Abstract
The Pseudomonas putida KT2440 strain was engineered in order to produce anthranilate (oAB, ortho-aminobenzoate), a precursor of the aromatic amino acid tryptophan, from glucose as sole carbon source. To enable the production of the metabolic intermediate oAB, the trpDC operon encoding an anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase (TrpD) and an indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase (TrpC), were deleted. In addition, the chorismate mutase (pheA) responsible for the conversion of chorismate over prephenate to phenylpyruvate was deleted in the background of the deletion of trpDC to circumvent a potential drain of precursor. To further increase the oAB production, a feedback insensitive version of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase encoded by the aroGD146N gene and an anthranilate synthase (trpES40FG) were overexpressed separately and simultaneously in the deletion mutants. With optimized production conditions in a tryptophan-limited fed-batch process a maximum of 1.54 ± 0.3 g L-1 (11.23 mM) oAB was obtained with the best performing engineered P. putida KT2440 strain (P. putida ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG).
Keywords: Pseudomonas putida KT2440, anthranilic acid, aromatic amino acid pathway, metabolic engineering, industrial biotechnology
Introduction
Anthranilate (oAB, ortho-aminobenzoate) is an aromatic acid used as a platform chemical for the production of food ingredients (Raffensperger and Vogt, 1961), dyes, perfumes (Wiklund and Bergman, 2006), crop protection compounds (Askham, 1992; Yadav and Krishnan, 1998; Chambers et al., 2013), pharmaceutical compounds (Bahia et al., 2011; Shafiq et al., 2011; Haynes et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2013; Loque and Weniger, 2013; Walsh et al., 2013), and plastics such as nylon (Sun et al., 2013). It is currently produced in energy intensive chemical processes from petroleum-based precursors, like phthalamic acid (Klipper and Gripper, 1981; Berg, 2009). Furthermore, the production of the precursors and the production of oAB accumulate toxic byproducts, such as hypochlorite which is used with molar equivalency to oAB (Berg, 2009). Thus, there is a strong motivation to find alternative routes to produce platform chemicals, such as oAB, in green production processes from renewable resources in an environmental friendly way. In addition, the development and application of green production processes is accelerated by an environmental and political interest to be less dependent on fossil resources.
Biocatalysis using living microbes as catalysts is a well-established alternative for the production of chemicals. The aromatic biosynthesis pathway and the derived compounds of the aromatic acids, such as oAB, have been intensively studied in the last decades (Bongaerts et al., 2001; Ikeda, 2003; Kramer et al., 2003; Leuchtenberger et al., 2005; Pittard and Yang, 2008). Microbial production of oAB with engineered Escherichia coli strains was reported by Balderas-Hernandez et al. (2009) followed by further publications on oAB-derived compounds such as catechol and muconic acid (Sun et al., 2013; Averesch and Krömer, 2014; Balderas-Hernandez et al., 2014; Jaeger et al., 2015). To enable oAB production in E. coli, Balderas-Hernandez et al. (2009, 2014) inserted a point mutation in the oAB phosphoribosyl transferase domain (trpD), whereas Sun et al. (2013) used the Keio collection deletion strain E. coli BW25113 Δtrp::kan to prevent the conversion of oAB to tryptophan. Additional targets to increase the production of oAB in E. coli, for example the overexpression of feedback insensitive variants of the 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase and the anthranilate synthase unit (trpES40FG) were investigated. A maximum titer of 14 g L-1 oAB was reported growing the engineered strains in complex medium containing 30 g L-1 yeast extract (Balderas-Hernandez et al., 2009).
Here, we present the first attempt of microbial production of oAB from glucose as sole carbon source with an engineered P seudomonas putida KT2440 strain. Due to its versatile metabolism and low nutritional requirements P. putida is an efficient production strain for various industrial relevant products (Tiso et al., 2014). In addition its high biomass yield, high growth rate, and low maintenance demand fulfill the rigorous demands of industrial biotechnology (Poblete-Castro et al., 2012). A broad portfolio of P. putida biocatalysts for bulk chemicals such as phenol (Wierckx et al., 2005), p-hydroxystyrene (Verhoef et al., 2009), p-hydroxybenzoate (Verhoef et al., 2007), rhamnolipids (Wittgens et al., 2011), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA; Wang et al., 2011), and (S)-styrene oxide (Blank et al., 2008) demonstrate the great potential of this species as a flexible cell factory for the production of chemicals in industrial biotechnology. In addition, P. putida strains have the capability to withstand various chemical stresses such as a second phase of toluene, octanol, or styrene (Heipieper and de Bont, 1994; Dominguez-Cuevas et al., 2006; Blank et al., 2008), as well as oxidative stress (Chavarria et al., 2013) and reduced water activity (Hallsworth et al., 2003), and thus providing a promising and versatile chassis for the production of toxic compounds such as oAB.
To ensure industrially relevant oAB production conditions a full, markerless deletion of trpDC was performed in P. putida, facilitated by the fact that in contrast to E. coli the trpEG and trpDC genes are encoded by separate open reading frames. Additionally the production of oAB was realized on glucose as sole carbon source, avoiding the addition of high amounts of complex media components such as yeast extract. A maximum titer of 1.54 ± 0.3 g L-1 (11.23 mM) oAB was obtained with the best performing engineered P. putida KT2440 strain (P. putida ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG) in tryptophan-limited fed-batch fermentations with glucose as sole carbon source.
Materials and Methods
Strains and Plasmids
The deletion of trpDC and pheA were performed by a clean and markerless deletion method described by Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo (2011) resulting in two knock out strains P. putida KT2440 trpDC and P. putida KT2440 trpDC pheA. To obtain the knockout vectors pEMG_ΔtrpDC and pEMG_ΔpheA were obtained via a standard restriction and ligation approach and were transformed into chemical competent E. coli DH5α (according to Choi et al., 2006) via electroporation. The 800-bp flanks upstream (TS1) and downstream (TS2) of the gene of interest (trpDC and pheA) were amplified by PCR using a Pfu polymerase (New England Biolabs) with the primers listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Primer sequences.
| Name | DNA sequence | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| TS1 ΔtrpDC | ||
| JK034f | agggataacagggtaatctgaatTCGTCAGCAAACTCTTGATG | 61.6 |
| JK035r | tttgactcgagGTTCGATCCTTAACGGCG | 61.6 |
| TS2 ΔtrpDC | ||
| JK036f | aggatcgaacctcgagTCAAATGAAGCCGGCGTT | 66.1 |
| JK037r | cctgcaggtcgactctagaggatccTCGAACCAAGGTGCTACCG | 66.1 |
| TS1 ΔpheA | ||
| JK038f | attcgagctcggtacccggggatccACTACATCGAAACCGGCATC | 61.8 |
| JK039r | ctgaactcgagTCAGCCATGCTCCTTCTC | 61.8 |
| TS2 ΔpheA | ||
| JK040f | gcatggctgactcgagTTCAGGGGCCTTGGGGCT | 70.2 |
| JK041r | tagaagcttgcatgcctgcaggCAGTGAGTCGACCAGGCCAAAG | 70.2 |
TS1 and TS2 were fused in a SOEing-PCR using Pfu polymerase according to Horton (1995). The backbone (pEMG) and the fused SOEing-PCR fragment were digested with BamHI and EcoRI for the deletion of trpDC and with BamHI and SbfI for the deletion of pheA. The digested backbones, TS1, and TS2 were purified (High Pure PCR Product Purification Kit, Roche), ligated with a T4 DNA ligase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and transformed into chemical competent E. coli DH5α (according to Choi et al., 2006) via electroporation. Constructs were verified by restriction analysis and sequencing, resulting in pEMG_ΔtrpDC and pEMG_ΔpheA. Genome integration of the knockout constructs into the P. putida strains was performed via tri-parental mating according to Ditta et al. (1980) using E. coli HB101 pRK2013 as the helper strain and facilitated as described in Zobel et al. (2015) where the three mating strains were streaked one above the other on a LB plate. The resulting strains were transformed with the plasmid expressing the ISce-I endonuclease (pSW-I; according to Choi et al., 2006). Induction with 3-methylbenzoate was omitted due to the leaky expression of the ISce-I nuclease. Successful construction of the knockout strains was verified via restriction, PCR and Sanger sequencing.
The feedback insensitive overexpression constructs were obtained via a standard restriction and ligation approach as described above using BamHI and EcoRI for aroGD146N and BamHI for trpES40FG. pSEVA234 (Silva-Rocha et al., 2013), which contains an IPTG inducible lacIQ-Ptrc expression system, was used as backbone. The genes aroGD146N (Kikuchi et al., 1997; Albermann et al., 2014) and trpES40FG (Kwak et al., 1999) were synthesized at Eurofins Genomics. A summary of the used and constructed plasmids and of the engineered strains is shown in Table 2. All primers were purchased at Eurofins Genomics and all restriction enzymes at Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Table 2.
Summary of plasmids and strains used in this study.
| Description | Reference | |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmids | ||
| pEMG | KmR, oriR6K, lacZa with two flanking I-SceI sites | Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo, 2011 |
| pSEVA234 | KmR, oriBBR1, lacIq-Ptrc | Silva-Rocha et al., 2013 |
| pSW-I | ApR, oriRK2, xylS, Pm→I-SceI | Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo, 2011 |
| pRK2013 | KmR, oriRK2, oriColE1 | Figurski et al., 1979 |
| pEMG_ΔtrpDC | trpDC deletion plasmid | This work |
| pEMG_ΔpheA | pheA deletion plasmid | This work |
| pSEVA234_trpES40FG | trpES40FG expression plasmid | This work |
| pSEVA234_aroGD146N | aroGD146N expression plasmid | This work |
| pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG | aroGD146N-trpES40FG expression plasmid | This work |
| Strain | ||
| Psuedomonas putida KT2440 | Wild-type strain derived of P. putida mt-2 cured of the pWW0 plasmid | Bagdasarian et al., 1981 |
| Escherichia coli DH5α | supE44, DlacU169 (f80 lacZDM15), hsdR17 (rk-mk+), recA1, endA1, thi1, gyrA, relA | Hanahan, 1985 |
| E. coli DH5α aaapir | aaapir phage lysogen of DH5α | De Lorenzo Lab collection |
| E. coli HB101 pRK2013 | SmR, hsdR-M+, pro, leu, thi, recA, KmR, oriRK2, oriColE1 | Figurski et al., 1979 |
| E. coli DH5α aaapir pEMG | Plasmid carrier strain | Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo, 2011 |
| E. coli DH5α aaapir pSW-I | Plasmid carrier strain | Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo, 2011 |
| E. coli DH5α aaapir pEMG_ΔtrpDC | Plasmid carrier strain | This work |
| E. coli DH5α aaapir pEMG_ΔpheA | Plasmid carrier strain | This work |
| E. coli DH5α pSEVA234_trpES40FG | Plasmid carrier strain | This work |
| E. coli DH5α pSEVA234_aroGD146N | Plasmid carrier strain | This work |
| E. coli DH5α pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG | Plasmid carrier strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 pSEVA234_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 pSEVA234_aroGD146N | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N | oAB production strain | This work |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG | oAB production strain | This work |
Cultivation Conditions
For cloning and maintenance processes, E. coli strains and P. putida strains were cultivated at 37 and 30°C, respectively, in LB medium supplemented with or without kanamycin (50 mg L-1) or ampicillin (100 mg L-1 for E. coli and 500 mg L-1 for P. putida), and/or with 1.5% (w/v) agar as needed.
Auxotrophies (tryptophan and phenylalanine) of the gene deletion mutants were verified on solid mineral medium plates (Wierckx et al., 2005) with 1.5% (w/v) agar, 20 mM glucose with and without 1 mM tryptophan, and/or 1 mM phenylalanine supplementation. Alternatively 1 mM phenylpyruvate was used instead of phenylalanine.
Batch-wise oAB production was performed in 500 mL shake flasks at 30°C and 200 rpm in 50 mL mineral medium as described in Wierckx et al. (2005) with 20 mM glucose (unless stated differently), 50 mg L-1 kanamycin, and 1 mM IPTG, supplemented with either 0.1 or 0.05 mM tryptophan and 1 mM phenlypyruvate for the ΔpheA strains. Two additional 20 mM glucose pulses were added after 10 and 24 h unless stated differently.
Tryptophan-limited fed-batch conditions were realized in controlled bioreactors (BioFlo 110 or BioFlo 115, Eppendorf / New Brunswick Scientific) with a starting volume of 400 mL. The initial fermentation medium consisted of mineral medium with 50 mM glucose, a twofold phosphate buffer concentration, a threefold (NH4)2SO4 concentration, a onefold trace element solution, 1 mM IPTG, 50 mM kanamycin, and 0.1 mM tryptophan. After the initial batch phase, the feed was switched on at a rate of 2 mL h-1 consisting of a mixed solution of 1 M glucose and 0.5 mM (glucose to tryptophan molar ratio of 2,000:1) or 1 mM (glucose to tryptophan molar ratio of 1,000:1) tryptophan. To compensate for the increasing biomass concentrations the 1 mM tryptophan feed was increased to 6 mL h-1. The fermentations were performed at 30°C, with 500–1,200 rpm agitation (dO2 regulated agitation cascade with a lower limit of 35%), with 1 vvm headspace aeration of compressed air. The pH was regulated to pH = 7 with 2 M KOH and 4 M H2SO4.
Analytics
The biomass concentration was measured with a spectrophotometer (Ultrospec 10, GE Healthcare Life Sciences). In this device the OD600 correlates to cell dry weight (CDW): 1 OD600 = 0.505 gCDW L-1. The samples taken during cultivation were centrifuged at 13,300 rpm for 3 min and stored at -20°C for further analysis. To follow the consumption of the glucose and derivatives (gluconate and 2-ketogluconate) by the P. putida KT2440 strains, a Beckman HPLC equipped with an organic acid resin column (polystyrol-divinylbenzol copolymer, PS-DVB: 300 × 8.0 mm, CS-Chromatographie) was used with 5 mM H2SO4 as eluent at a flow of 0.8 mL h-1 for 11 min at 75°C. Detection was realized with an UV detector at a wavelength of 210 nm and a RI detector. The oAB production was analyzed with a reverse phase column (LiChrosorb 100 RP-18, 250 × 4 mm, Merck), at a flow of 1.2 mL h-1 [pump gradient of H2O + 0.1% TFA (pump A) and of MeOH (pump B): 0–2 min 90% A, 2–12 min gradient 0–90% A, 12–14 min 0% A, 14–15 min gradient 0–90% A, and 15–16 min 90% A] at 30°C. Detection was realized with an UV detector at a wavelength of 257 nm and a RI detector.
Results and Discussion
Metabolic Engineering of oAB Production Strains
In order to establish oAB production in P. putida, the trpDC and pheA genes were knocked out using the I-SceI-based pEMG system (Martinez-Garcia and de Lorenzo, 2011). Disruption of the trpDC genes, which encode an anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase (TrpD) and an indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase (TrpC), leads to a tryptophan auxotrophy and enables the accumulation of oAB (Figure 1). Disruption of the pheA gene, which encodes a bifunctional chorismate mutase/prephenate dehydratase enzyme responsible for the first two steps of the synthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine, possibly increases the metabolic flux toward oAB by reducing the drain on its primary precursor chorismate (Zhao et al., 2011). Contrary to other established production hosts, the pheA deletion only requires phenylalanine to complement growth since P. putida can convert phenylalanine to tyrosine (Molina-Henares et al., 2009). The corresponding auxotrophies were verified on mineral medium plates (Table 3).
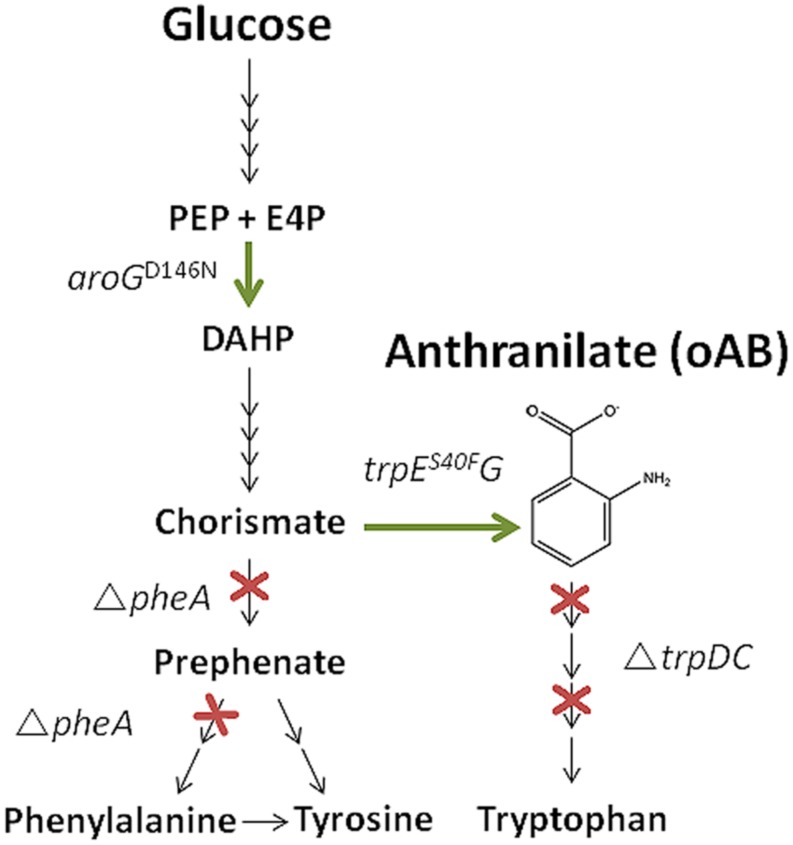
FIGURE 1.
Schematic oAB production pathway including the metabolic engineering targets investigated in this study (overexpression of aroGD146NtrpES40FG and deletion of trpDC and pheA). PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; E4P, erythrose-4-phosphate; DAHP, 3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate.
Table 3.
Auxotrophy supplementation of P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC and ΔpheA knockouts.
| Name | Supplementationa | Growth |
|---|---|---|
| P. putida KT2440 | None | + |
| trp | + | |
| phe | + | |
| trp + phe | + | |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC | None | - |
| Trp | + | |
| P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA | None | - |
| Trp | - | |
| trp + phe | + | |
| trp + pp | + |
aMineral medium plates with 20 mM glucose supplemented with 1 mM tryptophan (trp), phenylalanine (phe), or phenylpyruvate (pp).
In the knockout process, the deletion of pheA could only be obtained by supplementation with phenylpyruvate. The final step of the knockout procedure (induction of the double strand break) should theoretically yield a one-to-one ratio of wildtype to knockout allele. However, selection on LB- or LB medium with phenylalanine resulted in the wildtype allele only, even after testing >1,000 colonies either by PCR or by screening for phenylalanine auxotrophy. This may be attributed to the ability of P. putida to degrade phenylalanine and tyrosine. Possibly, supplementation with phenylpyruvate instead of phenylalanine reduced the induction of genes encoding the phenylalanine and tyrosine catabolic pathway (Arias-Barrau et al., 2004), facilitating the successful isolation of the knockout strain. The final pheA knockout auxotroph could be complemented with phenylalanine in mineral medium. However, in this case a severe negative effect on the fitness of the mutant caused by the deletion of pheA was observed. Therefore, all subsequent ΔpheA complementation were done with phenylpyruvate.
To further optimize the production of oAB in P. putida, feedback insensitive pSEVA234-based (Silva-Rocha et al., 2013) overexpression constructs for trpES40FG and aroGD146N, or both genes in one operon structure, were transformed to the respective mutants under the IPTG-inducible LacIQ-Ptrc system. These genes encode feedback insensitive variants of anthranilate synthase and 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate (DHAP) synthase, respectively, and are known to enhance oAB production in E. coli (Balderas-Hernandez et al., 2009, 2014; Sun et al., 2013). Figure 1 shows the exemplarily oAB production pathway and gives on overview over the metabolic engineering targets investigated in this study.
Evaluation of oAB Production Strains in Shake Flasks
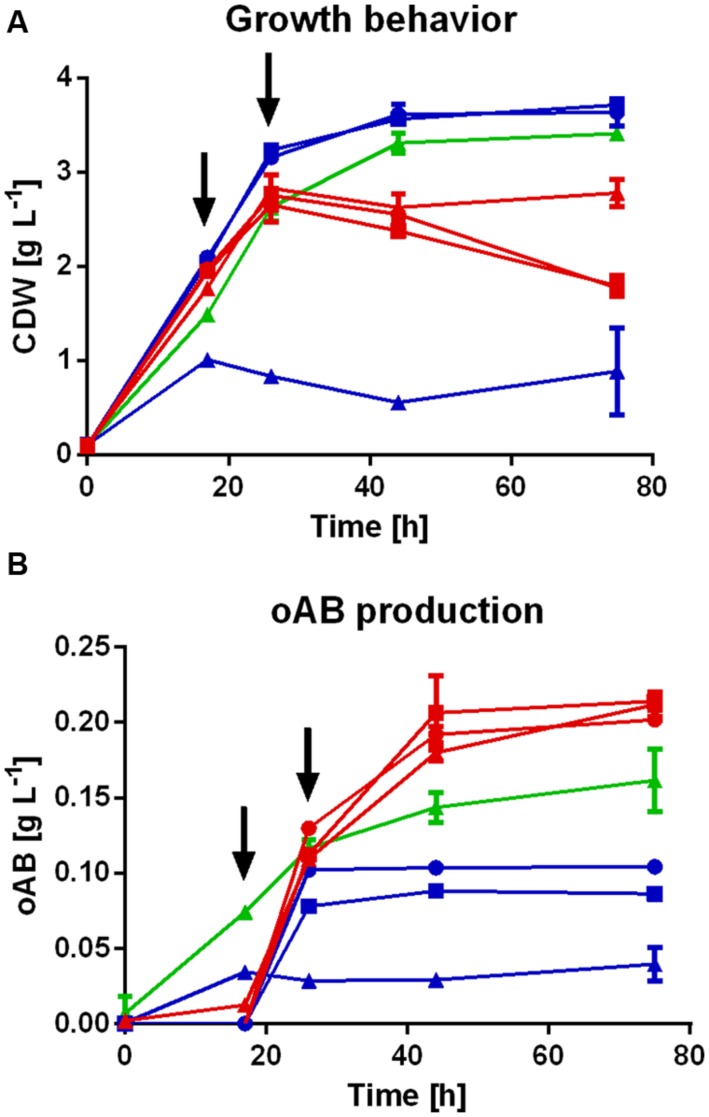
The P. putida strains engineered for the production of oAB (listed in Table 2) were initially assessed in shake flasks (Figures 2A,B) and under slightly optimized production conditions a maximum titer of 0.25 ± 0.004 g L-1 (1.83 mM) oAB with glucose as sole carbon source was achieved (Figure 3). The three ΔtrpDC strains bearing either trpES40FG, aroGD146N or both, have shown no significant differences in maximal oAB titers, although the onset of production was earlier in the P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG. Interestingly, oAB production was also observed with P. putida KT2440 pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG (without trpDC deletion) while no tryptophan was secreted, although the maximal titer was lower than that of the ΔtrpDC strains. This can be explained by the transcriptional repression of trp genes by tryptophan through the TrpR repressor (Maurer and Crawford, 1971; Wierckx et al., 2008). Likely, an increase of intracellular tryptophan caused repression of the native trp genes, leading to anthranilate accumulation due to the heterologous expression of trpES40FG.
FIGURE 2.
oAB production profiles of various P. putida KT2440 strains in shake flasks. Biomass growth (A) and oAB production (B) of the following Pseudomonas putida KT2440 strains in an initial screening experiment:  , ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG;
, ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG;  , ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N;
, ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N;  , ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG;
, ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG;  , ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_trpES40FG;
, ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_trpES40FG;  , ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N;
, ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N;  , ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG;
, ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG;  , pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG. All cultures were performed in mineral medium with 20 mM initial glucose concentration and addition of tryptophan and/or phenylpyruvate as described above. The arrows indicate the addition of glucose to a concentration of 20 mM.
, pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG. All cultures were performed in mineral medium with 20 mM initial glucose concentration and addition of tryptophan and/or phenylpyruvate as described above. The arrows indicate the addition of glucose to a concentration of 20 mM.
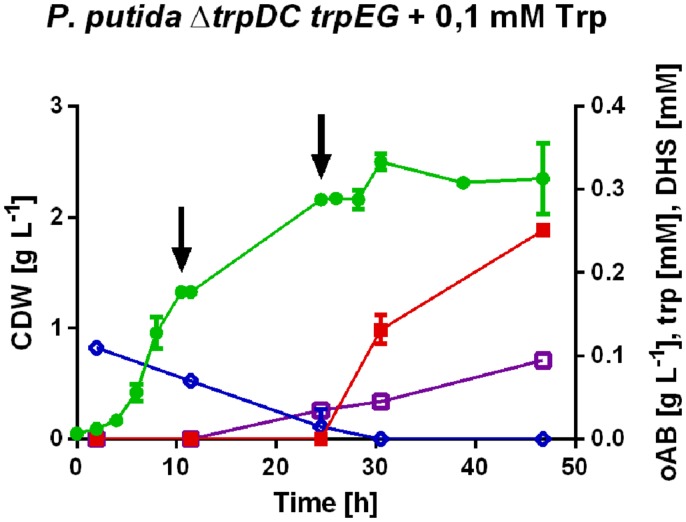
FIGURE 3.
Detailed profiles of  , cell dry weight;
, cell dry weight;  , oAB;
, oAB;  , tryptophan (trp);
, tryptophan (trp);  , dehydroshikimate (DHS) concentrations of the best selected strain P.putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG generated under slightly optimized production conditions. All cultures were performed in mineral medium with 20 mM initial glucose concentration and addition of tryptophan and/or phenylpyruvate as described above. The arrows indicate the addition of glucose to a concentration of 20 mM.
, dehydroshikimate (DHS) concentrations of the best selected strain P.putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG generated under slightly optimized production conditions. All cultures were performed in mineral medium with 20 mM initial glucose concentration and addition of tryptophan and/or phenylpyruvate as described above. The arrows indicate the addition of glucose to a concentration of 20 mM.
A strong connection was observed between tryptophan limitation and oAB production. When supplementing the auxotrophic strains with tryptophan the oAB production was induced only upon depletion of the added tryptophan. Strains expressing both aroGD146N and trpES40FG produced oAB at earlier time points compared to strains with only one of the feedback insensitive genes, indicating somewhat alleviated feedback insensitivity to tryptophan (Figure 2). With the non-auxotrophic P. putida pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG, where a supplementation with tryptophan was not required, oAB titers were significantly higher at earlier time points, indicating no inhibition by tryptophan. However, the final oAB titers were 34% lower compared to the P. putida ΔtrpDC strains, indicating a positive effect of the deletion of trpDC.
As indicated above, a clear negative effect of the deletion of pheA on the growth behavior was observed. Whereas P. putida KT2440 pSEVA234_trpES40FG and P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_trpES40FG were able to grow up to 3.6 g L-1 CDW and 2.4 g L-1 CDW, respectively; P.putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC ΔpheA pSEVA234_trpES40FG only reached a maximal CDW concentration of 1.4 g L-1 after 10 hours when supplemented with 1 mM phenylpyruvate. Further addition of glucose and/or tryptophan could neither initiate growth to higher CDW concentrations, nor did it improve oAB production. Normal growth was only fully rescued when supplementing high amounts of phenylpyruvate (≥5 mM) which would make the overall process highly uneconomical. Additionally, final oAB titers were still 49% lower than with the ΔtrpDC strains, indicating a negative effect of the pheA deletion for the production of oAB in this organism. Thus, the most promising strain engineered for the production of oAB is P. putida ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG as it reached high titers of oAB and showed reduced sensitivity to tryptophan.
Dehydroshikimate, a metabolic intermediate of the shikimate pathway and thus a precursor of oAB, accumulated as a by-product in all strains engineered for oAB production in shake flasks, indicating shikimate dehydrogenase as a likely bottleneck (Figure 3). This hypothesis is also supported by the transcriptome data sets of Wierckx et al. (2009) and Verhoef et al. (2010) showing upregulated 3-dehydroquinate and dehydroshikimate genes in the analyzed phenol and p-hydroxybenzoate production strains obtained by a fluoro-analog mutant screening.
Production of oAB in Controlled Bioreactors
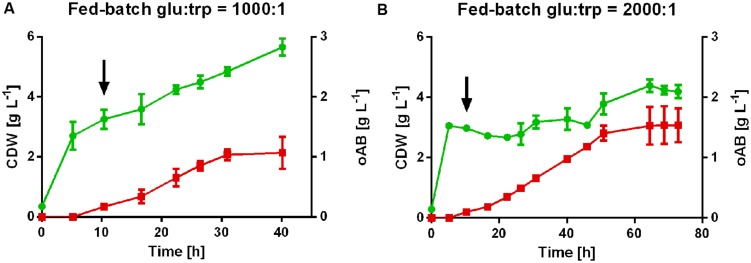
The potential of P. putida ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG to produce oAB was further assessed in tryptophan-limited fed batch cultures to circumvent the observed inhibition by tryptophan and maximize final oAB titers. A glucose-to-tryptophan molar ratio of 400:1 was estimated for biomass growth alone based on the initial shake flask experiments. Therefore, two different feeding approaches with a molar ratio of glucose to tryptophan of 1,000:1 and 2,000:1 were used to ensure a tryptophan limitation without excessive accumulation of glucose or its derivatives. Under these conditions a maximal titer of 1.54 ± 0.3 g L-1 oAB was reached from glucose as sole carbon source using the 2,000:1 feed (Figure 4). The higher ratio of glucose to tryptophan led to a more severe growth limitation, with CDW increasing only marginally during the production of oAB. In contrast, the 1,000:1 feed enabled more biomass growth at the cost of oAB production, leading to a final product titer of 1.0 ± 0.07 g L-1. The product per substrate yield (based on consumed carbon source) for both conditions is relatively similar at 3.6 ± 0.5% (g/g) for the 1,000:1 feed and 3.5 ± 0.5% (g/g) for the 2,000:1 feed. oAB levels increased fairly linearly until the production stopped abruptly. Since the level of oAB produced is well below growth-inhibiting concentrations for P. putida (data not shown), oAB production is most likely stopped due to product inhibition, a known phenomenon for the production of aromatics (Gibson and Pittard, 1968; Wierckx et al., 2008; Rodriguez et al., 2014). This product inhibition likely takes place at the level of the anthranilate synthase. Indeed, the anthranilate synthase complex of other organisms is already inhibited by oAB concentrations in the micromolar range (Cordaro et al., 1968; Henderson et al., 1970; Francis et al., 1978). The oAB titers obtained with P. putida KT2440 in this study are about 10-fold lower than those achieved by Balderas-Hernandez et al. (2009). The difference can most likely be attributed to the supplementation of 30 g/L yeast extract by these researchers, which can provide oAB precursors and increases the general stress tolerance of microorganisms. This apparent positive effect of yeast extract on oAB production should be further investigated in order to elucidate the responsible components.
FIGURE 4.
Tryptophan-limited fed-batch cultures of P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG in controlled bioreactors with different feeding approaches. (A) Feed molar ratio of glucose to tryptophan 1,000:1. (B) Feed molar ratio of glucose-to-tryptophan 2,000:1.  , cell dry weight;
, cell dry weight;  , oAB concentration. The arrows indicate the start of the feed after the initial batch phase.
, oAB concentration. The arrows indicate the start of the feed after the initial batch phase.
In the initial batch phase, the 50 mM glucose were entirely consumed for the production of biomass. Tryptophan limiting conditions were confirmed by HPLC analysis throughout the fermentation (<0.1 mM). Carbon source, either as glucose or as gluconate and 2-ketogluconate, were constantly present during the feed phase at total concentrations between 0.4 and 8.6 g L-1. In some fermenters, a prolonged incubation led to a decrease of oAB concentrations over time. Possibly, polymerization of oAB and/or its conversion products occurred.
Conclusion
Microbial production of oAB under industrial relevant conditions from glucose as sole carbon source was achieved in P. putida KT2440 via the biosynthesis pathway of aromatic amino acids. A strong connection between a tryptophan limitation and oAB production was observed even with strains bearing feedback insensitive overexpression constructs of aroGD146N and trpES40FG. Under tryptophan limiting fed-batch conditions, a maximum titer of 1.54 ± 0.3 g L-1 oAB was achieved with P. putida KT2440 ΔtrpDC pSEVA234_aroGD146N_trpES40FG. This final achieved concentration is in the same range as other aromatics produced by P. putida strains (Nijkamp et al., 2005, 2007; Verhoef et al., 2007); although the titer is lower than that of previously published works with E. coli (Balderas-Hernandez et al., 2009). However, the supplementation with yeast extract was avoided and oAB was only produced from glucose. In addition, to ensure long term strain stability, one of the main requirements in industrial biotechnology, a stable and markerless deletion of the genes responsible for the conversion of oAB towards tryptophan (trpDC) was used. Nevertheless, the oAB titer and yield reached with P. putida KT2440 are below those which are required to realize an industrial feasible process. Further improvement is required, e.g., by more in-depth metabolic engineering (e.g., overexpression of tkt: Balderas-Hernandez et al., 2009) as well as by in situ product removal to alleviate product inhibition. Further research on the mechanism of product inhibition of oAB production could also lead to additional metabolic engineering targets to improve microbial oAB production.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
NW was supported by the German Research Foundation through the Emmy Noether project WI 4255/1-1.
References
- Albermann C., Weiner M., Trondle J., Weuster-Botz D., Sprenger G. A. (2014). Utilization of organophosphate:phosphate antiporter for isotope-labeling experiments in E. coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 361 52–61. 10.1111/1574-6968.12612 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias-Barrau E., Olivera E. R., Luengo J. M., Fernandez C., Galan B., Garcia J. L., et al. (2004). The homogentisate pathway: a central catabolic pathway involved in the degradation of L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and 3-hydroxyphenylacetate in Pseudomonas putida. J. Bacteriol. 186 5062–5077. 10.1128/JB.186.15.5062-5077.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askham L. R. (1992). “Efficacy of methyl anthranilate as a bird repellent on cherries, blueberries and grapes,” in Proceeding of the 15th Vertebrate Pest Conference, eds Borrecco J. E., Marsh R. E. (Davis, CA: University of California; ), 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Averesch N. J. H., Krömer J. O. (2014). Tailoring strain construction strategies for muconic acid production in S. cerevisiae and E. coli. Metab. Eng. Commun. 1 19–28. 10.1016/j.meteno.2014.09.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Ruckert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., et al. (1981). Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene 16 237–247. 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahia M. S., Gunda S. K., Gade S. R., Mahmood S., Muttineni R., Silakari O. (2011). Anthranilate derivatives as TACE inhibitors: docking based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. J. Mol. Model. 17 9–19. 10.1007/s00894-010-0695-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balderas-Hernandez V. E., Sabido-Ramos A., Silva P., Cabrera-Valladares N., Hernandez-Chavez G., Baez-Viveros J. L., et al. (2009). Metabolic engineering for improving anthranilate synthesis from glucose in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 8:19 10.1186/1475-2859-8-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balderas-Hernandez V. E., Trevino-Quintanilla L. G., Hernandez-Chavez G., Martinez A., Bolivar F., Gosset G. (2014). Catechol biosynthesis from glucose in Escherichia coli anthranilate-overproducer strains by heterologous expression of anthranilate 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microb. Cell Fact. 13:136 10.1186/s12934-014-0136-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg C. (2009). Treatment of Aqueous Liquids and the Preparation of Anthranilic Acid. US 20090171116 A1. [Google Scholar]
- Blank L. M., Ionidis G., Ebert B. E., Buhler B., Schmid A. (2008). Metabolic response of Pseudomonas putida during redox biocatalysis in the presence of a second octanol phase. FEBS J. 275 5173–5190. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06648.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongaerts J., Kramer M., Muller U., Raeven L., Wubbolts M. (2001). Metabolic engineering for microbial production of aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Metab. Eng. 3 289–300. 10.1006/mben.2001.0196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers A. H., Evans S. A., Folta K. M. (2013). Methyl anthranilate and gamma-decalactone inhibit strawberry pathogen growth and achene Germination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61 12625–12633. 10.1021/jf404255a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavarria M., Nikel P. I., Perez-Pantoja D., De Lorenzo V. (2013). The Entner-Doudoroff pathway empowers Pseudomonas putida KT2440 with a high tolerance to oxidative stress. Environ. Microbiol. 15 1772–1785. 10.1111/1462-2920.12069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. H., Kumar A., Schweizer H. P. (2006). A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J. Microbiol. Methods 64 391–397. 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.06.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro J. C., Levy H. R., Balbinder E. (1968). Product inhibition of anthranilate synthetase in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 33 183–189. 10.1016/0006-291X(68)90765-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. (1980). Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77 7347–7351. 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Cuevas P., Gonzalez-Pastor J. E., Marques S., Ramos J. L., De Lorenzo V. (2006). Transcriptional tradeoff between metabolic and stress-response programs in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 cells exposed to toluene. J. Biol. Chem. 281 11981–11991. 10.1074/jbc.M509848200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Meyer R. J., Helinski D. R. (1979). Suppression of Co1E1 replication properties by the Inc P-1 plasmid RK2 in hybrid plasmids constructed in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 133 295–318. 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90395-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. M., Vining L. C., Westlake D. W. (1978). Characterization and regulation of anthranilate synthetase from a chloramphenicol-producing streptomycete. J. Bacteriol. 134 10–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X., Jiang W., Jimenez-Oses G., Choi M. S., Houk K. N., Tang Y., et al. (2013). An iterative, bimodular nonribosomal peptide synthetase that converts anthranilate and tryptophan into tetracyclic asperlicins. Chem. Biol. 20 870–878. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.04.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson F., Pittard J. (1968). Pathways of biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids and vitamins and their control in microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 32 465–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallsworth J. E., Heim S., Timmis K. N. (2003). Chaotropic solutes cause water stress in Pseudomonas putida. Environ. Microbiol. 5 1270–1280. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2003.00519.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. (1985). “Techniques for transformation of E. coli,” in DNA Cloning: A Practical Approach, ed. Glover D. M. (Oxford: IRL Press; ), 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. W., Gao X., Tang Y., Walsh C. T. (2012). Assembly of asperlicin peptidyl alkaloids from anthranilate and tryptophan: a two-enzyme pathway generates heptacyclic scaffold complexity in asperlicin E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134 17444–17447. 10.1021/ja308371z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heipieper H. J., de Bont J. A. M. (1994). Adaptation of Pseudomonas putida S12 to ethanol and toluene at the level of fatty acid composition of membranes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60 4440–4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. J., Nagano H., Zalkin H., Hwang L. H. (1970). The anthranilate synthetase-anthranilate 5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate phosphoribosyltransferase aggregate. Purification of the aggregate and regulatory properties of anthranilate synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 245 1416–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M. (1995). PCR-mediated recombination and mutagenesis. SOEing together tailor-made genes. Mol. Biotechnol. 3 93–99. 10.1007/BF02789105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M. (2003). Amino acid production processes. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 79 1–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger G., Magnus J., Moussa A. S., Olf G., Lolli G., Behnken S., et al. (2015). Recombinant Strain Producing O-Aminobenzoate and Fermentative Production of Aniline from Renewable Resources Via 2-Aminobenzoic Acid. Google Patents 2015124687. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Tsujimoto K., Kurahashi O. (1997). Mutational analysis of the feedback sites of phenylalanine-sensitive 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase of Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63 761–762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipper G., Gripper J. (1981). Continuous Preparation of Anthranilic Acid. US 4276433 A. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M., Bongaerts J., Bovenberg R., Kremer S., Muller U., Orf S., et al. (2003). Metabolic engineering for microbial production of shikimic acid. Metab. Eng. 5 277–283. 10.1016/j.ymben.2003.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak J. H., Hong K. W., Lee S. H., Hong J. H., Lee S. Y. (1999). Identification of amino acid residues involved in feedback inhibition of the anthranilate synthase in Escherichia coli. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Leuchtenberger W., Huthmacher K., Drauz K. (2005). Biotechnological production of amino acids and derivatives: current status and prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69 1–8. 10.1007/s00253-005-0155-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loque D., Weniger A. G. E. (2013). Host Cells and Methods for Producing Cinnamoyl Anthranilate and Analogs Thereof. US 20130078683 A1. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Garcia E., de Lorenzo V. (2011). Engineering multiple genomic deletions in Gram-negative bacteria: analysis of the multi-resistant antibiotic profile of Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ. Microbiol. 13 2702–2716. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02538.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Crawford I. P. (1971). New regulatory mutation affecting some of the tryptophan genes in Pseudomonas putida. J. Bacteriol. 106 331–338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina-Henares M. A., Garcia-Salamanca A., Molina-Henares A. J., De La Torre J., Herrera M. C., Ramos J. L., et al. (2009). Functional analysis of aromatic biosynthetic pathways in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Microb. Biotechnol. 2 91–100. 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00062.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp K., Van Luijk N., De Bont J. A., Wery J. (2005). The solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 as host for the production of cinnamic acid from glucose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69 170–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp K., Westerhof R. G., Ballerstedt H., De Bont J. A., Wery J. (2007). Optimization of the solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 as host for the production of p-coumarate from glucose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74 617–624. 10.1007/s00253-006-0703-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard J., Yang J. (2008). Biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids. EcoSal Plus 1 1–39. 10.1128/ecosalplus.3.6.1.8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poblete-Castro I., Becker J., Dohnt K., Dos Santos V. M., Wittmann C. (2012). Industrial biotechnology of Pseudomonas putida and related species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 93 2279–2290. 10.1007/s00253-012-3928-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffensperger S. P., Vogt R. D. (1961). Stabilization of Grape Flavored Soft Drink Mixes Containing Methyl Anthranilate. US 3005715 A. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez A., Martinez J. A., Flores N., Escalante A., Gosset G., Bolivar F. (2014). Engineering Escherichia coli to overproduce aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Microb. Cell. Fact. 13:126 10.1186/s12934-014-0126-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq M., Zia-Ur-Rehman M., Khan I. U., Arshad M. N., Khan S. A. (2011). Synthesis of novel anti-bacterial 2,1-benzothiazine 2,2-dioxides derived from methyl anthranilate. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 56 527–531. 10.4067/S0717-97072011000100001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Rocha R., Martinez-Garcia E., Calles B., Chavarria M., Arce-Rodriguez A., De Las Heras A., et al. (2013). The standard european vector architecture (SEVA): a coherent platform for the analysis and deployment of complex prokaryotic phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41 D666–D675. 10.1093/nar/gks1119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Lin Y., Huang Q., Yuan Q., Yan Y. (2013). A novel muconic acid biosynthesis approach by shunting tryptophan biosynthesis via anthranilate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79 4024–4030. 10.1128/AEM.00859-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiso T., Wierckx N., Blank L. M. (2014). Non-pathogenic Pseudomonas as Platform for Industrial Biocatalysis Singapore: Pan Stanford Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef S., Ballerstedt H., Volkers R. J. M., De Winde J. H., Ruijssenaars H. J. (2010). Comparative transcriptomics and proteomics of p-hydroxybenzoate producing Pseudomonas putida S12: novel responses and implications for strain improvement. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 87 679–690. 10.1007/s00253-010-2626-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef S., Ruijssenaars H. J., De Bont J. A., Wery J. (2007). Bioproduction of p-hydroxybenzoate from renewable feedstock by solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12. J. Biotechnol. 132 49–56. 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.08.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef S., Wierckx N., Westerhof R. G., De Winde J. H., Ruijssenaars H. J. (2009). Bioproduction of p-hydroxystyrene from glucose by the solvent-tolerant bacterium Pseudomonas putida S12 in a two-phase water-decanol fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75 931–936. 10.1128/AEM.02186-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Haynes S. W., Ames B. D., Gao X., Tang Y. (2013). Short pathways to complexity generation: fungal peptidyl alkaloid multicyclic scaffolds from anthranilate building blocks. ACS Chem. Biol. 8 1366–1382. 10.1021/cb4001684 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. H., Zhou X. R., Liu Q., Chen G. Q. (2011). Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate homopolymers by Pseudomonas putida. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 89 1497–1507. 10.1007/s00253-010-2964-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierckx N. J., Ballerstedt H., De Bont J. A., Wery J. (2005). Engineering of solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12 for bioproduction of phenol from glucose. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 8221–8227. 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8221-8227.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierckx N. J. P., Ballerstedt H., De Bont J. A. M., De Winde J. H., Ruijssenaars H. J., Wery J. (2008). Transcriptome analysis of a phenol-producing Pseudomonas putida S12 construct: genetic and physiological basis for improved production. J. Bacteriol. 190 2822–2830. 10.1128/JB.01379-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierckx N., Ruijssenaars H. J., De Winde J. H., Schmid A., Blank L. M. (2009). Metabolic flux analysis of a phenol producing mutant of Pseudomonas putida S12: verification and complementation of hypotheses derived from transcriptomics. J. Biotechnol. 143 124–129. 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.06.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund P., Bergman J. (2006). The chemistry of anthranilic acid. Curr. Organ. Synth. 3 379–402. 10.2174/157017906777934926 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wittgens A., Tiso T., Arndt T. T., Wenk P., Hemmerich J., Muller C., et al. (2011). Growth independent rhamnolipid production from glucose using the non-pathogenic Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Microb. Cell Fact. 10:80 10.1186/1475-2859-10-80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav G. D., Krishnan M. S. (1998). An ecofriendly catalytic route for the preparation of perfumery grade methyl anthranilate from anthranilic acid and methanol. Organ. Process. Res. Dev. 2 86–95. 10.1021/op980074j [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z. J., Zou C., Zhu Y. X., Dai J., Chen S., Wu D., et al. (2011). Development of L-tryptophan production strains by defined genetic modification in Escherichia coli. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38 1921–1929. 10.1007/s10295-011-0978-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobel S., Benedetti I., Eisenbach L., De Lorenzo V., Wierckx N., Blank L. M. (2015). A Tn7-based device for calibrated heterologous gene expression in Pseudomonas putida. ACS Synth. Biol. 10.1021/acssynbio.5b00058 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]