Abstract
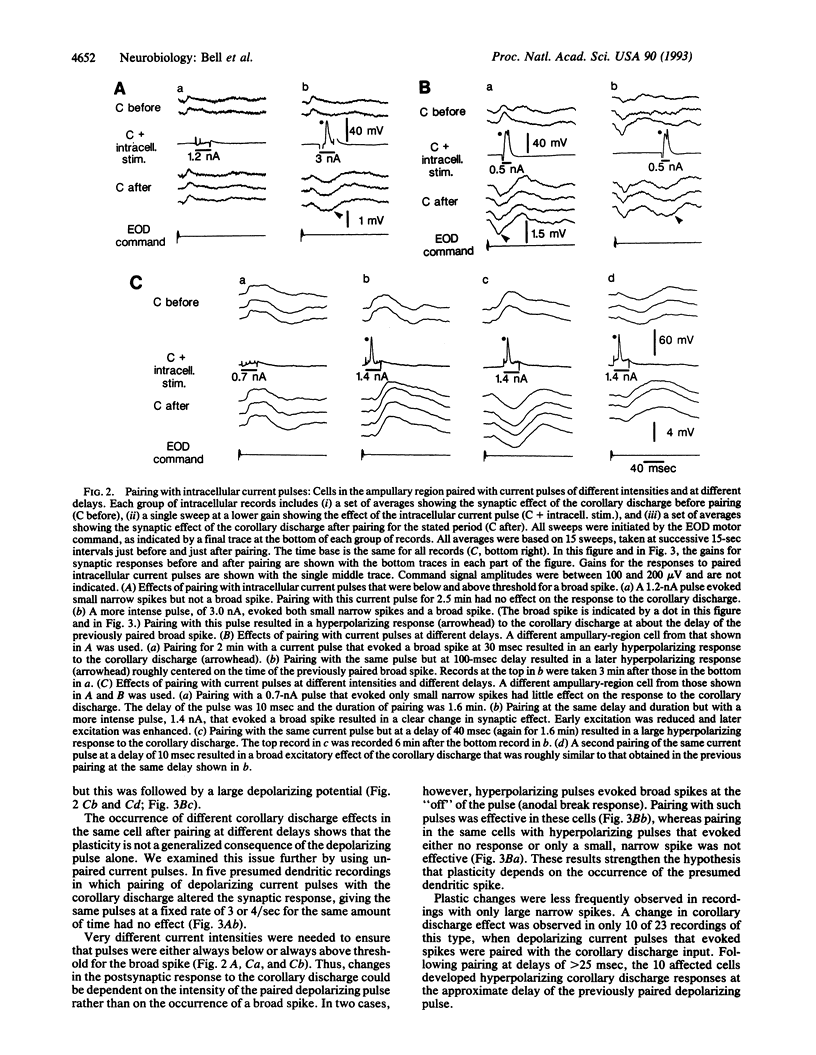
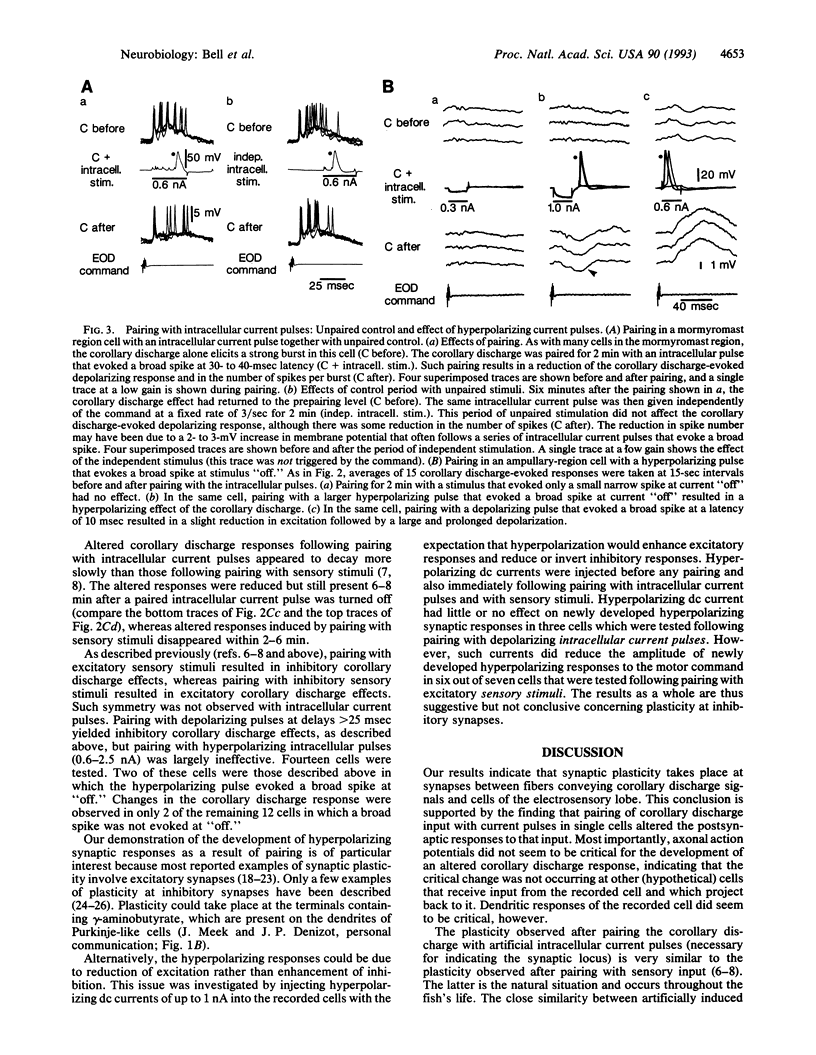
Synaptic plasticity occurs in several regions of the vertebrate brain and is believed to mediate the storage of behaviorally significant information during learning. Synaptic plasticity is well demonstrated in most cases, but the behavioral meaning of the relevant neural signals and the behavioral role of the plasticity are uncertain. In this paper we describe a case of synaptic plasticity which involves identifiable sensory and motor signals and which appears to mediate the storage of an image of past sensory input. Corollary discharge signals associated with the motor command that drives the electric organ are prominent in the electrosensory lobe of mormyrid electric fish. Some of these corollary discharge signals elicit a negative image or representation of the electrosensory input pattern that has followed recent motor commands. When the temporal and spatial pattern of sensory input changes, the corollary discharge effect also changes in a corresponding manner. The cellular mechanisms by which the corollary discharge-evoked representation is stored were investigated by intracellular recording from cells of the electrosensory lobe and pairing intracellular current pulses with the corollary discharge signal. The results indicate that the representation of recent sensory input is stored by means of anti-Hebbian plasticity at the synapses between corollary discharge-conveying fibers and cells of the electrosensory lobe. The results also suggest that dendritic spikes and plasticity at inhibitory synapses are involved in the phenomenon.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell C. C. An efference copy which is modified by reafferent input. Science. 1981 Oct 23;214(4519):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.7291985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C. Duration of plastic change in a modifiable efference copy. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C., Grant K. Sensory processing and corollary discharge effects in mormyromast regions of mormyrid electrosensory lobe. II. Cell types and corollary discharge plasticity. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Sep;68(3):859–875. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C., Grant K., Serrier J. Sensory processing and corollary discharge effects in the mormyromast regions of the mormyrid electrosensory lobe. I. Field potentials, cellular activity in associated structures. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Sep;68(3):843–858. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. C. Properties of a modifiable efference copy in an electric fish. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Jun;47(6):1043–1056. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.6.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Lomo T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):331–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepel F., Jaillard D. Pairing of pre- and postsynaptic activities in cerebellar Purkinje cells induces long-term changes in synaptic efficacy in vitro. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:123–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frégnac Y., Shulz D., Thorpe S., Bienenstock E. A cellular analogue of visual cortical plasticity. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):367–370. doi: 10.1038/333367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie B. L., Porter J. D., Sparks D. L. Corollary discharge provides accurate eye position information to the oculomotor system. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.6612334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Sakurai M., Tongroach P. Climbing fibre induced depression of both mossy fibre responsiveness and glutamate sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:113–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano M., Rexhausen U., Dreessen J., Konnerth A. Synaptic excitation produces a long-lasting rebound potentiation of inhibitory synaptic signals in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):601–604. doi: 10.1038/356601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Oda Y., Faber D. S. Long-term potentiation of inhibitory circuits and synapses in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):440–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden D. J., Dickinson M. H., Smeyne M., Connor J. A. A long-term depression of AMPA currents in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90076-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Leresche N., Marty A. Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maler L. The posterior lateral line lobe of a mormyrid fish--a Golgi study. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Dec 1;152(3):281–298. doi: 10.1002/cne.901520305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY R. W. Neural basis of the spontaneous optokinetic response produced by visual inversion. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1950 Dec;43(6):482–489. doi: 10.1037/h0055479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai M. Synaptic modification of parallel fibre-Purkinje cell transmission in in vitro guinea-pig cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:463–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton P. K., Sejnowski T. J. Associative long-term depression in the hippocampus induced by hebbian covariance. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):215–218. doi: 10.1038/339215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga N., Shimozawa T. Site of neural attenuation of responses to self-vocalized sounds in echolocating bats. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1211–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser B., Bennett M. V. Interaction of electrosensory and electromotor signals in lateral line lobe of a mormyrid fish. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jul;39(4):713–721. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



