Abstract
Angiogenesis is central to the growth of cancers and VEGFR-1/Flt-1 plays an important role during the neovascularization under pathological conditions. We previously founded a VEGFR1 antagonistic peptide, F56, by screening the phage peptide library. We showed that DHFR-F56 chimeric protein displayed anti-tumor activity and inhibited angiogenesis, however the anti-tumor activity of monomeric F56 and the mechanism remain unclear. In this study, we found that the F56 didn’t affect VEGF-A induced endothelial cell proliferation, but reduced migration and tube formation of endothelial cells. F56 also inhibited the sprout of rat aortic endothelial cells, the angiogenesis of chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane as well as the generation of subintestinal vein vessels (SIV) in zebrafish embryos. We found that F56 inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR1, as well as the phosphorylation of the downstream of PI3K-AKT axis. However, F56 had no effect on the phosphorylation of VEGFR2. Correlating with these effects, F56 inhibited xenograft growth of HT-29 and MGC-823 cells in BALB/c nude mice, and significantly suppressed the lung metastasis of B16 cells in C57BL/6 mice. Our study demonstrated that monomeric peptide F56 had a significant anti-tumor activity by inhibiting angiogenesis, and laid the foundation for its clinical application.
Keywords: Peptide, angiogenesis, endothelial cells, metastasis, VEGFR1, PI3K/Akt
Introduction
Besides serving as channels for transporting oxygen and nutrients required for metabolism as well as discharging the metabolite, blood vessels can also serve as an accomplice for cancer metastasis [1]. Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones, is a critical process for both physiological and pathological conditions [2]. Without the support of vessels, tumors are “starved” dormant and unable to migrate to distance through bloodstream. Therefore, angiogenesis plays an important role in the growth and metastasis of tumors [3].
The endothelial cells participate in various processes of angiogenesis, including endothelial cell proliferation, migration, adhesion, invasion, and tube formation [4-6]. Many cytokines can regulate the functions of vascular endothelial cells [7,8]. Of all these cytokines, the best known is VEGF-A [9]. VEGF-A binds to both Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 (VEGFR 1) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR 2), and induces angiogenesis by activating the tyrosine kinase activities of these receptors [10,11]. Since VEGFR2 has a stronger tyrosine kinase activity [12], it is usually viewed as the major player in the process of angiogenesis. VEGFR1, also named as fms-like tyrosine kinase receptor 1 (Flt-1), is a receptor of 180 kDa with seven Ig-like domains [13]. Compared with VEGFR2, VEGFR1 has a much higher affinity with VEGF-A, but with lower tyrosine kinase activity, making it more complex and subtle in the regulation of angiogenesis. It is reported that VEGFR1 played a dual role in the regulation process of angiogenesis [13]. At embryogenesis stage, with a high VEGF-A affinity, VEGFR1 can serve as a decoy receptor and negatively regulates the binding of VEGF-A with VEGFR2, thus avoiding the excessive proliferation of blood vessels. In adulthood, VEGFR1 positive regulates the process of angiogenesis. The expression of VEGFR1 is not limited to endothelial cells [14]. Themonocytes/macrophages, endothelial progenitor cells, mesangial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, dendritic cells (DC), and even some tumor cells can express VEGFR1 [14]. VEGFR1 can regulate the migration of endothelial cells. In addition, VEGFR1 positive hematopoietic progenitors could initiate the formation of pre-metastatic niche [15], which was closely related to the initial process of tumor metastasis. Many signaling pathways are involved in angiogenesis, and some proangiogenic cytokines regulate angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [16,17].
In our previous study, we obtained the 12-mer VEGFR1 antagonistic peptide F56 via phage display library screening, and found that DHFR-F56 chimeric protein had anti-tumor activity in the in vitro and in vivo assays [18]. Some groups utilized F56-conjugated nanoparticles for cell imaging or utilized the high specificity and affinity of F56 to improve the effects of cytotoxic drugs by directing them to target cells [19-22]. However, the anti-tumor efficiency of F56 peptide remains to be explored. In the present study, we found that F56 significantly inhibited the migration and tube formation of HUVEC cells, suppressed the sprout of endothelial cells in a 3D rat aortic ring assay, disrupted the embryo angiogenesis of chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM), reduced the generation of subintestinal vessels (SIVs) in zebrafish, inhibited the growth of BGC-823 and colon HT29 tumors in nude mice, and counteracted metastasis of B16 melanoma cells to lungs in C57BL/6 mice. Correlated with these actions, F56 suppressed the VEGFR1-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Experimental procedures
Reagents
EGM-2 Bulletkit (CC-3162), which includes Endothelial Basal Medium (EBM-2) (CC-3156), EGM-2 SingleQuot Kit Suppliment and Growth Factors (CC-7176), was obtained from Lonza (Basel, Switzerland). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (0175) was purchased from Amresco. The Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-labeled Phalloidin was obtained from Sigma (St. Louis). Collagenase was from was bought from Solarbio (Beijing, China). The recombinant human VEGF165 (239-VE-010) was obtained from R&D (Minneapolis). The Basement Membrane Matrix, Growth Factor Reduced (GFR) Matrigel, was obtained from BD Biosciences (New Jersey). Peptides were synthesized by A Peptide Co. Ltd (Shanghai, China). Scrambled F56 (scr-F56) peptide sequence was: LEHDGWSWLYMW. F56 peptide sequence was: WHSDMEWWYLLG. Both F56 and scr-F56 have a MW of 1622.84. The purity of the peptides was above 99% as confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Antibodies
Anti-VEGFR1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone ID: Y103, Catalog#1303-1) was ordered from Epitomics (California). Anti-phospho-Flt-1 (Tyr1213) rabbit antibody (#07-758) was purchased from Millipore (Massachusetts). Anti-VEGF Receptor 2 (55B11) rabbit monoclonal antibody (#2479), anti-phospho-VEGF Receptor 2 (Tyr1175) (19A10) rabbit monoclonal antibody (#2478), anti-PI3 Kinase p85 Antibody (#4292), anti-Phospho-PI3 Kinase p85 (Tyr458)/p55 (Tyr199) Antibody (#4228), anti-Akt (C67E7) Rabbit mAb (#4691) and anti-Phospho-Akt (Ser473) (D9E) Rabbit mAb (#4060) were from Cell Signaling Technology (Boston). The rabbit anti-CD31 monoclonal antibody and the rabbit anti-factor VIII antibody were purchased from Zhongshan Golden Bridge (Beijing, China).
Cells
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were isolated from undamaged section of fresh umbilical cords with collagenase [23]. Written Informed Consents were obtained from parturient women prior to delivery.
HUVEC cells were maintained in EBM-2 medium with 2% FBS and used between passages 2 to 5 for all experiments. The verification of HUVEC as endothelial cells was confirmed by morphological characteristics of cobblestone-like pattern and the immunoreactivities for Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31) and factor VIII-related antigens. The human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29 and the mouse melanoma cell line B16 were obtained from ATCC. The human gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 was kept in our lab. These cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with 10% FBS.
Small interference RNA (siRNA) transfection
Control and VEGFR1-specific siRNAs (siRNA-NC: 5’-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3’; siRNA-VEGFR1: 5’-GGCCAAGAUUUGCAGAACUTT-3’) were synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). siRNAs were transfected into HUVEC using siRNA-Mate reagent (GenePharma) for 48 hr. Efficiency of knock-down was validated by Western blotting.
Animals
Female C57BL/6 mice (8 weeks old), BALB/c nude mice (6 weeks old) and male Sprague-Dawley rats (6 weeks old) were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). All animals used in the experiments were treated humanely under the supervision of the Research Ethics Committee of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute.
Cell proliferation assay
Cell growth was evaluated by CCK-8 assay. HUVEC cells were seeded into 96-well plates in triplicate at a density of 3.5 × 103 cells per well in 150 μl EBM-2 medium with 2% FBS and other supplements of the SingleQuot Kit except growth factors. The cells were cultured overnight for adherence to the surface of plate and were exposed to indicated drugs and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 72 hr. Then 15 μl CCK-8 liquids were added into wells. After incubation for 3 hr, the absorbance was measured at 450 nm by a microplate reader.
Immunofluorescence
Cells were seeded onto sterile glass-coverslips in 24-well plates at about 30% confluence before serum starvation overnight. Then cells were treated with peptides for 2 hr before VEGF stimulation. After being incubated with VEGF for 1 hr, the culture medium was immediately aspirated. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature, and then permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 min. Then coverslips were washed twice with PBS for 10 min, and incubated with FITC-conjugated phalloidin at the concentration of 5 g/ml in dark for 1 hr. Cells were washed again with PBS, incubated with DAPI (5 mg/ml) for nuclear staining at room temperature for 6 min and visualized and photographed by a Leica SP2 confocal system.
Migration assay
HUVEC cell migration was tested in the Corning polycarbonate membrane transwell system (8.0 μm pore size) with 24-well plates. Cell monolayers were washed twice with serum free culture medium, trypsinized mildly, and resuspended in the serum free EBM-2 culture medium containing 0.1% BSA. Cell suspensions were pre-incubated with peptides as indicated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 30 min prior to migration assays. The bottom chambers were filled with 750 μl culture medium containing 0.1% BSA with or without peptides and VEGF (10 ng/ml). After the pretreatment process, each top chamber was seeded with 50,000 cells in a final volume of 250 μl. The cells were allowed to migrate at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 8 hr. Then, cells were fixed with cold methanol for 30 min and stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 40 min. The unmigrated cells remained on the top surface of the membrane were scraped with a cotton swab. The migrated cells were photographed and counted in 6 random fields under a microscope.
Tube formation assay
A 96-well plate coated with 50 μl growth factor reduced Matrigel was incubated at 37°C for 1 hr to solidify. Cells were trypsinized and resuspended in basal serum free EBM-2 culture medium containing 0.1% BSA. Then cell suspensions were pre-incubated with peptides as indicated for 30 min before exposure to VEGF (10 ng/ml). Each well with polymerized Matrigel was filled with 100 μl cell suspensions containing 20,000 cells. After 6 hr, the tubes were observed and photographed under a microscope.
Chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay
CAM assay was performed as previously describe [18]. Briefly, fresh fertilized SPF white leghorn chicken eggs (Meri Avignon Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China) were washed mildly with 95% ethanol. After incubation for 3 days in a 60% relative humidified environment at 37°C, eggs were sterilized and opened with the help of an electric drill. The whole egg contents were removed into Petri dishes, and incubated at 37.5°C. The folded filter papers were punched by a puncher at the size of 5.5 mm in diameter and were autoclaved and used as carriers for peptides and VEGF applied to the CAM. At least 5 embryos were used for each group. Then the embryos were cultured for 48 hr after drug administration. The vascular response to drugs was estimated by counting the number of large vessels, small vessels and capillaries of the photographed areas around the filter papers.
Rat aortic ring assay
A 48-well plate coated with 120 μl growth factor reduced Matrigel was incubated at 37°C for 1 hr to allow the Matrigel to solidify. 6 weeks old rats were killed and the thoracic aortas were isolated and washed with PBS. After remove of the excess perivascular adipose tissues, aortas were cut into 1 mm length segments and each fragment was embedded in polymerized Matrigel with additional fresh liquid of 60 μl Matrigel. The plate was then incubated at 37°C for 3 hr to allow the Matrigel polymerized firmly. Serum free culture medium (0.5 ml) with agents as indicated was administrated to the wells containing aortic rings, and the media were changed every 2 days. After 6 days of incubation, microvessel-like structures sprouting from the aortic rings were observed and photographed under an inverted microscope.
Zebrafish embryos assays
The vascular fluorescent transgenic zebrafish was used to perform the angiogenesis assay. The emission fluorescent of the vasculature endothelial cells can be observed under a fluorescence microscope. Zebrafish embryos were acquired by a natural pair-wise mating way. We prepared 4-5 pairs of adult zebrafish for mating every time, an average of 200 to 300 embryos were obtained from each pair. Six hr after fertilization (6 hpf) and 24 hpf, we surveyed the embryos and removed dead embryos. Embryos with suitable developmental stages were selected for experiment, and incubated at 28°C to maintain. With abundant nutrition of the yolk sac, there is no need to feed until 9 dpf. The drugs were injected into the yolk sac of 2 dpf zebrafish by a microinjection method. There were 30 zebrafish treated in each experimental group. When incubated to 3 dpf, 10 zebrafish of each group were randomly selected, fluorescence of the SIVs (subintestinal vein vessels) was detected using a fluorescence microscope and the images were photographed. Image analysis was performed by calculating the SIVs area with Nikon NIS-Elements D 3.10 Advanced image processing software. According to the rule of American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), embryos were sacrificed by anesthetizing.
Tumor growth assay in nude mice
Confluent HT-29 and BGC-823 cells were trypsinized and then resuspended in PBS. The single cell suspension was confirmed under the phase-contrast microscopy survey. 1 × 107 viable tumor cells were inoculated subcutaneously on the left dorsal flank region of 8-week-old female athymic nude BALB/c/nu/nu mice. After the tumor volume reached about 100 mm3, mice were daily intravenously injected with F56, srcF56, Endostatin (Simcere Inc., Jiangsu, China) and Vehicle. The drugs were administered for consecutive 14 days. Cyclophosphamide (CTX) was served as a positive control by subcutaneous injection weekly. The length and width of tumor nodules were measured every 2 or 3 days with a caliper, and the tumor volumes were calculated by the following formula: volume = length × (width)2 × 0.5. After drugs withdrawal, mice were observed for a week and then sacrificed. Tumor nodules were moved and weighted. Each experimental group had 8 mice.
Tumor metastasis assay in C57 mice
After inoculation of melanoma cells B16 in C57 mice by veins, drugs were delivered. Bevacizumab (Roche, Germany) was administered intravenously, at the dosage of 100 μg per mouse weekly. The administration of other groups was as mentioned before. Each group had 7 mice. After continuous administration of drugs for 14 days, mice were killed, lungs were dissected and the number of metastatic foci per lung was counted carefully by naked eyes.
Western blotting
After different treatment, total protein of HUVEC cells was extracted in 1x loading buffer. Equal amounts of protein were subjected to (8-10%) reducing sodium dodecyl sulfate-poly acrylamide gel (SDS-PAGE) according to proteins’ molecular weight, followed by electro-transferring onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. Membranes were blocked for 1 hr in 5% nonfat dry milk in TBST at room temperature and incubated with primary antibodies over-night at 4°C, the dilution ratio of the primary antibodies in blocking buffer were according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The membranes were then washed three times for about 15 min with TBST, and incubated with corresponding HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 45 min at room temperature. After three additional washes with TBST, the membranes were incubated with enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Pierce) and the bands were visualized by exposing to Kodak film. GAPDH or β-actin was used as a loading control.
Statistical methods
The differences between the groups were statistically analyzed with ANOVA by a student’s two-tailed t-test. In all experiments, P-value < 0.05 was identified as statistically significant.
Results
F56 reduced the migration of HUVEC cells
To examine the effect of F56 in vitro, we firstly detected the proliferation of HUVEC cells. The results showed that VEGF enhanced the proliferation of HUVEC cells, but F56 couldn’t inhibit VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation (Figure 1A). To minimize the influence of VEGF-promoted cell growth, migration assay was terminated at 8 hr after seeding cells in the top chamber. Compared with the vehicle control, VEGF promoted HUVEC cells migration, which was inhibited by F56 (Figure 1B), while Scr-F56 had no effects on VEGF promoted migration (Figure 1B). Similar results were obtained by wound heal assay (Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
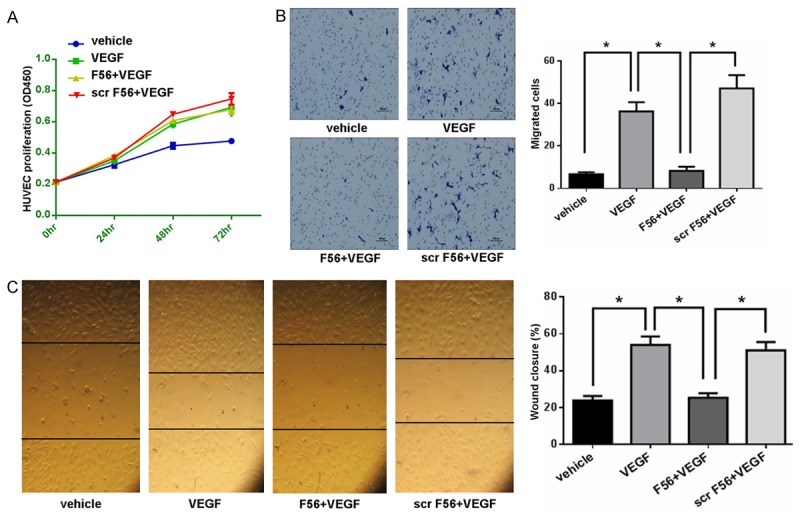
F56 inhibited the migration of HUVECs. A. HUVECs were treated with VEGF alone or in combination with F56 or scr F56 for 24, 48 and 72 hr. The proliferation of HUVECs was measured by CCK-8. B. The migration of HUVECs was measured by the transwell system. Representative images of migrated were shown (left) and the bar graph (right) showed the number of migrated cells. C. The migration of HUVECs was measured by the wound healing assay. Representative images of wound closure were shown (left) and the bar graph (right) showed the percentages of wound closure. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.
F56 disrupted VEGF-induced HUVEC tube formation and endothelial cells sprouting in 3D rat aortic ring assay
The tube formation assay can mimic the reorganization stage of angiogenesis with direct view. We examined the effect of F56 on the tube formation ability of HUVEC cells by planting the HUVEC cells on Matrigel. As showed in Figure 2A, F56 inhibited the tube formation of endothelial cells induced by VEGF, but scr-F56 had no inhibitory effect. We further examined the effect of F56 on angiogenesis by using the 3D model of rat aortic ring (Figure 2B). In the serum-free condition, VEGF promoted endothelial cell sprout to matrix, which was reduced by F56, but not by scr-F56 (Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
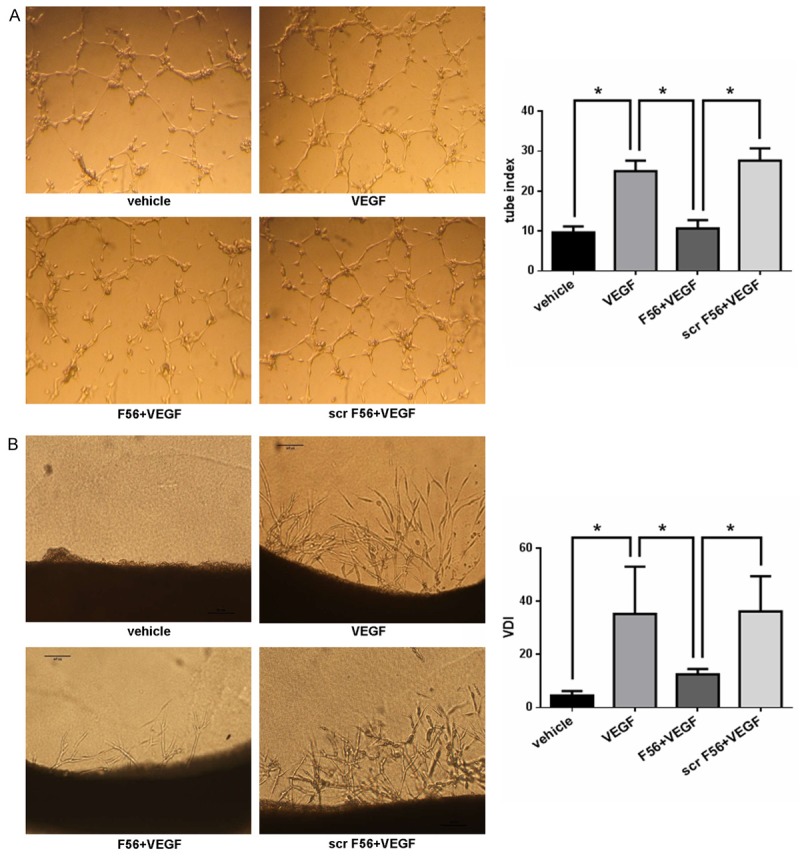
F56 inhibited VEGF induced HUVEC tube formation and endothelial cell sprouting in 3D rat aortic ring assay. A. HUVEC suspensions were pre-incubated with peptides for 30 min before exposure to VEGF (10 ng/ml). Each well with polymerized Matrigel was filled with 100 μl cell suspensions containing 20,000 cells. After 6 hr, the tubes were photographed and analysed. B. Rats were killed and the thoracic aortas were cut into 1 mm length segments and embedded in polymerized Matrigel with additional fresh liquid of 60 μl Matrigel. The plate was then incubated at 37°C for 3 hr to allow the Matrigel polymerized firmly, and then 0.5 ml serum free culture medium with agents as indicated was added, the media were changed every 2 days. After 6 days of incubation, microvessel-like structures sprouting from the aortic rings were photographed and analysed. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.
F56 inhibited the angiogenesis of CAM and zebrafish embryo SIVs
To further verify the anti-angiogenesis ability of F56, we utilized the CAM and zebrafish models. We observed that F56 significantly inhibited the growth of capillaries and small blood vessels in CAM, whereas with minimal effect on large vessels (Figure 3A). Due to the sufficient supply of endogenous growth factors to embryo by yolk, the additional VEGF-induced pro-angiogenic efficacy was not very obvious (Figure 3A). Meanwhile, we didn’t detect signs of disappearing of existing vessels (Figure 3A), indicating F56 is an anti-angiogenesis drug rather than a vascular disrupting agent.
Figure 3.
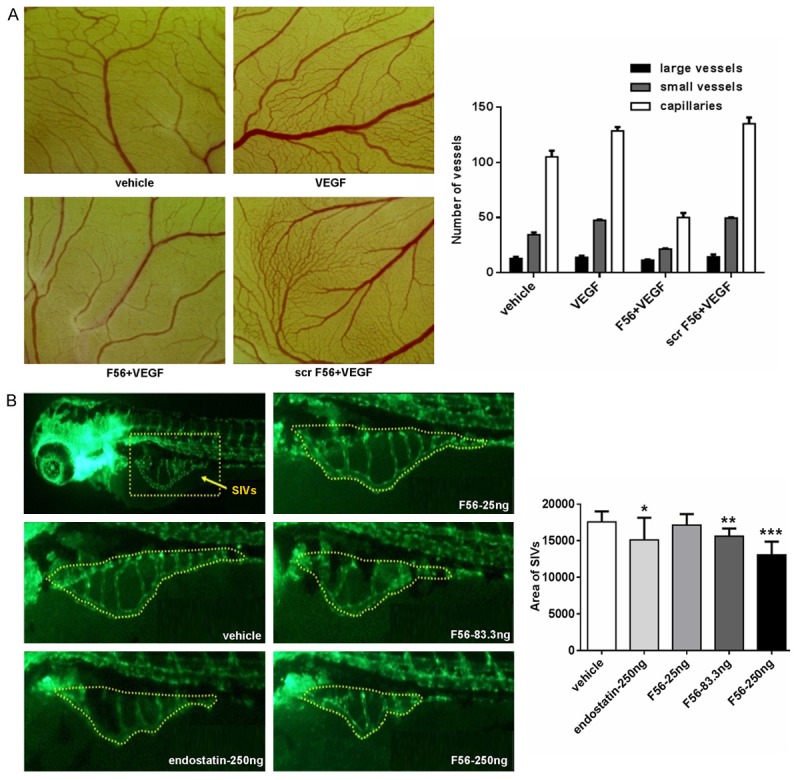
Inhibitory effects of F56 on angiogenesis of the CAM and zebrafish embryo. A. Chicken eggs (n = 5 per group) were incubated for 3 days and then opened with electric drill, whole egg contents were removed into Petri dishes. The autoclaved filter papers were used as carriers for peptides and VEGF applied to the CAM. After cultured for 48 hr, areas around the filter papers were photographed and the number of large vessels, small vessels and capillaries were counted. B. Embryos with suitable developmental stages were selected, then drugs were injected into the yolk sac of 2 dpf (2 days after fertilization) zebrafish. There were 30 zebrafish treated each experimental group. When incubated to 3 dpf, 10 zebrafish of each group were randomly selected, fluorescence of the SIVs (subintestinal vein vessels) was detected and photographed. Image analysis was performed by calculating the SIVs area. Data are expressed as mean + SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
We next used the endothelial cell fluorescently labeled transgenic zebrafish to examine the effect of F56 on angiogenesis (Figure 3B). The data showed that, both F56 and the endostatin (as a positive control) inhibited the angiogenesis of sub-intestinal vascular plexus in zebrafish embryos. F56 reduced the angiogenesis of zebrafish embryos in a dose-dependent way, and at the dosage of 250 ng, the inhibition effect of F56 was comparable to endostatin (Figure 3B). Based on the results from CAM and zebrafish models, we concluded that F56 had anti-angiogenic effect in vivo.
F56 associated with HUVEC cells in VEGFR1-dependent fashion and reduced phosphorylation of VEGFR1, PI3K and Akt in HUVEC cells
Consistent with F56’s effects on endothelial cells, FITC-conjugated F56 associated with HUVEC cells (Figure 4A). It’s of note that F56 colocalized with VEGFR1 (Figure 4A). When VEGFR1 expression was ablated by transfection with a specific siRNA (Figure 4B), F56 failed to associated with HUVEC cells (Figure 4A), indicating that VEGFR1 facilitates binding of F56 to HUVEC cells. To clarify the signaling events associated with F56’s functions, we investigated the effect of peptides on the phosphorylations of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, PI3K and AKT in HUVEC cells. It turned out that, the phosphorylation of VEGFR1 induced by VEGF was markedly down-regulated by F56 treatment, and the phosphorylations of PI3K and AKT were also reduced, but VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 was unchanged (Figure 4C). These results further support the specificity of F56 in counteracting VEGFR1 signaling.
Figure 4.
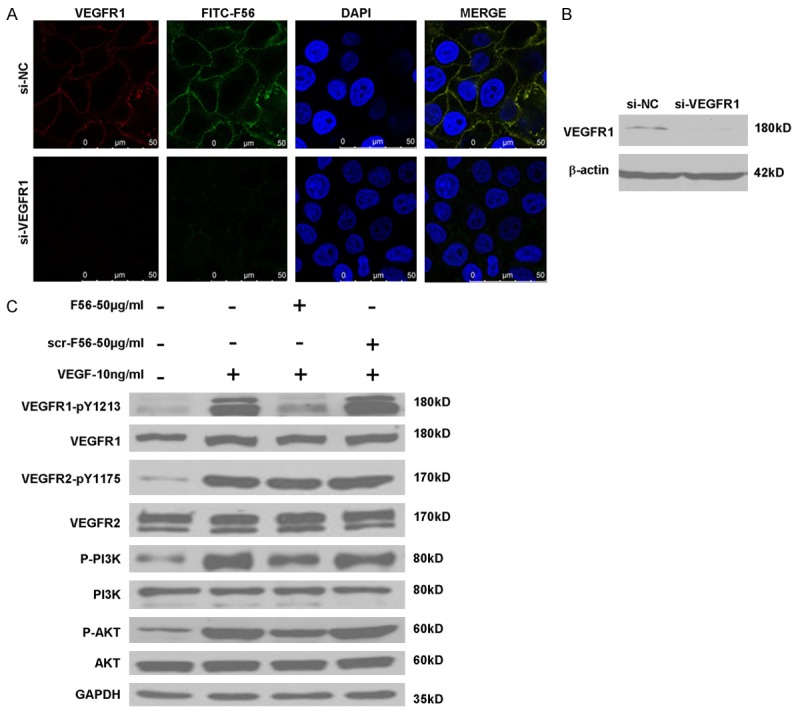
Effects of F56 on VEGFR1, VEGFR2, PI3K and AKT signaling pathways. A. HUVECs seeded on coverslips were transfected with indicated siRNAs for 48 hr, treated with FITC-F56 (green) for 30 min, followed by immunostaining of VEGFR1 (red) and counterstaining of DNA with DAPI (blue). B. HUVECs were transfected with indicated siRNAs for 48 hr, followed by Western blotting. C. HUVECs were starved overnight, after the treatment of F56 or scr-F56 at the concentration of 50 g/mL for 30 min, 10 ng/mL VEGF-A was added to the medium for 10 min stimulation, and the expression of indicated proteins were assayed by western blotting.
F56 suppressed tumor growth and metastasis
Using xenograft model in Balb/c nude mice, we examined the anti-tumor effect of F56 on HT-29 (Figure 5A and 5B) and MGC-823 (Figure 5C and 5D). As a positive control, cyclophosphamide effectively inhibited xenograft growth compared with the negative vehicle control. Endostatin also suppressed MGC-823 tumor growth well, but not as effectively as F56 at the same dosage of 2.5 mg/kg. Moreover, F56 inhibited MGC-823 xenograft growth in a dose-dependent way (Figure 5C and 5D), and at the dosage of 2.5 mg/kg, the inhibitory rate of F56 was more than 50% for both HT-29 and MGC-823 (Figure 5B and 5D). To further investigate the effect of F56 on tumor metastasis, we injected B16 melanoma cells in C57 mice via caudal veins, and then observed the lung metastasis. As shown in Figure 5E and 5F, F56 significantly inhibited lung metastasis of B16 cells as effective as cyclophosphamide and endostatin. Bevacizumab also inhibited the lung metastasis in our observation, but its efficiency was much lower than that of F56, cyclophosphamide, or endostatin.
Figure 5.
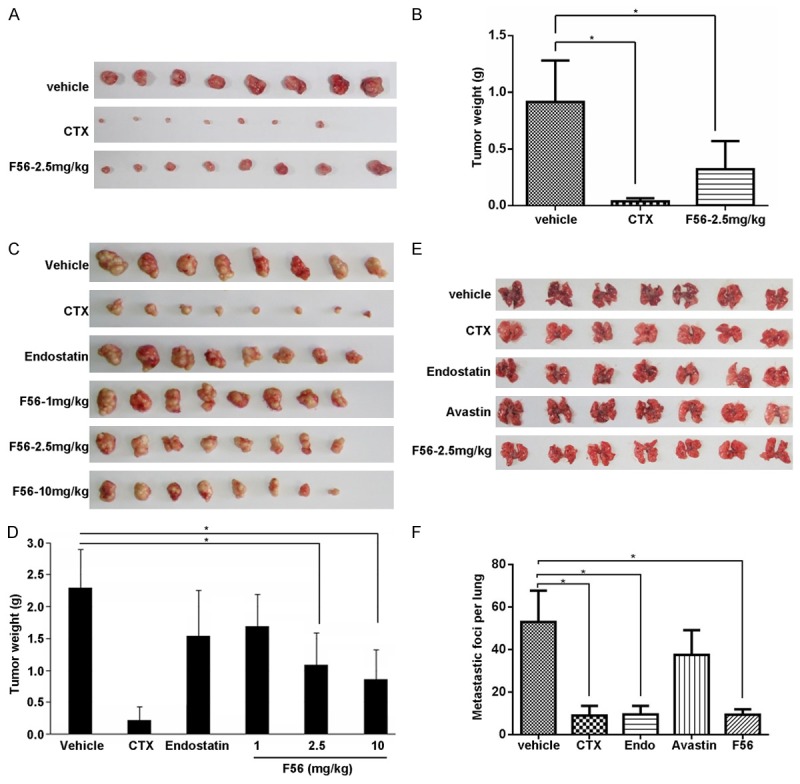
F56 inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in xenograft mice model. A. BALB/c nu/nu mice were implanted subcutaneously with 1 × 107 HT-29 cells. After the tumor volume reached about 100 mm3, these mice were treated daily with vehicle or indicated drugs for consecutive 14 days. The tumor nodules were isolated one week after drug withdrawal. B. The weight of tumor nodules from A (n = 8). C. Tumor nodules formed by BGC-823 cells in the BALB/c nu/nu mice models were shown. D. The weight of tumor nodules from C (n = 8). E. C57 mice (n = 7) were injected with 4 × 106 B16 melanoma cells via tail vein. Indicated drugs were delivered as described in the Methods. After continuous administration of drugs for 14 days, mice were killed, lungs were dissected and the number of metastatic foci per lung was counted carefully by naked eyes. F. The number of metastatic foci per lung from E was counted and analyzed. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.
Discussion
Angiogenesis is one of the hallmarks of tumor [24]. Ever since Folkman raised the hypothesis that anti-angiogenesis strategy would have anti-tumor effect [3], researchers and pharmaceutical companies tried to develop anti-angiogenic drugs with great enthusiasm. Because the VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathway is the key driver of angiogenesis, numerous therapies have been developed to target angiogenesis by blocking this pathway [2]. There are four major strategies to target this signaling system: (1) Monoclonal antibodies targeting VEGF or the VEGF receptors. (2) Chimeric soluble receptors such as the “VEGF-trap”. (3) Extracellular inhibitors such as aptamers that bind the heparin-binding domain of VEGF. (4) A variety of small-molecule VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors that suppress ligand-dependent receptor autophosphorylations of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2. Currently, the antibodies and small-molecular inhibitors are most widely used in clinical settings.
Besides the above mentioned methods to target angiogenesis, peptides emerge as a new class of anti-tumor agents. Peptides are capable of eliciting a therapeutic response by modulation of targets within or on the surface of cells. Unlike the protein drugs such as antibodies that have high molecular weights, low tissue penetration and poor cellular uptake, or the small molecule inhibitors with cardiotoxicity or other toxicity symptoms, peptides are more amenable to rational design, and thus usually possess favorable pharmacokinetic profiles, distinct tissue distribution patterns, and good solubility properties. These characteristics could ensure high uptake into target tissues and rapid clearance from non-target tissues. Besides, peptides have high specificity for their targets and can be made to target almost any protein of interest, including proteins without small-molecule drugs. Owing to this versatility, peptides have a great potential for cancer therapy. Up until now, there are already several peptides that are found to possess anti-tumor and anti-angiogenesis properties, and several therapeutic peptides for cancer have been approved for clinical usage. However, in the process of cancer therapy with anti-tumor peptides, there are still many challenges, such as short half-lives in systemic circulation, susceptibility to proteolytic digestion, and low membrane permeability. Therefore, it is still urgent to find ways of overcoming these hurdles and discover new tumor-targeting peptides with good effect and stability.
Previous research of our group using phage display library screening have identified a VEGFR1 specific peptide F56, and found that DHFR-F56 chimeric protein showed both in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effect. Since the discovery of F56, many groups have tried to utilize the high affinity of F56 to VEGFR1 to target cytotoxic agents to tumors, or use fluorescein conjugated F56 to image VEGFR1 positive cancers in vivo [19]. However, the anti-angiogenesis or anti-tumor effect of F56 peptide alone has yet to be explored. VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 have different roles in angiogenesis. Previous studies showed that, compared with physiological angiogenesis, VEGFR1-mediated signaling involved more in pathological conditions, such as cancer, ischemia and inflammation. Therefore, VEGFR1 might be a good target for anti-angiogenesis strategy [14]. In the present study, we focused on the anti-angiogenesis and anti-tumor effect of F56. As endothelial cells play a key role in angiogenesis, including proliferation, migration and tube formation, we first studied the effect of F56 on HUVEC. We found that F56 significantly inhibited VEGF induced migration of HUVEC, including the formation of pseudopodia and the elongation of cell, while with no effect on HUVEC proliferation. These results suggest that the F56 may exert the anti-angiogenesis effect through endothelial cell migration inhibition.
Angiogenesis is a complex and sequential process which involves at least three components, endothelial cells, stromal cells and extracellular matrix [14]. However, most of the in vitro two-dimensional angiogenesis assays measure only one or two components of this process. The 2D nature of these assays also ignores the differences in endothelial phenotype seen in vivo. Therefore, we performed the in vitro serum-free three-dimensional rat aortic model. This 3D model closely approximates the complexities of angiogenesis in vivo, such as endothelial activation, basement membrane degradation, endothelial sprouting from the existing vessel, and invasion [25]. In consistent with the results of the 2D angiogenesis assays, we observed significant inhibition of branching and anatomosing of microvessel networks after F56 pretreatment even though in the presence of VEGF. Therefore, both the 2D and 3D in vitro assays demonstrated the potent inhibitory effect of monomeric F56 on angiogenesis.
A substrate which has efficacy in vitro, may not show any activity in vivo [26], therefore the in vivo evaluation of agents is a vital step in drug development. CAM and zebrafish embryo SIVs assays are good measures for the in vivo efficacy of an agent. Because of its extensive vascularization and living system, the CAM provides a physiological platform to study the morpho-functional aspects of the angiogenesis process in vivo and to investigate the efficacy and mechanisms of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic agents [27,28]. The zebrafish share many genes and mechanisms of angiogenesis regulation with mammals, making this organism a valuable system to analyze the development and function of vasculature [29]. Our data show that although F56 had no effect on large vessels, it could inhibit the growth of capillaries and small blood vessels markedly in CAM, further supporting the idea that the anti-angiogenesis of F56 resides on its effect of blocking the migration of endothelial cells from existing vessels. Moreover, the zebrafish embryo SIVs assay showed that F56 had as comparable inhibitory effect as endostatin. Taken together, these results indicate that F56 is a potent anti-angiogenesis agent in vivo.
Like normal tissues, tumors require nutrients and oxygen to grow as well as the ability to discard metabolic waste. The tumor-associated neovasculature, the process of angiogenesis, addresses these needs [24]. Besides, in order to metastasize, cancer cells must invade the tumor-associated neovasculature to gain access to distant site in the body [30]. This event occurs partly through induced outgrowth of the preexisting vasculature, which is controlled by countervailing factors that either induce or oppose angiogenesis [31,32]. In nude mice that bear the human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29 and gastric carcinoma cell line BGC-823, treatment with F56 resulted in inhibition of tumor growth. The CCK-8 assay showed no direct suppression of F56 on the proliferation of both cell lines (data not shown), suggesting that the reduction in the size of tumor nodules was most likely the consequence of inadequate formation of neovasculature as a result of the anti-angiogenic effect of F56. Besides, with a melanoma mouse model, F56 significantly inhibited the lung metastasis of B16 cells as effective as cyclophosphamide and endostatin, validating F56 as a potential anti-tumor agent.
PI3K/Akt signaling has been implicated in multiple cellular functions, including cell survival, growth, glucose metabolism and protein synthesis. PI3K/Akt serves as a signal transducer, channeling information from cell surface, including growth factors, hormones and cytokines, to downstream changes [33]. Abid et al. showed that VEGF could activate PI3K/Akt signaling in endothelial cells [34]. In endothelial cells, the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is crucial in mediating cell migration and angiogenesis [35]. Therefore, F56 might exert its anti-angiogenesis effect through suppressing the PI3K/Akt signaling. Indeed, in our study, we found that VEGF could activate the PI3K/Akt signaling, as well as both of it receptors, whereas treatment with F56 reduced the phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt.
In conclusion, our findings demonstrate a role for the monomeric peptide F56 in inhibiting the angiogenesis as well as the growth and metastasis of tumor. Because of easy accessibility and low immunogenicity of F56, it might be a good candidate for anti-tumor drugs.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Major Project on Drug Research and Development for the 12th Five-Year Plan of China (2012ZX09103301-013), the National 973 Program of China (2015CB553906), intramural funding of Tasly Holding Group (B1136), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81301966).
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
Abbreviations
- VEGF
vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- PI3K/Akt
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B
- SIVs
subintestinal vein vessels
- CTX
cyclophosphamide
- Scr-F56
scrambled F56
- PFS
progression free survival
- CAM
chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane
- DHFR
dihydrofolate reductase
- HUVEC
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
References
- 1.Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P. Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell. 2011;146:873–887. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. doi: 10.1038/nature04478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Folkman J, Kalluri R. Cancer without disease. Nature. 2004;427:787. doi: 10.1038/427787a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sumpio BE, Riley JT, Dardik A. Cells in focus: endothelial cell. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34:1508–1512. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91:3527–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Saharinen P, Alitalo K. The yin, the yang, and the angiopoietin-1. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:2157–2159. doi: 10.1172/JCI58196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sulpice E, Ding S, Muscatelli-Groux B, Berge M, Han ZC, Plouet J, Tobelem G, Merkulova-Rainon T. Cross-talk between the VEGF-A and HGF signalling pathways in endothelial cells. Biol Cell. 2009;101:525–539. doi: 10.1042/BC20080221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cross MJ, Claesson-Welsh L. FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:201–207. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)01676-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ruhrberg C. Growing and shaping the vascular tree: multiple roles for VEGF. Bioessays. 2003;25:1052–1060. doi: 10.1002/bies.10351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:549–560. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vieira JM, Ruhrberg C, Schwarz Q. VEGF receptor signaling in vertebrate development. Organogenesis. 2010;6:97–106. doi: 10.4161/org.6.2.11686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shibuya M. Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;39:469–478. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2006.39.5.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shibuya M. Structure and dual function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (Flt-1) Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;33:409–420. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shibuya M. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1/Flt-1): a dual regulator for angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2006;9:225–230. doi: 10.1007/s10456-006-9055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA, Zhu Z, Hicklin D, Wu Y, Port JL, Altorki N, Port ER, Ruggero D, Shmelkov SV, Jensen KK, Rafii S, Lyden D. VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature. 2005;438:820–827. doi: 10.1038/nature04186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koch S, Tugues S, Li X, Gualandi L, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem J. 2011;437:169–183. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Graupera M, Guillermet-Guibert J, Foukas LC, Phng LK, Cain RJ, Salpekar A, Pearce W, Meek S, Millan J, Cutillas PR, Smith AJ, Ridley AJ, Ruhrberg C, Gerhardt H, Vanhaesebroeck B. Angiogenesis selectively requires the p110alpha isoform of PI3K to control endothelial cell migration. Nature. 2008;453:662–666. doi: 10.1038/nature06892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.An P, Lei H, Zhang J, Song S, He L, Jin G, Liu X, Wu J, Meng L, Liu M, Shou C. Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis by a VEGFR-1 antagonizing peptide identified from a phage display library. Int J Cancer. 2004;111:165–173. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Xu QH, Shi JY, Zhang J, Sun YF, Chang AH, Zhao YM, Cai WJ, Liu D, Zhou CC, Fan LH, Su B. Comparison of tumor neovasculature-targeted paramagnetic nanoliposomes for MRI in mice xenograft models. Clin Transl Oncol. 2014;16:395–401. doi: 10.1007/s12094-013-1091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Herringson TP, Altin JG. Effective tumor targeting and enhanced anti-tumor effect of liposomes engrafted with peptides specific for tumor lymphatics and vasculature. Int J Pharm. 2011;411:206–214. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.03.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brunel FM, Lewis JD, Destito G, Steinmetz NF, Manchester M, Stuhlmann H, Dawson PE. Hydrazone ligation strategy to assemble multifunctional viral nanoparticles for cell imaging and tumor targeting. Nano Lett. 2010;10:1093–1097. doi: 10.1021/nl1002526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang C, Zhao M, Liu YR, Luan X, Guan YY, Lu Q, Yu DH, Bai F, Chen HZ, Fang C. Suppression of colorectal cancer subcutaneous xenograft and experimental lung metastasis using nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery to tumor neovasculature. Biomaterials. 2014;35:1215–1226. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Baudin B, Bruneel A, Bosselut N, Vaubourdolle M. A protocol for isolation and culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nat Protocols. 2007;2:481–485. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nicosia RF, Ottinetti A. Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest. 1990;63:115–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liekens S, De Clercq E, Neyts J. Angiogenesis: regulators and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001;61:253–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ribatti D. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for tumor biology. Exp Cell Res. 2014;328:314–324. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cimpean AM, Ribatti D, Raica M. The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model to study tumor metastasis. Angiogenesis. 2008;11:311–319. doi: 10.1007/s10456-008-9117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rubinstein AL. Zebrafish: from disease modeling to drug discovery. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2003;6:218–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996;86:353–364. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Baeriswyl V, Christofori G. The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009;19:329–337. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bergers G, Benjamin LE. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:401–410. doi: 10.1038/nrc1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brazil DP, Park J, Hemmings BA. PKB binding proteins. Getting in on the Akt. Cell. 2002;111:293–303. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Abid MR, Guo S, Minami T, Spokes KC, Ueki K, Skurk C, Walsh K, Aird WC. Vascular endothelial growth factor activates PI3K/Akt/forkhead signaling in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:294–300. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000110502.10593.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shiojima I, Walsh K. Role of Akt signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 2002;90:1243–1250. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000022200.71892.9f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


