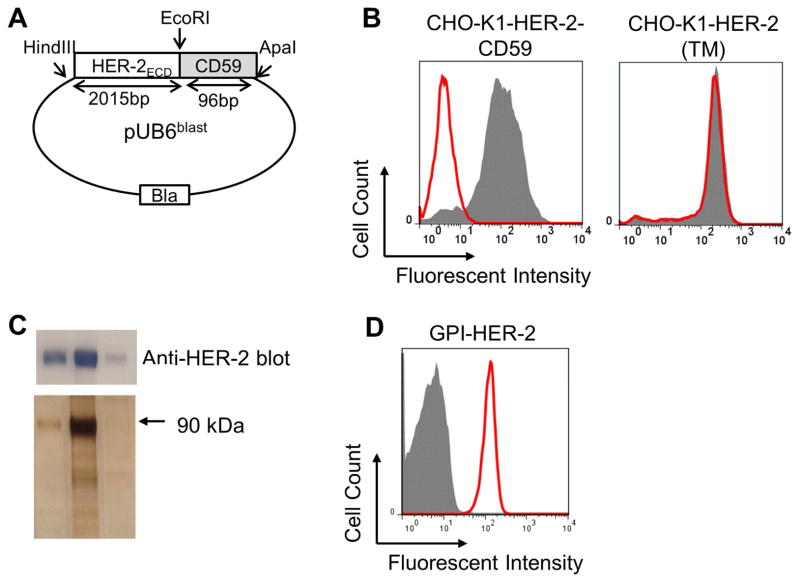
Figure 2. Construction, expression and purification of GPI-HER-2.
(A) Construction of GPI-HER-2. The extracellular domain (ECD) of HER-2 is attached to the GPI-anchor signal sequence from CD59 and cloned into a pUB6 vector (B) PI-PLC treatment of CHO-K1 cells transfected with HER-2. PI-PLC treatment was performed on CHO-K1 cells transfected with HER-2-CD59 (left panel) or on CHO-K1 cells transfected with full-length transmembrane (TM) HER-2 (right panel) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Grey – not treated with PI-PLC. Red – after PI-PLC treatment. (C) Purification of GPI-HER-2. GPI-HER-2 was purified from transfected CHO-K1 cells by mAb affinity chromatography. SDS PAGE and western blot (top panel) or silver staining (bottom panel) was performed on the purified fractions. (D) Protein transfer of purified GPI-HER-2 onto sheep red blood cells (RBCs). Sheep RBCs were incubated with purified GPI-HER-2 or buffer control for 4 h at 37°C. Flow cytometry analysis was performed to determine incorporation levels. Grey – buffer control. Red – GPI-HER-2 added during protein transfer.