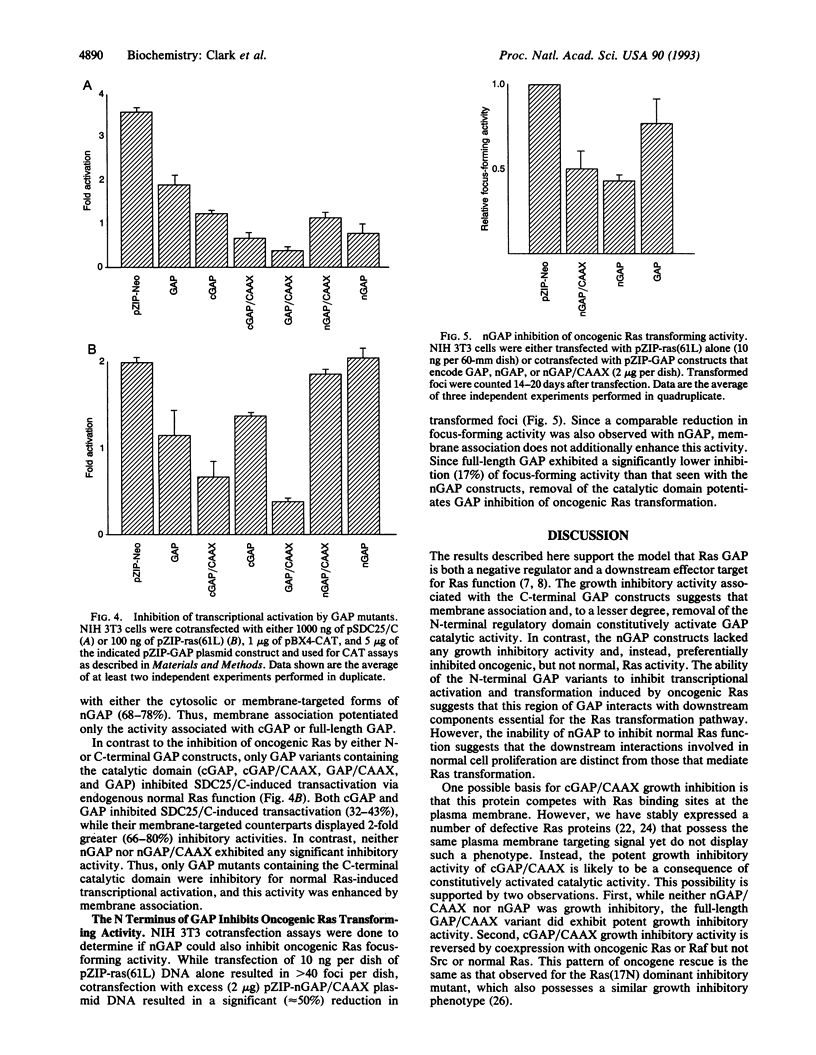
Abstract
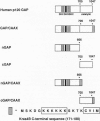
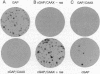
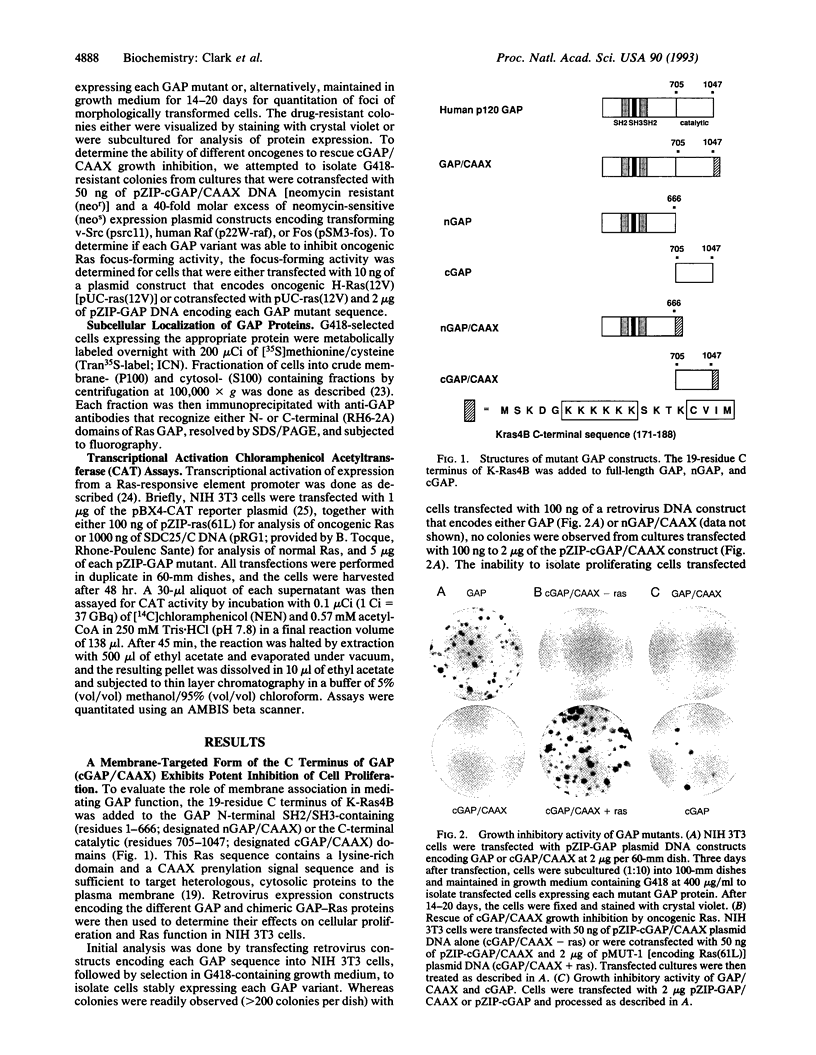
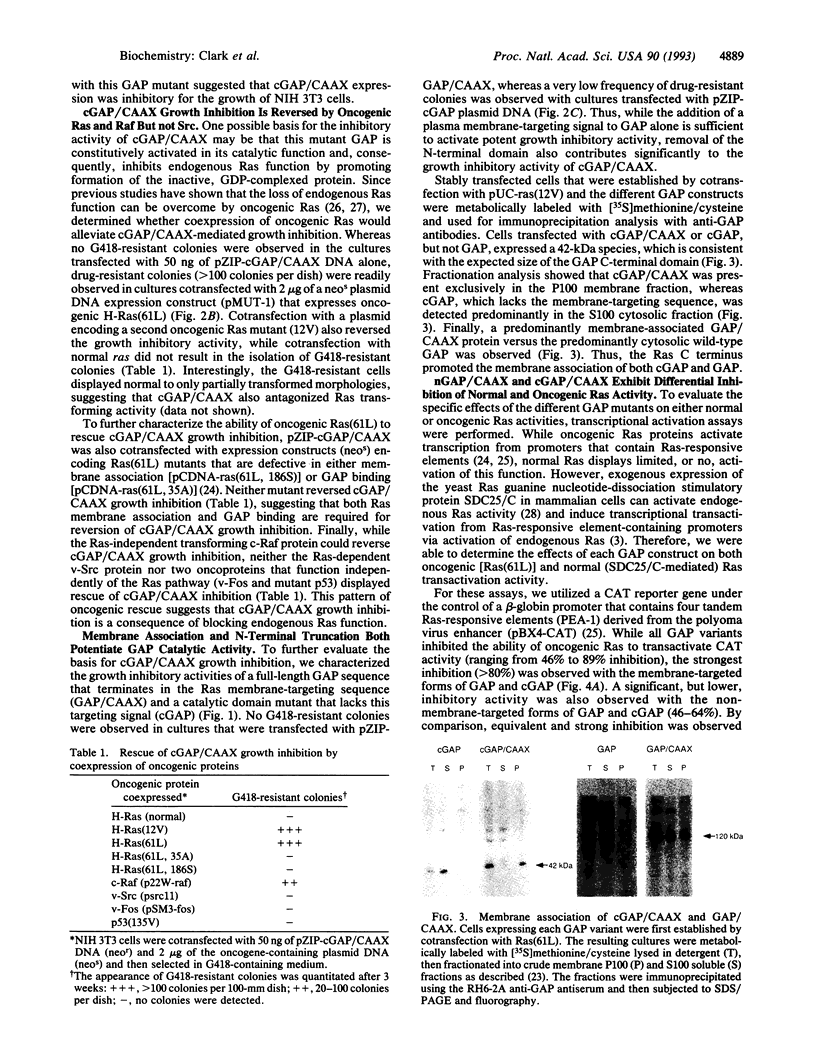
Ras p120 GTPase activation protein (GAP), a cytosolic protein, is a negative mediator and potential downstream effector of Ras function. Since membrane association is critical for Ras function, we introduced the Ras membrane-targeting signal (a 19-residue peptide ending in CAAX, where C = cysteine, A = aliphatic amino acid, and X = any amino acid) onto the GAP N-terminal Src homology 2 and 3 and the C-terminal catalytic domains (designated nGAP/CAAX and cGAP/CAAX, respectively) to determine the role of membrane association in GAP function. cGAP/CAAX and full-length GAP/CAAX, but not GAP or nGAP/CAAX, exhibited potent growth inhibitory activity. Whereas both oncogenic and normal Ras activity were inhibited by cGAP/CAAX, nGAP/CAAX, despite lacking the Ras binding domain, inhibited the activity of oncogenic Ras without affecting the action of normal Ras. Altogether, these results demonstrate that membrane association potentiates GAP catalytic activity, support an effector function for GAP, and suggest that normal and oncogenic Ras possess different downstream interactions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortner D. M., Ulivi M., Roussel M. F., Ostrowski M. C. The carboxy-terminal catalytic domain of the GTPase-activating protein inhibits nuclear signal transduction and morphological transformation mediated by the CSF-1 receptor. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1777–1785. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruice T. C., Mei H. Y., He G. X., Lopez V. Rational design of substituted tripyrrole peptides that complex with DNA by both selective minor-groove binding and electrostatic interaction with the phosphate backbone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1700–1704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Solski P. A., Schaeffer J. P., MacDonald M. J., Der C. J. Activation of the cellular proto-oncogene product p21Ras by addition of a myristylation signal. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1600–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2648572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Der C. J. The ras/cholesterol connection: implications for ras oncogenicity. Crit Rev Oncog. 1992;3(4):365–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créchet J. B., Poullet P., Mistou M. Y., Parmeggiani A., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Damak F., Jacquet M. Enhancement of the GDP-GTP exchange of RAS proteins by the carboxyl-terminal domain of SCD25. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.2188363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Allard W. J., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Purification of ras GTPase activating protein from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5026–5030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Schofield T. L., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Xenopus oocyte germinal-vesicle breakdown induced by [Val12]Ras is inhibited by a cytosol-localized Ras mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6630–6634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. ras and GAP--who's controlling whom? Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90054-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Cadwallader K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4033–4039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90294-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Cox A. D., Kato K., Der C. J. Protein prenylation: key to ras function and cancer intervention? Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jul;3(7):461–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee T., Newman C. The role of lipid anchors for small G proteins in membrane trafficking. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90172-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martegani E., Vanoni M., Zippel R., Coccetti P., Brambilla R., Ferrari C., Sturani E., Alberghina L. Cloning by functional complementation of a mouse cDNA encoding a homologue of CDC25, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS activator. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Yatani A., Clark R., Conroy L., Polakis P., Brown A. M., McCormick F. GAP domains responsible for ras p21-dependent inhibition of muscarinic atrial K+ channel currents. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1553544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., de Laat W. L., Martin G. A., McCormick F., Bos J. L. GTPase-activating protein SH2-SH3 domains induce gene expression in a Ras-dependent fashion. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3425–3430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Field J., Ballester R., O'Neill K., Wigler M. Mutants of H-ras that interfere with RAS effector function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey I., Schweighoffer F., Barlat I., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Guilbaud R., Jacquet M., Tocque B. The COOH-domain of the product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SCD25 gene elicits activation of p21-ras proteins in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):347–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Der C. J., Verma I. M. ras-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells: possible involvement of fos and jun. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3174–3183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer F., Barlat I., Chevallier-Multon M. C., Tocque B. Implication of GAP in Ras-dependent transactivation of a polyoma enhancer sequence. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):825–827. doi: 10.1126/science.1317056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou C., Farnsworth C. L., Neel B. G., Feig L. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor for Ras p21. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):351–354. doi: 10.1038/358351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Feig L. A., Gibbs J. B. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants selectively inhibit the activity of either cellular or oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4053–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Heidecker G., Huleihel M., Rapp U. R. Expression of raf oncogenes activates the PEA1 transcription factor motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2247–2250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., McCormick F., Lowy D. R. Suppression of c-ras transformation by GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):754–756. doi: 10.1038/346754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]