Abstract
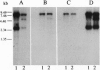
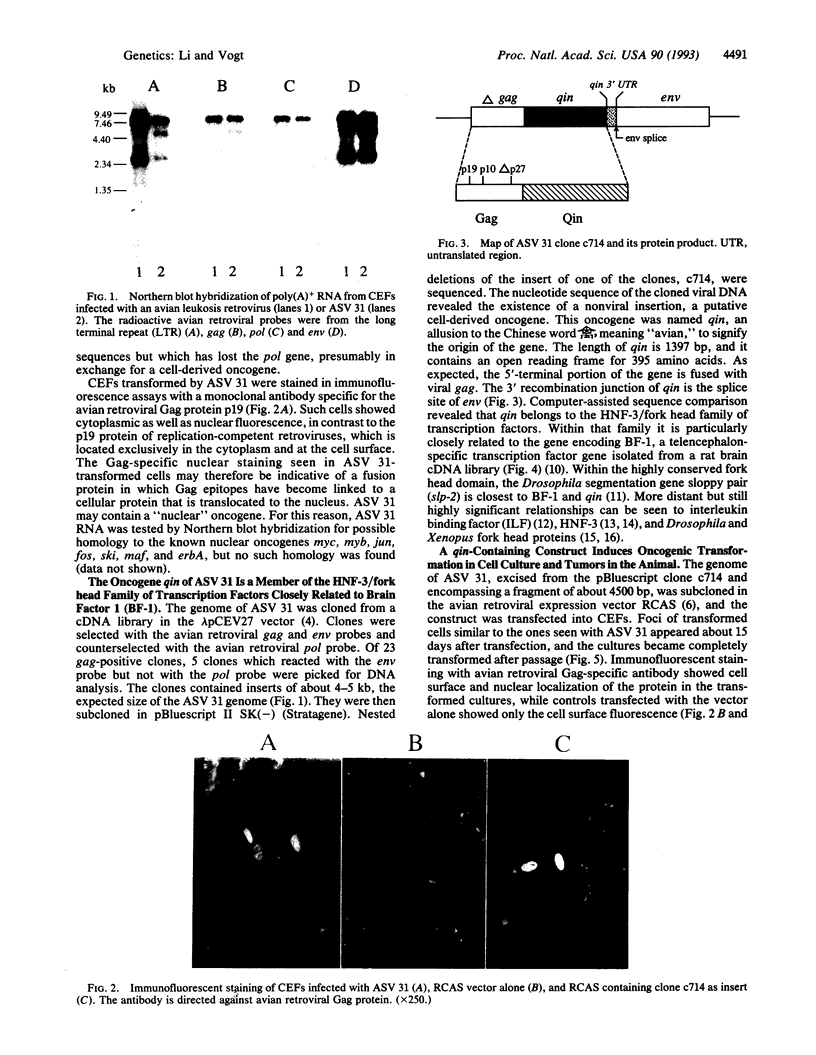
Avian sarcoma virus 31 contains an oncogene that we have named qin. qin codes for a nuclear protein, Qin, that is a member of the HNF-3/fork head family of transcriptional regulators. Within this family Qin is particularly closely related to rat brain factor 1 (BF-1), a telencephalon-specific gene presumed to play an important role in the development of the mammalian brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberdam D., Negreanu V., Sachs L., Blatt C. The oncogenic potential of an activated Hox-2.4 homeobox gene in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):554–557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Aberdam D., Schwartz R., Sachs L. DNA rearrangement of a homeobox gene in myeloid leukaemic cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4283–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Monteclaro F. S., Mitsunobu F., Ball A. R., Jr, Chang C. H., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K. Efficient transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by c-Jun requires structural modification in coding and noncoding sequences. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1677–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M. L., Jamrich M. A novel, activin-inducible, blastopore lip-specific gene of Xenopus laevis contains a fork head DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):599–608. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. The Drosophila sloppy paired locus encodes two proteins involved in segmentation that show homology to mammalian transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1030–1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häcker U., Grossniklaus U., Gehring W. J., Jäckle H. Developmentally regulated Drosophila gene family encoding the fork head domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Look A. T., Baltimore D. The human t(1;19) translocation in pre-B ALL produces multiple nuclear E2A-Pbx1 fusion proteins with differing transforming potentials. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):358–368. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. A., Gonzalez-Sarmiento R., Kees U. R., Lampert F., Dear N., Boehm T., Rabbitts T. H. HOX11, a homeobox-containing T-cell oncogene on human chromosome 10q24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8900–8904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Allen J., Adams J. M. Expression of Hox-2.4 homeobox gene directed by proviral insertion in a myeloid leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1881–1892. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Chen L., Sladek F. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Crabtree G. R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):457–461. doi: 10.1038/355457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lai C. F., Sigman D. S., Gaynor R. B. Cloning of a cellular factor, interleukin binding factor, that binds to NFAT-like motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Crescenzi M., Molloy C. J., Blam S. B., Reynolds S. H., Aaronson S. A. Development of a highly efficient expression cDNA cloning system: application to oncogene isolation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5167–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Matsui T., Heidaran M. A., Aaronson S. A. An efficient directional cloning system to construct cDNA libraries containing full-length inserts at high frequency. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Mellentin J. D., Galili N., Wilkinson J., Stanbridge E., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90657-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao W., Lai E. Telencephalon-restricted expression of BF-1, a new member of the HNF-3/fork head gene family, in the developing rat brain. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchie H., Chang C. H., Yoshida M., Vogt P. K. A newly isolated avian sarcoma virus, ASV-1, carries the crk oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1281–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jäckle H. The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):455–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]