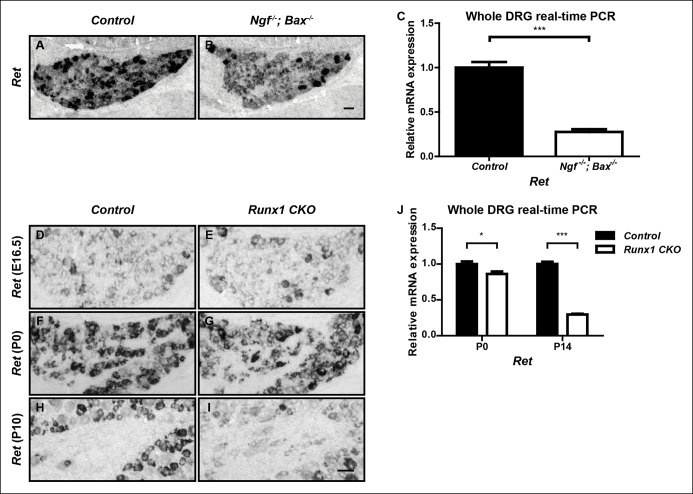
Figure 2. Ret is an unusual nonpeptidergic nociceptor-specific gene whose expression is differentially dependent on NGF and Runx1.
(A and B) Greatly diminished Ret expression in Ngf-/-Bax-/- DRGs compared to controls at P0, assessed by in situ hybridization. The NGF-independent Ret+ neurons are mechanoreceptors (Aβ RA-LTMRs). (C) Real-time PCR analysis of Ret expression in control and Ngf-/-Bax-/- DRGs at P0 confirms its strong NGF dependence in small diameter neurons. Statistical analysis was done using an unpaired t test, N = 4, ***p ≤ 0.001. (D–I) Ret expression in control and Runx1 CKO DRGs at E16.5 (D and E), P0 (F and G) and P10 (H and I), assessed by in situ hybridization. Note that while Ret expression is almost completely eliminated in Ngf-/-Bax-/- DRGs at P0, its expression at this same time point in Runx1 CKO DRGs is only modestly affected, indicating different temporal requirements of NGF and Runx1 for Ret expression. Shown are representative results of at least two independent animals per genotype at each time point. (J) Real-time PCR analysis of Ret expression in control and Runx1 CKO DRGs at P0 and P14 confirms the progressive nature of the Ret expression deficit in Runx1 CKO DRGs. Statistical analyses were done using unpaired t tests, N = 3 for each time point, *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001. Ngf +/-; Bax-/- or Ngf +/+; Bax-/- and Runx1f/f mice were used as control animals for analysis of Ngf-/-; Bax-/- and Runx1 CKO mutants, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm.