Abstract
Introduction
Migraine affects 15% of the population, and has substantial health and socioeconomic costs. Pharmacological management is first-line treatment. However, acute and/or prophylactic medicine might not be tolerated due to side effects or contraindications. Thus, we aim to assess the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy (CSMT) for migraineurs in a single-blinded placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial (RCT).
Method and analysis
According to the power calculations, 90 participants are needed in the RCT. Participants will be randomised into one of three groups: CSMT, placebo (sham manipulation) and control (usual non-manual management). The RCT consists of three stages: 1 month run-in, 3 months intervention and follow-up analyses at the end of the intervention and 3, 6 and 12 months. The primary end point is migraine frequency, while migraine duration, migraine intensity, headache index (frequency x duration x intensity) and medicine consumption are secondary end points. Primary analysis will assess a change in migraine frequency from baseline to the end of the intervention and follow-up, where the groups CSMT and placebo and CSMT and control will be compared. Owing to two group comparisons, p values below 0.025 will be considered statistically significant. For all secondary end points and analyses, a p value below 0.05 will be used. The results will be presented with the corresponding p values and 95% CIs.
Ethics and dissemination
The RCT will follow the clinical trial guidelines from the International Headache Society. The Norwegian Regional Committee for Medical Research Ethics and the Norwegian Social Science Data Services have approved the project. Procedure will be conducted according to the declaration of Helsinki. The results will be published at scientific meetings and in peer-reviewed journals.
Trial registration number
Keywords: STATISTICS & RESEARCH METHODS
Strengths and limitations of this study.
The study will be the first three-armed manual therapy randomised clinical trial (RCT) assessing the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy versus placebo (sham manipulation) and control (continue usual pharmacological management without receiving manual intervention) for migraineurs.
Strong internal validity, since a single chiropractor will conduct all interventions.
The RCT has the potential to provide a non-pharmacological treatment option for migraineurs.
Risk for dropouts is increased due to strict exclusion criteria and 17 months duration of the RCT.
A generally accepted placebo has not been established for manual therapy; thus, there is a risk for unsuccessful blinding, while the investigator who provides the interventions cannot be blinded for obvious reasons.
Background
Migraine is a common health problem with substantial health and socioeconomic costs. On the recent Global Burden of Disease study, migraine was ranked as the third most common condition.1
About 15% of the general population have migraine.2 3 Migraine is usually unilateral with pulsating and moderate/severe headache which is aggravated by routine physical activity, and is accompanied by photophobia and phonophobia, nausea and sometimes vomiting.4 Migraine exists in two major forms, migraine without aura and migraine with aura (box 1). Aura is reversible neurological disturbances of the vision, sensory and/or speech function, occurring prior to the headache. However, intraindividual variations from attack to attack are common.5 6 The origin of migraine is debated. The painful impulses may originate from the trigeminal nerve, central and/or peripheral mechanisms.7 8 Extracranial pain sensitive structures include the skin, muscles, arteries, periosteum and joints. The skin is sensitive to all usual forms of pain stimuli, while temporal and neck muscles may especially be sources for pain and tenderness in migraine.9–11 Similarly, the frontal supraorbital, superficial temporal, posterior and occipital arteries are sensitive to pain.9 12
Box 1. The International Classification of Headache Disorders-II diagnostic criteria for migraine.
Migraine without aura
A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B–D
B. Headache attacks lasting 4–72 h (untreated or unsuccessfully treated)
C. Headache has at least two of the following characteristics:
1. Unilateral location
2. Pulsating quality
3. Moderate or severe pain intensity
4. Aggravated by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
D. During headache at least one of the following:
1. Nausea and/or vomiting
2. Photophobia and phonophobia
E. Not attributed to another disorder
Migraine with aura
A. At least two attacks fulfilling criteria B–D
B. Aura consisting of at least one of the following, but no motor weakness:
1. Fully reversible visual symptoms including positive features (ie, flickering lights, spots or lines) and/or negative features (ie, loss of vision). Moderate or severe pain intensity
2. Fully reversible sensory symptoms including positive features (ie, pins and needles) and/or negative features (ie, numbness)
3. Fully reversible dysphasic speech disturbance
C. At least two of the following:
1. Homonymous visual symptoms and/or unilateral sensory symptoms
2. At least one aura symptom develops gradually over ≥5 min and/or different aura symptoms occur in succession over ≥5 min
3. Each symptom lasts ≥5 and ≤60 min
D. Headache fulfilling criteria B-D for 1.1 Migraine without aura begins during the aura or follows the aura within 60 min
E. Not attributed to another disorder
Pharmacological management is the first treatment option for migraineurs. However, some patients do not tolerate acute and/or prophylactic medicine due to side effects or contraindications due to comorbidity of other diseases or due to a wish to avoid medication for other reasons. The risk of medication overuse due to frequent migraine attacks represents a major health hazard with direct and indirect cost concerns. The prevalence of medication overuse headache (MOH) is 1–2% in the general population,13–15 that is, about half the population suffering chronic headache (15 headache days or more per month) have MOH.16 Migraine causes loss of 270 workdays per year per 1000 persons from the general population.17 This corresponds to about 3700 work years lost per year in Norway due to migraine. The economic cost per migraineur was estimated to be $655 in USA and €579 in Europe per year.18 19 Owing to the high prevalence of migraine, the total cost per year was estimated to be $14.4 billion in the USA and €27 billion in the EU countries, Iceland, Norway and Switzerland at that time. Migraine costs more than neurological disorders such as dementia, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and stroke.20 Thus, non-pharmacological treatment options are warranted.
The Diversified technique and the Gonstead method are the two most commonly used chiropractic manipulative treatment modalities in the profession, used by 91% and 59%, respectively,21 22 along with other manual and non-manual interventions, that is, soft tissue techniques, spinal and peripheral mobilisation, rehabilitation, postural corrections and exercises as well as general nutrition and dietetic advice.
A few spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) randomised controlled trials (RCTs) using the Diversified technique have been conducted for migraine, suggesting an effect on migraine frequency, migraine duration, migraine intensity and medicine consumption.23–26 However, common for previous RCTs are the methodological shortcomings such as inaccurate headache diagnosis, that is, questionnaire diagnoses used are imprecise,27 inadequate or no randomisation procedure, lack of placebo group, and primary and secondary end points not prespecified.28–31 In addition, previous RCTs did not consequently adhere to the recommended clinical guidelines from the International Headache Society (IHS).32 33 At present, no RCTs have applied the Gonstead chiropractic SMT (CSMT) method. Thus, considering the methodological shortcomings in previous RCTs, a clinical placebo-controlled RCT with improved methodological quality remains to be conducted for migraine.
The SMT mechanism of action on migraine is unknown. It is argued that migraine might originate from a complexity of nociceptive afferent responses involving the upper cervical spine (C1, C2 and C3), leading to a hypersensitivity state of the trigeminal pathway conveying sensory information for the face and much of the head.34 35 Research has thus suggested that SMT may stimulate neural inhibitory systems at different spinal cord levels, and might activate various central descending inhibitory pathways.36–40 However, although the proposed physiological mechanisms are not fully understood, there are most likely additional unexplored mechanisms which could explain the effect SMT has on mechanical pain sensitisation.
The objective of this study is to assess the efficacy of CSMT versus placebo (sham manipulation) and controls (continue usual pharmacological management without receiving manual intervention) for migraineurs in an RCT.
Method and design
This is a single-blinded placebo-controlled RCT with three parallel groups (CSMT, placebo and control). Our primary hypothesis is that CSMT gives at least 25% reduction in the average number of migraine days per month (30 days/month) as compared to placebo and control from baseline to the end of intervention, and we expect the same reduction to be maintained at 3, 6 and 12 months follow-up. If the CSMT treatment is effective, it will be offered to participants who received placebo or control after study completion, that is, after 12 months follow-up. The study will adhere to the recommended clinical trial guidelines from the IHS,32 33 and the methodological CONSORT and SPIRIT guidelines.41 42
Patient population
Participants will be recruited in the period January to September 2013 through the Akershus University Hospital, through general practitioners and media advertisement, that is, posters with general information will be put up at general practitioners’ offices along with oral information in the Akershus and Oslo counties, Norway. Participants will receive posted information about the project followed by a short telephone interview. Those recruited from the general practitioners’ offices will have to contact the clinical investigator whose contact details have been provided on the posters in order to obtain extensive information about the study.
Eligible participants are between 18 and 70 years of age and have at least one migraine attack per month. Participants are diagnosed according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-II) by a neurologist at the Akershus University Hospital.43 They are only allowed to have co-occurrence of tension-type headache and not other primary headaches.
Exclusion criteria are contraindication to SMT, spinal radiculopathy, pregnancy, depression and CSMT within the previous 12 months. Participants whom during the RCT receive any manual interventions by physiotherapists, chiropractors, osteopaths or other health professionals to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability, including massage therapy, joint mobilisation and manipulation,44 changed their prophylactic headache medicine or pregnancy will be withdrawn from the study at that time and be regarded as dropouts. They are allowed to continue and change their usual acute migraine medication throughout the trial.
In response to initial contact, participants fulfilling the inclusion criteria will be invited to further assessment by the chiropractic investigator. The assessment includes an interview and a physical examination with special emphasis on the whole spinal column. Oral and written information about the project will be provided in advance and oral and written consent will be obtained from all accepted participants during the interview and by the clinical investigator. In accordance with good clinical practice, all patients will be informed about the harms and benefits as well as possible adverse reactions of the intervention primarily including local tenderness and tiredness on the treatment day. No serious adverse events have been reported for the chiropractic Gonstead method.45 46 Participants randomised into active or placebo interventions will undergo a full spine radiographic examination and be scheduled for 12 intervention sessions. The control group will not be exposed to this assessment.
Clinical RCT
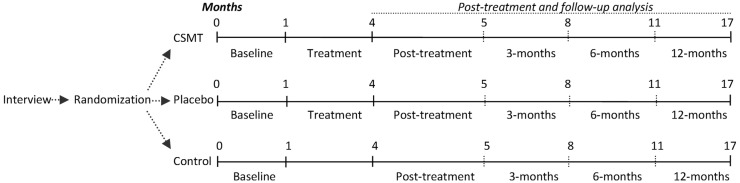
The clinical RCT consists of a 1 month run-in and 3 months intervention. Time profile will be assessed from baseline to the end of follow-up for all end points (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Study flow chart. CSMT, chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy; Placebo, sham manipulation; Control, continue usual pharmacological management without receiving manual intervention.
Run-in
The participants will fill in a validated diagnostic paper headache diary 1 month prior to intervention which will be used as baseline data for all participants.47 48 The validated diary includes questions directly related to the primary and secondary end points. X-rays will be taken in standing position in the anterioposterior and lateral planes of the entire spine. The X-rays will be assessed by the chiropractic investigator.
Randomisation
Prepared sealed lots with the three interventions, that is, active treatment, placebo and the control group, will be subdivided into four subgroups by age and gender, that is, 18–39 and 40–70 years of age and men and women, respectively. Participants will be equally allocated to the three groups by allowing the participant to draw one lot only. The block randomisation will be administrated by an external trained party with no involvement from the clinical investigator.
Intervention
Active treatment consists of CSMT using the Gonstead method,21 that is, a specific contact, high-velocity, low-amplitude, short-lever spinal with no postadjustment recoil directed to spinal biomechanical dysfunction (full spine approach) as diagnosed by standard chiropractic tests.
The placebo intervention consists of sham manipulation, that is, a broad non-specific contact, low-velocity, low-amplitude sham push manoeuvre in a non-intentional and non-therapeutic directional line. All the non-therapeutic contacts will be performed outside the spinal column with adequate joint slack and without soft tissue pretension so that no joint cavitations occur. In some sessions, the participant lay either prone on a Zenith 2010 HYLO bench with the investigator standing at the participant's right side with his left palm placed on the participant's right lateral scapular edge with the other hand reinforcing. In other sessions, the investigator will stand at the participant's left side and place his right palm over the participant's left scapular edge with the left hand reinforcing, delivering a non-intentional lateral push manoeuvre. Alternatively, the participant lay in the same side posture position as the active treatment group with the bottom leg straight and the top leg flexed with the top leg's ankle resting on the bottom leg's knee fold, in preparation for a side posture push move, which will be delivered as a non-intentional push in the gluteal region. The sham manipulation alternatives will be equally interchanged among the placebo participants according to protocol during the 12-week treatment period to strengthen the study validity. The active and the placebo groups will receive the same structural and motion assessment prior to and after each intervention. No additional cointerventions or advice will be given to participants during the trial period. The treatment period will include 12 consultations, that is, twice per week in the first 3 weeks followed by once a week in the next 2 weeks and once every second week until 12 weeks are reached. Fifteen minutes will be allocated per consultation for each participant. All interventions will be conducted at the Akershus University Hospital and administered by an experienced chiropractor (AC).
The control group will continue usual care, that is, pharmacological management without receiving manual intervention by the clinical investigator. The same exclusion criteria apply for the control group during the whole study period.
Blinding
After each treatment session, the participants who receive active or placebo intervention will complete a de-blinding questionnaire administrated by an external trained independent party with no involvement from the clinical investigator, that is, providing a dichotomous ‘yes’ or ‘no’ answer as to whether active treatment was received. This response was followed by a second question regarding how certain they were that active treatment was received on a 0–10 numeric rating scale (NRS), where 0 represents absolutely uncertain and 10 represents absolutely certainty. The control group and the clinical investigator can for obvious reasons not be blinded.49 50
Follow-up
Follow-up analysis will be conducted on the end points measured after the end of intervention and at 3, 6 and 12 months follow-up. During this period, all participants will continue to fill in a diagnostic paper headache diary and return it on a monthly basis. In the case of unreturned diary or missing values in the diary, the participants will be contacted immediately on detection to minimise recall bias. Participants will be contacted by phone to secure compliance.
Primary and secondary end points
The primary and secondary end points are listed in box 2. The end points adhere to the recommended IHS clinical trial guidelines.32 33 We define number of migraine days as the primary end point and expect at least a 25% reduction in average number of days from baseline to the end of intervention, with the same level of reduction being maintained at follow-up. On the basis of previous reviews on migraine, a 25% reduction is considered to be a conservative estimate.30 A 25% reduction is also expected in secondary end points from baseline to the end of intervention, retaining at follow-up for migraine duration, migraine intensity and headache index, where the index is calculated as number of migraine days (30 days)×average migraine duration (hours per day)×average intensity (0–10 NRS). A 50% reduction in medication consumption from baseline to the end of intervention and to follow-up is expected.
Box 2. Primary and secondary end points.
Primary end points
1. Number of migraine days in active treatment versus placebo group.
2. Number of migraine days in active treatment versus control group.
Secondary end points
3. Migraine duration in hours in active treatment versus placebo group.
4. Migraine duration in hours in active treatment versus control group.
5. Self-reported VAS in active treatment versus placebo group.
6. Self-reported VAS in active treatment versus control group.
7. Headache index (frequency x duration x intensity) in active treatment versus placebo group.
8. Headache index in active treatment versus control group.
9. Headache medication dosage in active treatment versus placebo group.
10. Headache medication dosage in active treatment versus control group.
*The data analysis is based on the run-in period versus end of intervention. Point 11–40 will be duplicate of point 1–10 above at 3, 6 and 12 months follow-up, respectively.
Data processing
A flow chart of the participants is shown in figure 2. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics will be tabulated as means and SDs for continuous variables and proportions and percentages for categorical variables. Each of three groups will be described separately. Primary and secondary end points will be presented by suitable descriptive statistics in each group and for each time point. Normality of end points will be assessed graphically and transformation will be considered if necessary.
Figure 2.
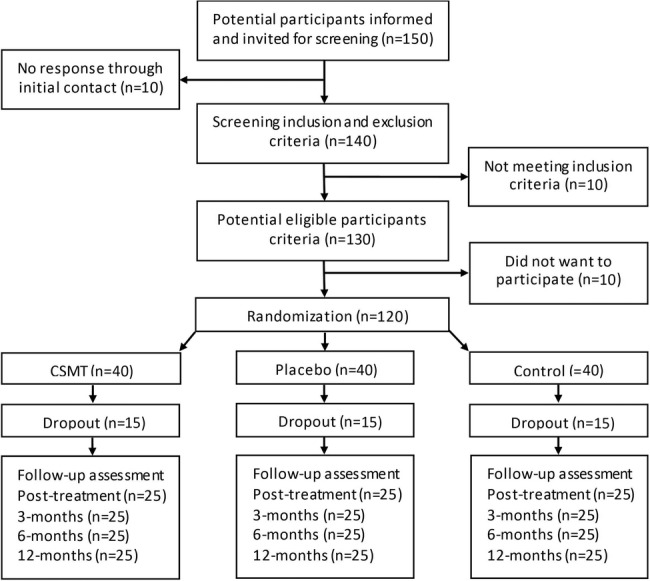
Expected participant's flow diagram. CSMT, chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy; Placebo, sham manipulation; Control, continue usual pharmacological management without receiving manual intervention.
Change in primary and secondary end points from baseline to the end of intervention and to follow-up will be compared between the active and placebo groups and the active and control groups. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference between the groups in average change, while the alternative hypothesis states that a difference of at least 25% exists.
Owing to the follow-up period, repeated recordings of primary and secondary end points will be available, and analyses of trend in primary and secondary end points will be of main interest. Intra-individual correlations (cluster effect) are likely to be present in data with repeated measurements. Cluster effect will thus be assessed by calculating intraclass correlation coefficient quantifying the proportion of total variation attributable to the intraindividual variations. The trend in end points will be assessed by a linear regression model for longitudinal data (linear mixed model) to correctly account for the possible cluster effect. The linear mixed model handles unbalanced data, enabling all available information from randomised patients to be included, as well as from dropouts. Regression models with fixed effects for time component and group allocation as well as the interaction between the two will be estimated. The interaction will quantify possible differences between groups regarding time trend in the end points and serve as an omnibus test. Random effects for patients will be included to adjust the estimates for intraindividual correlations. Random slopes will be considered. The linear mixed models will be estimated by the SAS PROC MIXED procedure. The two pairwise comparisons will be performed by deriving individual time point contrasts within each group with the corresponding p values and 95% CIs.
Both per-protocol and intention-to-treat analyses will be conducted if relevant. All analyses will be performed by a statistician, blinded for group allocation and participants. All adverse effects will also be registered and presented. Participants who experience any sort of adverse effects during the trial period will be entitled to call the clinical investigator on the project cell phone. The data will be analysed with SPSS V.22 and SAS V.9.3. Owing to two group comparisons in the primary end point, p values below 0.025 will be considered statistically significant. For all secondary end points and analyses, a significance level of 0.05 will be used. Missing values might appear in incomplete interview questionnaires, incomplete headache diaries, missed intervention sessions and/or due to dropouts. The pattern of missingness will be assessed and missing values handled adequately.
Power calculation
Sample size calculations are based on the results in a recently published group comparison study on topiramate.51 We hypothesise that the average difference in reduction of number of days with migraine per month between the active and the placebo groups is 2.5 days. The same difference is assumed between the active and control groups. SD for reduction in each group is assumed to be equal to 2.5. Under the assumption of, on average, 10 migraine days per month at baseline in each group and no change in the placebo or control group during the study, 2.5 days reduction corresponds to a reduction by 25%. Since primary analysis includes two group comparisons, we set a significance level at 0.025. A sample size of 20 patients is required in each group to detect a statistically significant average difference in reduction of 25% with 80% power. To allow for dropouts, the investigators plan to recruit 120 participants.
Discussion
Methodological considerations
Current SMT RCTs on migraine suggest treatment efficacy regarding migraine frequency, duration and intensity. However, a firm conclusion requires clinical single-blinded placebo-controlled RCTs with few methodological shortcomings.30 Such studies should adhere to the recommended IHS clinical trial guidelines with migraine frequency as the primary end point and migraine duration, migraine intensity, headache index and medication consumption as secondary end points.32 33 The headache index, as well as a combination of frequency, duration and intensity, gives an indication of the total level of suffering. Despite the lack of consensus, the headache index has been recommended as an accepted standard secondary end point.33 52 53 The primary and secondary end points will be collected prospectively in a validated diagnostic headache diary for all participants in order to minimise recall bias.47 48 To the best of our knowledge, this is the first prospective manual therapy in a three-armed single-blinded placebo-controlled RCT to be conducted for migraine. The study design adheres to the recommendations for pharmacological RCTs as far as possible. RCTs that include a placebo group and a control group are advantageous to pragmatic RCTs that compare two active treatment arms. RCTs also provide the best approach for producing safety as well as efficacy data.
Unsuccessful blinding is a possible risk to the RCT. Blinding is often difficult as there is no single validated standardised chiropractic sham intervention which can be used as a control group for this date. It is, however, necessary to include a placebo group in order to produce a true net effect of the active intervention. Consensus about an appropriate placebo for a clinical trial of SMT among experts representing clinicians and academics has, however, not been reached.54 No previous studies have, to the best of our knowledge, validated a successful blinding of a CSMT clinical trial with multiple treatment sessions. We intend to minimise this risk by following the proposed protocol for the placebo group.
The placebo response is furthermore high in pharmacological and assumed similarly high for non-pharmacological clinical studies; however, it might even be higher in manual therapy RCTs were attention and physical contact is involved.55 Similarly, a natural concern with regard to attention bias will be involved for the control group as it is not being seen by anyone or not seen as much by the clinical investigator as the other two groups.
There are always risks for dropouts due to various reasons. Since the trial duration is 17 months with a 12 month follow-up period, the risk for loss to follow-up is thus enhanced. Co-occurrence of other manual intervention during the trial period is another possible risk, as those who receive manipulation or other manual physical treatments elsewhere during the trial period will be withdrawn from the study and regarded as dropouts at the time of violation.
The external validity of the RCT might be a weakness as there is only one investigator. However, we found that advantageous to multiple investigators, in order to provide similar information to participants in all three groups and manual intervention in the CSMT and the placebo groups. Thus, we intend to eliminate inter-investigator variability which might be present if there are two or more investigators. Although the Gonstead method is the second most commonly used technique among chiropractors, we do not see an issue of concern when it comes to generalisability and external validity. Furthermore, the block randomisation procedure will provide a homogeneous sample across the three groups.
The internal validity is, however, strong by having one treating clinician. It reduces the risk of potential selection, information and experimental biases. Furthermore, the diagnosis of all participants is performed by experienced neurologists and not by questionnaires. A direct interview has higher sensitivity and specificity as compared to a questionnaire.27 Individual motivational factors which can influence a participant's perception and personal preferences when treating are both reduced by having one investigator. In addition, the internal validity is further strengthened by a concealed validated randomisation procedure. Since age and genders may play a role in migraine, block randomisation was found necessary to balance arms by age and gender in order to reduce possible age-related and/or gender-related bias.
Conducting X-rays prior to the active and placebo interventions was found to be applicable in order to visualise posture, joint and disc integrity.56 57 Since the total X-ray radiation dose varies from 0.2–0.8 mSv, the radiation exposure was considered low.58 59 X-ray assessments were also found to be necessary in order to determine if full spine X-rays are useful in future studies or not.
Since we are unaware of the mechanisms of possible efficacy, and both spinal cord and central descending inhibitory pathways have been postulated, we see no reasons to exclude a full spine treatment approach for the intervention group. It has furthermore been postulated that pain in different spinal regions should not be regarded as separate disorders but rather as a single entity.60 Similarly, including a full spine approach limits the differentiations between the CSMT and the placebo groups. Thus, it might strengthen the likelihood of successful blinding in the placebo group being achieved. In addition, all the placebo contacts will be performed outside the spinal column, thus minimising a possible spinal cord afferent input.
Innovative and scientific value
This RCT will highlight and validate the Gonstead CSMT for migraineurs, which has not previously been studied. If CSMT proves to be effective, it will provide a non-pharmacological treatment option. This is especially important as some migraineurs do not have efficacy of prescript acute and/or prophylactic medications, while others have non-tolerable side effects or comorbidity of other diseases that contradict medication while others wish to avoid medication for various reasons. Thus, if CSMT works, it can really have an impact on migraine treatment. The study also bridges cooperation between chiropractors and physicians, which is important in order to make healthcare more efficient. Finally, our method might be applied in future chiropractic and other manual therapy RCTs on headache.
Ethics and dissemination
Ethics
The study has been approved by the Norwegian Regional Committee for Medical Research Ethics (REK) (2010/1639/REK) and the Norwegian Social Science Data Services (11–77). The declaration of Helsinki is otherwise followed. All data will be anonymised while participants must give oral and written informed consent. Insurance is provided through “The Norwegian System of Compensation to Patients” (NPE), which is an independent national body set up to process compensation claims from patients who have suffered an injury as a result of treatment under the Norwegian health service. A stopping rule was defined for withdrawing participants from this study in accordance with recommendations in the CONSORT extension for Better Reporting of Harms.61 If a participant reports to their chiropractor or research staff a severe adverse event, he or she will be withdrawn from the study and referred to their general practitioner or hospital emergency department depending on the nature of the event. The final data set will be available to the clinical investigator (AC), the independent and blinded statistician (JSB) and Study Director (MBR). Data will be stored in a locked cabinet at the Research Centre, Akershus University Hospital, Norway, for 5 years.
Dissemination
This project is due for completion 3 years after the start. Results will be published in peer-reviewed international scientific journals in accordance with the CONSORT 2010 Statement. Positive, negative, as well as inconclusive results will be published. In addition, a written lay summary of the results will be available to study participants on request. All authors should qualify for authorship according to the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, 1997. Each author should have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content. The final decision on the order of authorship will be decided when the project has been finalised. The results from the study may, moreover, be presented as posters or oral presentations at national and/or international conferences.
Acknowledgments
Akershus University Hospital kindly provided research facilities. Chiropractor Clinic1, Oslo, Norway, performed X-ray assessments.
Footnotes
Contributors: AC and PJT had the original idea for the study. AC and MBR obtained funding. MBR planned the overall design. AC prepared the initial draft and PJT commented on the final version of the research protocol. JSB performed all the statistical analyses. AC, JSB, PJT and MBR were involved in the interpretation and assisted in the revision and preparation of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: The study has received funding from Extrastiftelsen (grant number: 2829002), the Norwegian Chiropractic Association (grant number: 2829001), Akershus University Hospital (grant number: N/A) and University of Oslo in Norway (grant number: N/A).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Ethics approval: The Norwegian Regional Committee for Medical Research Ethics approved the project (ID of the approval: 2010/1639/REK).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M et al. . Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380:2163–96. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Russell MB, Kristiansen HA, Saltyte-Benth J et al. . A cross-sectional population-based survey of migraine and headache in 21,177 Norwegians: the Akershus sleep apnea project. J Headache Pain 2008;9:339–47. 10.1007/s10194-008-0077-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Katsarava Z et al. . The impact of headache in Europe: principal results of the Eurolight project. J Headache Pain 2014;15:31 10.1186/1129-2377-15-31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013;33:629–808. 10.1177/0333102413485658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Russell MB, Iversen HK, Olesen J. Improved description of the migraine aura by a diagnostic aura diary. Cephalalgia 1994;14:107–17. 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1994.1402107.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Russell MB, Olesen J. A nosographic analysis of the migraine aura in a general population. Brain 1996;119(Pt 2):355–61. 10.1093/brain/119.2.355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M et al. . Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:679–90. 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70090-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Amin FM, Asghar MS, Hougaard A et al. . Magnetic resonance angiography of intracranial and extracranial arteries in patients with spontaneous migraine without aura: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:454–61. 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70067-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wolff HGF. Headache and other head pain. 2nd edn Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jensen K. Extracranial blood flow, pain and tenderness in migraine. Clinical and experimental studies. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 1993;147:1–8. 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09466.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Svensson P, Ashina M. Human studies of experimental pain from muscles. In: Olesen J, Tfelt-Hansen P, Welch KMA et al., eds Headache. 3rd edn Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006:627–35. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ray BS, Wolff HG. Experimental studies on headache. Pain sensitive structures of the head and their significance in headache. Arch Surg 1940;41:813–56. 10.1001/archsurg.1940.01210040002001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grande RB, Aaseth K, Gulbrandsen P et al. . Prevalence of primary chronic headache in a population-based sample of 30- to 44-year-old persons. The Akershus study of chronic headache. Neuroepidemiology 2008;30:76–83. 10.1159/000116244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aaseth K, Grande RB, Kvaerner KJ et al. . Prevalence of secondary chronic headaches in a population-based sample of 30–44-year-old persons. The Akershus study of chronic headache. Cephalalgia 2008;28:705–13. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01577.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jensen R, Stovner LJ. Epidemiology and comorbidity of headache. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:354–61. 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70062-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lundqvist C, Grande RB, Aaseth K et al. . Dependence scores predict prognosis of medication overuse headache: a prospective cohort from the Akershus study of chronic headache. Pain 2012;153:682–6. 10.1016/j.pain.2011.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Olesen J. Impact of headache on sickness absence and utilisation of medical services: a Danish population study. J Epidemiol Community Health 1992;46:443–6. 10.1136/jech.46.4.443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hu XH, Markson LE, Lipton RB et al. . Burden of migraine in the United States: disability and economic costs. Arch Intern Med 1999;159:813–18. 10.1001/archinte.159.8.813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Berg J, Stovner LJ. Cost of migraine and other headaches in Europe. Eur J Neurol 2005;12(Suppl 1):59–62. 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2005.01192.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Andlin-Sobocki P, Jonsson B, Wittchen HU et al. . Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe. Eur J Neurol 2005;12(Suppl 1):1–27. 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2005.01202.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cooperstein R. Gonstead Chiropractic Technique (GCT). J Chiropr Med 2003;2:16–24. 10.1016/S0899-3467(07)60069-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cooperstein R, Gleberson BJ. Technique systems in chiropractic. 1st edn New York: Churchill Livingston, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parker GB, Tupling H, Pryor DS. A controlled trial of cervical manipulation of migraine. Aust NZ J Med 1978;8:589–93. 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1978.tb04845.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Parker GB, Pryor DS, Tupling H. Why does migraine improve during a clinical trial? Further results from a trial of cervical manipulation for migraine. Aust NZ J Med 1980;10:192–8. 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1980.tb03712.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nelson CF, Bronfort G, Evans R et al. . The efficacy of spinal manipulation, amitriptyline and the combination of both therapies for the prophylaxis of migraine headache. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 1998;21:511–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tuchin PJ, Pollard H, Bonello R. A randomized controlled trial of chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy for migraine. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2000;23:91–5. 10.1016/S0161-4754(00)90073-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Olesen J. Questionnaire versus clinical interview in the diagnosis of headache. Headache 1991;31:290–5. 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1991.hed3105290.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vernon HT. The effectiveness of chiropractic manipulation in the treatment of headache: an exploration in the literature. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 1995;18:611–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fernandez-de-las-Penas C, Alonso-Blanco C, San-Roman J et al. . Methodological quality of randomized controlled trials of spinal manipulation and mobilization in tension-type headache, migraine, and cervicogenic headache. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2006;36:160–9. 10.2519/jospt.2006.36.3.160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chaibi A, Tuchin PJ, Russell MB. Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review. J Headache Pain 2011;12:127–33. 10.1007/s10194-011-0296-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chaibi A, Russell MB. Manual therapies for primary chronic headaches: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J Headache Pain 2014;15:67 10.1186/1129-2377-15-67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tfelt-Hansen P, Block G, Dahlof C et al. . International Headache Society Clinical Trial Subcommittee. Guidelines for controlled trials of drugs in migraine: second edition. Cephalalgia 2000;20:765–86. 10.1046/j.1468-2982.2000.00117.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Silberstein S, Tfelt-Hansen P, Dodick DW et al. , Task Force of the International Headache Society Clinical Trial Subcommittee . Guidelines for controlled trials of prophylactic treatment of chronic migraine in adults. Cephalalgia 2008;28:484–95. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01555.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kerr FW. Central relationships of trigeminal and cervical primary afferents in the spinal cord and medulla. Brain Res 1972;43:561–72. 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90408-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bogduk N. The neck and headaches. Neurol Clin 2004;22:151–71, vii 10.1016/S0733-8619(03)00100-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.McLain RF, Pickar JG. Mechanoreceptor endings in human thoracic and lumbar facet joints. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:168–73. 10.1097/00007632-199801150-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vernon H. Qualitative review of studies of manipulation-induced hypoalgesia. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2000;23:134–8. 10.1016/S0161-4754(00)90084-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vicenzino B, Paungmali A, Buratowski S et al. . Specific manipulative therapy treatment for chronic lateral epicondylalgia produces uniquely characteristic hypoalgesia. Man Ther 2001;6:205–12. 10.1054/math.2001.0411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Boal RW, Gillette RG. Central neuronal plasticity, low back pain and spinal manipulative therapy. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2004;27:314–26. 10.1016/j.jmpt.2004.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.De Camargo VM, Alburquerque-Sendin F, Berzin F et al. . Immediate effects on electromyographic activity and pressure pain thresholds after a cervical manipulation in mechanical neck pain: a randomized controlled trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2011;34:211–20. 10.1016/j.jmpt.2011.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF et al. . CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010;340:c869 10.1136/bmj.c869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I et al. . Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 2014;348:g1687 10.1136/bmj.g1687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24(Suppl 1):9–10. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2003.00824.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.French HP, Brennan A, White B et al. . Manual therapy for osteoarthritis of the hip or knee - a systematic review. Man Ther 2011;16:109–17. 10.1016/j.math.2010.10.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cassidy JD, Boyle E, Cote P et al. . Risk of vertebrobasilar stroke and chiropractic care: results of a population-based case-control and case-crossover study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33(4Suppl):S176–S83. 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181644600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tuchin P. A replication of the study ‘Adverse effects of spinal manipulation: a systematic review’. Chiropr Man Therap 2012;20:30 10.1186/2045-709X-20-30 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Russell MB, Rasmussen BK, Brennum J et al. . Presentation of a new instrument: the diagnostic headache diary. Cephalalgia 1992;12:369–74. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.1992.00369.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lundqvist C, Benth JS, Grande RB et al. . A vertical VAS is a valid instrument for monitoring headache pain intensity. Cephalalgia 2009;29:1034–41. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01833.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bang H, Ni L, Davis CE. Assessment of blinding in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 2004;25:143–56. 10.1016/j.cct.2003.10.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Johnson C. Measuring Pain. Visual Analog Scale Versus Numeric Pain Scale: What is the Difference? J Chiropr Med 2005;4:43–4. 10.1016/S0899-3467(07)60112-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Silberstein SD, Neto W, Schmitt J et al. . Topiramate in migraine prevention: results of a large controlled trial. Arch Neurol 2004;61:490–5. 10.1001/archneur.61.4.490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bendtsen L, Jensen R, Olesen J. A non-selective (amitriptyline), but not a selective (citalopram), serotonin reuptake inhibitor is effective in the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1996;61:285–90. 10.1136/jnnp.61.3.285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hagen K, Albretsen C, Vilming ST et al. . Management of medication overuse headache: 1-year randomized multicentre open-label trial. Cephalalgia 2009;29:221–32. 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01711.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hancock MJ, Maher CG, Latimer J et al. . Selecting an appropriate placebo for a trial of spinal manipulative therapy. Aust J Physiother 2006;52:135–8. 10.1016/S0004-9514(06)70049-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Meissner K, Fassler M, Rucker G et al. . Differential Effectiveness of Placebo Treatments: A Systematic Review of Migraine Prophylaxis. JAMA Inter Med 2013;173:1941–51. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Taylor JA. Full-spine radiography: a review. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 1993;16:460–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.International Chiropractic Assocoation Practicing Chiropractors’ Committee on Radiology Protocols (PCCRP) for biomechanical assessment of spinal subluxation in chiropractic clinical practice. Secondary International Chiropractic Assocoation Practicing Chiropractors’ Committee on Radiology Protocols (PCCRP) for biomechanical assessment of spinal subluxation in chiropractic clinical practice 2009. http://www.pccrp.org/
- 58.Cracknell DM, Bull PW. Organ dosimetry in spinal radiography: a comparison of 3-region sectional and full-spine techniques. Chiropr J Austr 2006;36:33–9. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Borretzen I, Lysdahl KB, Olerud HM. Diagnostic radiology in Norway trends in examination frequency and collective effective dose. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 2007;124:339–47. 10.1093/rpd/ncm204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Leboeuf-Yde C, Fejer R, Nielsen J et al. . Pain in the three spinal regions: the same disorder? Data from a population-based sample of 34,902 Danish adults. Chiropr Man Ther 2012;20:11 10.1186/2045-709X-20-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ioannidis JP, Evans SJ, Gotzsche PC et al. . Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: an extension of the CONSORT statement. Ann Intern Med 2004;141:781–8. 10.7326/0003-4819-141-10-200411160-00009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]