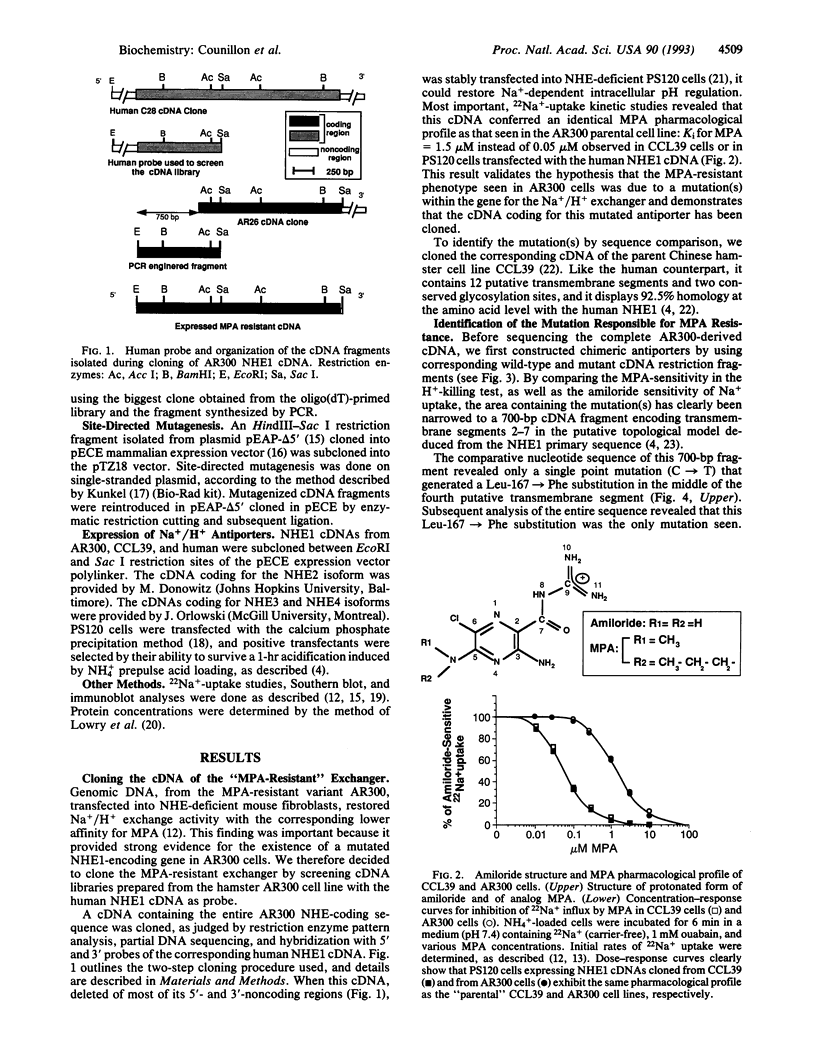
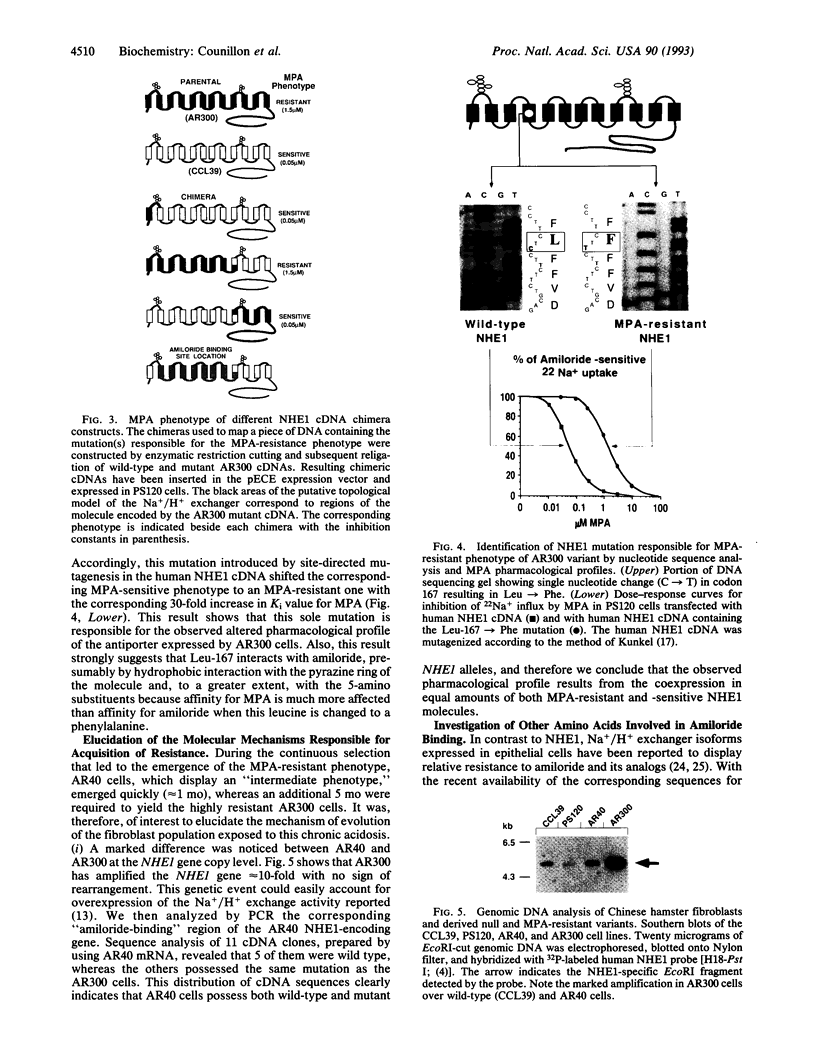
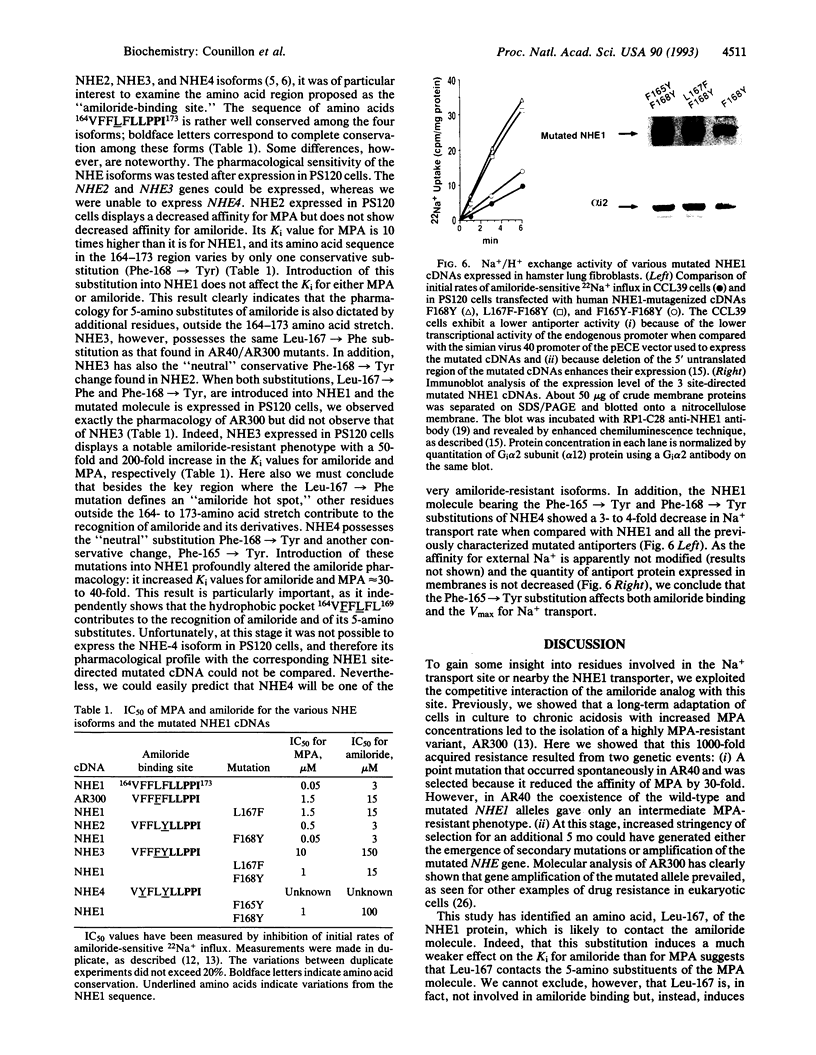
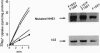Abstract
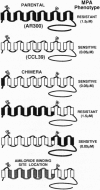
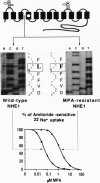
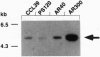
The diuretic drug amiloride and its 5-amino substitute N5-methyl-N5-propylamiloride (MPA) are potent inhibitors of the growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1). This inhibitor competes with Na+, presumably by interacting with the ion-transport site of the NHE molecule. As an approach to identify this site, we previously reported the use of a specific H(+)-killing selection technique for isolating amiloride-resistant variants of Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. After long-term selection, two variants, AR40 and AR300, 100- and 1000-fold, respectively, resistant to MPA, were isolated. By comparing NHE1 cDNA sequences of parental and two variant cell lines, we show that the 1000-fold resistance to MPA results from two sequential genetic events. (i) In one AR40 allele a point mutation, Phe-167--> Leu, occurs in the middle of the fourth putative transmembrane segment of NHE1. Producing this mutant protein from human NHE1 cDNA by site-directed mutagenesis increased the Ki for MPA by 30-fold, as seen in AR300 cells. (ii) An approximately 10-fold amplification of the mutated allele, which contributes to the acquired MPA resistance, accounts for the Vmax increase. Mutating a close residue, Phe-165--> Tyr, increased by 40-fold the Ki for amiloride and reduced Na+ transport rate 3- to 4-fold, indicating that we have identified a critical domain of the NHE molecule that controls amiloride binding and Na+ transport. Interestingly, the epithelial amiloride-resistant NHE isoforms that occurred naturally possess some of the amino acid substitutions described here.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counillon L., Pouysségur J. Nucleotide sequence of the Chinese hamster Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 20;1172(3):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. Importance of guanidinium groups of blocking sodium channels in epithelia. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):945–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchi A., Cragoe E., Jr, Pouysségur J. Isolation and properties of fibroblast mutants overexpressing an altered Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14614–14620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchi A., Perucca-Lostanlen D., Pouyssegur J. Functional expression of a human Na+/H+ antiporter gene transfected into antiporter-deficient mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9388–9392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Barros F., Dethmers J. K., Trumble M. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in pituitary plasma membrane vesicles by analogues of amiloride. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Paris S., Pouysségur J. Growth factor action and intracellular pH regulation in fibroblasts. Evidence for a major role of the Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5809–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski M., Frelin C., Vigne P. The sodium/hydrogen exchange system in cardiac cells: its biochemical and pharmacological properties and its role in regulating internal concentrations of sodium and internal pH. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Nov;17(11):1029–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., DeGrado W. F. A thermodynamic scale for the helix-forming tendencies of the commonly occurring amino acids. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):646–651. doi: 10.1126/science.2237415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Kandasamy R. A., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9331–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Sardet C., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. A specific mutation abolishing Na+/H+ antiport activity in hamster fibroblasts precludes growth at neutral and acidic pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran V. M., Binder H. J. Characterization of Na-H exchange in apical membrane vesicles of rat colon. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8408–8414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiporter, glycoprotein of 110 kD. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.2154036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. Ethylisopropyl-amiloride: a new and highly potent derivative of amiloride for the inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchange system in various cell types. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 14;116(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Sardet C., Fafournoux P., Counillon L., Meloche S., Pagés G., Pouysségur J. Structure function of the growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE1). Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:157–186. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]