Abstract
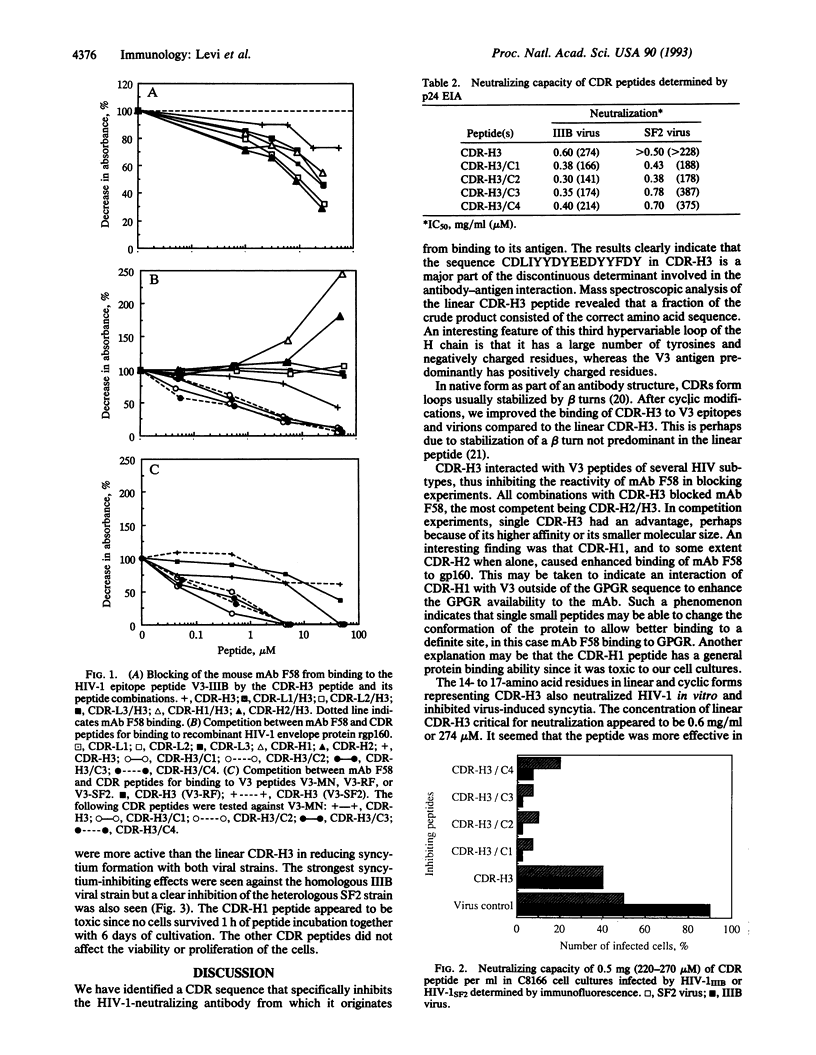
A complementarity-determining region (CDR) of the mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) F58 was constructed with specificity to a neutralization-inducing region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). The mAb has its major reactivity to the amino acid sequence I--GPGRA in the V3 viral envelope region. All CDRs including several framework amino acids were synthesized from the sequence deduced by cloning and sequencing mAb F58 heavy- and light-chain variable domains. Peptides derived from the third heavy-chain domain (CDR-H3) alone or in combination with the other CDR sequences competed with F58 mAb for the V3 region. The CDR-H3 peptide was chemically modified by cyclization and then inhibited HIV-1 replication as well as syncytium formation by infected cells. Both the homologous IIIB viral strain to which the F58 mAb was induced and the heterologous SF2 strain were inhibited. This synthetic peptide had unexpectedly potent antiviral activity and may be a potential tool for treatment of HIV-infected persons.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom L., Hinkula J., Broliden P. A., Mäkitalo B., Fridberger T., Rosen J., Villacres-Eriksson M., Morein B., Wahren B. Neutralizing cross-reactive and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to HIV-1 gp120. AIDS. 1990 Oct;4(10):953–960. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199010000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., Mäkitalo B., Akerblom L., Rosen J., Broliden K., Utter G., Jondal M., Norrby E., Wahren B. Identification of amino acids in the V3 region of gp120 critical for virus neutralization by human HIV-1-specific antibodies. Immunology. 1991 Aug;73(4):371–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Tramontano A., Levitt M., Smith-Gill S. J., Air G., Sheriff S., Padlan E. A., Davies D., Tulip W. R. Conformations of immunoglobulin hypervariable regions. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):877–883. doi: 10.1038/342877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Nunberg J. H., Conley A. J., Eda Y., Tokiyoshi S., Putney S. D., Matsushita S., Cobb K. E., Jett C. M. Prevention of HIV-1 infection in chimpanzees by gp120 V3 domain-specific monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):728–730. doi: 10.1038/355728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferre F., Garduno F. Preparation of crude cell extract suitable for amplification of RNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2141–2141. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Identification of the principal neutralizing determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 as a fusion domain. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):190–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.190-194.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Rajewsky K. Stable expression and somatic hypermutation of antibody V regions in B-cell developmental pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:537–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi R., Güssow D. H., Jones P. T., Winter G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts V. A., Iverson B. L., Iverson S. A., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A., Getzoff E. D., Tainer J. A. Antibody remodeling: a general solution to the design of a metal-coordination site in an antibody binding pocket. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6654–6658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Magnius L. O., Norrby E., Wahren B. Rapid "tea-bag" peptide synthesis using 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) protected amino acids applied for antigenic mapping of viral proteins. Immunol Lett. 1991 Sep;30(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90090-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sällberg M., Rudén U., Wahren B., Noah M., Magnius L. O. Human and murine B-cells recognize the HBeAg/beta (or HBe2) epitope as a linear determinant. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jul;28(7):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90114-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Gould R. J., Garsky V. M., Ciccarone T. M., Hoxie J., Friedman P. A., Shattil S. J. A monoclonal antibody against the platelet fibrinogen receptor contains a sequence that mimics a receptor recognition domain in fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling G. W., van Gorkum J., Damhof R. A., Drijfhout J. W., Bloemhoff W., Welling-Wester S. A ten-residue fragment of an antibody (mini-antibody) directed against lysozyme as ligand in immunoaffinity chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1991 Jul 12;548(1-2):235–242. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)88605-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. V., Kieber-Emmons T., VonFeldt J., Greene M. I., Weiner D. B. Design of bioactive peptides based on antibody hypervariable region structures. Development of conformationally constrained and dimeric peptides with enhanced affinity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5182–5190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. V., Moss D. A., Kieber-Emmons T., Cohen J. A., Myers J. N., Weiner D. B., Greene M. I. Development of biologically active peptides based on antibody structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5537–5541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



