Abstract
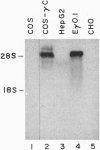
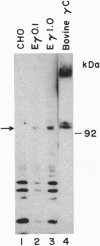
Coagulation factor IX is a serine protease for which high-level expression of biologically active protein in heterologous cells is limited due to inefficient proteolytic removal of the propeptide as well as vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of multiple amino-terminal glutamic acid residues. We have overexpressed the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase cDNA and monitored its ability to improve factor IX processing in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. From amino acid sequence analysis of bovine liver vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase, degenerate oligonucleotides were used to isolate a 3.5-kbp bovine cDNA that encoded a 758-residue open reading frame. Expression of the cDNA in COS-1 and CHO cells yielded 17- and 16-fold increases in the in vitro gamma-carboxylase activity of microsomal preparations, respectively. Anti-serum raised against a predicted peptide sequence reacted with a 94-kDa polypeptide in the partially purified bovine liver preparation as well as in stably transfected CHO cells. The amount of antibody reactivity correlated with the increased ability to carboxylate a peptide substrate in vitro. These results strongly support the conclusion that the cDNA encodes the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase. Transient transfection of the gamma-carboxylase expression vector into factor IX-expressing CHO cells did not improve the specific procoagulant activity of secreted factor IX. In contrast, transfection of an expression vector encoding the propeptide processing enzyme PACE (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) did improve the specific activity of secreted factor IX by 3-fold. These results demonstrate that the ability of CHO cells to modify glutamic acid residues to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in secreted factor IX is not limited by the expression of the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase alone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Harbeck M., Lingenfelter S., Bailey C., Sanders-Hinck C. M., Suttie J. W. Purification and identification of bovine liver gamma-carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6242–6246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J. Internal translation initiation in the design of improved expression vectors. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1992 Oct;3(5):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(92)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derian C. K., VanDusen W., Przysiecki C. T., Walsh P. N., Berkner K. L., Kaufman R. J., Friedman P. A. Inhibitors of 2-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases block aspartyl beta-hydroxylation of recombinant human factor IX in several mammalian expression systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6615–6618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Kaufman R. J. Overexpression of GRP78 mitigates stress induction of glucose regulated proteins and blocks secretion of selective proteins in Chinese hamster ovary cells. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1563–1571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. Molecular basis of vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation. Blood. 1990 May 1;75(9):1753–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai K., Fukuoka S., Fushiki T., Kido K., Sengoku Y., Semba T. Preparation of a verifiable peptide-protein immunogen: direction-controlled conjugation of a synthetic fragment of the monitor peptide with myoglobin and application for sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jun;171(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen M. J., Cantor A. B., Furie B. C., Brown C. L., Shoemaker C. B., Furie B. Recognition site directing vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation resides on the propeptide of factor IX. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Wasley L. C., Michnick D. Improved vectors for stable expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells by use of the untranslated leader sequence from EMC virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4485–4490. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Selection and coamplification of heterologous genes in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:537–566. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85044-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Dorner A. J. Synthesis, processing, and secretion of recombinant human factor VIII expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6352–6362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Furie B. C., Furie B., Shoemaker C. B. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant gamma-carboxylated factor IX synthesized in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9622–9628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuliopulos A., Cieurzo C. E., Furie B., Furie B. C., Walsh C. T. N-bromoacetyl-peptide substrate affinity labeling of vitamin K dependent carboxylase. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9436–9444. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman H. A., Furie B. C., Furie B. The factor IX phospholipid-binding site is required for calcium-dependent activation of factor IX by factor XIa. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7605–7612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Jenny R. J., Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehemtulla A., Kaufman R. J. Preferred sequence requirements for cleavage of pro-von Willebrand factor by propeptide-processing enzymes. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2349–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehemtulla A., Kaufman R. J. Protein processing within the secretory pathway. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1992 Oct;3(5):560–565. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(92)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:459–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlon D. S., Sadowski J. A., Suttie J. W. Mechanism of coumarin action: significance of vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibition. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1371–1377. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Cheung W. F., Frazier D., Stafford D. W. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for human gamma-glutamyl carboxylase. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1634–1636. doi: 10.1126/science.1749935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Morris D. P., Stafford D. W. Identification and purification to near homogeneity of the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]