such reverse protocol include higher specificity in screening and its enhanced speed made possible with computer automation of assays. Thus said, the quantitative value of VDRL test is more useful for monitoring the disease progression and response to treatment.[8]
Stages of syphilis infection
Primary syphilis is characterized by a painless ulcer (chancre) that emerges after an average incubation period of up to 90 days of exposure. The site of chancre depends on the mode of sexual contact, which commonly involve the external genitalia and less commonly, the cervix,[26] anus,[27] lips,[28] tongue,[29] oral cavity,[30] fingers[31] and upper arm.[32] Often, there is painless local lymphadenopathy. Left untreated, the local syphilitic chancres heal spontaneously within 3 to 6 weeks, when the disease progresses to secondary syphilis, with widespread systemic dissemination of the T. pallidum bacteria. A generalized rash is the most characteristic finding of secondary syphilis, which is classically a diffuse copper-color maculopapular eruption over the trunk and extremities, involving the palms and soles in 75% of cases.[8] Individual lesions are discrete, measuring 0.5-2 cm in diameter. However, the rash of secondary syphilis can take on other forms such as follicular, pustular, nodular[33] or even wart-like in genital areas. It can mimic a variety of dermatological conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, tinea versicolor, lichen planus, erythema multiforme and alopecia areata;[34,35] hence, earning the eponymous nickname of the “great mimicker”. From secondary syphilis, patient can proceed either to latent stage having no symptoms but positive syphilitic serology, or, to tertiary syphilis which can affect the central nervous system (neurosyphilis), the cardiovascular system (cardiosyphilis), the skeletal system and the visceral organs. Gummas are pathognomonic lesions of tertiary syphilis, which are proliferative granulomas as a result of inflammatory reaction in a vain attempt to destroy the treponemes. Gummas are found on the skin and other internal organs such as the liver,[36] heart,[37] brain,[38] testicles[39] and the bones.[40,41] Cutaneous gummas present as painless necrotic ulcers with rubbery margins and hyaline base that chronically erode into and destroy the deeper tissues. Since the era of antibiotics and penicillin, gummas and other complications from tertiary syphilis are rarely seen nowadays.
Treatment
Since its official use around the World War II, penicillin given intramuscularly (primary, secondary, tertiary and cardiovascular disease) or intravenously (neurosyphilis) remain to be the drug of choice for syphilis.[42] Doxycycline and azithromycin are alternatives for patients with penicillin allergy. Drug resistance of syphilis to penicillin has yet to be discovered but there were reports of resistance to azithromycin due to an adenosine to guanosine mutation at the 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene.[43] Within 3-12 h after administration of antibiotics, the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may occur in 30% of patients with primary syphilis and 60% of secondary syphilis. This is a febrile reaction thought to be due to endotoxin release from the walls of the lysed treponemes and is self-limiting within 24 h. Treatment of contacts who have been exposed to the index patient with 3 months is done empirically subject to results of syphilitic serology.
Prognosis
Patients should be re-examined clinically and serologically at 6 and 12 months after treatment. A fourfold reduction in titer of a non-treponemal test (e.g., from 1:16 to 1:4) is confirmatory of an effective therapy. A titer that fails to drop or even rises can indicate either a treatment failure or re-infection over the time course.
Conclusions
Despite its 600-year history in our civilization, syphilis remains to be one of the most challenging infectious diseases yet to be eradicated, due to its high infectivity, innate ability of the treponemes to evade the human immune response and finally, its protean dermatological and systemic manifestations that mimic a variety of clinical diagnoses. Recently, there seems to be a trend of syphilis resurgence especially as a co-infection with HIV. As illustrated by our clinical case, syphilis as the great mimicker should once again be included in the list of differential diagnoses for generalized rashes that include the palms and soles.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared
References
- 1.Willcox RR. Venereal disease in the Bible. Br J Vener Dis. 1949;25:28–33. doi: 10.1136/sti.25.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rothschild BM. History of syphilis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:1454–63. doi: 10.1086/429626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Harper KN, Zuckerman MK, Harper ML, Kingston JD, Armelagos GJ. The origin and antiquity of syphilis revisited: An appraisal of old world Pre-Columbian evidence for Treponemal infection. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2011;146(Suppl 53):99–133. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Armelagos GJ, Zuckerman MK, Harper KN. The science behind Pre-Columbian evidence of syphilis in Europe: Research by documentary. Evol Anthropol. 2012;21:50–7. doi: 10.1002/evan.20340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Münch R. Robert koch. Microbes Infect. 2003;5:69–74. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(02)00053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lafond RE, Lukehart SA. Biological basis for syphilis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:29–49. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.29-49.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Giacani L, Molini BJ, Kim EY, Godornes BC, Leader BT, Tantalo LC, et al. Antigenic variation in Treponema pallidum: TprK sequence diversity accumulates in response to immune pressure during experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 2010;184:3822–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Read PJ, Donovan B. Clinical aspects of adult syphilis. Intern Med J. 2012;42:614–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2012.02814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Azariah S. Is syphilis resurgent in New Zealand in the 21st century? A case series of infectious syphilis presenting to the Auckland sexual health service. N Z Med J. 2005;118:U1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Simms I, Fenton KA, Ashton M, Turner KM, Crawley-Boevey EE, Gorton R, et al. The re-emergence of syphilis in the United Kingdom: The new epidemic phases. Sex Transm Dis. 2005;32:220–6. doi: 10.1097/01.olq.0000149848.03733.c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Velicko I, Arneborn M, Blaxhult A. Syphilis epidemiology in Sweden: Re-emergence since 2000 primarily due to spread among men who have sex with men. Euro Surveill. 2008;13(50) doi: 10.2807/ese.13.50.19063-en. pii=19063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vall-Mayans M, Casals M, Vives A, Loureiro E, Armengol P, Sanz B. Reemergence of infectious syphilis among homosexual men and HIV coinfection in Barcelona, 2002-2003. Med Clin (Barc) 2006;126:94–6. doi: 10.1157/13083877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mattei PL, Beachkofsky TM, Gilson RT, Wisco OJ. Syphilis: A reemerging infection. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:433–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Klausner JD, Kent CK, Wong W, McCright J, Katz MH. The public health response to epidemic syphilis, San Francisco, 1999-2004. Sex Transm Dis. 2005;32:S11–8. doi: 10.1097/01.olq.0000180456.15861.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tucker JD, Yin YP, Wang B, Chen XS, Cohen MS. An expanding syphilis epidemic in China: Epidemiology, behavioural risk and control strategies with a focus on low-tier female sex workers and men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Infect. 2011;87(Suppl 2):ii16–8. doi: 10.1136/sti.2010.048314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hvistendahl M. China. An explosive return of the ‘great pox’. Science. 2012;335:390. doi: 10.1126/science.335.6067.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zoni AC, González MA, Sjögren HW. Syphilis in the most at-risk populations in Latin America and the Caribbean: A systematic review. Int J Infect Dis. 2013;17:e84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2012.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buchacz K, Greenberg A, Onorato I, Janssen R. Syphilis epidemics and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) incidence among men who have sex with men in the United States: Implications for HIV prevention. Sex Transm Dis. 2005;32:S73–9. doi: 10.1097/01.olq.0000180466.62579.4b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jakopanec I, Grjibovski AM, Nilsen Ø, Blystad H, Aavitsland P. Trends in HIV infection surveillance data among men who have sex with men in Norway, 1995-2011. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:144. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang X, Wang C, Hengwei W, Li X, Li D, Ruan Y, et al. Risk factors of HIV infection and prevalence of co-infections among men who have sex with men in Beijing, China. AIDS. 2007;21(Suppl 8):S53–7. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000304697.39637.4c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pathela P, Braunstein SL, Schillinger JA, Shepard C, Sweeney M, Blank S. Men who have sex with men have a 140-fold higher risk for newly diagnosed HIV and syphilis compared with heterosexual men in New York City. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011;58:408–16. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318230e1ca. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Adolf R, Bercht F, Aronis ML, Lunardi LW, Schechter M, Sprinz E. Prevalence and risk factors associated with syphilis in a cohort of HIV positive individuals in Brazil. AIDS Care. 2012;24:252–8. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2011.597706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Leader BT, Godornes C, VanVoorhis WC, Lukehart SA. CD4+ lymphocytes and gamma interferon predominate in local immune responses in early experimental syphilis. Infect Immun. 2007;75:3021–6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01973-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Binnicker MJ. Which algorithm should be used to screen for syphilis? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012;25:79–85. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e32834e9a3c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bala M, Toor A, Malhotra M, Kakran M, Muralidhar S, Ramesh V. Evaluation of the usefulness of Treponema pallidum hemagglutination test in the diagnosis of syphilis in weak reactive venereal disease research laboratory sera. Indian J Sex Transm Dis. 2012;33:102–6. doi: 10.4103/2589-0557.102117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gallup DG, Cowherd DW. Syphilitic cervicitis. A report of a case. Obstet Gynecol. 1978;52:12S–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Drusin LM, Homan WP, Dineen P. The role of surgery in primary syphilis of the anus. Ann Surg. 1976;184:65–7. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197607000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Qiao J, Fang H. Syphilitic chancre of the mouth. CMAJ. 2011;183:2015. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.110664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Staines K, Sloan P. Images in clinical medicine. Syphilitic chancre of the tongue. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:e11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMicm1011576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Veraldi S, Lunardon L, Persico MC, Francia C, Bottini S. Multiple aphthoid syphilitic chancres of the oral cavity. Int J STD AIDS. 2008;19:486–7. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2007.007262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ramoni S, Cusini M, Boneschi V, Galloni C, Marchetti S. Primary syphilis of the finger. Sex Transm Dis. 2010;37:468. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181e2cfac. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aichelburg MC, Rieger A. Primary syphilitic chancre on the upper arm in an HIV-1-infected patient. Int J STD AIDS. 2012;23:597–8. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2011.011442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tsai KY, Brenn T, Werchniak AE. Nodular presentation of secondary syphilis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:S57–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jordaan HF, Louw M. The moth-eaten alopecia of secondary syphilis. A histopathological study of 12 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:158–62. doi: 10.1097/00000372-199504000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schnirring-Judge M, Gustaferro C, Terol C. Vesiculobullous syphilis: A case involving an unusual cutaneous manifestation of secondary syphilis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:96–101. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2010.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Parnis R. Gumma of the liver. Br J Surg. 1975;62:236. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Soscia JL, Fusco JM, Grace WJ. Complete heart block due to a solitary gumma. Am J Cardiol. 1964;13:553–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(64)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fargen KM, Alvernia JE, Lin CS, Melgar M. Cerebral syphilitic gummata: A case presentation and analysis of 156 reported cases. Neurosurgery. 2009;64:568–75. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000337079.12137.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mackenzie H, Mahmalji W, Raza A. The gumma and the gonad: Syphilitic orchitis, A rare presentation of testicular swelling. Int J STD AIDS. 2011;22:531–3. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Plon´ski A, Machniewska J, Woszczyk B. Gumma of right clavicle in acquired syphilis. Pol Tyg Lek. 1973;28:612–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Little JP, Gardner G, Acker JD, Land MA. Otosyphilis in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus: Internal auditory canal gumma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;112:488–92. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989570292-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wise CR, Pillsbury DM. Penicillin in the treatment of syphilis. Proc R Soc Med. 1944;37:491–2. doi: 10.1177/003591574403700903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Katz KA, Klausner JD. Azithromycin resistance in Treponema pallidum. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008;21:83–91. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3282f44772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


