Abstract
The immunogenicity of malignant cells has recently been acknowledged as a critical determinant of efficacy in cancer therapy. Thus, besides developing direct immunostimulatory regimens, including dendritic cell-based vaccines, checkpoint-blocking therapies, and adoptive T-cell transfer, researchers have started to focus on the overall immunobiology of neoplastic cells. It is now clear that cancer cells can succumb to some anticancer therapies by undergoing a peculiar form of cell death that is characterized by an increased immunogenic potential, owing to the emission of the so-called “damage-associated molecular patterns” (DAMPs). The emission of DAMPs and other immunostimulatory factors by cells succumbing to immunogenic cell death (ICD) favors the establishment of a productive interface with the immune system. This results in the elicitation of tumor-targeting immune responses associated with the elimination of residual, treatment-resistant cancer cells, as well as with the establishment of immunological memory. Although ICD has been characterized with increased precision since its discovery, several questions remain to be addressed. Here, we summarize and tabulate the main molecular, immunological, preclinical, and clinical aspects of ICD, in an attempt to capture the essence of this phenomenon, and identify future challenges for this rapidly expanding field of investigation.
Keywords: anti-tumor immunity, immunogenicity, immunotherapy, molecular medicine, oncoimmunology, patient prognosis, translational medicine
Introduction and Historical Background
Augmenting the immunogenicity of cancer cells to improve the efficacy of cancer therapy is a paradigm that has gained significant momentum over the past 5 years (1–5). Researchers have realized that besides therapeutically exploiting innate or adaptive immune cells directly (e.g., through dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccines or adoptive T-cell transfer) and/or improving the effector functions of T cells (through checkpoint-blocking therapies), cancer cells also need to be made immunogenic (1, 4, 6, 7). This has diverted attention toward studying the interface between stressed or dying cancer cells and the immune system, in the hope of efficiently exploiting it for therapeutic purposes (1).
Early indications regarding immune system-driven tumor control emerged in the eighteenth century, when feverish infections in cancer patients were circumstantially associated with tumor remission (8). The first evidence that immunotherapy can be applied to achieve tumor regression emerged from the work of William Coley, who in the 1890s achieved tumor regression in some sarcoma/lymphoma patients upon the intra-tumoral injection of streptococcal cultures (provided by Robert Koch) (8, 9). In the following 43 years, Coley injected nearly 900 (mostly sarcoma) patients with his bacterial preparation (achieving a cure rate >10%), which later became known as “Coley’s toxin” (8, 10). However, the Coley’s toxin came under intense scrutiny owing to an elevated toxicity and some difficulties in reproducing remission rates (8). Eventually, the first experimental evidence that virus-unrelated tumors can indeed be recognized by the host immune system emerged in the 1940s, and by the 1960s, coupled with the discovery of T cells, it was proposed that the human immune system may also react against tumors (11). The ability of anticancer therapies to enhance the immunogenic potential of malignant cells gained some appreciation by the 1970s (12–14). It was recognized that if specific treatments are applied (e.g., radiotherapy, the bacillus Calmette–Guerin, or some chemotherapeutics), the immunogenicity of malignant cells increases enough to induce durable anti-tumor immunity (12–14). By the 1980s, researchers started to report more specific observations regarding the therapeutic impact of cancer cell immunogenicity, e.g., the ability of curative hyperthermia to cause the (heat-shock based) generation of circumstantial anti-tumor immunity (15), the fact that the immunogenicity of cancer cells influences patient prognosis after radiotherapy (16), and the increase in tumor immunogenicity due to hydrostatic pressure (17). However, these early studies (especially those published before the 1980s) had several issues linked to a lack in consensus. For instance, due to early controversies on the existence of tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) (11), the target of tumor-specific immune responses was unclear, and the mechanism of action of some therapies came under scrutiny. Moreover, such therapies could operate by directly modulating immune effector cells rather than improving the immunogenic potential of tumors (18). In particular, the death of cancer cells exposed to therapy was never suspected to drive anti-tumor immunity, since it was considered to be a relatively “silent” process in terms of immunogenicity (19). Moreover, the classical “self/non-self” theory was unable to explain the possibility that dying cancer cells could elicit an immune response (20).
By the early 1990s, the molecular characterization of mice and human TAAs clarified the entities targeted by anti-tumor immune responses (11). Similarly, the so-called “danger theory” started to emerge, challenging the classical model of “self/non-self” immune recognition, especially in a diseased or damaged tissue (20, 21). This model proposed that the immune recognition is not restricted to “non-self” entities, but rather discriminates between “dangerous” and “safe” entities, irrespective of source (20–22). Indeed, “dangerous” entities include pathogens as well as injured, infected, diseased and necrotic tissues, or cells undergoing non-physiological cell death which emit danger signals (or alarmins) with pro-inflammatory activity (21, 22). These danger signals are now collectively referred to as “damage-associated molecular patterns” (DAMPs) (23). DAMPs are endogenous molecules that are concealed intracellularly in normal conditions, but are exposed or released upon stress, injury, cell death, thereby becoming able to bind cognate receptors on immune cells (3, 24–27). Table 1 summarizes the most prominent DAMPs characterized to date and their mode of emission, the cell death pathway they are associated with, and their known cognate receptors. It is important to consider that not all DAMPs may act as immunogenic danger signals. Several DAMPs exist that are crucial for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis, and the avoidance of auto-immune responses, as they exert immunosuppressive effects, including phosphatidylserine (PS), annexin A1 (ANXA1), death domain 1α (DD1α), B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL2) and some extracellular matrix-derived molecules (Table 1). Accordingly, the blockade of these anti-inflammatory DAMPs accentuates the immunogenic potential of dying cells, or renders immunogenic otherwise tolerogenic forms of cell death (28, 29). Moreover, some danger signals are not always involved in the immunogenicity of cell death, but act as “bystanders.” This is the case for heat shock protein 90 kDa alpha (cytosolic), class A member 1 (HSP90AA1, best known as HSP90) exposed on the cell surface after melphalan treatment (30). Last (but not least), several DAMPs may be subjected to post-translational modifications (e.g., oxidation, reduction, citrullination) that may potentially neutralize, increase, or change their immunogenic properties (31, 32) – a process that is still incompletely understood.
Table 1.
A list of prominent damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) associated with cell death pathways or extracellular matrix.
| DAMPs | Localization and mode-of-emission | Relevant cell death pathway | Receptors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annexin A1 | Surface exposed or actively/passively released? | Apoptosis | FPR-1 receptor | (33) |
| Adenosine triphosphate | Actively or passively released | ICD, apoptosis/secondary necrosis and necrosis | P2Y2 and P2×7 | (34–37) |
| B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 | Passive release | Necrosis | TLR2 | (38) |
| Biglycan | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR2, TLR4, P2×4, and P2×7 | (39, 40) |
| Calreticulin | Mostly surface exposed; sometimes passively released | ICD | CD91 | (35, 41–44) |
| Cardiolipin | Surface exposed? | Apoptosis | ? | (45, 46) |
| Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate | Surface exposed | Apoptosis | ? | (47) |
| Covalent/cross-linked dimer of ribosomal protein S19 | Passively released? | Apoptosis | CD88 | (48–51) |
| Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 | ? | ? | ? | (52) |
| Cyclophilin A | Passive release | Necrosis | CD147 | (53) |
| Cytochrome c | Passively released? | Secondary necrosis and necrosis? | LPG? | (54, 55) |
| Death domain 1α | Surface exposed | Apoptosis | DD1α | (56) |
| Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II | Passively released? | Apoptosis | CXCR3? | (50, 57, 58) |
| F-actin | Passive release | Necrosis | DNGR-1/Clec9a | (59) |
| Fibrinogen | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR4 | (40) |
| Fibronectin extra domain A | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR4? | (40) |
| Fragments of human tyrosyl tRNA synthetase | Passively released? | Apoptosis | ? | (50) |
| Genomic DNA, mRNA, snRNPs | Passive release | Necrosis | TLR3 | (3, 60, 61) |
| GRP78/BiP | Passive release | Necrosis, apoptosis? | ? | (31) |
| H202 | ? | Apoptosis | ? | (62) |
| Heat shock proteins (HSP70, HSP90, HSP60, HSP72, and GP96) | Surface exposure, active secretion, or passive release | ICD, apoptosis/secondary necrosis, necrosis | CD91, TLR2, TLR4, SREC-1 and FEEL-1 | (63–67) |
| Heparan sulfate fragments | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR4 | (40) |
| Hepatoma-derived growth factor | Passively released | Necrosis | ? | (68) |
| Histones | Passively released | Necrosis | TLR-9 | (69) |
| High-mobility group box 1 | Mostly passively released; sometimes actively released | ICD, secondary necrosis and necrosis | TLR2, TLR4, RAGE and TIM3 | (70–73) |
| High-mobility group nucleosome binding domain 1 | Passive release | Necrosis | TLR4 | (74) |
| Hyaluronan | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR2 and TLR4 | (40) |
| IL-1α | Passive release | Necrosis | IL-1R | (75) |
| IL-33 | Passive release | Necrosis | ST2 | (3, 61) |
| IL-6 | Passive release | Necrosis | IL-6R and GP130 | (76) |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine | Passively released? | Apoptosis | G2A | (50, 77) |
| Mit DNA | Passively released | Necrosis | TLR-9 | (78–80) |
| Monosodium urate or uric acid | Passively released | Necrosis | Purinergic receptors | (50, 81) |
| N-formylated peptides | Passively released | Necrosis | FPR-1 | (78, 82–84) |
| Oxidation-associated molecular patterns (reactive protein carbonyls, per-oxidized phospholipids, oxidized low-density lipoprotein) | Passively released | Necrosis, Secondary necrosis | CD36, SR-A, TLR-2/4, CD14 | (85–87) |
| Peroxiredoxin 1 | Actively secreted or passively released | Apoptosis, necrosis | TLR4 | (88) |
| Phosphatidylserine | Actively externalized on the surface | Apoptosis | TIM-1/-3/-4, BAI1, Stabilin-2, MFG-E8, C1q | (56, 89–93) |
| S100/calgranulin protein family members (S100A8, S100A9, S100A12/EN-RAGE) | Passively released | Necrosis | RAGE | (50, 94) |
| Tenascin-C | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR4? | (95) |
| Thrombospondin 1 and its heparin-binding domain | Passively released or surface associated | Apoptosis | αvβ3 integrin | (50, 96) |
| Versican | Extracellular matrix | – | TLR2, TLR6, and CD14 | (40) |
CD, cluster of differentiation; CLEC9A, C-type lectin domain family 9, member A; CPS-1, carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1, mitochondrial; CXCR3, C-X-C motif receptor 3; FEEL-1/CLEVER-1, fasciclin EGF-like/common lymphatic endothelial and vascular endothelial receptor-1; FPR-1, formyl peptides receptor-1; G2A, G2 accumulation; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; HSP, heat shock proteins; ICD, immunogenic cell death; IL, interleukin; LPG, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein-1; MFG-E8, milk fat globule-egf factor 8 protein; Mit DNA, mitochondrial DNA; P2XR, P2X receptor; P2YR, P2Y receptor; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation endproducts; SREC-1, scavenger receptor class f member 1; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; TIM, transmembrane immunoglobulin and mucin domain; TLR, toll-like receptor(s).
Glossary (5, 19, 97): (1) Necrosis: primary necrosis is a form of cell death that can occur in a regulated or accidental manner, characterized by cellular swelling and rapid breakdown of the plasma membrane; (2) Necroptosis: necroptosis is a form of regulated cell death (RCD) manifesting with necrotic morphology and controlled by a signaling cascade involving (among other proteins) RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL; (3) Apoptosis: apoptosis is a form of RCD largely dependent on caspases activity and morphologically characterized by cell shrinkage, membrane blebbing, formation of apoptotic bodies, chromatin condensation, and systematic DNA fragmentation; (4) Secondary Necrosis: Secondary necrosis is a terminal process experienced by late-apoptotic cells if they are not cleared by phagocytes in time, and is characterized by general spill-over of apoptotic cellular contents.
“?” Unclear or not determined yet.
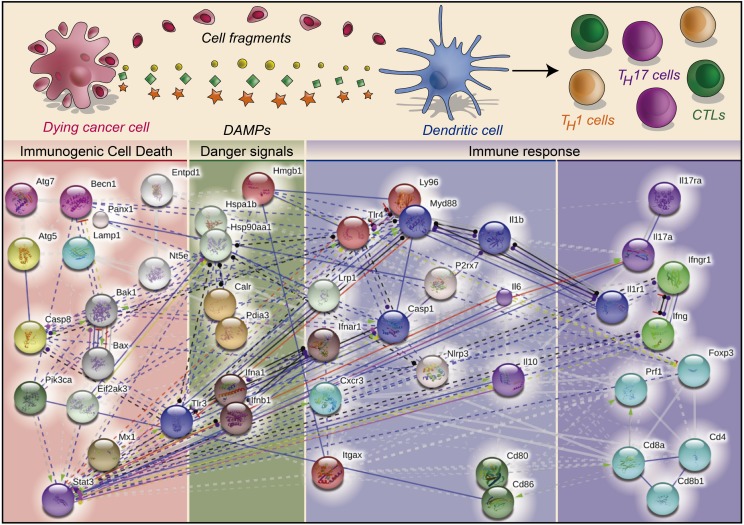
Despite these advances, the overall role of regulated cell death (RCD) (97) in augmenting cancer immunogenicity remained obscure. Initial observations involving the immunogenicity of cell death in the efficacy of cancer therapy were published between 1998 and 2004, when it was proposed that the non-apoptotic demise of malignant cells (within the context of the so-called “immunogenic death”) could be associated with the emission of the danger signal heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A (HSPA1A, best known as HSP70) (Table 1), enhancing the immunogenic potential of dying cancer cells in vivo (98, 99). The dogmatic view that only necrotic or non-apoptotic (as postulated by the “immunogenic death” concept) cancer cells are characterized by an elevated immunogenic potential started to be questioned by a series of studies published between 2005 and 2007 (41, 70, 100, 101). These publications outlined that cancer cells undergoing apoptosis in response to specific anticancer therapies are immunogenic [a subroutine termed immunogenic cell death (ICD)], as long as they emit precise DAMPs in a spatiotemporally defined fashion (26, 102, 103). Cells succumbing to ICD are sufficient for the elicitation of durable anti-tumor immune responses (1, 26, 53, 102, 104). ICD is indeed paralleled by the redirection and emission of DAMPs, owing to the stimulation of distinct danger signaling pathways occurring in synchrony with cell death signaling (103). Table 2 summarizes the main signaling pathways that play a role in the trafficking and emission of DAMPs. ICD-associated DAMPs and other immunostimulatory factors released by cells destined to undergo ICD favor the establishment of a productive interface between dying cancer cells and innate immune cells (like DCs or macrophages), thereby leading to the initiation of a therapeutically relevant adaptive immune response (Figure 1) (102, 105). In some contexts, DAMPs may regulate the function of specific innate immune cell subsets, e.g., following anthracycline treatment, extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) assists in recruitment and differentiation of CD11c+Cd11b+Ly6Chigh cells into CD11c+CD86+MHCII+ DCs (106); similarly, necrosis associated F-actin exposure activates an immune response by directing the dead cell debris to specifically CD8α+ DCs (59, 107). Indeed, DCs and other antigen-presenting cells exposed to cancer cells succumbing to ICD can then prime CD4+ T cells (and polarize them into TH1, TH17, or TH1/TH17-like phenotype), CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and γδ T lymphocytes against one or several TAAs (Figure 1) (102). Of note, residual cancer cells that survive ICD inducers can also show some enduring immunogenic characteristics that make them susceptible to immunological control by CTLs (108–110).
Table 2.
Danger signaling pathways characterized as traffickers of DAMPs.
| DAMPs | Role of ROS | Role of ER stress | Role of autophagy | Role of chaperone-mediated autophagy | Role of secretory pathway | Caspase activity | Role of lysosomes | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secreted ATP | + | +/0 | +/0 | 0 | +/0 | + | +/0 | Underlying pathway is highly inducer dependent | (34, 35, 111–113) |
| Released HMGB1 | 0 | 0 | + | ? | 0 | – | ? | Mostly released passively on account of necrosis; only DT-EGF reported to cause active secretion so far | (73, 114, 115) |
| Secreted or surface HSP70 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | + | + | ABC transporters help in endolysosomal-secretion; HSP70 has also been reported to be secreted in an exosome surface-bound format | (116–122) |
| Surface CRT | + | + | −/0 | + | + | +/0 | ? | LRP1/lipid rafts mediate surface tethering; components that positively regulate surface-CRT in an inducer-dependent fashion: ERp57, PI3K p110α, BAX/BAK, cytosolic ER-Ca2+, BAP31; of note, anthracycline-induced pathway of surface CRT induction has been found to be conserved from yeast to mammals | (34, 35, 111, 112, 116, 123, 124) |
| Surface HSP90 | + | + | – | ? | + | + | ? | – | (30, 125) |
“+” denotes ability to positively regulate trafficking; “−” denotes ability to negatively regulate trafficking; “0” denotes confirmation of no role in regulation of trafficking and “?” denotes that the role in regulating the trafficking is unknown; “+/0” denotes positive or no role in regulation of trafficking in an inducer-dependent fashion; “−/0” denotes negative or no role in regulation of trafficking in an inducer-dependent fashion.
ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CRT, calreticulin; DT-EGF, epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted diphtheria toxin; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1 protein; HSP, heat shock protein; LRP1, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Figure 1.
The molecular complexity of immunogenic cell death in cancer. Cancer cells undergoing immunogenic cell death (ICD) emit danger signals for establishing a productive interface with components of the host immune system, including dendritic cells (DCs). DCs exposed to cancer cells succumbing to ICD “prime” the adaptive arm of the immune system, consisting of various effector T-cell populations, which in turn targets therapy-resistant cancer cells. Various molecules are critical for the execution of these processes. The molecular network of ICD-relevant proteins was build using the STRING modeling database (http://string-db.org/) (126).
Immunogenic Cell Death Inducers
Over the past few years, a number of single-agent ICD inducers have been discovered, encompassing conventional chemotherapeutics, targeted anticancer agents and various other biological and physicochemical therapies (18, 102, 104, 127). Table 3 summarizes single-agent ICD inducers characterized so far, as per consensus guidelines (104), and the spectra of DAMPs and other immunostimulatory signals associated with them. For combinatorial therapeutic strategies capable of achieving ICD, readers may want to refer to other recent publications (18, 128, 129). It is clear that a general structure–function relationship capable of clustering all existing ICD inducers and predicting new ones does not exist (130), an issue that makes discovering new ICD-inducing therapies based on cheminformatic analyses challenging, if not impossible. A peculiar characteristic of most, if not all, ICD inducers is their ability to induce reactive oxygen species (ROS)-based/associated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, as first delineated for anthracyclines (30, 34, 35, 42, 123, 131–133). This peculiarity was exploited for the targeted discovery of hypericin-based photodynamic therapy (Hyp-PDT) – a therapeutic modality that can trigger ICD through the induction of ROS that target the ER (35, 116, 134). Along with an ever more precise characterization of the links between ROS, ER stress, and ICD induction (135, 136), it became clear that the more “focused” ER stress is, the higher the probability of inducing ICD (3, 26, 53, 137). These observations paved way for a classification system based on how ICD inducers engage ER stress for cell death and danger signaling (3, 26, 53, 138). Based on this classification, Type I ICD inducers are defined as anticancer agents that act on non-ER proteins for the induction of cell death, but promote collateral ER stress for danger signaling, thereby operating on multiple targets (3, 26, 53), while Type II ICD inducers are anticancer agents that target the ER for both cell death induction and danger signaling (3, 26, 53). Table 4 summarizes the classification of current ICD inducers into Type I and Type II, and their cell death/danger signaling targets. Such a classification suggest that while Type I ICD inducers can be discovered through various approaches (e.g., DAMP-based drug screening platforms) (130, 139), putative Type II ICD inducers can be characterized rapidly on the basis of their ability to selectively or predominantly target the ER. Recent findings comforted the purpose and usefulness of this classification system, as two novel Type II ICD inducers [i.e., PtII N-heterocyclic carbene complex (140) and Newcastle disease virotherapy (NDV) (43)] were identified based on the notion that they induce predominant ROS-based ER stress (138). Nevertheless, as more ICD inducers and features are discovered, this classification system is expected to evolve or be substituted by a more refined one.
Table 3.
A list of prominent single-agent immunogenic cell death (ICD) inducers in cancer and their specific associations with danger signaling and other immunostimulatory signaling.
| ICD inducers | Associated ICD-relevant DAMPs |
Other immunostimulatory activities or danger signals and other comments on immunomodulatory activity | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAMP | Stage of cell death | |||
| Anthracyclines (epirubicin, doxorubicin, idarubicin, mitoxantrone), oxaliplatin, UVC radiation and radiotherapy | Surface CRT Surface HSP70 Secreted ATP Released HMGB1 |
Pre-apoptotic Mid-apoptotic Early/mid-apoptotic Post-apoptotic |
Activation of Type I IFN response comprising MX-1 centered signature, consisting of IFN-α/β and CXCL10; surface exposure of mannose-6-phopshate receptor, which enables better interface with CTLs and facilitates GZMB-mediated cell death; radiotherapy is known to increase expression levels of various antigens in number of cancer models as well as induce “abscopal effect” in both preclinical and clinical models; overall CALR levels were predictive of prolonged OS in radiotherapy-treated lung cancer patients | (26, 42, 102, 127, 141–144) |
| Anti-EGFR antibody – 7A7 | Surface CRT | Pre-apoptotic | – | (145) |
| Surface HSP70 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Surface HSP90 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Bleomycin | Surface CRT | Mid/post-apoptotic | Induces ambivalent immune response, i.e., all valid ICD markers but also increased Treg differentiation and, thus, a good candidate for anti-Treg combinatorial therapy | (146) |
| Secreted ATP | Mid/post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Bortezomib | Surface HSP90 | Early/mid-apoptotic | – | (26, 66, 100, 127) |
| Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Surface HSP70 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Oncolytic Adenovirus | Surface CRT | ? | Immunogenicity of these viruses can be further increased by producing transgenic versions producing CD40L or GM-CSF | (147, 148) |
| Released ATP | ||||
| Released HMGB1 | ||||
| Clostridium difficile toxin B | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | – | (149) |
| Released ATP | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HSP70/90 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3)# | Surface CRT | Early-apoptotic | – | (150, 151) |
| Secreted ATP | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Cyclophosphamide | Surface CRT | Pre-apoptotic | Facilitates an interface between gut microbiota (leaked due to gut perforation) and host immune system thereby allowing Th17 cells-dependent anti-tumor immune responses; cyclophosphamide’s effects on anti-tumor immunity are strongly dose dependent. High doses of this chemotherapeutic can be immunosuppressive yet low or metronomic doses facilitate anti-tumor immunity through targeted depletion of Tregs/MDSCs. In ICD set-up, a low dose (100 mg/kg in mice) of cyclophosphamide was shown to exert anti-tumor immunity | (18, 152, 153) |
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| High hydrostatic pressure | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | – | (154–156) |
| Surface HSP70 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Surface HSP90 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Secreted ATP | Mid/post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Mid/post-apoptotic | |||
| Hypericin-based PDT | Surface CRT | Pre-apoptotic | High accumulation of OAMPs like protein carbonyls; down-regulates CD47; induces up-regulation of various molecules associated with Type I IFN response (IRF7, IRF1, OASL, IL18, CXCL2, IL15, IL8) but not IFN-α secretion | (26, 30, 34, 35, 112, 116, 157) |
| Surface HSP70 | Pre-apoptotic | |||
| Surface HSP90 | Pre-apoptotic | |||
| Secreted ATP | Pre-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HSP70/90 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released CRT | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Microwave thermal ablation | Surface CRT | ? | – | (158) |
| Secreted ATP | ||||
| Released HMGB1 | ||||
| Newcastle disease virus (NDV) | Surface CRT | Early/mid-necroptotic | Increases expression levels of PMEL17 antigen in glioma cells; NDV treatment has also been shown to induce “abscopal effect” in a murine melanoma model | (43, 159) |
| Released HMGB1 | Post-necroptotic | |||
| Paclitaxel | Surface CRT Released HMGB1 |
Early/mid-apoptotic Post-apoptotic |
Overall CALR levels were predictive of prolonged OS or PFS in paclitaxel-treated ovarian cancer patients thereby establishing clinical validity of ICD in paclitaxel treatment set-up; paclitaxel has also been reported to enhance overall antigen levels | (42, 144, 160) |
| Patupilone | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | – | (128) |
| Photofrin-based PDT | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | The only anticancer modality for which a comparison between DAMPs induced by in vitro versus in vivo treatment was carried out – however, none of ICD-related DAMPs were tested | (47, 161–164) |
| Surface HSP70/60 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Surface ceramide | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Surface S1P | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| PtII N-heterocyclic carbene complex | Surface CRT | Pre-apoptotic | – | (140) |
| Released ATP | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| RIG-I-like helicases (RLH) ligand | Surface CRT | Early-apoptotic | Induces Type I IFN response | (165) |
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HSP70 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Septacidin | Surface CRT | Pre-apoptotic | – | (139) |
| Secreted ATP | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Shikonin | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | Also, causes surface exposure of GRP78 a prominent inducer of pro-tumorigenic effects; enhances overall cancer antigen levels | (160) |
| Surface HSP70 | Early/mid-apoptotic | |||
| Vorinostat | Surface CRT | Early/mid-apoptotic | – | (166) |
| Secreted ATP | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Wogonin | Surface CRT | Early-apoptotic | Surface-Annexin A1 is also induced by wogonin. In an ICD set-up, the role of Annexin A1 is not clear since it is a noted anti-inflammatory factor | (167) |
| Released ATP | Post-apoptotic | |||
| Released HMGB1 | Post-apoptotic | |||
CRT or CALR, calreticulin; CTLs, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GZMB, granzyme B; HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1 protein; HSP, heat shock protein; ICD, immunogenic cell death; IFN, interferon; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; OAMPs, oxidation-associated molecular patterns; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
Important note: It is worth noting that recently various promising candidate therapies have emerged that induce in vitro DAMPs relevant for ICD, e.g., Rose Bengal-based PDT (168), Docosahexaenoic acid (169), and Capsaicin (170, 171). Such agents may emerge as potent inducers of ICD in future, however, in order to establish them as inducers of ICD-like immunogenicity, it is imperative to confirm their (i.e., cancer cells treated with these agents) ability to stimulate T cells (in vitro or in vivo) and/or induce anti-cancer vaccination effect, in vivo, as per the consensus guidelines (104).
Glossary: In the current setting, it is crucial to differentiate between the meanings of the words, “immunogenic” and “immunogenicity” as they are not supposed to have inter-changeable meanings. Immunogenic, derives from the word immunogen, which refers to any substance that can elicit an immune response; this includes, whole cells or organisms (eukaryotic or prokaryotic), specific cellular entities or specific proteins (e.g., antigens) (172). On the other hand, immunogenicity is a much more specific terms that is closer to antigenicity in operational sense, since it refers to the ability of a specific entity (e.g., an antigen or an epitope) to be recognized by the immune system through binding interactions with T or B cells, which may or may not result in an overt immunological response (4, 11).
“?” Unclear or not determined yet.
“#” Unconfirmed anti-tumour immune responses in adaptive immune system-competent.
Table 4.
Classification of ICD inducers into Type I and Type II based on their ER or non-ER-targeting modus operandi.
| ICD inducer | Site of Cell-death inducing effects | Site of danger signaling induction | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I inducers – agents that induce icd through a “collateral” er stress effect | |||
| Anthracyclines (epirubicin, doxorubicin, idarubicin, mitoxantrone), oxaliplatin, UVC radiation and radiotherapy | Nucleus (DNA or the DNA replication machinery proteins) | ER, autophagy, pannexin channels, lysosomes | (36, 41, 70, 111, 130, 173, 174) |
| Anti-EGFR antibody – 7A7 | Cell surface (epidermal growth factor receptor or EGFR) | ER | (145) |
| Bleomycin | Nucleus (causes DNA strand-breaks) | ER? | (146) |
| Bortezomib | Cytosol (26S proteasome or ERAD machinery; CIP2A/cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A) | ER | (100, 175, 176) |
| Clostridium difficile toxin B | Cytoskeleton (causes cytoskeletal disruption by targeting RhoA, CDC42 and Rac1) | ER | (149, 177) |
| Cyclophosphamide | Nucleus (DNA) | ER | (152) |
| High hydrostatic pressure | Broad disrupting/denaturing effects on membranes, and proteins | ER (mitochondria?) | (154, 178) |
| Microwave thermal ablation | Hyperthermic ablation of cellular components | ER? | (158) |
| Paclitaxel, patupilone | Cytoskeleton (target microtubules thereby disrupting cytoskeletal functions) | ER | (42, 104, 179) |
| Photofrin-based PDT | Cellular membranes (ROS-based damage of membranes) | ER? | (180, 181) |
| RIG-I-like helicases (RLH) ligand | Cytosol (targets RIG-I-like helicases) | ER? | (165) |
| Septacidin | ? | ER | (139) |
| Shikonin | Cytosol (tumor-specific pyruvate kinase-M2 protein) | ER | (160, 182) |
| Vorinostat | Nucleus/Cytosol (targets histone deacetylase) | ER? | (166) |
| Wogonin | Mitochondria (generates mitochondria-derived ROS) | ER | (167, 183) |
| Type II inducers – agents that induce icd through a “focused” er stress effect | |||
| Hypericin-based PDT | ER (ROS-based damage at the ER membrane) | ER | (35, 63, 116, 181, 184, 185) |
| Oncolytic adenovirus | ER (ER membranes and lumen) | ER | (104, 147) |
| Oncolytic coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) | ER (ER membranes and lumen) | ER | (150, 186) |
| Oncolytic Newcastle disease virus (NDV) | ER (ER membranes and lumen) | ER | (43, 159, 187) |
| PtII N-heterocyclic carbene complex | Predominantly targets ER (generates ER-directed ROS) | ER | (140) |
EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ICD, immunogenic cell death; PDT, photodynamic therapy; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
“?” Unclear or not determined yet.
Since its discovery, a plethora of molecular and immunological components responsible for ICD have been discovered (Figure 1) (26, 102, 188). Table 5 summarizes the molecular and immunological determinants of ICD characterized so far, as well as the models of ICD in which they operate (in a positive, negative or dispensable manner). Anthracyclines and oxaliplatin are the most common ICD inducers employed in experimental settings, followed by Hyp-PDT. According to current understanding, cancer cell-associated determinants of ICD can be subdivided into those that are common to all ICD inducers (i.e., “core” signaling components), and those that operate in an ICD inducer-dependent manner (i.e., “private” signaling components) (26, 189). Thus, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 (EIF2AK3, best known as PERK) and the ER-to-Golgi secretory machinery are considered “core” signaling components on the cancer cell side (26, 102). Similarly, from the immune system side, a general role for (IFNγ-producing) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells has been confirmed for most, if not all, ICD inducers (Table 5). Interestingly, some components that are required for ICD induction by some agents (like autophagy for anthracyclines and oxaliplatin) (190) might be either dispensable for ICD induction by other agents, e.g., autophagy for NDV (43) and phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), caspase-8 (CASP8) activation or cytosolic Ca2+ levels for Hyp-PDT (35); or even negatively regulate ICD in some settings, e.g., autophagy in case of Hyp-PDT (34) (Table 5). Thus, it will be important to expand our molecular knowledge of ICD to as many experimental settings as possible.
Table 5.
A list of molecular and immunological components crucial for regulation of ICD.
| Molecular or immunological components | Acting on the level of? | Role in regulating ICD or ICD-related determinants for various therapies/inducers |
Confirmed by which experimental intervention? | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive regulation | Negative regulation | No role in regulation | ||||
| Actin cytoskeleton | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, hypericin-PDT | – | – | Pharmacological inhibitors of actin polymerization | (35, 123) |
| ATG5, ATG7, or BECN1 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, oxaliplatin | Hypericin-PDT | Newcastle disease virotherapy | ATG5, ATG7 or BECN1 si/shRNA, ATG5 KO MEFs, or transgenic mice model of spontaneous melanoma with Atg7−/− phenotype or pharmacological inhibitors of macroautophagy | (34, 43, 112) |
| BAX/BAK | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, hypericin-PDT | – | – | BAX/BAK KO MEFs or Bax/Bak si/shRNA | (35, 123) |
| Calreticulin | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, radiotherapy, oxaliplatin, hypericin-PDT | – | – | CRT si/shRNA | (35, 41, 116, 123) |
| Caspase 1 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Casp1−/− mice | (36) |
| Caspase-8 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines | – | Hypericin-PDT | Caspase-8 si/shRNA or HeLa cancer cells expressing CrmA (a caspase-8 inhibitory protein) | (35, 123) |
| CD4+/CD8+ T cells | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin, hypericin-PDT, high hydrostatic pressure, bortezomib, vorinostat, photofrin-PDT, Newcastle disease virotherapy, cyclophosphamide | – | – | Antibody-based depletion; Ex vivo co-culture experiments | (34, 43, 100, 102, 152, 161, 162, 166, 191) |
| CXCL10 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Recombinant protein | (102, 141) |
| CXCR3 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Cxcr3−/− mice or antibody-based blockade | (141) |
| eIF2α-P | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines | – | Hypericin-PDT | MEFs expressing non-phosphorylable version of eIF2α-P, salubrinal or pharmacological inhibitors of GADD34 | (35, 123) |
| ER-Ca2+ | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines | – | Hypericin-PDT | BAPTA, a Ca2+ chelator or Reticulon-1C overexpression; | (35) |
| ERp57 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines | – | Hypericin-PDT | ERp57 si/shRNA or ERp57 KO MEFs | (35, 116) |
| ER-to-Golgi transport | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, hypericin-PDT | – | – | Brefeldin A, a secretory pathway inhibitor | (35, 123) |
| HMGB1 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines | – | – | HMGB1 si/shRNA | (70) |
| HSP90 | Cancer cells | Bortezomib | – | – | Pharmacological HSP90 inhibitors | (66, 67, 100) |
| HSP70 | Cancer cells | Shikonin | – | – | Antibody-mediated protein depletion | (192) |
| IFN-α/β or IFN-α-receptor | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, cyclophosphamide, and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Antibody-based blockade or recombinant proteins (wherever applicable) | (141, 152) |
| IFN-γ and IFN-γ-receptor | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Ifng−/− or Ifngr1−/− mice | (70, 102) |
| IL17A or IL17A-receptor | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Il17a−/− or Il17ra−/− mice | (36, 193) |
| IL1-receptor | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Il1r1−/− mice | (36) |
| IL-1β | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Antibody-based blockade | (36) |
| Lipid rafts | Cancer cells | Mitoxantrone | – | Hypericin-PDT | MBC, a cholesterol-chelator that disrupts lipid rafts | (35) |
| LRP1 | Cancer cells | Mitoxantrone, hypericin-PDT | – | – | LRP1 shRNA, LRP1 KO MEFs, LRP1 KO CHO cells and LRP1 overexpression in CHO cells | (35) |
| LY96 and MyD88 (TLR-adaptors) | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Ly96−/− or Myd88−/− mice | (102) |
| NLRP3 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Nlrp3−/− mice | (36) |
| P2 × 7 receptor | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | P2rx7−/− mice | (36) |
| Perforin | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Prf1−/− mice | (36, 70, 102) |
| PERK | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, hypericin-PDT, wogonin | – | – | PERK si/shRNA, PERK KO MEFs | (35, 123, 167) |
| PI3K p110α | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines, hypericin-PDT, wogonin | – | – | PI3K p110α shRNA or wortmannin, a pharmacological inhibitor | (35, 167) |
| Rag2 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin, vorinostat, cyclophosphamide, photofrin-PDT, Newcastle disease virotherapy | – | – | Rag2−/− mice | (43, 70, 102, 152, 161, 162, 166) |
| STAT3 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Stat3−/− cancer cells | (194) |
| TLR3 | Cancer cells | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | TLR3 si/shRNA or Tlr3−/− cancer cells | (141) |
| TLR4 | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Tlr4−/− mice | (70, 102) |
| TNF or TNF-receptor | Host immune system | Anthracyclines and/or oxaliplatin | – | – | Tnf−/− or Tnfr1−/− mice | (102) |
| LAMP2A | Cancer cells? | Mitoxantrone and hypericin-PDT | – | – | LAMP2A KO MEFs | (112) |
ATG, autophagy-related protein; BECN1, beclin-1; CD, cluster of differentiation; CRT, calreticulin; CXCL, C-X-C ligand; CXCR, C-X-C motif receptor; eIF2, eukaryotic initiation factor 2; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERp57, endoplasmic reticulum protein 57; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; HSP, heat shock protein; Hyp-PDT, hypericin-based photodynamic therapy; ICD, immunogenic cell death; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; KO MEFs, knock-out murine embryonic fibroblasts; LAMP, lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein; LRP1, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; MBC, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PRF, perforin; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Immunogenic Cell Death from Bench to Bedside
The relevance of ICD has been verified in a number of rodent models, with a variety of chemical and physicochemical ICD inducers (26, 102). Table 6 summarizes the most prominent mouse or rat models used so far for the characterization and study of ICD. For the moment, ICD has been mostly investigated in heterotopic syngeneic subcutaneous models (195). Within such models, inter-species differences (mouse versus rats), inter-strain differences (among BALB/c, C57BL/6, C3H and KMF mice), and inter-cell line differences, as well as differences in therapeutic setups (prophylactic versus curative) have been amply accounted for (Table 6). Nevertheless, there is predominance in the use of cancer cells derived from carcinogen-induced tumors and transplanted subcutaneously (Table 6). In very few cases, ICD has been characterized in either orthotopic (for NDV) or spontaneous (for anthracyclines) tumor murine models (Table 6). This has been questioned as a prominent Achilles’ heel of ICD research (195). While this criticism is valid, it has to be recognized that no rodent model is perfect at all immunological levels (196).
Table 6.
A list of prominent preclinical mice or rat models used for analysis of ICD.
| ICD inducer | Mice tumor models utilized for positive ICD characterization or ICD “restoration/rescue” analysis |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterotopic subcutaneous mice or rat models | Orthotopic mice models | Spontaneous tumor mice models | Carcinogen-induced tumor models | |
| Anthracyclines | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (41, 70, 111, 123, 197) and curative tumor model (41, 70, 111, 197); MCA205 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization and curative tumor model (36, 70, 111, 130); MCA-2/-4 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (36); D122 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization model (145); AY27 cells in Fischer 344 rats – prophylactic immunization model (42) | – | MMTV-NeuT breast cancer mice model – curative set-up (198); BrafCa/+; Ptenfl/fl-melanoma mice model – curative set-up (199) | – |
| Anti-EGFR antibody (7A7) | D122 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model and prophylactic immunization model (145) | – | – | – |
| Bleomycin | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – curative tumor model (146) | – | – | – |
| Bortezomib | 67NR cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model with use of stimulated DCs (200); B16 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model, combination treatment with AdVMART1/DC and bortezomib is significantly better than bortezomib alone (201); HM-1 cells in C57BL/6 x C3/He F1 origin mice – prophylactic immunization model (202) | – | – | – |
| CD40L-encoding Oncolytic Adenovirus | MB49 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (147) | – | – | – |
| Clostridium difficile toxin B | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (149) | – | – | – |
| Coxsackievirus B3 | A549 and EBC-1 cells in nude BALB/c mice – curative tumor model (150) | – | – | – |
| Cyclophosphamide | EG7 cells in C57BL/6 mice (152); AB1-HA cells in BALB/c mice – curative tumor model followed by resistance to challenge with live cells (203) | – | – | – |
| Hypericin-based PDT | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (35); – curative tumor model (184); AY27 cells in Fischer 344 rats – prophylactic immunization model (42); B78 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization model (30) | – | – | – |
| Microwave thermal ablation | K7M2 cells in BALB/c mice or UMR106 cells in SD rats – prophylactic immunization model (158) | – | – | – |
| Newcastle disease virus (NDV) | B16 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (159) | GL261 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (43) | – | – |
| Oxaliplatin | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (123, 197); – curative tumor model (197); EL4 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (36); EG7 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (36); EG7 cells in C3H mice – prophylactic immunization model (70) | – | – | – |
| Photofrin-based PDT | EMT6 cells in BALB/c mice – curative tumor model (161); SCCVII cells in C3H/HeN mice – curative tumor model (162, 163) | – | – | – |
| Radiotherapy | CT26 cells in BALB/c – prophylactic immunization model (204); 410.4 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (205); EG7 cells in C57BL/6 mice and SCC VII cells in C3H mice – prophylactic immunization model (206); B16F10 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization model with the use of irradiated cancer cells, as well as DCs stimulated with irradiated cancer cells (207) | – | – | – |
| RIG-I-like helicases (RLH) ligand | Panc02 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization and curative tumor model (165) | – | – | – |
| Septacidin | MCA205 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic set-up (139); | – | – | – |
| Shikonin | B16 cells in C57BL/6 mice – prophylactic immunization model (160); P388 cells in KMF mice – curative tumor model (208) | 4T1 cells in BALB/c mice – curative tumor model (192); | – | – |
| UVC irradiation | CT26 cells in BALB/c mice – prophylactic immunization model (204); EG7 cells in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor model (152) | – | – | – |
| Vorinostat | MC38 or Eμ-myc 4242/299 lymphoma in C57BL/6 mice – curative tumor set-up (166) | – | – | – |
| High hydrostatic pressure | No mice or rat based preclinical data available to support their ICD-functions | |||
| PtII N-heterocyclic carbene complex | ||||
DC, dendritic cell; ICD, immunogenic cell death; PDT, photodynamic therapy.
As a recent systematic review summarized (196), heterotopic murine models suffer from a number of caveats, including the inability to recapitulate the early interaction between transformed cells and the immune system and the incompatibility between the cancer type and the site-of-transplantation (196). Orthotopic murine models are useful as they overcome the cancer cell-tissue type incompatibility issue (196). While genetically engineered tumor murine models (GEMMs) overcome most of the issues mentioned above, they come with their own set of shortcomings, including a limited genetic mosaicism, a low tumor heterogeneity, a lack of well-defined immunogenic TAAs, the presence of unintended “passenger” genetic modifications, and a reduced mutational spectrum (196). Many of these parameters are critical for responses to immunotherapy/ICD. For instance, the lack of well-defined immunogenic TAAs was the reason why preliminary results obtained in spontaneously developing murine tumors disputed the very existence of TAAs (11). Similarly, a high mutational spectrum (which produces considerable amounts of neo-antigens) has been found to be mandatory for the clinical efficacy of checkpoint blockers (209). Last (but not least), laboratory rodent models in general are associated with some critical issues, including the fact that a high level of inbreeding (which produces a number of shortcomings e.g., homozygous recessive defects) reduces the general immunological fitness, responsiveness and diversity in these models (196, 210, 211). Moreover, numerous immunological differences between mouse and humans tend to affect the translational relevance of the findings obtained (26, 211, 212). Also, the time frames of tumor growth rates between rodent models and humans are relatively divergent (196, 213, 214). This further complicates clinical translation of immunotherapeutic paradigms since the level of immunosurveillance and immunoediting experienced by human tumors can be much higher than any rodent tumor model.
In summary, it would be ideal to test ICD across as many different rodent models as possible, in order to determine the features that can be exploited for therapeutic purposes in humans. Moreover, if ICD fails in a specific experimental model, active effort should be made to characterize the mechanisms behind such failure, since resistance phenotypes can have profound clinical implications. This emerges from various studies summarized in Table 7. Indeed, several ICD resistance mechanisms exist operating at both the cancer cell and the immune system level, which have been characterized in different experimental models. Several of these resistance mechanisms have also been identified in cancer patients, thereby justifying further studies along these lines Table 7.
Table 7.
Existence of intrinsic or naturally occurring resistance to ICD in experimental cancer models.
| ICD inducer(s) | Experimental set-up where resistance was observed | Reason behind resistance | Rescued by? | Clinical applicability verified? | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vivo preclinical setting (cancer cell or host immune system-level resistance) | |||||
| Anthracyclines or anthracycline plus oxaliplatin | C3H mice with naturally occurring tlr4 mutation | Host immune system-level resistance: defective TLR4 in C3H mice causes failure of HMGB1-mediated immunity thereby leading to resistance to anti-cancer vaccination effect associated with anthracyclines treatment | Adoptive transfer of TLR4-expressing DCs loaded with dying tumor cells | Yes; breast cancer, colon cancer, and lung cancer patients carrying TLR4 gene mutation that ablates its ability to bind its ligands is associated with worse prognosis post-treatment | (215) |
| Doxorubicin | AT-3 or 4T1.2 breast cancer cells in C57BL/6 or BALB/c mice, respectively | Cancer cell-level resistance: CD73 overexpression confers chemo-resistance to doxorubicin by suppressing anti-tumor immunity through A2A adenosine receptors | Blockade of CD73 | Yes; in triple-negative breast cancer patients, high CD73 in anthracycline-treatment set-up associated with lower rate of complete responses | (216) |
| Mitoxantrone and Hypericin-PDT | AY27 rat bladder cancer cells in Fischer 344 rats | Cancer cell-level resistance: low endogenous CRT levels, resulted in severely reduced surface-CRT upon treatment with mitoxantrone or Hyp-PDT; this in turn compromised immunogenic phagocytic clearance and anti-cancer vaccination effect | Exogenous addition of recombinant CRT | Yes; high tumoral CALR levels correlated with high expression of phagocytosis-associated genes and predicted for prolonged survival after RT or PTX treatment of lung or ovarian cancer patients respectively | (42) |
| Oxaliplatin | Autochthonous transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model of metastatic prostate cancer | Host immune system-level resistance: immunosuppressive B cells expressing IgA, IL10 and PD-L1 cause resistance to anti-tumorigenic effects of oxaliplatin | Genetic or pharmacological depletion of B cells | Not directly, but possible validity is supported by human patient data showing that IL-10 expressing IgA+ cells are abundant in therapy-resistant prostate cancer and are negative prognostic indicators | (217) |
| In vitro preclinical setting (cancer cell-level resistance) | |||||
| Anthracycline | SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line | Anthracycline treatment of these cells failed to induce surface-CRT due to reduced capacity to efflux ER-Ca2+ into cytosol | Overexpression of reticulon-1C | – | (132) |
| Doxorubicin | HT29-dx and HT29 iNOS-cells (human colon cancer cells) | Doxorubicin failed to induce NO synthesis, which resulted in reduced toxicity, reduced surface-CRT and subsequently compromised immunogenic phagocytic clearance and DC stimulation | Addition of sodium nitroprusside or a NO donor | – | (218) |
| Doxorubicin | MDR+ human cancer cells (HT29-dx, A549-dx and MCF-7-dx) | Increased MDR levels caused increased P-glycoprotein expression which caused resistance to doxorubicin-induced ICD by affecting immunogenic phagocytic removal | Addition of zoledronic acid | Not directly | (219) |
CD, cluster of differentiation; CRT or CALR, calreticulin; DC, dendritic cells; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1 protein; HSP, heat shock protein; Hyp-PDT, hypericin-photodynamic therapy; ICD, immunogenic cell death; IL, interleukin; MDR, multiple drug-resistance; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; PD-L1, programed cell death protein ligand 1; PTX, paclitaxel; RT, radiotherapy; TLR, toll-like receptor.
A considerable amounts of clinical findings support the relevance of ICD or ICD-related signatures in (at least subsets of) cancer patients. As summarized in Table 8, various ICD-linked (specific) parameters have been associated with the prognosis of cancer patients treated with clinically relevant ICD inducers (like anthracyclines, oxaliplatin, paclitaxel, or radiotherapy). Moreover, it is becoming clear that ICD-related or ICD-derived (immunological) genetic signatures (e.g., a MX1-centered metagene, a CXCR3-PRF1-CASP1-centered metagene, an ASAH1-centered metagene) can be positively associated with good prognosis in patients affected by various neoplasms, including breast, lung, and ovarian malignancies (141, 188, 220). These observations indicate that ICD or ICD-relevant parameters may have prognostic or predictive relevance in at least a subset of cancer patients. It will be important to characterize new and more specific ICD-associated parameters linked to patient prognosis as well as biomarkers that may predict improved disease outcome in cancer patient treated with ICD inducers. Of note, considering the current clinical experience with immunotherapies (209, 221), the patients with an increased likelihood to benefit from ICD inducers are probably those that display pre-existing (baseline) immune reactivity against cancer cells (220, 222, 223). This may depend on the ability of ICD to reboot and/or revive pre-existing TAA-directed immunity rather to prime de novo immune reactivity (5, 191, 224). In future, it would be crucial to characterize biomarkers that allow clinicians to delineate patients with reduced baseline immune reactivity against malignant cells so that proper combinatorial therapies involving ICD inducers can be implemented.
Table 8.
A list of clinical observations supporting the existence of ICD in cancer patients.
| ICD inducer | Standard-of-care therapy or regularly applied palliative therapy in clinic? | ICD-related characteristics regulating clinical patient prognosis or treatment-responsiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Anthracyclines | Yes | P2RX7 loss-of-function mutation that compromises ICD also negatively affects MFS in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant anthracyclines (36); breast cancer patients possessing a wild-type TLR4 benefited more from the anthracyclines than those who possessed a mutated TLR4 that compromises ICD (70); an MX1-centered Type I IFN signature in anthracycline-treated breast cancer patients predicts for improved disease outcome (141); combined positivity for cytoplasmic LC3B+ puncta and nuclear HMGB1 is a positive predictor of improved survival following adjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy (225) |
| High hydrostatic pressure | No; but HHP-based anticancer DC vaccines are currently being applied in clinical trials against prostate cancer and ovarian cancer (155) | No data are available |
| Hypericin-based PDT | No; but few clinical trials have been carried out for non-melanoma skin cancer (226), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (227), mesothelioma (228), and basal or squamous cell carcinoma (229) | No data are available |
| Oncolytic adenoviruses | No; but oncolytic adenoviruses are currently being applied in various clinical trials in cancer patients | Serum HMGB1 levels and the temporal change in their levels during treatment was identified as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in cancer patients (230) |
| Oxaliplatin | Yes | Similar to anthracyclines, cancer patients possessing wild-type TLR4 exhibited prolonged PFS and OS in comparison to patients bearing the loss-of-function allele of TLR4 (197) |
| Paclitaxel | Yes | High tumoral CALR levels in paclitaxel-treated ovarian cancer patients associated with prolonged OS/PFS as well as increased expression levels of various phagocytosis-associated genes (42) |
| Photofrin-based PDT | Yes; FDA-approved for application in esophageal and lung cancer (231) | No data available |
| Radiotherapy | Yes | In patients of eosophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) receiving chemo-radiotherapy significant increase in serum HMGB1-levels and increased intra-tumoral staining of HMGB1 correlated with better patient survival (232); high tumoral CALR levels in radiotherapy-treated lung cancer patients associated with prolonged OS as well as increased expression levels of various phagocytosis-associated genes (42) |
| Shikonin | No; but shikonin is currently being applied in an observational clinical study of breast cancer patients (NCT01287468) | No data are available |
| UVC irradiation | No; but UV treatment is sometimes applied for the preparation of clinical cell-based anticancer vaccines (233) | No data are available |
| Bortezomib, Anti-EGFR antibody (7A7), bleomycin, cyclophosphamide, microwave thermal ablation, vorinostat | Yes | No data are available |
| Coxsackievirus B3; Clostridium difficile toxin B; Microwave thermal ablation; Newcastle disease virus (NDV); RIG-I-like helicases (RLH) ligand; Septacidin; PtII N-heterocyclic carbene complex; Patupilone | No | No data are available |
CRT or CALR, calreticulin; HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1 protein; Hyp-PDT, hypericin-photodynamic therapy; ICD, immunogenic cell death; IFN, interferon; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; TLR, toll-like receptor.
Confronting the Clinical Realities of Anti-Tumor Immunity
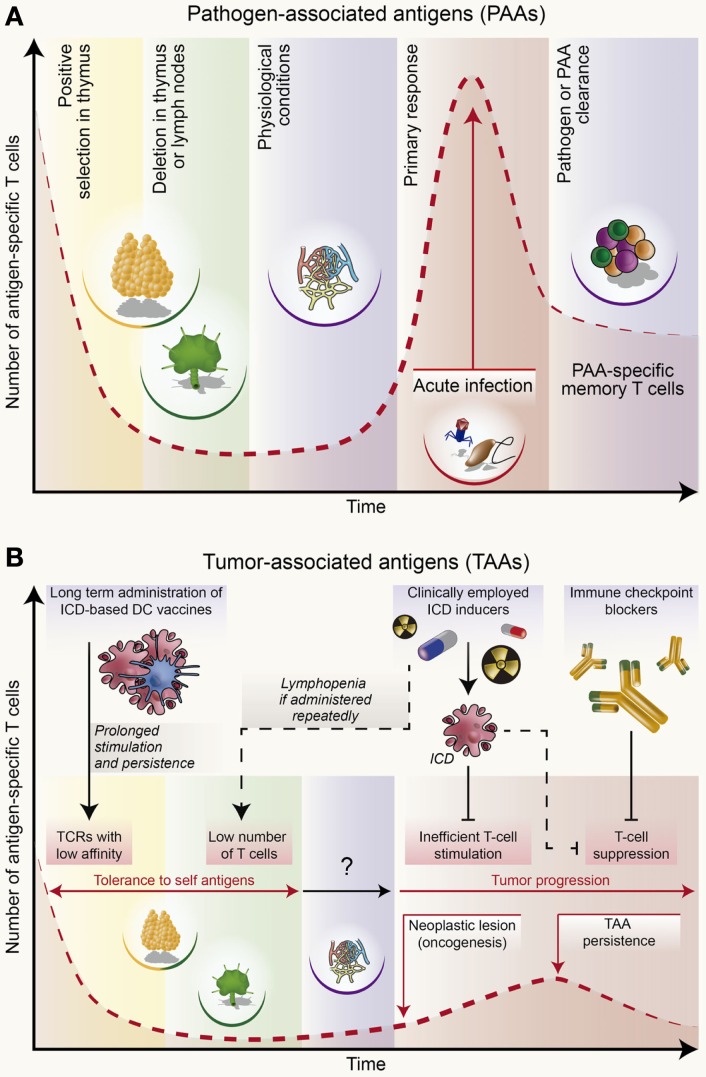
It is well-established that the response of cancer patients to immunotherapy relies on the activity of effector T cells [that employ their T-cell receptors (TCRs) for recognizing TAAs]. However, these TAA-targeting T cells may also constitute obstacles for effective anti-tumor immunity (234). As opposed to T lymphocytes recognizing pathogen-associated antigens (PAAs) (Figure 2), indeed, T cells directed against some TAAs (derived from non-mutated proteins that are source of self or near-to-self antigens) are developmentally subjected to negative selection in the thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs (234, 235) (Figure 2). As a result, T cells bearing TCRs with high affinity for self antigens (including some TAAs) are clonally deleted to avoid auto-immunity (234–237) (Figure 2). However, some “leakiness” in this process allows TAA-specific T cells possessing TCRs with low affinity to escape deletion (234, 236, 237) and persist, although at low precursor frequencies (238) (Figure 2). Unfortunately, as compared to PAA-specific T cells, which bear high-affinity TCRs (Figure 2), TAA-specific T cells exhibit limited effector and memory functions (234, 239). Coupled with the tendency of progressing tumors to generate a highly immunosuppressive microenvironment, this renders the insurgence of lifelong protective immunity nearly impossible (234). Of note, central and peripheral tolerance may not affect T cells reactive toward neo-tumor-specific antigens (neo-TSAs) e.g., tumor-specific neo-antigens that are generated de novo in the course of tumor progression because of mutational events (240, 241). However, the extent to which such neo-TSAs can elicit consistent “immunodominant” T cell reactivity is still a matter of investigation (240, 241). Nevertheless, in this context, inefficient T-cell stimulation can be overcome through the ICD-based improvement of effector T-cell functions (102). ICD can be further combined with checkpoint-blocking therapies, which potently reverse immunosuppression (209, 242). However, the lifelong maintenance of anti-tumor T cells remains a particularly hard challenge.
Figure 2.
Population dynamics of antigen-specific T cells during an immune response to infection or cancer. (A) T cells capable of putatively recognizing non-self, pathogen-associated antigens (PAAs) are not exposed to negative selection in the thymus or peripheral organs like lymph nodes. This allows for the constitutive presence of T lymphocytes bearing high-affinity T-cell receptor (TCR) in naïve conditions. Upon infection, these cells undergo robust expansion and acquire potent effector functions, hence driving an immune response that clears the pathogen and PAAs. Finally, PAA-specific T cells undergo contraction along with the establishment of immunological memory. To a limited extent, T cells reacting against PAAs expressed by virus-induced tumors may exhibit similar (although not identical) responses. (B) T cells that may recognize self or close-to-self antigens expressed by virus-unrelated malignancies undergo robust negative selection in the thymus and lymph nodes. Thus, all putative T lymphocytes bearing a high-affinity TCR against tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) are eliminated. However, some leakiness in this process allows for the persistence of TAA-specific T lymphocytes with low-affinity TCR, although at very low precursor frequencies. This is one of the reasons why in some individuals immunosurveillance at some stage fails to impede tumor progression. As malignant lesions progress, the amount of TAAs increases, causing a weak rise in TAA-specific T cells. However, tumor progression is generally coupled with the establishment of robust immunosuppressive networks that potently inhibit such TAA-targeting T cells. In this context, the administration of immunogenic cell death (ICD) according to a schedule that does not lead to lymphodepletion can favor the stimulation of TAA-targeting T cells and (re)instate immunosurveillance. Combining ICD inducers with checkpoint-blocking agents may further boost TAA-targeting immune responses. However, these treatments may not ensure the lifelong persistence of TAA-recognizing T cells, some of which are susceptible to elimination through tolerance mechanisms. Anticancer vaccines may counteract, at least to some extent, such loss. The figure was partly inspired from Baitsch et al. (234).
In the clinical reality, anticancer agents are administered to patients in a limited number of cycles. Even if these therapeutic regimens may attain optimal efficacy in terms of ICD induction, they are unlikely to ensure the lifelong persistence of TAA-directed T cells with low-affinity TCR (234, 243). This probably reflects the contraction of TAA-targeting T cells occurring once the immunostimulatory stimulus provided by ICD ceases, owing to peripheral tolerance mechanisms (234). Clinically, it may not be feasible to administer ICD inducers repeatedly over time, since many of them can cause lymphopenia (which negatively affects disease outcome), or are associated with other side effects (244). It has been proposed that active immunization with ICD-based anticancer vaccines (which are associated with robust immunogenicity) given in a repetitive manner may achieve this goal (Figure 2) (234, 243, 245). Thus, it will be important to test whether the long-term administration of ICD-based anticancer vaccines can sustain the effector function of TAA-specific T cells bearing low-affinity TCRs, hence, ensuring lifelong disease-free survival. Of note, in the case of hematological malignancies, this issue could be overcome upon the adoptive transfer of CTLs expressing chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) (1). However, whether CAR-expressing CTLs generate protective immunological memory in the absence of considerable side effects remains to be determined. Moreover, the use of this therapeutic strategy against solid malignancies is relatively challenging owing to lack of well-defined “unique” TAAs (1, 246).
Conclusion
The model of ICD has been considerably refined since the initial identification of a cell death modality manifesting apoptotic features but able to induce an adaptive immune response. This model strives to integrate several phenomena observed throughout the second half of the twentieth century in one therapeutically relevant platform. However, as discussed above, several challenges still need to be addressed. First, comprehensive testing should be performed in advanced experimental settings like GEMMs or orthotopic tumor models. Second, ICD resistance mechanisms should be characterized with precision. Third, various issues linked to the successful translation of ICD to cancer therapy will have to be resolved, including (but not limited to) treatment schedules, dosages, and combinatorial strategies. This translational drive also needs to be coupled with effective strategies for the discovery of new and effective ICD inducers. Drug screening programs are often complicated by the possibility of false-positive (due to bystander presence of DAMPs) (30) or false-negative (due to limited number of biomarkers used for screening) hits. This issue can only be ironed out by discovering new and common regulators of ICD, and integrating them into existing screening platforms. Last, but not least, it will be important to identify new ICD-related/derived biomarkers that can be used to improve current protocols of patient stratification and clinical decision making. We are positive that all these objectives are at reach.
Author Contributions
ADG did the literature study, data collection, as well as conceived and wrote the manuscript. PA provided senior supervision and guidance, conceived the paper, helped in writing, and critically revised the manuscript. LG improved and edited the manuscript. JMBSP helped with the preparation of figures. All authors participated in the critical reading of the manuscript (wherever applicable), approved content and conclusions, as well as helped in ensuring the accuracy of cited literature.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Akseli Hemminki is shareholder in Targovax AG and TILT Biotherapeutics Ltd. The remaining authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
We would like to explicitly declare that this manuscript does not aim to describe guidelines for the fields of ICD and DAMP research. Rather, it is meant to be a comprehensive classification and review of relevant literature expressing consensus discussions, opinions, and conclusions endorsed and/or supported by a number of researchers and clinicians investigating ICD and DAMPs. We would also like to acknowledge the following colleagues for their support, reading and/or positive appraisal of this manuscript: Wee Han Ang, Vincenzo Barnaba, Marco E. Bianchi, Karin de Visser, Sandra O. Gollnick, Peter Henson, Polly Matzinger, Marek Michalak, Kodi Ravichandran, and Andrew Thorburn. ADG is a recipient of the FWO postdoctoral fellowship 2013. This work was supported by grants from the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen; G.0661.09, G.0728.10 and G.0584.12N) and KU Leuven (GOA/11/009) to PA; This paper presents research results of the IAP7/32, funded by the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Programme, initiated by the Belgian State, Science Policy Office.
Abbreviations
DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; DC, dendritic cell; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GEMM, genetically engineered murine model; HSP, heat shock protein; Hyp, hypericin; ICD, immunogenic cell death; NDV, Newcastle disease virotherapy; PDT, photodynamic therapy; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
References
- 1.Galluzzi L, Vacchelli E, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Buque A, Senovilla L, Baracco EE, et al. Classification of current anticancer immunotherapies. Oncotarget (2014) 5(24):12472–508. 10.18632/oncotarget.2998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kepp O, Tesniere A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. The immunogenicity of tumor cell death. Curr Opin Oncol (2009) 21(1):71–6. 10.1097/CCO.0b013e32831bc375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Garg AD, Dudek AM, Agostinis P. Cancer immunogenicity, danger signals, and DAMPs: what, when, and how? Biofactors (2013) 39(4):355–67. 10.1002/biof.1125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Blankenstein T, Coulie PG, Gilboa E, Jaffee EM. The determinants of tumour immunogenicity. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(4):307–13. 10.1038/nrc3246 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Garg AD, Nowis D, Golab J, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, Agostinis P. Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and anticancer therapeutics: an emerging amalgamation. Biochim Biophys Acta (2010) 1805(1):53–71. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anguille S, Smits EL, Lion E, van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN. Clinical use of dendritic cells for cancer therapy. Lancet Oncol (2014) 15(7):e257–67. 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70585-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chiang CL, Kandalaft LE, Coukos G. Adjuvants for enhancing the immunogenicity of whole tumor cell vaccines. Int Rev Immunol (2011) 30(2–3):150–82. 10.3109/08830185.2011.572210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parish CR. Cancer immunotherapy: the past, the present and the future. Immunol Cell Biol (2003) 81(2):106–13. 10.1046/j.0818-9641.2003.01151.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coley WB. The treatment of malignant tumors by repeated inoculations of erysipelas: with a report of ten original cases. Am J Med Sci (1893) 105:487–511. 10.1097/00000441-189305000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tsung K, Norton JA. Lessons from Coley’s toxin. Surg Oncol (2006) 15(1):25–8. 10.1016/j.suronc.2006.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, van der Bruggen P, Boon T. Tumour antigens recognized by T lymphocytes: at the core of cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer (2014) 14(2):135–46. 10.1038/nrc3670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liao SK, Carr DH. Comparative immunogenicity of irradiated, neuraminidase treated, and fused cells of a strain-restricted sarcoma. Z Krebsforsch klin Onkol Cancer Res Clin Oncol (1974) 82(2):133–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Milas L, Withers HR. Nonspecific immunotherapy of malignant tumors. Radiology (1976) 118(1):211–8. 10.1148/118.1.211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bogden AE, Esber HJ. Influence of surgery, irradiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy on growth of a metastasizing rat mammary adenocarcinoma. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr (1978) (49):97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dickson JA, Shah SA. Hyperthermia: the immune response and tumor metastasis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr (1982) 61:183–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Suit HD, Walker AM. Assessment of the response of tumours to radiation: clinical and experimental studies. Br J Cancer Suppl (1980) 4:1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Richert L, Or A, Shinitzky M. Promotion of tumor antigenicity in EL-4 leukemia cells by hydrostatic pressure. Cancer Immunol Immunother (1986) 22(2):119–24. 10.1007/BF00199125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. The secret ally: immunostimulation by anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2012) 11(3):215–33. 10.1038/nrd3626 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Green DR, Ferguson T, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat Rev Immunol (2009) 9(5):353–63. 10.1038/nri2545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Matzinger P. Tolerance, danger, and the extended family. Annu Rev Immunol (1994) 12:991–1045. 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.005015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matzinger P. The danger model: a renewed sense of self. Science (2002) 296(5566):301–5. 10.1126/science.1071059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Land W, Schneeberger H, Schleibner S, Illner WD, Abendroth D, Rutili G, et al. The beneficial effect of human recombinant superoxide dismutase on acute and chronic rejection events in recipients of cadaveric renal transplants. Transplantation (1994) 57(2):211–7. 10.1097/00007890-199401001-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seong SY, Matzinger P. Hydrophobicity: an ancient damage-associated molecular pattern that initiates innate immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol (2004) 4(6):469–78. 10.1038/nri1372 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rubartelli A, Lotze MT. Inside, outside, upside down: damage-associated molecular-pattern molecules (DAMPs) and redox. Trends Immunol (2007) 28(10):429–36. 10.1016/j.it.2007.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li G, Tang D, Lotze MT. Menage a trois in stress: DAMPs, redox and autophagy. Semin Cancer Biol (2013) 23(5):380–90. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Garg AD, Martin S, Golab J, Agostinis P. Danger signalling during cancer cell death: origins, plasticity and regulation. Cell Death Differ (2014) 21(1):26–38. 10.1038/cdd.2013.48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bianchi ME. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol (2007) 81(1):1–5. 10.1189/jlb.0306164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bondanza A, Zimmermann VS, Rovere-Querini P, Turnay J, Dumitriu IE, Stach CM, et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylserine recognition heightens the immunogenicity of irradiated lymphoma cells in vivo. J Exp Med (2004) 200(9):1157–65. 10.1084/jem.20040327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stach CM, Turnay X, Voll RE, Kern PM, Kolowos W, Beyer TD, et al. Treatment with annexin V increases immunogenicity of apoptotic human T-cells in Balb/c mice. Cell Death Differ (2000) 7(10):911–5. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400715 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dudek-Peric AM, Ferreira GB, Muchowicz A, Wouters J, Prada N, Martin S, et al. Antitumor immunity triggered by melphalan is potentiated by melanoma cell surface-associated calreticulin. Cancer Res (2015) 75(8):1603–14. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rondas D, Crevecoeur I, D’Hertog W, Ferreira GB, Staes A, Garg AD, et al. Citrullinated glucose-regulated protein 78 is an autoantigen in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes (2015) 64(2):573–86. 10.2337/db14-0621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Venereau E, Casalgrandi M, Schiraldi M, Antoine DJ, Cattaneo A, De Marchis F, et al. Mutually exclusive redox forms of HMGB1 promote cell recruitment or proinflammatory cytokine release. J Exp Med (2012) 209(9):1519–28. 10.1084/jem.20120189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Weyd H, Abeler-Dorner L, Linke B, Mahr A, Jahndel V, Pfrang S, et al. Annexin A1 on the surface of early apoptotic cells suppresses CD8+ T cell immunity. PLoS One (2013) 8(4):e62449. 10.1371/journal.pone.0062449 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Garg AD, Dudek AM, Ferreira GB, Verfaillie T, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, et al. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy (2013) 9(9):1292–307. 10.4161/auto.25399 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Garg AD, Krysko DV, Verfaillie T, Kaczmarek A, Ferreira GB, Marysael T, et al. A novel pathway combining calreticulin exposure and ATP secretion in immunogenic cancer cell death. EMBO J (2012) 31(5):1062–79. 10.1038/emboj.2011.497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A, Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C, et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat Med (2009) 15(10):1170–8. 10.1038/nm.2028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Elliott MR, Chekeni FB, Trampont PC, Lazarowski ER, Kadl A, Walk SF, et al. Nucleotides released by apoptotic cells act as a find-me signal to promote phagocytic clearance. Nature (2009) 461(7261):282–6. 10.1038/nature08296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Iwata A, Morgan-Stevenson V, Schwartz B, Liu L, Tupper J, Zhu X, et al. Extracellular BCL2 proteins are danger-associated molecular patterns that reduce tissue damage in murine models of ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One (2010) 5(2):e9103. 10.1371/journal.pone.0009103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Babelova A, Moreth K, Tsalastra-Greul W, Zeng-Brouwers J, Eickelberg O, Young MF, et al. Biglycan, a danger signal that activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via toll-like and P2X receptors. J Biol Chem (2009) 284(36):24035–48. 10.1074/jbc.M109.014266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schaefer L. Extracellular matrix molecules: endogenous danger signals as new drug targets in kidney diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol (2010) 10(2):185–90. 10.1016/j.coph.2009.11.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, et al. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med (2007) 13(1):54–61. 10.1038/nm1523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Garg AD, Elsen S, Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, de Witte P, Agostinis P. Resistance to anticancer vaccination effect is controlled by a cancer cell-autonomous phenotype that disrupts immunogenic phagocytic removal. Oncotarget (2015) 6(29):26841–60. 10.18632/oncotarget.4754 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Koks CA, Garg AD, Ehrhardt M, Riva M, Vandenberk L, Boon L, et al. Newcastle disease virotherapy induces long-term survival and tumor-specific immune memory in orthotopic glioma through the induction of immunogenic cell death. Int J Cancer (2015) 136(5):E313–25. 10.1002/ijc.29202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gardai SJ, McPhillips KA, Frasch SC, Janssen WJ, Starefeldt A, Murphy-Ullrich JE, et al. Cell-surface calreticulin initiates clearance of viable or apoptotic cells through trans-activation of LRP on the phagocyte. Cell (2005) 123(2):321–34. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Garcia Fernandez M, Troiano L, Moretti L, Nasi M, Pinti M, Salvioli S, et al. Early changes in intramitochondrial cardiolipin distribution during apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ (2002) 13(9):449–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sorice M, Circella A, Cristea IM, Garofalo T, Di Renzo L, Alessandri C, et al. Cardiolipin and its metabolites move from mitochondria to other cellular membranes during death receptor-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ (2004) 11(10):1133–45. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Korbelik M, Banath J, Sun J, Canals D, Hannun YA, Separovic D. Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate act as photodynamic therapy-elicited damage-associated molecular patterns: cell surface exposure. Int Immunopharmacol (2014) 20(2):359–65. 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.03.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Horino K, Nishiura H, Ohsako T, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Kitamura N, et al. A monocyte chemotactic factor, S19 ribosomal protein dimer, in phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells. Lab Invest (1998) 78(5):603–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nishimura T, Horino K, Nishiura H, Shibuya Y, Hiraoka T, Tanase S, et al. Apoptotic cells of an epithelial cell line, AsPC-1, release monocyte chemotactic S19 ribosomal protein dimer. J Biochem (2001) 129(3):445–54. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002876 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Peter C, Wesselborg S, Lauber K. Role of attraction and danger signals in the uptake of apoptotic and necrotic cells and its immunological outcome. In: Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, editors. Phagocytosis of Dying Cells. Berlin: Springer Science + Business Media B.V. (2009). p. 63–101. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamamoto T. Roles of the ribosomal protein S19 dimer and the C5a receptor in pathophysiological functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Pathol Int (2007) 57(1):1–11. 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2007.02049.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Struck J, Uhlein M, Morgenthaler NG, Furst W, Hoflich C, Bahrami S, et al. Release of the mitochondrial enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthase under septic conditions. Shock (2005) 23(6):533–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(12):860–75. 10.1038/nrc3380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pullerits R, Bokarewa M, Jonsson IM, Verdrengh M, Tarkowski A. Extracellular cytochrome c, a mitochondrial apoptosis-related protein, induces arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) (2005) 44(1):32–9. 10.1093/rheumatology/keh406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Codina R, Vanasse A, Kelekar A, Vezys V, Jemmerson R. Cytochrome c-induced lymphocyte death from the outside in: inhibition by serum leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein-1. Apoptosis (2010) 15(2):139–52. 10.1007/s10495-009-0412-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yoon KW, Byun S, Kwon E, Hwang SY, Chu K, Hiraki M, et al. Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53. Science (2015) 349(6247):1261669. 10.1126/science.1261669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kao J, Houck K, Fan Y, Haehnel I, Libutti SK, Kayton ML, et al. Characterization of a novel tumor-derived cytokine. Endothelial-monocyte activating polypeptide II. J Biol Chem (1994) 269(40):25106–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Knies UE, Behrensdorf HA, Mitchell CA, Deutsch U, Risau W, Drexler HC, et al. Regulation of endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II release by apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1998) 95(21):12322–7. 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ahrens S, Zelenay S, Sancho D, Hanc P, Kjaer S, Feest C, et al. F-actin is an evolutionarily conserved damage-associated molecular pattern recognized by DNGR-1, a receptor for dead cells. Immunity (2012) 36(4):635–45. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chiba S, Baghdadi M, Akiba H, Yoshiyama H, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita H, et al. Tumor-infiltrating DCs suppress nucleic acid-mediated innate immune responses through interactions between the receptor TIM-3 and the alarmin HMGB1. Nat Immunol (2012) 13(9):832–42. 10.1038/ni.2376 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Decoding cell death signals in inflammation and immunity. Cell (2010) 140(6):798–804. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pletjushkina OY, Fetisova EK, Lyamzaev KG, Ivanova OY, Domnina LV, Vyssokikh MY, et al. Long-distance apoptotic killing of cells is mediated by hydrogen peroxide in a mitochondrial ROS-dependent fashion. Cell Death Differ (2005) 12(11):1442–4. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401685 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Garg AD, Nowis D, Golab J, Agostinis P. Photodynamic therapy: illuminating the road from cell death towards anti-tumour immunity. Apoptosis (2010) 15(9):1050–71. 10.1007/s10495-010-0479-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Suzuki S, Kulkarni AB. Extracellular heat shock protein HSP90beta secreted by MG63 osteosarcoma cells inhibits activation of latent TGF-beta1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2010) 398(3):525–31. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Korbelik M, Sun J, Cecic I. Photodynamic therapy-induced cell surface expression and release of heat shock proteins: relevance for tumor response. Cancer Res (2005) 65(3):1018–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cirone M, Di Renzo L, Lotti LV, Conte V, Trivedi P, Santarelli R, et al. Primary effusion lymphoma cell death induced by bortezomib and AG 490 activates dendritic cells through CD91. PLoS One (2012) 7(3):e31732. 10.1371/journal.pone.0031732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zunino B, Rubio-Patino C, Villa E, Meynet O, Proics E, Cornille A, et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy leads to an anticancer immune response via exposure of cell surface heat shock protein 90. Oncogene (2015). 10.1038/onc.2015.82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhou Z, Yamamoto Y, Sugai F, Yoshida K, Kishima Y, Sumi H, et al. Hepatoma-derived growth factor is a neurotrophic factor harbored in the nucleus. J Biol Chem (2004) 279(26):27320–6. 10.1074/jbc.M308650200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Huang H, Evankovich J, Yan W, Nace G, Zhang L, Ross M, et al. Endogenous histones function as alarmins in sterile inflammatory liver injury through toll-like receptor 9 in mice. Hepatology (2011) 54(3):999–1008. 10.1002/hep.24501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, et al. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat Med (2007) 13(9):1050–9. 10.1038/nm1622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Semino C, Angelini G, Poggi A, Rubartelli A. NK/iDC interaction results in IL-18 secretion by DCs at the synaptic cleft followed by NK cell activation and release of the DC maturation factor HMGB1. Blood (2005) 106(2):609–16. 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature (2002) 418(6894):191–5. 10.1038/nature00858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Thorburn J, Horita H, Redzic J, Hansen K, Frankel AE, Thorburn A. Autophagy regulates selective HMGB1 release in tumor cells that are destined to die. Cell Death Differ (2009) 16(1):175–83. 10.1038/cdd.2008.143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yang D, Postnikov YV, Li Y, Tewary P, de la Rosa G, Wei F. High-mobility group nucleosome-binding protein 1 acts as an alarmin and is critical for lipopolysaccharide-induced immune responses. J Exp Med (2012) 209(1):157–71. 10.1084/jem.20101354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cohen I, Rider P, Carmi Y, Braiman A, Dotan S, White MR, et al. Differential release of chromatin-bound IL-1alpha discriminates between necrotic and apoptotic cell death by the ability to induce sterile inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010) 107(6):2574–9. 10.1073/pnas.0915018107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Vanden Berghe T, Kalai M, Denecker G, Meeus A, Saelens X, Vandenabeele P. Necrosis is associated with IL-6 production but apoptosis is not. Cell Signal (2006) 18(3):328–35. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lauber K, Bohn E, Krober SM, Xiao YJ, Blumenthal SG, Lindemann RK, et al. Apoptotic cells induce migration of phagocytes via caspase-3-mediated release of a lipid attraction signal. Cell (2003) 113:717–30. 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00422-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature (2010) 464(7285):104–7. 10.1038/nature08780 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Collins LV, Hajizadeh S, Holme E, Jonsson IM, Tarkowski A. Endogenously oxidized mitochondrial DNA induces in vivo and in vitro inflammatory responses. J Leukoc Biol (2004) 75(6):995–1000. 10.1189/jlb.0703328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Mitochondria: master regulators of danger signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2012) 13(12):780–8. 10.1038/nrm3479 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Shi Y, Evans JE, Rock KL. Molecular identification of a danger signal that alerts the immune system to dying cells. Nature (2003) 425(6957):516–21. 10.1038/nature01991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Carp H. Mitochondrial N-formylmethionyl proteins as chemoattractants for neutrophils. J Exp Med (1982) 155(1):264–75. 10.1084/jem.155.1.264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Rabiet MJ, Huet E, Boulay F. The N-formyl peptide receptors and the anaphylatoxin C5a receptors: an overview. Biochimie (2007) 89(9):1089–106. 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.02.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Czapiga M, Gao JL, Kirk A, Lekstrom-Himes J. Human platelets exhibit chemotaxis using functional N-formyl peptide receptors. Exp Hematol (2005) 33(1):73–84. 10.1016/j.exphem.2004.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Moghaddam AE, Gartlan KH, Kong L, Sattentau QJ. Reactive carbonyls are a major Th2-inducing damage-associated molecular pattern generated by oxidative stress. J Immunol (2011) 187(4):1626–33. 10.4049/jimmunol.1003906 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Miller YI, Choi SH, Wiesner P, Fang L, Harkewicz R, Hartvigsen K, et al. Oxidation-specific epitopes are danger-associated molecular patterns recognized by pattern recognition receptors of innate immunity. Circ Res (2011) 108(2):235–48. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Vandenberk L, Garg AD, Verschuere T, Koks C, Belmans J, Beullens M, et al. Irradiation of necrotic cancer cells employed for pulsing dendritic cells (DCs), potentiates DC vaccine-induced antitumor immunity against high-grade glioma. Oncoimmunology (2015). 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1083669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Riddell JR, Wang XY, Minderman H, Gollnick SO. Peroxiredoxin 1 stimulates secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by binding to TLR4. J Immunol (2010) 184(2):1022–30. 10.4049/jimmunol.0901945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Franz S, Herrmann K, Furnrohr BG, Sheriff A, Frey B, Gaipl US, et al. After shrinkage apoptotic cells expose internal membrane-derived epitopes on their plasma membranes. Cell Death Differ (2007) 14(4):733–42. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Petrovski G, Zahuczky G, Katona K, Vereb G, Martinet W, Nemes Z, et al. Clearance of dying autophagic cells of different origin by professional and non-professional phagocytes. Cell Death Differ (2007) 14(6):1117–28. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bratton DL, Fadok VA, Richter DA, Kailey JM, Guthrie LA, Henson PM. Appearance of phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells requires calcium-mediated nonspecific flip-flop and is enhanced by loss of the aminophospholipid translocase. J Biol Chem (1997) 272(42):26159–65. 10.1074/jbc.272.42.26159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, LaFace DM, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med (1995) 182(5):1545–56. 10.1084/jem.182.5.1545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Brouckaert G, Kalai M, Krysko DV, Saelens X, Vercammen D, Ndlovu MN, et al. Phagocytosis of necrotic cells by macrophages is phosphatidylserine dependent and does not induce inflammatory cytokine production. Mol Biol Cell (2004) 15(3):1089–100. 10.1091/mbc.E03-09-0668 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Donato R. RAGE: a single receptor for several ligands and different cellular responses: the case of certain S100 proteins. Curr Mol Med (2007) 7(8):711–24. 10.2174/156652407783220688 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Goh FG, Piccinini AM, Krausgruber T, Udalova IA, Midwood KS. Transcriptional regulation of the endogenous danger signal tenascin-C: a novel autocrine loop in inflammation. J Immunol (2010) 184(5):2655–62. 10.4049/jimmunol.0903359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Krispin A, Bledi Y, Atallah M, Trahtemberg U, Verbovetski I, Nahari E, et al. Apoptotic cell thrombospondin-1 and heparin-binding domain lead to dendritic-cell phagocytic and tolerizing states. Blood (2006) 108(10):3580–9. 10.1182/blood-2006-03-013334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, et al. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ (2015) 22(1):58–73. 10.1038/cdd.2014.137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Melcher A, Todryk S, Hardwick N, Ford M, Jacobson M, Vile RG. Tumor immunogenicity is determined by the mechanism of cell death via induction of heat shock protein expression. Nat Med (1998) 4(5):581–7. 10.1038/nm0598-581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Gough MJ, Melcher AA, Crittenden MR, Sanchez-Perez L, Voellmy R, Vile RG. Induction of cell stress through gene transfer of an engineered heat shock transcription factor enhances tumor immunogenicity. Gene Ther (2004) 11(13):1099–104. 10.1038/sj.gt.3302274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Spisek R, Charalambous A, Mazumder A, Vesole DH, Jagannath S, Dhodapkar MV. Bortezomib enhances dendritic cell (DC)-mediated induction of immunity to human myeloma via exposure of cell surface heat shock protein 90 on dying tumor cells: therapeutic implications. Blood (2007) 109(11):4839–45. 10.1182/blood-2006-10-054221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N, et al. Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med (2005) 202(12):1691–701. 10.1084/jem.20050915 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol (2013) 31:51–72. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Garg AD, Dudek-Peric AM, Romano E, Agostinis P. Immunogenic cell death. Int J Dev Biol (2015) 59:131–40. 10.1387/ijdb.150061pa [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Kepp O, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Vacchelli E, Adjemian S, Agostinis P, et al. Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3(9):e955691. 10.4161/21624011.2014.955691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dudek AM, Martin S, Garg AD, Agostinis P. Immature, semi-mature, and fully mature dendritic cells: toward a DC-cancer cells interface that augments anticancer immunity. Front Immunol (2014) 4:438. 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ma Y, Adjemian S, Mattarollo SR, Yamazaki T, Aymeric L, Yang H, et al. Anticancer chemotherapy-induced intratumoral recruitment and differentiation of antigen-presenting cells. Immunity (2013) 38(4):729–41. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zhang JG, Czabotar PE, Policheni AN, Caminschi I, Wan SS, Kitsoulis S, et al. The dendritic cell receptor Clec9A binds damaged cells via exposed actin filaments. Immunity (2012) 36(4):646–57. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Garnett CT, Palena C, Chakraborty M, Tsang KY, Schlom J, Hodge JW. Sublethal irradiation of human tumor cells modulates phenotype resulting in enhanced killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Res (2004) 64(21):7985–94. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Hodge JW, Garnett CT, Farsaci B, Palena C, Tsang KY, Ferrone S, et al. Chemotherapy-induced immunogenic modulation of tumor cells enhances killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and is distinct from immunogenic cell death. Int J Cancer (2013) 133(3):624–36. 10.1002/ijc.28070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Gameiro SR, Jammeh ML, Wattenberg MM, Tsang KY, Ferrone S, Hodge JW. Radiation-induced immunogenic modulation of tumor enhances antigen processing and calreticulin exposure, resulting in enhanced T-cell killing. Oncotarget (2014) 5(2):403–16. 10.18632/oncotarget.1719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, et al. Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science (2011) 334(6062):1573–7. 10.1126/science.1208347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Garg AD, Dudek AM, Agostinis P. Calreticulin surface exposure is abrogated in cells lacking, chaperone-mediated autophagy-essential gene, LAMP2A. Cell Death Dis (2013) 4:e826. 10.1038/cddis.2013.372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Martins I, Wang Y, Michaud M, Ma Y, Sukkurwala AQ, Shen S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ATP secretion during immunogenic cell death. Cell Death Differ (2014) 21(1):79–91. 10.1038/cdd.2013.75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kazama H, Ricci JE, Herndon JM, Hoppe G, Green DR, Ferguson TA. Induction of immunological tolerance by apoptotic cells requires caspase-dependent oxidation of high-mobility group box-1 protein. Immunity (2008) 29(1):21–32. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.05.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Jube S, Rivera Z, Bianchi ME, Powers A, Wang E, Pagano IS, et al. Cancer cell secretion of the DAMP protein HMGB1 supports progression in malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res (2012) 72(13):3290–301. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3481 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Garg AD, Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, Agostinis P. Hypericin-based photodynamic therapy induces surface exposure of damage-associated molecular patterns like HSP70 and calreticulin. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2012) 61(2):215–21. 10.1007/s00262-011-1184-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lancaster GI, Febbraio MA. Exosome-dependent trafficking of HSP70: a novel secretory pathway for cellular stress proteins. J Biol Chem (2005) 280(24):23349–55. 10.1074/jbc.M502017200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Mambula SS, Calderwood SK. Heat shock protein 70 is secreted from tumor cells by a nonclassical pathway involving lysosomal endosomes. J Immunol (2006) 177(11):7849–57. 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.7849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Vega VL, Rodriguez-Silva M, Frey T, Gehrmann M, Diaz JC, Steinem C, et al. Hsp70 translocates into the plasma membrane after stress and is released into the extracellular environment in a membrane-associated form that activates macrophages. J Immunol (2008) 180(6):4299–307. 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.4299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kotter B, Frey B, Winderl M, Rubner Y, Scheithauer H, Sieber R, et al. The in vitro immunogenic potential of caspase-3 proficient breast cancer cells with basal low immunogenicity is increased by hypofractionated irradiation. Radiat Oncol (2015) 10(1):197. 10.1186/s13014-015-0506-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Multhoff G, Botzler C, Wiesnet M, Muller E, Meier T, Wilmanns W, et al. A stress-inducible 72-kDa heat-shock protein (HSP72) is expressed on the surface of human tumor cells, but not on normal cells. Int J Cancer (1995) 61(2):272–9. 10.1002/ijc.2910610222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Gastpar R, Gehrmann M, Bausero MA, Asea A, Gross C, Schroeder JA, et al. Heat shock protein 70 surface-positive tumor exosomes stimulate migratory and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells. Cancer Res (2005) 65(12):5238–47. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Brockmeier U, Tesniere A, Bjorklund AC, Chapman DC, et al. Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death. EMBO J (2009) 28(5):578–90. 10.1038/emboj.2009.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Madeo F, Durchschlag M, Kepp O, Panaretakis T, Zitvogel L, Frohlich KU, et al. Phylogenetic conservation of the preapoptotic calreticulin exposure pathway from yeast to mammals. Cell Cycle (2009) 8(4):639–42. 10.4161/cc.8.4.7794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Martin S, Dudek-Peric AM, Maes H, Garg AD, Gabrysiak M, Demirsoy S, et al. Concurrent MEK and autophagy inhibition is required to restore cell death associated danger-signalling in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol (2015) 93(3):290–304. 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, et al. STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res (2015) 43(Database issue):D447–52. 10.1093/nar/gku1003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Dudek AM, Garg AD, Krysko DV, De Ruysscher D, Agostinis P. Inducers of immunogenic cancer cell death. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev (2013) 24(4):319–33. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Bezu L, Gomes-de-Silva LC, Dewitte H, Breckpot K, Fucikova J, Spisek R, et al. Combinatorial strategies for the induction of immunogenic cell death. Front Immunol (2015) 6:187. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Siurala M, Bramante S, Vassilev L, Hirvinen M, Parviainen S, Tahtinen S, et al. Oncolytic adenovirus and doxorubicin-based chemotherapy results in synergistic antitumor activity against soft-tissue sarcoma. Int J Cancer (2015) 136(4):945–54. 10.1002/ijc.29048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Menger L, Vacchelli E, Adjemian S, Martins I, Ma Y, Shen S, et al. Cardiac glycosides exert anticancer effects by inducing immunogenic cell death. Sci Transl Med (2012) 4(143):143ra99. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003807 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Panaretakis T, Joza N, Modjtahedi N, Tesniere A, Vitale I, Durchschlag M, et al. The co-translocation of ERp57 and calreticulin determines the immunogenicity of cell death. Cell Death Differ (2008) 15(9):1499–509. 10.1038/cdd.2008.67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Tufi R, Panaretakis T, Bianchi K, Criollo A, Fazi B, Di Sano F, et al. Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels favors plasma membrane surface exposure of calreticulin. Cell Death Differ (2008) 15(2):274–82. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Martins I, Kepp O, Schlemmer F, Adjemian S, Tailler M, Shen S, et al. Restoration of the immunogenicity of cisplatin-induced cancer cell death by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncogene (2011) 30(10):1147–58. 10.1038/onc.2010.500 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Verfaillie T, Rubio N, Garg AD, Bultynck G, Rizzuto R, Decuypere JP, et al. PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ (2012) 19(11):1880–91. 10.1038/cdd.2012.74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G. Organelle-specific initiation of cell death. Nat Cell Biol (2014) 16(8):728–36. 10.1038/ncb3005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Chaurio RA, Munoz LE, Maueroder C, Janko C, Harrer T, Furnrohr BG, et al. The progression of cell death affects the rejection of allogeneic tumors in immune-competent mice – implications for cancer therapy. Front Immunol (2014) 5:560. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Garg AD, Maes H, van Vliet AR, Agostinis P. Targeting the hallmarks of cancer with therapy-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Mol Cell Oncol (2015) 2(1):e975089. 10.4161/23723556.2014.975089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.van Vliet AR, Martin S, Garg AD, Agostinis P. The PERKs of damage-associated molecular patterns mediating cancer immunogenicity: from sensor to the plasma membrane and beyond. Semin Cancer Biol (2015) 33:74–85. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Senovilla L, Michaud M, Spaggiari S, Vacchelli E, et al. Screening of novel immunogenic cell death inducers within the NCI mechanistic diversity set. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3:e28473. 10.4161/onci.28473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Wong DY, Ong WW, Ang WH. Induction of immunogenic cell death by chemotherapeutic platinum complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl (2015) 54(22):6483–7. 10.1002/anie.201500934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Sistigu A, Yamazaki T, Vacchelli E, Chaba K, Enot DP, Adam J, et al. Cancer cell-autonomous contribution of type I interferon signaling to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Nat Med (2014) 20(11):1301–9. 10.1038/nm.3708 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Ramakrishnan R, Gabrilovich DI. The role of mannose-6-phosphate receptor and autophagy in influencing the outcome of combination therapy. Autophagy (2013) 9(4):615–6. 10.4161/auto.23485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Kaminski JM, Shinohara E, Summers JB, Niermann KJ, Morimoto A, Brousal J. The controversial abscopal effect. Cancer Treat Rev (2005) 31(3):159–72. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2005.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Golden EB, Frances D, Pellicciotta I, Demaria S, Helen Barcellos-Hoff M, Formenti SC. Radiation fosters dose-dependent and chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3:e28518. 10.4161/onci.28518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Garrido G, Rabasa A, Sanchez B, Lopez MV, Blanco R, Lopez A, et al. Induction of immunogenic apoptosis by blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor activation with a specific antibody. J Immunol (2011) 187(10):4954–66. 10.4049/jimmunol.1003477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Bugaut H, Bruchard M, Berger H, Derangere V, Odoul L, Euvrard R, et al. Bleomycin exerts ambivalent antitumor immune effect by triggering both immunogenic cell death and proliferation of regulatory T cells. PLoS One (2013) 8(6):e65181. 10.1371/journal.pone.0065181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Diaconu I, Cerullo V, Hirvinen ML, Escutenaire S, Ugolini M, Pesonen SK, et al. Immune response is an important aspect of the antitumor effect produced by a CD40L-encoding oncolytic adenovirus. Cancer Res (2012) 72(9):2327–38. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2975 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Hemminki O, Parviainen S, Juhila J, Turkki R, Linder N, Lundin J, et al. Immunological data from cancer patients treated with Ad5/3-E2F-Delta24-GMCSF suggests utility for tumor immunotherapy. Oncotarget (2015) 6(6):4467–81. 10.18632/oncotarget.2901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Sun C, Wang H, Mao S, Liu J, Li S, Wang J. Reactive oxygen species involved in CT26 immunogenic cell death induced by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Immunol Lett (2015) 164(2):65–71. 10.1016/j.imlet.2015.02.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Miyamoto S, Inoue H, Nakamura T, Yamada M, Sakamoto C, Urata Y, et al. Coxsackievirus B3 Is an oncolytic virus with immunostimulatory properties that is active against lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res (2012) 72(10):2609–21. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, et al. Trial watch: oncolytic viruses for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology (2013) 2(6):e24612. 10.4161/onci.22789 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Schiavoni G, Sistigu A, Valentini M, Mattei F, Sestili P, Spadaro F, et al. Cyclophosphamide synergizes with type I interferons through systemic dendritic cell reactivation and induction of immunogenic tumor apoptosis. Cancer Res (2011) 71(3):768–78. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2788 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Viaud S, Saccheri F, Mignot G, Yamazaki T, Daillere R, Hannani D, et al. The intestinal microbiota modulates the anticancer immune effects of cyclophosphamide. Science (2013) 342(6161):971–6. 10.1126/science.1240537 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Fucikova J, Moserova I, Truxova I, Hermanova I, Vancurova I, Partlova S, et al. High hydrostatic pressure induces immunogenic cell death in human tumor cells. Int J Cancer (2014) 135(5):1165–77. 10.1002/ijc.28766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Adkins I, Fucikova J, Garg AD, Agostinis P, Spisek R. Physical modalities inducing immunogenic tumor cell death for cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3:e968434. 10.4161/21624011.2014.968434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Weiss EM, Meister S, Janko C, Ebel N, Schlucker E, Meyer-Pittroff R, et al. High hydrostatic pressure treatment generates inactivated mammalian tumor cells with immunogeneic features. J Immunotoxicol (2010) 7(3):194–204. 10.3109/15476911003657414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Garg AD, Agostinis P. ER stress, autophagy and immunogenic cell death in photodynamic therapy-induced anti-cancer immune responses. Photochem Photobiol Sci (2014) 13(3):474–87. 10.1039/c3pp50333j [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Yu Z, Geng J, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Fan Q, Chen J. Treatment of osteosarcoma with microwave thermal ablation to induce immunogenic cell death. Oncotarget (2014) 5(15):6526–39. 10.18632/oncotarget.2310 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Zamarin D, Holmgaard RB, Subudhi SK, Park JS, Mansour M, Palese P, et al. Localized oncolytic virotherapy overcomes systemic tumor resistance to immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med (2014) 6(226):226ra32. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Chen HM, Wang PH, Chen SS, Wen CC, Chen YH, Yang WC, et al. Shikonin induces immunogenic cell death in tumor cells and enhances dendritic cell-based cancer vaccine. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2012) 61(11):1989–2002. 10.1007/s00262-012-1258-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Korbelik M, Dougherty GJ. Photodynamic therapy-mediated immune response against subcutaneous mouse tumors. Cancer Res (1999) 59(8):1941–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Krosl G, Korbelik M, Dougherty GJ. Induction of immune cell infiltration into murine SCCVII tumour by photofrin-based photodynamic therapy. Br J Cancer (1995) 71(3):549–55. 10.1038/bjc.1995.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Korbelik M, Stott B, Sun J. Photodynamic therapy-generated vaccines: relevance of tumour cell death expression. Br J Cancer (2007) 97(10):1381–7. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Korbelik M, Zhang W, Merchant S. Involvement of damage-associated molecular patterns in tumor response to photodynamic therapy: surface expression of calreticulin and high-mobility group box-1 release. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2011) 60(10):1431–7. 10.1007/s00262-011-1047-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Duewell P, Steger A, Lohr H, Bourhis H, Hoelz H, Kirchleitner SV, et al. RIG-I-like helicases induce immunogenic cell death of pancreatic cancer cells and sensitize tumors toward killing by CD8 T cells. Cell Death Differ (2014) 21(12):1825–37. 10.1038/cdd.2014.96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.West AC, Mattarollo SR, Shortt J, Cluse LA, Christiansen AJ, Smyth MJ, et al. An intact immune system is required for the anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Res (2013) 73(24):7265–76. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Yang Y, Li XJ, Chen Z, Zhu XX, Wang J, Zhang LB, et al. Wogonin induced calreticulin/annexin A1 exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cells in a PERK/AKT dependent manner. PLoS One (2012) 7(12):e50811. 10.1371/journal.pone.0050811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Panzarini E, Inguscio V, Fimia GM, Dini L. Rose Bengal acetate photodynamic therapy (RBAc-PDT) induces exposure and release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in human HeLa cells. PLoS One (2014) 9(8):e105778. 10.1371/journal.pone.0105778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Molinari R, D’Eliseo D, Manzi L, Zolla L, Velotti F, Merendino N. The n3-polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid induces immunogenic cell death in human cancer cell lines via pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2011) 60(10):1503–7. 10.1007/s00262-011-1074-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.D’Eliseo D, Manzi L, Velotti F. Capsaicin as an inducer of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of immunogenic cell death (ICD) in human bladder cancer cells. Cell Stress Chaperones (2013) 18(6):801–8. 10.1007/s12192-013-0422-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Gilardini Montani MS, D’Eliseo D, Cirone M, Di Renzo L, Faggioni A, Santoni A, et al. Capsaicin-mediated apoptosis of human bladder cancer cells activates dendritic cells via CD91. Nutrition (2015) 31(4):578–81. 10.1016/j.nut.2014.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Janeway C. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 6th ed New York, NY: Garland Science; (2005). 823 p. [Google Scholar]
- 173.Fucikova J, Kralikova P, Fialova A, Brtnicky T, Rob L, Bartunkova J, et al. Human tumor cells killed by anthracyclines induce a tumor-specific immune response. Cancer Res (2011) 71(14):4821–33. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0950 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Krysko DV, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Heyndrickx L, Woznicki J, Bogaert P, et al. TLR-2 and TLR-9 are sensors of apoptosis in a mouse model of doxorubicin-induced acute inflammation. Cell Death Differ (2011) 18(8):1316–25. 10.1038/cdd.2011.4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Tseng LM, Liu CY, Chang KC, Chu PY, Shiau CW, Chen KF. CIP2A is a target of bortezomib in human triple negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res (2012) 14(2):R68. 10.1186/bcr3175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Davies AM, Lara PN, Jr, Mack PC, Gandara DR. Incorporating bortezomib into the treatment of lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res (2007) 13(15 Pt 2):s4647–51. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Huang T, Li S, Li G, Tian Y, Wang H, Shi L, et al. Utility of Clostridium difficile toxin B for inducing anti-tumor immunity. PLoS One (2014) 9(10):e110826. 10.1371/journal.pone.0110826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Bravim F, de Freitas JM, Fernandes AA, Fernandes PM. High hydrostatic pressure and the cell membrane: stress response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ann N Y Acad Sci (2010) 1189:127–32. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05182.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Senovilla L, Vitale I, Martins I, Tailler M, Pailleret C, Michaud M, et al. An immunosurveillance mechanism controls cancer cell ploidy. Science (2012) 337(6102):1678–84. 10.1126/science.1224922 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Korbelik M. Cancer vaccines generated by photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci (2011) 10(5):664–9. 10.1039/c0pp00343c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Garg AD, Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, Agostinis P. DAMPs and PDT-mediated photo-oxidative stress: exploring the unknown. Photochem Photobiol Sci (2011) 10(5):670–80. 10.1039/c0pp00294a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Chen J, Xie J, Jiang Z, Wang B, Wang Y, Hu X. Shikonin and its analogs inhibit cancer cell glycolysis by targeting tumor pyruvate kinase-M2. Oncogene (2011) 30(42):4297–306. 10.1038/onc.2011.137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Tsai CF, Yeh WL, Huang SM, Tan TW, Lu DY. Wogonin induces reactive oxygen species production and cell apoptosis in human glioma cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci (2012) 13(8):9877–92. 10.3390/ijms13089877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Sanovic R, Verwanger T, Hartl A, Krammer B. Low dose hypericin-PDT induces complete tumor regression in BALB/c mice bearing CT26 colon carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther (2011) 8(4):291–6. 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2011.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Garg AD, Krysko DV, Vandenabeele P, Agostinis P. The emergence of phox-ER stress induced immunogenic apoptosis. OncoImmunology (2012) 1(5):787–9. 10.4161/onci.19750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Liu Z, Zhang HM, Yuan J, Ye X, Taylor GA, Yang D. The immunity-related GTPase Irgm3 relieves endoplasmic reticulum stress response during Coxsackievirus B3 infection via a PI3K/Akt dependent pathway. Cell Microbiol (2012) 14(1):133–46. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01708.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Bian J, Wang K, Kong X, Liu H, Chen F, Hu M, et al. Caspase- and p38-MAPK-dependent induction of apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells by Newcastle disease virus. Arch Virol (2011) 156(8):1335–44. 10.1007/s00705-011-0987-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Garg AD, De Ruysscher D, Agostinis P. Immunological metagene signatures derived from immunogenic cancer cell death associate with improved survival of patients with lung, breast or ovarian malignancies: a large-scale meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology (2015). 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1069938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Enlightening the impact of immunogenic cell death in photodynamic cancer therapy. EMBO J (2012) 31(5):1055–7. 10.1038/emboj.2012.2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, et al. Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J (2015) 34(7):856–80. 10.15252/embj.201490784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Mattarollo SR, Loi S, Duret H, Ma Y, Zitvogel L, Smyth MJ. Pivotal role of innate and adaptive immunity in anthracycline chemotherapy of established tumors. Cancer Res (2011) 71(14):4809–20. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Lin TJ, Lin HT, Chang WT, Mitapalli SP, Hsiao PW, Yin SY, et al. Shikonin-enhanced cell immunogenicity of tumor vaccine is mediated by the differential effects of DAMP components. Mol Cancer (2015) 14:174. 10.1186/s12943-015-0435-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Ma Y, Aymeric L, Locher C, Mattarollo SR, Delahaye NF, Pereira P, et al. Contribution of IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells to the efficacy of anticancer chemotherapy. J Exp Med (2011) 208(3):491–503. 10.1084/jem.20100269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Yang H, Yamazaki T, Pietrocola F, Zhou H, Zitvogel L, Ma Y, et al. STAT3 inhibition enhances the therapeutic efficacy of immunogenic chemotherapy by stimulating type 1 interferon production by cancer cells. Cancer Res (2015) 75(18):3812–22. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Ciampricotti M, Hau CS, Doornebal CW, Jonkers J, de Visser KE. Chemotherapy response of spontaneous mammary tumors is independent of the adaptive immune system. Nat Med (2012) 18(3):344–6. 10.1038/nm.2652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Gould SE, Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ. Translational value of mouse models in oncology drug development. Nat Med (2015) 21(5):431–9. 10.1038/nm.3853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O, Martins I, Ghiringhelli F, et al. Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene (2010) 29(4):482–91. 10.1038/onc.2009.356 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Hannesdottir L, Tymoszuk P, Parajuli N, Wasmer MH, Philipp S, Daschil N, et al. Lapatinib and doxorubicin enhance the Stat1-dependent antitumor immune response. Eur J Immunol (2013) 43(10):2718–29. 10.1002/eji.201242505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Michaud M, Xie X, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Zitvogel L, White E, Kroemer G. An autophagy-dependent anticancer immune response determines the efficacy of melanoma chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3(7):e944047. 10.4161/21624011.2014.944047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Demaria S, Santori FR, Ng B, Liebes L, Formenti SC, Vukmanovic S. Select forms of tumor cell apoptosis induce dendritic cell maturation. J Leukoc Biol (2005) 77(3):361–8. 10.1189/jlb.0804478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Schumacher LY, Vo DD, Garban HJ, Comin-Anduix B, Owens SK, Dissette VB, et al. Immunosensitization of tumor cells to dendritic cell-activated immune responses with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341, Velcade). J Immunol (2006) 176(8):4757–65. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.4757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Chang CL, Hsu YT, Wu CC, Yang YC, Wang C, Wu TC, et al. Immune mechanism of the antitumor effects generated by bortezomib. J Immunol (2012) 189(6):3209–20. 10.4049/jimmunol.1103826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.van der Most RG, Currie AJ, Mahendran S, Prosser A, Darabi A, Robinson BW, et al. Tumor eradication after cyclophosphamide depends on concurrent depletion of regulatory T cells: a role for cycling TNFR2-expressing effector-suppressor T cells in limiting effective chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2009) 58(8):1219–28. 10.1007/s00262-008-0628-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Obeid M, Panaretakis T, Joza N, Tufi R, Tesniere A, van Endert P, et al. Calreticulin exposure is required for the immunogenicity of gamma-irradiation and UVC light-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ (2007) 14(10):1848–50. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Carr-Brendel V, Markovic D, Smith M, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Cohen EP. Immunity to breast cancer in mice immunized with X-irradiated breast cancer cells modified to secrete IL-12. J Immunother (1999) 22(5):415–22. 10.1097/00002371-199909000-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Strome SE, Voss S, Wilcox R, Wakefield TL, Tamada K, Flies D, et al. Strategies for antigen loading of dendritic cells to enhance the antitumor immune response. Cancer Res (2002) 62(6):1884–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Prasad SJ, Farrand KJ, Matthews SA, Chang JH, McHugh RS, Ronchese F. Dendritic cells loaded with stressed tumor cells elicit long-lasting protective tumor immunity in mice depleted of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol (2005) 174(1):90–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.174.1.90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Yang H, Zhou P, Huang H, Chen D, Ma N, Cui QC, et al. Shikonin exerts antitumor activity via proteasome inhibition and cell death induction in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer (2009) 124(10):2450–9. 10.1002/ijc.24195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Sharma P, Allison JP. The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science (2015) 348(6230):56–61. 10.1126/science.aaa8172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Viney M, Lazarou L, Abolins S. The laboratory mouse and wild immunology. Parasite Immunol (2015) 37(5):267–73. 10.1111/pim.12150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Davis MM. A prescription for human immunology. Immunity (2008) 29(6):835–8. 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Mestas J, Hughes CC. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol (2004) 172(5):2731–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.172.5.2731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Tubiana M. Klaas Breur medal lecture 1985. The growth and progression of human tumors: implications for management strategy. Radiother Oncol (1986) 6(3):167–84. 10.1016/S0167-8140(86)80151-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Klein CA. Parallel progression of primary tumours and metastases. Nat Rev Cancer (2009) 9(4):302–12. 10.1038/nrc2627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Yamazaki T, Hannani D, Poirier-Colame V, Ladoire S, Locher C, Sistigu A, et al. Defective immunogenic cell death of HMGB1-deficient tumors: compensatory therapy with TLR4 agonists. Cell Death Differ (2014) 21(1):69–78. 10.1038/cdd.2013.72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Loi S, Pommey S, Haibe-Kains B, Beavis PA, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ, et al. CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2013) 110(27):11091–6. 10.1073/pnas.1222251110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Shalapour S, Font-Burgada J, Di Caro G, Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Dhar D, et al. Immunosuppressive plasma cells impede T-cell-dependent immunogenic chemotherapy. Nature (2015) 521(7550):94–8. 10.1038/nature14395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.De Boo S, Kopecka J, Brusa D, Gazzano E, Matera L, Ghigo D, et al. iNOS activity is necessary for the cytotoxic and immunogenic effects of doxorubicin in human colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer (2009) 8:108. 10.1186/1476-4598-8-108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Riganti C, Castella B, Kopecka J, Campia I, Coscia M, Pescarmona G, et al. Zoledronic acid restores doxorubicin chemosensitivity and immunogenic cell death in multidrug-resistant human cancer cells. PLoS One (2013) 8(4):e60975. 10.1371/journal.pone.0060975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 220.Stoll G, Enot D, Mlecnik B, Galon J, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immune-related gene signatures predict the outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2014) 3(1):e27884. 10.4161/onci.27884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(4):252–64. 10.1038/nrc3239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Galon J, Angell HK, Bedognetti D, Marincola FM. The continuum of cancer immunosurveillance: prognostic, predictive, and mechanistic signatures. Immunity (2013) 39(1):11–26. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(4):298–306. 10.1038/nrc3245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Zitvogel L, Tesniere A, Kroemer G. Cancer despite immunosurveillance: immunoselection and immunosubversion. Nat Rev Immunol (2006) 6(10):715–27. 10.1038/nri1936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Ladoire S, Penault-Llorca F, Senovilla L, Dalban C, Enot D, Locher C, et al. Combined evaluation of LC3B puncta and HMGB1 expression predicts residual risk of relapse after adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Autophagy (2015) 11(10):1878–90. 10.1080/15548627.2015.1082022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Kacerovska D, Pizinger K, Majer F, Smid F. Photodynamic therapy of nonmelanoma skin cancer with topical Hypericum perforatum extract – a pilot study. Photochem Photobiol (2008) 84(3):779–85. 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00260.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Rook AH, Wood GS, Duvic M, Vonderheid EC, Tobia A, Cabana B. A phase II placebo-controlled study of photodynamic therapy with topical hypericin and visible light irradiation in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol (2010) 63(6):984–90. 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Koren H, Schenk GM, Jindra RH, Alth G, Ebermann R, Kubin A, et al. Hypericin in phototherapy. J Photochem Photobiol B (1996) 36(2):113–9. 10.1016/S1011-1344(96)07357-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Alecu M, Ursaciuc C, Halalau F, Coman G, Merlevede W, Waelkens E, et al. Photodynamic treatment of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with hypericin. Anticancer Res (1998) 18(6B):4651–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Liikanen I, Koski A, Merisalo-Soikkeli M, Hemminki O, Oksanen M, Kairemo K, et al. Serum HMGB1 is a predictive and prognostic biomarker for oncolytic immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2015) 4(3):e989771. 10.4161/2162402X.2014.989771 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH, Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: an update. CA Cancer J Clin (2011) 61(4):250–81. 10.3322/caac.20114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Suzuki Y, Mimura K, Yoshimoto Y, Watanabe M, Ohkubo Y, Izawa S, et al. Immunogenic tumor cell death induced by chemoradiotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res (2012) 72(16):3967–76. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Zappasodi R, Pupa SM, Ghedini GC, Bongarzone I, Magni M, Cabras AD, et al. Improved clinical outcome in indolent B-cell lymphoma patients vaccinated with autologous tumor cells experiencing immunogenic death. Cancer Res (2010) 70(22):9062–72. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Baitsch L, Fuertes-Marraco SA, Legat A, Meyer C, Speiser DE. The three main stumbling blocks for anticancer T cells. Trends Immunol (2012) 33(7):364–72. 10.1016/j.it.2012.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Redmond WL, Sherman LA. Peripheral tolerance of CD8 T lymphocytes. Immunity (2005) 22(3):275–84. 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Cole DK, Pumphrey NJ, Boulter JM, Sami M, Bell JI, Gostick E, et al. Human TCR-binding affinity is governed by MHC class restriction. J Immunol (2007) 178(9):5727–34. 10.4049/jimmunol.178.9.5727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Schmid DA, Irving MB, Posevitz V, Hebeisen M, Posevitz-Fejfar A, Sarria JC, et al. Evidence for a TCR affinity threshold delimiting maximal CD8 T cell function. J Immunol (2010) 184(9):4936–46. 10.4049/jimmunol.1000173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Zehn D, Bevan MJ. T cells with low avidity for a tissue-restricted antigen routinely evade central and peripheral tolerance and cause autoimmunity. Immunity (2006) 25(2):261–70. 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.06.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Baumgaertner P, Jandus C, Rivals JP, Derre L, Lovgren T, Baitsch L, et al. Vaccination-induced functional competence of circulating human tumor-specific CD8 T-cells. Int J Cancer (2012) 130(11):2607–17. 10.1002/ijc.26297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Gubin MM, Artyomov MN, Mardis ER, Schreiber RD. Tumor neoantigens: building a framework for personalized cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Invest (2015) 125(9):3413–21. 10.1172/JCI80008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science (2015) 348(6230):69–74. 10.1126/science.aaa4971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A, Rengan R, Pauken KE, Stelekati E, et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature (2015) 520(7547):373–7. 10.1038/nature14292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Ochsenbein AF, Klenerman P, Karrer U, Ludewig B, Pericin M, Hengartner H, et al. Immune surveillance against a solid tumor fails because of immunological ignorance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1999) 96(5):2233–8. 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Chu-Yuan H, Jing P, Yi-Sheng W, He-Ping P, Hui Y, Chu-Xiong Z, et al. The impact of chemotherapy-associated neutrophil/lymphocyte counts on prognosis of adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer (2013) 13:177. 10.1186/1471-2407-13-177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Inoges S, Rodriguez-Calvillo M, Zabalegui N, Lopez-Diaz de Cerio A, Villanueva H, Soria E, et al. Clinical benefit associated with idiotypic vaccination in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst (2006) 98(18):1292–301. 10.1093/jnci/djj358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Kakarla S, Gottschalk S. CAR T cells for solid tumors: armed and ready to go? Cancer J (2014) 20(2):151–5. 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]