Abstract
A 77 year old man with an eight month history of polymyalgia rheumatica treated by steroids underwent left lower lobectomy for a non-small cell carcinoma. Following discharge he developed a pneumothorax, empyema, septicaemia, and acute renal failure. Reinvestigation and reoperation showed this to be caused by a non-malignant non-traumatic direct gastropleural fistula.
Full text
PDF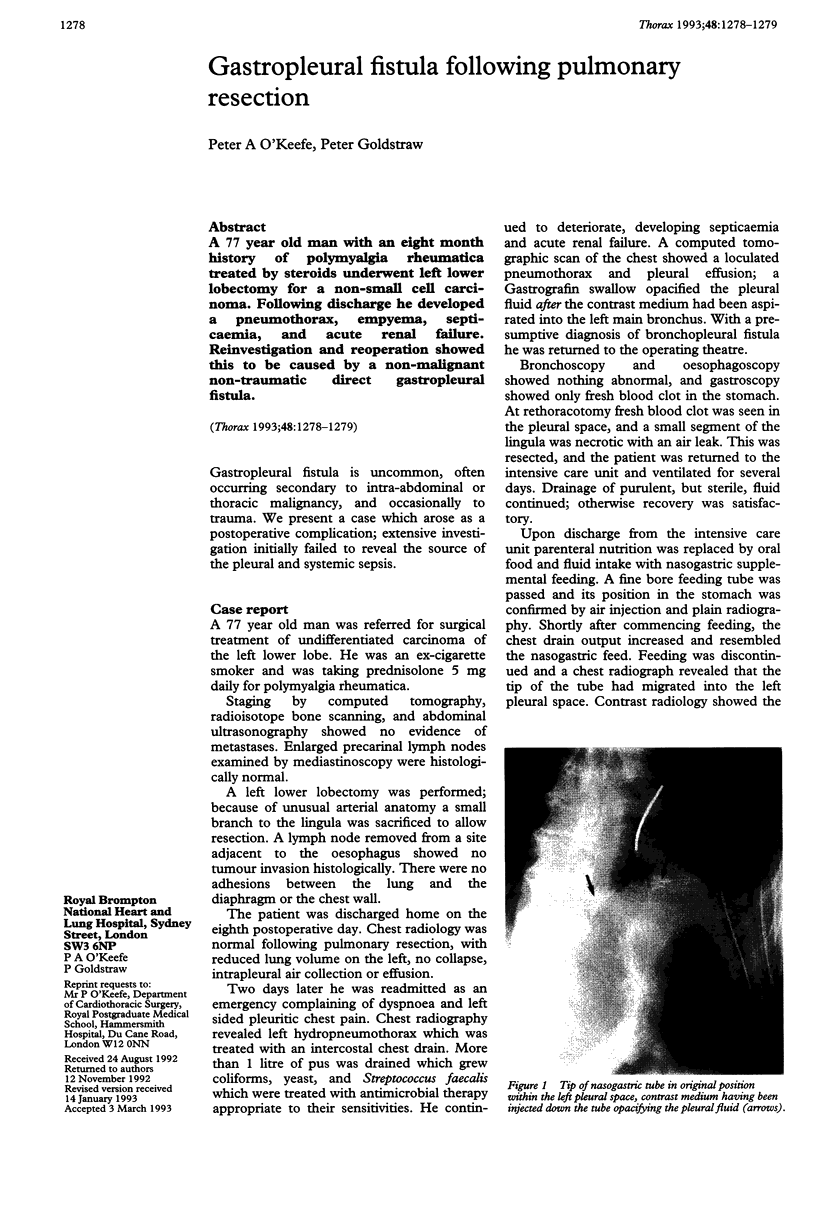

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronchick J. M., Epstein D. M., Gefter W. B., Miller W. T. Pneumothorax as a complication of placement of a nasoenteric tube. JAMA. 1984 Dec 21;252(23):3287–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladergroen M. R., Lowe J. E., Postlethwait R. W. Diagnosis and recommended management of esophageal perforation and rupture. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986 Sep;42(3):235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62725-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. W., Feilding L. P. Hydropneumothorax complicating perforated peptic ulcer. Br J Surg. 1972 Jan;59(1):72–73. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800590120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak I. N., Lawrence D. Tension pneumothorax from a perforated gastric ulcer. Br J Surg. 1976 Mar;63(3):245–247. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. A., Elliott M. J., Featherstone G., Blesovsky A. Perforation of intrathoracic colon causing acute pneumothorax. Thorax. 1983 Dec;38(12):959–960. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.12.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. J., Tait N., O'Rourke I. O. Gastrobronchial fistula owing to non-malignant causes. Br J Surg. 1992 Apr;79(4):331–332. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. J., Tait N., O'Rourke I. O. Gastrobronchial fistula owing to non-malignant causes. Br J Surg. 1992 Apr;79(4):331–332. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. M., Gelder C. M., Goldstraw P., Spiro S. G. Tension pneumothorax and empyema as a consequence of gastro-pleural fistulae. Respir Med. 1990 May;84(3):253–254. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]