Abstract
Excitatory commissural V3 interneurons (INs) of the ventral spinal cord have been shown to balance locomotor rhythm regularity and robustness in vivo. Unfortunately, due to the scarcity of these cells in the spinal cord, in vitro studies of dissociated V3 INs have yet to be reported. In this study, we developed an induction protocol for V3 INs from mouse embryonic stem cells. The effect of the concentration of a strong sonic hedgehog (Shh) agonist (smoothened agonist [SAG]) and retinoic acid (RA) on expression of progenitor p3 and postmitotic V3 IN transcription factor markers (ie, Nkx2.2 and Sim1) was examined. Cells were differentiated toward a more ventral fate by increasing the duration of SAG exposure from 4 days in a previously established motoneuron induction protocol to 6 days. At the end of the induction period, transcription factor expression was assessed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunocytochemistry, in situ hybridization, and flow cytometry. Lower concentrations of RA and a longer duration of SAG exposure led to increased levels of p3 and V3 marker expression. This novel induction protocol reveals the importance of Shh signaling duration in the dorsal-ventral patterning of the neural tube, and it provides a method to obtain V3 INs for future studies to allow better understanding their role in rewiring and regeneration after spinal cord injury.
Introduction
V3 interneurons (INs) are commissural glutamatergic neurons that have been shown to be involved in rhythm generation networks within the spinal cord known as central pattern generators (CPGs) [1–3]. They can be identified by the p3 progenitor domain markers, Nkx2.2 and Ngn3, and the postmitotic IN marker, Sim1 [4,5]. More recently Uncx has been shown to be a mature V3 marker [6,7].
Initial fictive locomotor assays in Sim1 knockout mice suggest that V3 INs have a role in balancing locomotor outputs in the spinal cord to regulate left-right alternation in gait [3]. More recent studies have demonstrated that spatially separated and functionally distinct subpopulations of V3 INs (termed V3ds and V3vs) can be differentially recruited for running and/or swimming [2]. V3 INs also have the ability to cross the midline and synapse onto motoneurons (MNs) and other INs across multiple spinal segments [5]. These findings suggest that V3 INs play a critical role in locomotor coordination and may be involved in local reorganization after spinal cord injury (SCI). An efficient method to obtain V3 INs is necessary for enhanced understanding of CPGs and recovery after SCI.
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can provide a plentiful cell source for cell replacement therapies and to study developmental biology. Protocols using retinoic acid (RA) and sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling to direct differentiation of ESCs into various ventral spinal cell identities including MNs [8] and V2a INs [9] by mimicking conditions found in the developing ventral neural tube have been reported.
During development, RA released from laterally positioned somites [10,11] and Shh released from the notochord and floor plate (FP) generate overlapping gradients on the neural tube [8,12–14]. Shh diffuses dorsally from the FP and notochord, generating a ventral to dorsal signaling gradient (Fig. 1A). RA is a caudalizing factor in neuronal differentiation [10,11,15,16] (Fig. 1D) and may help pattern the dorsal-ventral identity of embryoid body (EB)-derived neuronal populations in vitro [11]. These two overlapping gradients specify different progenitor domains (pMN and p0–p3) within the ventral cord, which give rise to MNs and ventral IN classes (V0–V3), and are identified by distinct transcription factors [5,13,17–21]. This complex interplay between Shh and RA serves as a basis for specifying ventral neural differentiation from ESCs.
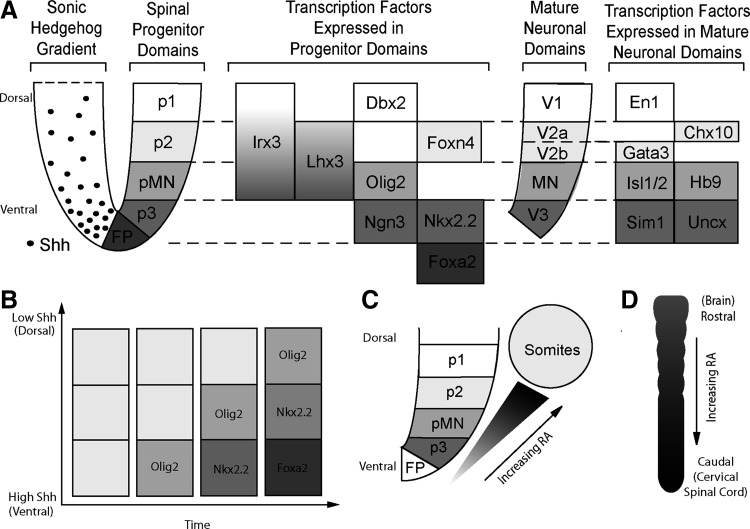
FIG. 1.
(A) Diagram depicting the ventral developing neural tube. The gradient of sonic hedgehog (Shh) arising from the floor plate establishes the ventral progenitor domains (p1–p3 and pMN). Specific transcription factors expressed in these domains drive the maturation of the committed domains (V1–V3 and motoneuron), which are defined by specific transcription factors (shown on the far right). Adapted from Brown et al. and Dessaud [9,19]. (B) A schematic depicting the effect of time and concentration on establishing progenitor domains. With increasing duration of high Shh exposure, more ventral domains are established. Adapted from Dessaud et al. [19]. (C) Schematic depicting the distance from retinoic acid (RA)-expressing somites. (D) Illustration of the rostral-caudal axis and direction of increasing RA expression.
In this study, we establish a novel protocol to generate V3 INs from ESCs by assessing the effects of increasing Shh signaling, prolonging the duration of Shh exposure, and decreasing RA concentration on p3 progenitor and postmitotic V3 IN marker expression in ESC-derived neural cultures. V2a INs, which lie dorsal to MNs, require a weaker Shh signaling agonist than do MNs. Since V3 INs lie ventral to both V2s and MNs [13,22], we hypothesized that further increasing the Shh signaling level would promote increased differentiation of V3 INs.
Previous studies suggested that a more ventral spinal fate is specified by increasing the duration of Shh exposure, therefore we also chose to study the effects of varying the duration of Shh exposure of cell fate (Fig. 1B) [19,20,22]. Furthermore, because the progenitor p3 domain lies further from the RA-releasing somites than the pMNs, we hypothesized that a lower RA concentration could further improve V3 IN induction. Cells obtained with our protocol can be used for studying CPG connectivity and cell-based transplantation therapies.
Materials and Methods
Culture of ESCs
RW4 mouse ESCs (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were cultured on T-25 flasks coated in 0.1% gelatin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Cells were cultured in complete media consisting of Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM 11965; Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) containing 10% newborn calf serum, 10% fetal bovine serum, and a 1:100 dilution of a 100× nucleosides mix (EMD Millipore, Bellerica, MA). Cells were routinely passaged every other day by washing with DMEM 11965 containing 25 mM HEPES (Life Technologies) and dissociating with 1 mL 0.25% trypsin ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA; Life Technologies), quenching with 4 mL complete media, and plating 1 mL into a new T-25 gelatin-coated flask containing a final volume of 5 mL media with 1,000 U/mL leukemia inhibitory factor (EMD Millipore) and 100 μM β-mercaptoethanol (Life Technologies).
Formation and induction of EBs
RW4 ESCs were aggregated to form EBs on a nonadhesive agar-coated surface and induced to generate neural progenitors using our previously established 6-day induction protocol (2−/4+) [8,16,23] or an 8-day induction protocol (2−/6+). Cells were cultured in suspension for 2 days on 100 mm petri dishes precoated with 0.1% agar (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) in DFK-5 media comprised of 1:1 DMEM/F12 (Life Technologies) with 5% knockout serum replacement (Life Technologies), 1× insulin transferrin selenium (Life Technologies), 100 μM β-mercaptoethanol, 50 μM nonessential amino acids (Life Technologies), and a 1:200 dilution of a 100× nucleosides mix.
During the first 2 days, the cells are not exposed to RA or smoothened agonist (SAG) (hence 2−), allowing the cells to aggregate into multicellular EBs. After the first 2 days of aggregation, EBs were plated on gelatin. Two hundred microliters of EBs were removed from the 100 mm plate and replated onto one well of a gelatinized six-well plate. DFK-5 media was added to a final volume of 2 mL and supplemented with RA (0–10 μM; Sigma) and SAG (EMD Millipore) (0–1.25 μM) on day 3 through the end of the induction (either 4 days or 6 more days for 4+ or 6+, respectively). Media with RA and SAG was replaced every 2 days for 4 (2−/4+) or 6 (2−/6+) days (Fig. 2A).
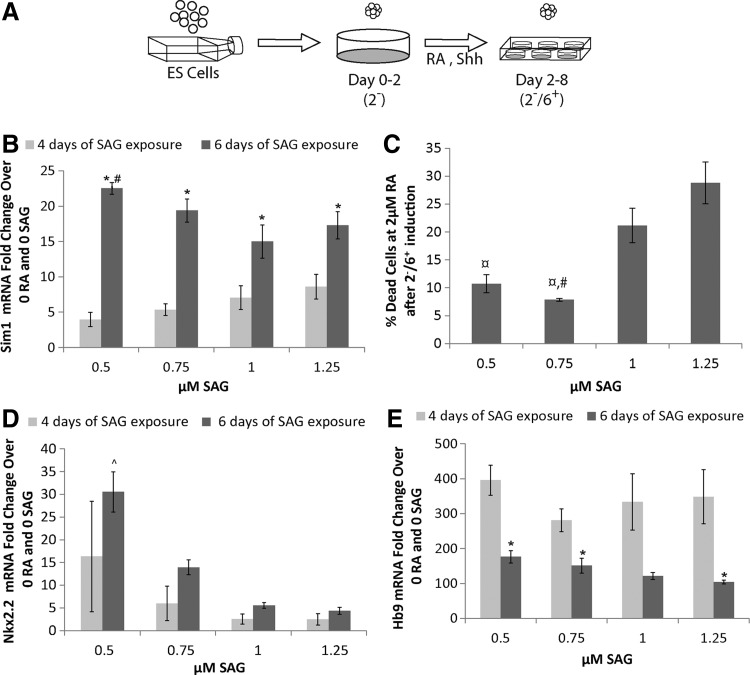
FIG. 2.
Effect of smoothened agonist (SAG) concentration and duration of exposure on gene expression. (A) Schematic depicting the 2−/6+ induction protocol where embryonic stem cells are aggregated in agar-coated plates for 2 days and then exposed to 6 days of RA and Shh signaling. (B, D, E) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction results (n = 3) at the end of a 2−/4+ and 2−/6+ induction for mRNA levels compared to the uninduced (no RA, no SAG) control. (B) Sim1 gene expression after induction. All 2−/6+ groups express significantly more Sim1 than their 2−/4+ counterparts. 0.5 μM SAG at 2−/6+ was significantly >1 and 1.25 μM groups. *P < 0.05 versus the same SAG concentration with the 2−/4+ induction; #P < 0.05 versus 1 μM SAG group at the same time point. (C) The effect of SAG concentration on cell death. #P < 0.05 versus 1 μM SAG; ¤P < 0.05 versus 1.25 μM SAG. (D) Nkx2.2 gene expression after induction. At 0.5 μM SAG, Nkx2.2 expression at 2−/6+ was significantly greater than at 0.75, 1, and 1.25 μM. ^P < 0.05 versus 0.75, 1, and 1.25 μM at the same time point (2−/6+). (E) Hb9 expression after induction. No significance was observed across SAG concentration groups for Hb9 at either time points. *P < 0.05 versus 2−/4+ induction groups at the same SAG concentration.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
Following induction, each well of a six-well plate was lysed with 750 μL of buffer RLT from the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). RNA was extracted per the manufacturer's instructions. High Capacity RNA-to-cDNA Kit (Life Technologies) generated cDNA from extracted RNA. TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Life Technologies; Table 1) and TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix (Life Technologies) were subsequently combined with the purified cDNA for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Reactions were then performed using a Step One Plus Applied Biosystems thermocycler with the default protocol: 95°C for 20 s, 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 s, and 60°C for 20 s.
Table 1.
Taqman Probes for qRT-PCR
| Marker | Life Tech identification |
|---|---|
| Beta-actin | Mm00607939_S1 |
| Sim1 | Mm00441390_m1 |
| Nkx2.2 | Mm00839794_m1 |
| HB9 | Mm00658300_G1 |
| RAX | Mm01258704_m1 |
Ct values, the number of cycles necessary for the fluorescent intensity to increase exponentially, were recorded and normalized to β-actin expression. The comparative ΔCt method [24] was used to analyze the mRNA expression levels in cultures postinduction (2−/4+ and 2−/6+). Fold differences in relative mRNA expression levels over the control cultures are reported for each gene (n ≥ 3 for all groups).
Live/Dead viability assay
Live/Dead reagent (Life Technologies) consisting of calcien-AM and ethidium homodimer was used to visualize live and dead cells, respectively. Cells were dissociated and incubated in Live/Dead reagents as per manufacturer instructions for flow cytometry. For each culture, 30,000 events were recorded using a BD LSRII flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). Data analysis was performed using FloJo software (FloJo, Ashland, OR).
Dissociation and plating of EBs
Standard tissue culture plates were precoated with 0.01% poly(ornithine) solution (Sigma) at 37°C for 1 h. Poly(ornithine) was removed and plates were washed thrice with a HEPES-buffered saline solution. Plates were then coated with 0.01 mg/mL laminin (Life Technologies) in HEPES-buffered saline solution overnight and washed thrice before use as laminin-coated plates. Induced 2−/6+ EBs were allowed to settle and supernatant was collected. Then, 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA was used to dissociate the EBs. Dissociated cells were plated at a density of 100,000 cells/cm2 in the collected DFK-5 supernatant.
Immunocytochemistry
For plated cultures, cells were fixed by adding 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to the cultures for 20 min at room temperature, permeabilized with 0.01% Triton X-100 (Sigma) for 20 min. Cells were then blocked with 5% normal goat serum (Sigma) in PBS for 1 h and stained overnight in 2% normal goat serum in PBS with added primary antibody (mouse anti-Nkx2.2, 1:100, Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA; mouse anti-Ngn3, 1:100, Developmental Studies Hybridoma bank; mouse anti-Uncx, 1:500, EMD Millipore) overnight at 4°C. Cells were then stained for 1 h in 2% normal goat serum in PBS with Alexa Fluor-conjugated antibodies (goat anti-mouse IgG 488; Life Technologies) at 4°C, then Hoechst 33258 (1:1,000; Life Technologies) for 15 min at room temperature, and stored in PBS at 4°C.
Probe synthesis for in situ hybridization
Plasmids for in situ hybridization probes were a generous gift from Dr. Paul Gray (Washington University) [25]. Gene fragments from verified plasmids were linearized by direct PCR amplification using ReadyMade Primers (SP6 Promoter and T7 Promoter; Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA). Digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled antisense and sense RNA probes were made using PCR products as template and T7 RNA polymerases (Roche, Indianapolis, IN). Probes were used at a concentration of 1–2 μg/mL. Sense counterparts of all probes were tested to ensure probe specificity.
In situ hybridization
Cell cultures were fixed and stained with modifications protocol from previously described [25–27]. Cell cultures were fixed in 4% PFA for 10 min and washed thrice in diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC; Sigma)-treated PBS at room temperature. Next, cells were treated with RIPA buffer [150 mM NaCl (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1% NP-40 (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 0.5% Na deoxycholate (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (Sigma), 1 mM EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 50 mM Tris in DEPC (Sigma)-treated water at pH 8.0], and washed twice with DEPC-treated PBS. Then, the cells were incubated in 0.1 M triethanolamine-HCl [1.3% triethanol amine (Sigma) and 0.4% HCl (Thermo Fisher Scientific)] with 0.25% acetic anhydride (Sigma) for 10 min. Cells were washed in 1× saline sodium citrate (SSC) buffer for 5 min at room temperature.
Three additional washes with DEPC-treated PBS were performed before cells were blocked in hybridization buffer [50% formaldehyde (Sigma), 5× SSC buffer (Life Technologies), 0.3 mg/mL yeast RNA (Sigma), 0.1 mg/mL heparin (Sigma), 1× Denhardt's solution (Life Technologies), 0.1% tween (Sigma), and 5 mM EDTA] for 4–6 h at room temperature. Cells were incubated in hybridization buffer containing 1–2 μg/mL DIG-labeled antisense cRNA overnight at 65°C. Probed cells were washed twice in 0.2× SSC at 62°C, and incubated in 0.2× SSC for 60 min at 65°C.
Washed cells were adjusted to room temperature and blocked with 10% deactivated horse serum (Life Technologies) in PBS with 2 mg/mL bovine serum albumin and 0.1% Triton X-100 (PBT), and incubated in alkaline phosphatase-labeled anti-DIG antibody (1:2,000 in 10% deactivated horse serum in PBT; Roche) overnight. Cells were further washed with PBT and color was visualized using nitro blue tetrazolium and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (Roche). Staining was stopped with 4% PFA after visual inspection. Cell nuclei were stained with the DNA binding dye Hoechst (1:1,000, Life Technologies) and by immunocytochemistry with Nkx2.2.
Flow cytometry
Immediately following the induction protocol, EBs were stained for flow cytometry. Cultures were dissociated with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA for 20 min at 37°C. An excess volume of complete media was added to quench the trypsin-EDTA, and cultures were triturated to obtain single cell suspensions. The cells were centrifuged at 360g for 6 min, the media was removed, and the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained according to the Transcription Factor Buffer Set (562725; BD Pharmingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ) manufacturer's instructions with mouse anti-Nkx2.2 (1:100), mouse anti-Isl1 (1:100; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank), and mouse anti-Hb9 (1:20; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank) primary antibodies and appropriate Alexa Fluor secondary antibodies (1:200; Life Technologies).
Following the induction protocol, nuclei were stained with Hoechst (0.5 μg/mL; Life Technologies) for 15 min. For each culture, 10,000 events were recorded using a Canto II flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). Data analysis was performed using FloJo software (FloJo). Debris was removed by gating using the forward scatter versus side scatter and Hoechst fluorescence versus forward scatter plots. Control groups of cells stained with only secondary antibodies were used to determine gating parameters. Results of the flow cytometry are presented as percentage primary antibody+ cells out of the total Hoechst+ population. Sample gating is presented along side flow cytometry data.
Statistics
For quantitative experiments, at least three replicates of each condition were analyzed. For cell counting, at least three images were analyzed of every replicate to provide a representative sample of the replicate. Statistica software (version 5.5, StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK) was used for statistical analysis. Significance was determined using Scheffe's post hoc test for analysis of variance with 95% confidence. Average values are reported with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean.
Results
Effect of SAG concentration and duration of exposure on gene expression
The effect of increasing the concentration and duration of exposure of SAG on gene expression was examined using qRT-PCR to evaluate expression of V3 and pMN ventral neural markers (Sim1, Nkx2.2, and Hb9). Concentrations of SAG were varied from 0.5 to 1.25 μM with 2 μM RA present, and samples were collected after 2−/4+ and 2−/6+ inductions. In this notation, “2−” refers to the number of days ES cells are allowed to aggregate into EBs without (−) RA and SAG (middle section of Fig. 2A). The “4+” or “6+” refers to the number of days the EBs are exposed to (+) RA and SAG (right section of Fig. 2A).
mRNA expression fold change was determined by comparing qRT-PCR Ct values of induced cells to uninduced cells that were not exposed to RA or SAG over the same culture period (n ≥ 3 for all conditions). Expression of the postmitotic V3 marker, Sim1, increased across all concentrations of SAG when the SAG exposure time increased from 4 to 6 days (2−/4+ to a 2−/6+ induction) (Fig. 2B). After the 2−/6+ induction, the group treated with 0.5 μM SAG exhibited significantly higher levels of Sim1 expression than the group treated with 1 μM SAG (22.5 ± 0.5-fold greater versus 15.0 ± 1.3-fold greater than uninduced control).
Further reduction of the SAG concentration to as low as 0.05 μM did not alter Sim1 expression significantly. Additionally, after the 2−/6+ induction, the group treated with 0.5 μM SAG exhibited significantly higher levels of Nkx2.2 mRNA (30.5 ± 4.4-fold greater than uninduced control) compared to other SAG concentrations tested (Fig. 2C). Furthermore, Hb9 expression did not significantly change with SAG concentration at a given time point, but it was lower for the 2−/6+ induction compared to the 2−/4+ induction in most groups (Fig. 2D). Hb9 and Nkx2.2 expression levels showed similar trends to the Sim1 results, indicating that prolonged exposure promotes the targeted gene expression for V3 INs. We observed, at higher SAG concentrations, more EBs detached in cultures on gelatin-coated plates.
To understand why we were observing a decrease in Sim1 induction efficiency, we assessed the percentage of cells surviving after the 2−/6+ induction with 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, and 1.25 μM SAG. We found that there was a significant increase in cell death at 1.25 and 1.0 μM SAG (Fig. 2C). Therefore, 0.5 μM SAG and the 2−/6+ induction protocol were used for subsequent studies.
Effect of RA concentration on gene expression
To investigate the effect of RA concentration on ventral neural identity, qRT-PCR was used to evaluate changes in Sim1, Nkx2.2, and Hb9 expression. The concentration of RA was varied from 0.005 to 10 μM in combination with SAG (at a constant level of 0.5 μM), and samples were collected at the end of the 2−/6+ induction protocol. Gene expression levels were compared to baseline concentration for the motor neuron induction protocol (2 μM RA), mRNA expression fold change was established by comparing qRT-PCR Ct values of all induced groups to the group treated with 2 μM RA and 0.5 μM SAG (n ≥ 3 for all conditions, highest Nkx2.2 and Sim1 levels in Fig. 2).
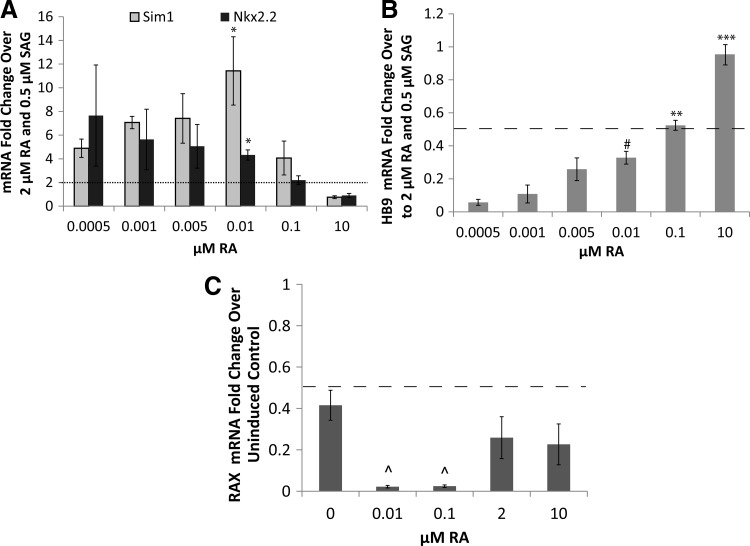
When RA concentration decreased to 0.01 μM, Sim1 expression was found to increase 11.4 ± 2.9-fold versus the 2 μM RA group (Fig. 3A). Similarly, decreasing RA concentration to 0.01 μM significantly increased Nkx2.2 mRNA levels (4.3 ± 0.4-fold) versus the 2 μM RA group. Hb9 expression levels decreased significantly when the RA concentration was lowered for all concentrations tested compared with the 2 μM RA group (Fig. 3B). Further lowering of RA concentration beyond 0.01 μM did not significantly change Sim1 or Nkx2.2 expression levels. The increase in Sim1 and Nkx2.2 combined with the decrease in Hb9 matched gene expression patterns expected for V3 INs, indicating lowering the concentration of RA did induce further ventralization of our culture.
FIG. 3.
The effect of RA concentration on ventral neural marker gene expression. (A) Sim 1 and Nkx2.2 expression after induction compared to 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA. *P < 0.05 versus 0.1 and 10 μM RA groups. Dotted line denotes upregulation threshold compared to 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA. (B) Hb9 expression after induction compared to 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA. ***P < 0.001 versus all other groups; **P < 0.01 versus 0.0005 and 0.001 μM RA groups; #P < 0.05 versus 0.0005 μM RA group. Dashed line denotes downregulation threshold compared to 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA. (C) RAX expression after 2−/6+ induction compared to 0 μM SAG and 0 nM RA. ^P < 0.05 versus 0 nM RA group. Dashed line denotes downregulation threshold compared to uninduced control.
To test for unwanted rostralization with lower RA levels, gene expression levels of retina and anterior neural fold homeobox (RAX, a hypothalamus marker) were examined using qRT-PCR. We tested the effect of varying the RA concentration from 0 to 10 μM with 0.5 μM SAG using a 2−/6+ induction protocol. All data were compared to the uninduced condition at the same time point to investigate the extent of rostralization for each RA concentration. All conditions showed decreased RAX expression compared with uninduced controls (Fig. 3C, dashed line). Additionally, RAX expression was significantly lower for groups at 0.01 and 0.1 μM RA compared with the groups at 0 μM RA and 0.5 μM SAG. The downregulation of RAX suggests that Sim1 expression was not an indicator of hypothalamus induction in these cultures.
Immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry
To confirm the results observed by qRT-PCR, immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry were used to assess transcription factor expression at the protein level. Nkx2.2 immuno-cytochemistry on intact EBs (Fig. 4A–I) qualitatively suggested an increase in Nkx2.2 mRNA levels with decreasing RA. To quantify this difference, immunocytochemistry was performed on dissociated EBs to see whether p3 and V3 marker expression was increased in induced cultures. Total cell nuclei and nuclei positive for the markers were counted and the percentage of cells positive for the following markers: Nkx2.2, Ngn3, and Uncx was calculated. For all three markers, the percentage of cells positive for the given marker increased when RA concentration was decreased from 2.0 to 0.01 μM RA.
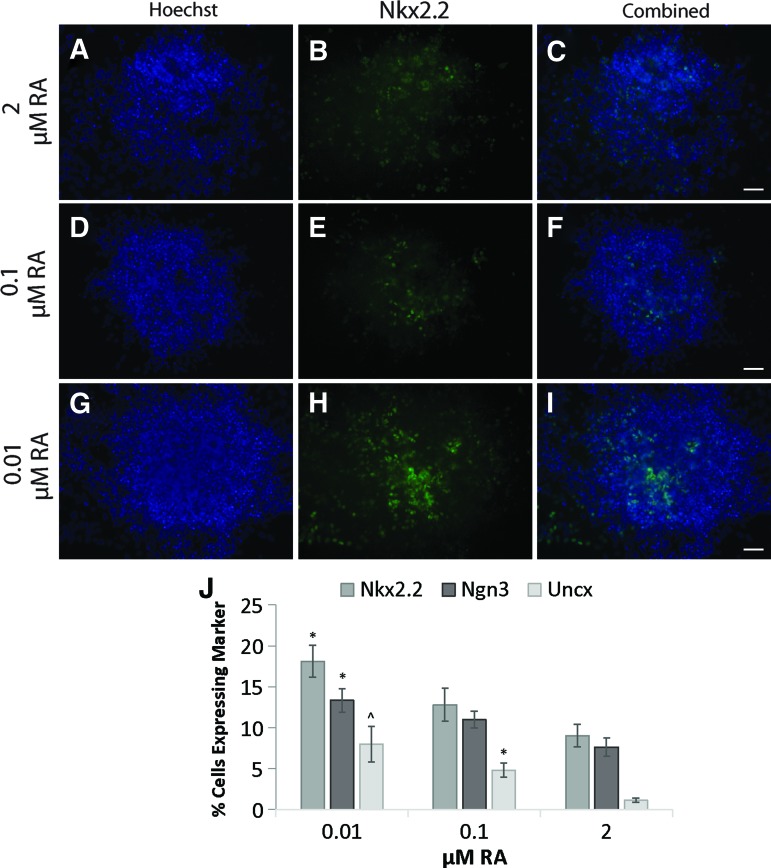
FIG. 4.
The effect of decreasing RA concentration on Nkx2.2 expression by immunocytochemistry. Embryoid bodies (EBs) fixed at the end of 2−/6+ induction with 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA (A–C), 0.1 μM RA (D–F), 0.01 μM RA (G–I). Hoechst nuclear staining (A, D, G), Nkx2.2 antibody staining (B, E, H), and overlay of the two stains (C, F, I) are shown. (J) Quantification of p3 (Nkx2.2 and Ngn3) and V3 (Uncx) marker immunocytochemistry on dissociated EBs plated onto laminin-coated plates. Values given as percentage cells positive for marker. *Significance (P <0.05) compared to 2 μM RA; ^significance (P < 0.05) compared to 0.1 and 2 μM RA. Scale bar = 50 μm. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd
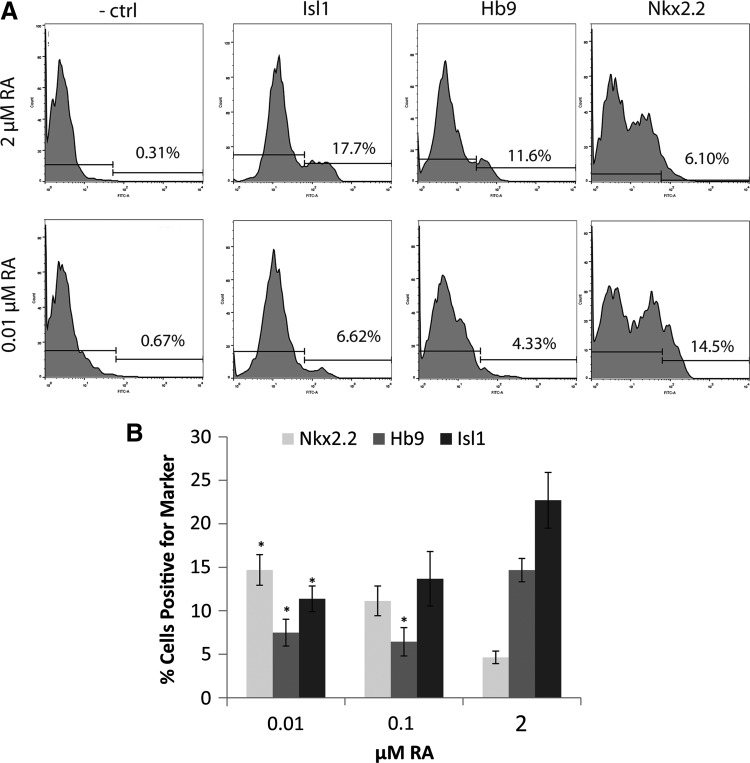
Nkx2.2+ cells increased from 9% to 18%, Uncx+ cells increased from 1% to 8%, and Ngn3+ cells increased from 7% to 13% (Fig. 4J). Similarly, flow cytometry showed the percentage of Nkx2.2+ cells increased with decreasing RA concentration down to 0.01 μM RA (Fig. 5). Groups induced with 0.01 μM RA (and 0.5 μM SAG) using the 2−/6+ induction protocol generated significantly more Nkx2.2+ cells than those induced with 2 μM RA (and 0.5 μM SAG) (Fig. 5C). The percentage of cells positive for MN marker Isl1 also significantly decreased at 0.01 μM RA compared with 2 μM RA (Fig. 5D). The percentage of Hb9+ cells significantly decreased at both 0.01 and 0.1 μM RA compared with 2 μM RA, similar to the low Hb9 mRNA levels seen in Fig. 3B. The decrease in MN marker expression and increase in p3 marker expression corroborated that lowering RA further ventralized the induced neural population.
FIG. 5.
The effects of RA concentration on neuronal marker expression by flow cytometry. Flow cytometry performed on induced EBs after the 2−/6+ induction with 0.5 μM SAG and varying RA concentrations (0.01, 0.1, and 2 μM). (A) Sample gating of flow cytometry for 2 μM RA and 10 nM RA for negative control (secondary antibody only, −ctrl), Nkx2.2, Hb9, and Isl1 stains. Region on left is negative while region on right is positive. (B) Quantification of percentage cells staining positive for Nkx2.2, Hb9, and Isl1 across various RA concentrations. *Significance (P < 0.05) versus compared to 2 μM RA groups.
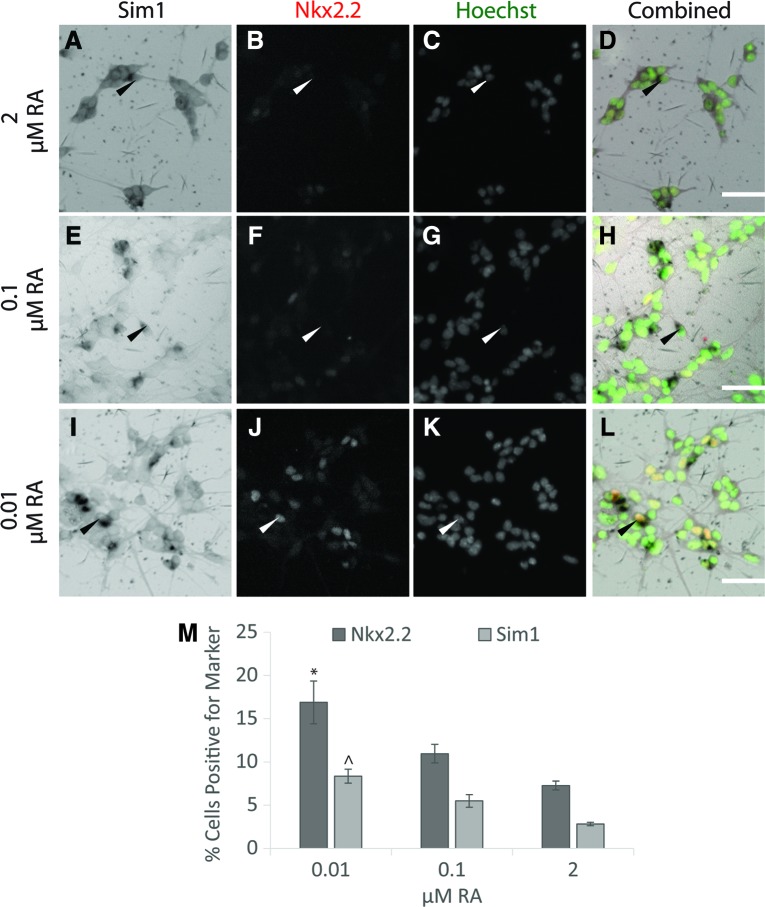
In situ hybridization of Sim1 on EBs
Due to the lack of a specific Sim1 antibody, in situ hybridization was used to confirm the presence of Sim1+ cells. EBs were dissociated after 2−/6+ induction (varying RA from 0.01 to 2 μM and constant 0.5 μM SAG). Performing in situ hybridization for Sim1 showed that lowering the RA concentration resulted in an increase in Sim1+ cells. At 0.01 μM RA, more Sim1+ cells were observed than at 0.1 and 2 μM RA (Fig. 6M). When dissociated EBs were stained with Nkx2.2 antibody after in situ hybridization, Nkx2.2 and Sim1 expression was observed to colocalize (Fig. 6I–L, arrowheads). This observation suggested that the induced cells are spinal V3 INs.
FIG. 6.
Sim1 and Nkx2.2 in dissociated EBs indicated by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Cultures induced with the 2−/6+ protocol with 0.5 μM SAG and 2 μM RA (A–D), 0.1 μM RA (E–H), 0.01 μM RA (I–L) were dissociated and plated and then stained by in situ hybridization for Sim1 and immunocytochemistry for Nkx2.2. Sim1 in situ hybridization (A, E, I), Nkx2.2 antibody staining (B, F, J), Hoechst nuclear staining (C, G, K) and overlay of all three stains with Nkx2.2 false colored as red and Hoechst false colored as green (D, H, L) are shown. Arrowheads mark Sim1+ cells. (M) Quantification of scale bar = 50 μm. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd
Discussion
Commissural glutamatergic V3 INs have been shown to be involved in rhythm regulation in the CPGs [1,28] by helping regulate left-right walking gait and generating robust rhythmic bursting [2,3]. Their role in regulating CPGs makes V3 INs an interesting target for understanding the development of the locomotor pathway and local rewiring after SCI. However, a readily available cell source for isolation of V3 INs in culture would allow greater understanding of their role at a cellular level. In this article we present data on establishing a novel induction protocol for generating V3 INs from mouse ESCs.
Using a previously established 2−/4+ protocol for the induction of MNs from mouse ESCs as a starting point, we explored the effects of varying level and duration of exposure to Shh signaling on p3 and V3 marker expression [8]. Although we hypothesized that increasing both the magnitude and duration of Shh exposure would drive more ventral neural identities, qRT-PCR data indicated that increasing the duration rather than the concentration of Shh signaling agonist appeared to be more effective for induction of V3 INs. While the expectation that lower Shh exposure will result in more dorsal cell types has proven true for V2a and V0 differentiation, it has been observed in our lab that higher concentrations of SAG do not improve MN induction and appear to have a negative effect on EB health. The decreased efficacy of SAG at concentrations higher than 1 μM has been reported at early time points (30 h) [29].
Gli, a downstream target of SAG, was coupled to a luciferase assay and luciferase activity was reported to peak between 0.1 and 1 μM SAG, indicating peak SAG-driven Gli activation occurs somewhere between these values [29]. We surmised the observed decrease in Sim1 expression in our studies at concentrations of 1 μM or greater could be due to toxic effects of high SAG levels. This was confirmed with live–dead quantification of our induced cultures (Fig. 2C). Since SAG efficacy was limited at higher concentrations, an increase in Sim1 expression levels was only observed with increasing SAG exposure time and not concentration.
Because V3 INs are further than MNs from RA-releasing somites along the neural tube [10], we hypothesized that lowering the RA concentration would increase V3 IN differentiation. Our qRT-PCR data showed that decreasing RA concentration not only increased Nkx2.2 and Sim1 gene expression but also decreased Hb9 expression, indicated that lowering RA allows differentiation of more ventral populations. These data were further supported by flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry for Nkx2.2 and Isl1, and in situ hybridization for Sim1. Others have also shown that lowering RA to the 0.001–0.01 μM range increases Nkx2.2 expression [11], which matches with our observations.
While we observed increases in Sim1 expression by qRT-PCR, validation of the induction protocol required the presence of cells with high levels of Sim1 expression. Since a specific Sim1 antibody is not available we used in situ hybridization to confirm that the increase in overall Sim1 expression, as seen in qRT-PCR, can be attributed to some cells with high levels of Sim1 expression and not low levels of Sim1 expression in most cells. When dissociated EBs were stained with Nkx2.2 antibody after in situ hybridization, Nkx2.2 and Sim1 expression was observed to colocalize (Fig. 6I–L, arrowheads). This observation suggested that the induced cells are spinal V3 INs.
Because Sim1 is not uniquely expressed in V3 INs, it was necessary to ensure that the induction protocol did not give rise to other Sim1+ neural populations. One concern with decreasing RA concentration is potential rostralization of the resulting cells. Since Sim1 is also expressed in the hypothalamus [30], we wanted to ensure the cells we obtained were not hypothalamus cells. To this end, the level of gene expression of the hypothalamus marker RAX was measured in the Sim1+ cultures generated in the low RA, high SAG induction protocol. Due to the heterogeneity of induction protocols [8,11,15], if the induced Sim1+ EBs upregulate RAX they could have hypothalamic identity [31–33]. The drastic downregulation of RAX after induction (Fig. 5) suggests that the Sim1+ cells observed in the induced culture are not hypothalamic in nature.
One caveat worth noting is that qRT-PCR experiments report population averaged data. Fold changes of mRNA expression levels are reflective of an average value across the whole experimental population in comparison to a control population. A large increase in expression level in qRT-PCR could represent a large increase in a few cells or a small increase in many cells. While we see a decrease in RAX expression across the whole population, the existence of a rare RAX+ cell cannot be ruled out. Unfortunately, a reliable antibody for RAX does not exist and thus population averaged experiments are the most direct way to quantify the extent of RAX expression.
This study establishes a novel induction protocol for inducing V3 INs from mouse ESCs by demonstrating successful differentiation of Sim1+, nonhypothalamic cells in cultures that also express the p3 progenitor marker Nkx2.2. A scarce population of V3 INs exists in the developing spinal cord, totaling ∼10% of the four ventral spinal cell types, making dissection tedious and expensive. The duration and potentially scalable nature of this protocol make our method an easier, cheaper, and faster way to obtain V3 INs than dissection. Based on the Uncx and Sim1 staining, about 8% of the induced cells are V3 INs.
One 100 mm Petri-dish of induced 2−/6+ EBs has about 21 million cells. This means about 1.6 million V3 INs can be obtained from one induction culture on this small bench scale, which would generally be sufficient for a rodent transplantation study. This work paves the way for future transgenic drug-selectable or lineage tracing cell lines to better understand the role of V3 INs in the spinal cord. Additionally, this protocol for V3 IN induction could potentially be adapted for human ESCs or induced pluripotent stem cells, much as the MN differentiation protocols from mouse ESCs have been adapted for these human cell types [34,35]. This method to generate Sim1+ cells can serve as a cell source for future studies exploring the role of V3 INs in CPGs and SCI therapy.
Acknowledgments
The authors were funded by the NIH RO1 grant nos. R01NS051454 and R01NS051454. The authors acknowledge Dr. Paul Gray for help and guidance on in situ hybridization techniques. The authors also acknowledge Sara Oswald for technical assistance. The authors would also like to thank the Washington University in St. Louis Medical School Pathology Department Flow Cytometry Core, and Nisha Iyer for assistance in flow cytometry.
Author Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
References
- 1.Arber S. (2012). Motor circuits in action: specification, connectivity, and function. Neuron 74:975–989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Borowska J, Jones CT, Zhang H, Blacklaws J, Goulding M. and Zhang Y. (2013). Functional subpopulations of V3 interneurons in the mature mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci 33:18553–18565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang Y, Narayan S, Geiman E, Lanuza GM, Velasquez T, Shanks B, Akay T, Dyck J, Pearson K, et al. (2008). V3 spinal neurons establish a robust and balanced locomotor rhythm during walking. Neuron 60:84–96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Briscoe J, Sussel L, Serup P, Hartigan-O'Connor D, Jessell TM, Rubenstein JL. and Ericson J. (1999). Homeobox gene Nkx2.2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature 398:622–627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alaynick WA, Jessell TM. and Pfaff SL. (2011). SnapShot: spinal cord development. Cell 146:178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blacklaws J, Deska-Gauthier D, Jones CT, Petracca YL, Liu M, Zhang H, Fawcett JP, Glover JC, Lanuza GM. and Zhang Y. (2015). Sim1 is required for the migration and axonal projections of V3 interneurons in the developing mouse spinal cord. Dev Neurobiol [Epub ahead of print]; DOI: 10.1002/dneu.22266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mansouri A, Voss AK, Thomas T, Yokota Y. and Gruss P. (2000). Uncx4.1 is required for the formation of the pedicles and proximal ribs and acts upstream of Pax9. Development 127:2251–2258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wichterle H, Lieberam I, Porter JA. and Jessell TM. (2002). Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 110:385–397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brown CR, Butts JC, McCreedy DA. and Sakiyama-Elbert SE. (2014). Generation of V2a interneurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 23:1765–1776 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maden M. (2006). Retinoids and spinal cord development. J Neurobiol 66:726–738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Okada Y, Shimazaki T, Sobue G. and Okano H. (2004). Retinoic-acid-concentration-dependent acquisition of neural cell identity during in vitro differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Dev Biol 275:124–142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ericson J, Morton S, Kawakami A, Roelink H. and Jessell TM. (1996). Two critical periods of sonic hedgehog signaling required for the specification of motor neuron identity. Cell 87:661–673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ericson J, Briscoe J, Rashbass P, van Heyningen V. and Jessell TM. (1997). Graded sonic hedgehog signaling and the specification of cell fate in the ventral neural tube. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 62:451–466 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ericson J, Rashbass P, Schedl A, Brenner-Morton S, Kawakami A, van Heyningen V, Jessell TM. and Briscoe J. (1997). Pax6 controls progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in response to graded Shh signaling. Cell 90:169–180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim M, Habiba A, Doherty JM, Mills JC, Mercer RW. and Huettner JE. (2009). Regulation of mouse embryonic stem cell neural differentiation by retinoic acid. Dev Biol 328:456–471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wichterle H. and Peljto M. (2008). Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells to spinal motor neurons. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol Chapter 1:Unit 1H.1.1–1H.1.9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ribes V. and Briscoe J. (2009). Establishing and interpreting graded sonic hedgehog signaling during vertebrate neural tube patterning: the role of negative feedback. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a002014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stamataki D, Ulloa F, Tsoni SV, Mynett A. and Briscoe J. (2005). A gradient of Gli activity mediates graded sonic hedgehog signaling in the neural tube. Genes Dev 19:626–641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dessaud E, McMahon AP. and Briscoe J. (2008). Pattern formation in the vertebrate neural tube: a sonic hedgehog morphogen-regulated transcriptional network. Development 135:2489–2503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lek M, Dias JM, Marklund U, Uhde CW, Kurdija S, Lei Q, Sussel L, Rubenstein JL, Matise MP, et al. (2010). A homeodomain feedback circuit underlies step-function interpretation of a Shh morphogen gradient during ventral neural patterning. Development 137:4051–4060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ribes V, Balaskas N, Sasai N, Cruz C, Dessaud E, Cayuso J, Tozer S, Yang LL, Novitch B, Marti E. and Briscoe J. (2010). Distinct sonic hedgehog signaling dynamics specify floor plate and ventral neuronal progenitors in the vertebrate neural tube. Genes Dev 24:1186–1200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dessaud E, Ribes V, Balaskas N, Yang LL, Pierani A, Kicheva A, Novitch BG, Briscoe J. and Sasai N. (2010). Dynamic assignment and maintenance of positional identity in the ventral neural tube by the morphogen sonic hedgehog. PLoS Biol 8:e1000382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McCreedy DA, Rieger CR, Gottlieb DI. and Sakiyama-Elbert SE. (2012). Transgenic enrichment of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived progenitor motor neurons. Stem Cell Res 8:368–378 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schmittgen TD. and Livak KJ. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gray PA, Fu H, Luo P, Zhao Q, Yu J, Ferrari A, Tenzen T, Yuk DI, Tsung EF, et al. (2004). Mouse brain organization revealed through direct genome-scale TF expression analysis. Science 306:2255–2257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gray PA. (2013). Transcription factors define the neuroanatomical organization of the medullary reticular formation. Front Neuroanat 7:7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.VanDunk C, Hunter LA. and Gray PA. (2011). Development, maturation, and necessity of transcription factors in the mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Neurosci 31:6457–6467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stepien AE. and Arber S. (2008). Probing the locomotor conundrum: descending the ‘V’ interneuron ladder. Neuron 60:1–4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen JK, Taipale J, Young KE, Maiti T. and Beachy PA. (2002). Small molecule modulation of smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:14071–14076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Holder JL, Jr., Butte NF. and Zinn AR. (2000). Profound obesity associated with a balanced translocation that disrupts the SIM1 gene. Hum Mol Genet 9:101–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Furukawa T, Kozak CA. and Cepko CL. (1997). Rax, a novel paired-type homeobox gene, shows expression in the anterior neural fold and developing retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:3088–3093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shimogori T, Lee DA, Miranda-Angulo A, Yang Y, Wang H, Jiang L, Yoshida AC, Kataoka A, Mashiko H, et al. (2010). A genomic atlas of mouse hypothalamic development. Nat Neurosci 13:767–775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lu FQ, Kar D, Gruenig N, Zhang ZW, Cousins N, Rodgers HM, Swindell EC, Jamrich M, Schuurmans C, Mathers PH. and Kurrasch DM. (2013). Rax is a selector gene for mediobasal hypothalamic cell types. J Neurosci 33:259–272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li XJ, Hu BY, Jones SA, Zhang YS, Lavaute T, Du ZW. and Zhang SC. (2008). Directed differentiation of ventral spinal progenitors and motor neurons from human embryonic stem cells by small molecules. Stem Cells 26:886–893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li XJ, Du ZW, Zarnowska ED, Pankratz M, Hansen LO, Pearce RA. and Zhang SC. (2005). Specification of motoneurons from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 23:215–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]