Abstract
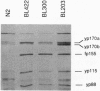
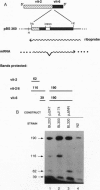
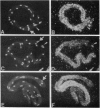
We have produced strains carrying a synthetic fusion of parts of two vitellogenin genes, vit-2 and vit-6, integrated into the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. In most of the 63 transformant strains, the plasmid sequences are integrated at random locations in the genome. However, in two strains the transgene integrated by homologous recombination into the endogenous vit-2 gene. In both cases the reciprocal exchange between the chromosome and the injected circular plasmid containing a promoter deletion led to switching of the plasmid-borne promoter and the endogenous promoter, with a reduction in vit-2 expression. Thus in nematodes, transforming DNA can integrate by homologous recombination to result in partial inactivation of the chromosomal locus. The simplicity of the event and its reasonably high frequency suggest that gene targeting by homologous recombination should be considered as a method for directed inactivation of C. elegans genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aamodt E. J., Chung M. A., McGhee J. D. Spatial control of gut-specific gene expression during Caenorhabditis elegans development. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):579–582. doi: 10.1126/science.2020855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Squire M., Kirtland S., Cane J., Donegan M., Spieth J., Sharrock W. Cloning of a yolk protein gene family from Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Fink G. R. Yeast: an experimental organism for modern biology. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1439–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3287619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. The new mouse genetics: altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A., Beverley S. M. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):171–173. doi: 10.1038/348171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain gene by homologous recombination. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.3576222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C., Capecchi M. R. Reexamination of gene targeting frequency as a function of the extent of homology between the targeting vector and the target locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3365–3371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Rosenzweig B., Hirsh D. Arrangement of repeated sequences in the DNA of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):481–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A. Integrative transformation of Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2673–2680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Waterston R. H. Proper expression of myosin genes in transgenic nematodes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3419–3428. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham S., Holloman W. K. Cloning and disruption of Ustilago maydis genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4052–4055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter U., Morris P. C., Willmitzer L. Gene targeting in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jan;231(2):186–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00279790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine U., Blumenthal T. Characterization of regions of the Caenorhabditis elegans X chromosome containing vitellogenin genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Horvitz H. R., Brenner S. Nondisjunction Mutants of the Nematode CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS. Genetics. 1979 Jan;91(1):67–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Klass M., Wolf N., Hirsh D. Expression of chimeric genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90624-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Recombination in mouse L cells between DNA introduced into cells and homologous chromosomal sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1391–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMorris M., Blumenthal T. In situ analysis of C. elegans vitellogenin fusion gene expression in integrated transgenic strains: effect of promoter mutations on RNA localization. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):27–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMorris M., Broverman S., Greenspoon S., Lea K., Madej C., Blumenthal T., Spieth J. Regulation of vitellogenin gene expression in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans: short sequences required for activation of the vit-2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1652–1662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello C. C., Kramer J. M., Stinchcomb D., Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C.elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper F. R., de Wit I. C., Pronk A. C., Kooiman P. M., Strijker R., Krimpenfort P. J., Nuyens J. H., de Boer H. A. Efficient generation of functional transgenes by homologous recombination in murine zygotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1259–1264. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedin P., Hunter C. P., Wood W. B. Autonomy and nonautonomy of sex determination in triploid intersex mosaics of C. elegans. Development. 1991 Jul;112(3):863–879. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.3.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock W. J. Yolk proteins of Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spieth J., Denison K., Zucker E., Blumenthal T. The nucleotide sequence of a nematode vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7129–7138. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spieth J., MacMorris M., Broverman S., Greenspoon S., Blumenthal T. Regulated expression of a vitellogenin fusion gene in transgenic nematodes. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Shaw J. E., Carr S. H., Hirsh D. Extrachromosomal DNA transformation of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3484–3496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Brenner S. The DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):95–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Chalfie M. mec-3, a homeobox-containing gene that specifies differentiation of the touch receptor neurons in C. elegans. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernars K., Goosen T., Wennekes B. M., Swart K., van den Hondel C. A., van den Broek H. W. Cotransformation of Aspergillus nidulans: a tool for replacing fungal genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00329838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Riele H., Maandag E. R., Berns A. Highly efficient gene targeting in embryonic stem cells through homologous recombination with isogenic DNA constructs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5128–5132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]