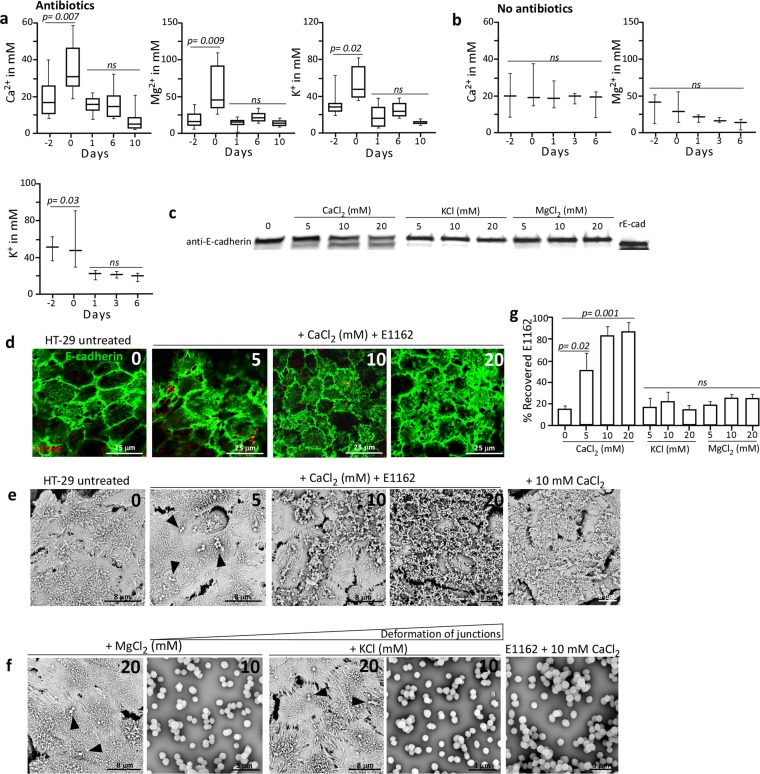
FIG 6 .
Cation levels, E-cadherin cleavage, and adherence of enterococci to deformed junctions. (a, b) Calcium, magnesium, and potassium concentrations determined in antibiotic-treated animals (n = 8) (a) and in untreated control animals (n = 3) (b). (c) Western blotting of HT-29 cell extracts demonstrating E-cadherin cleavage in the presence of elevated Ca2+ concentrations. (d) IF assays with specific anti-E-cadherin antibodies of HT-29 monolayers incubated with E1162 and increasing Ca2+ concentrations. (e) SEM analysis of HT-29 monolayers incubated in increasing Ca2+ concentrations with and without E1162 (arrowheads). (f) No extracellular matrix/deformed junctions are detected in the presence of increasing concentrations of Mg2+ and K+ and the presence of E1162 (arrowheads) on HT-29 cells or by E1162 alone in the presence of 10 mM Ca2+, Mg2+, or K+. Images representative of two independent experiments are shown. (g) Increased percent recovery of E. faecium E1162 added to HT-29 monolayers versus the inoculum in the presence of different concentrations of Ca2+, K+, and Mg2+. Values are averages of three independent experiments. ns, not significant.