Abstract
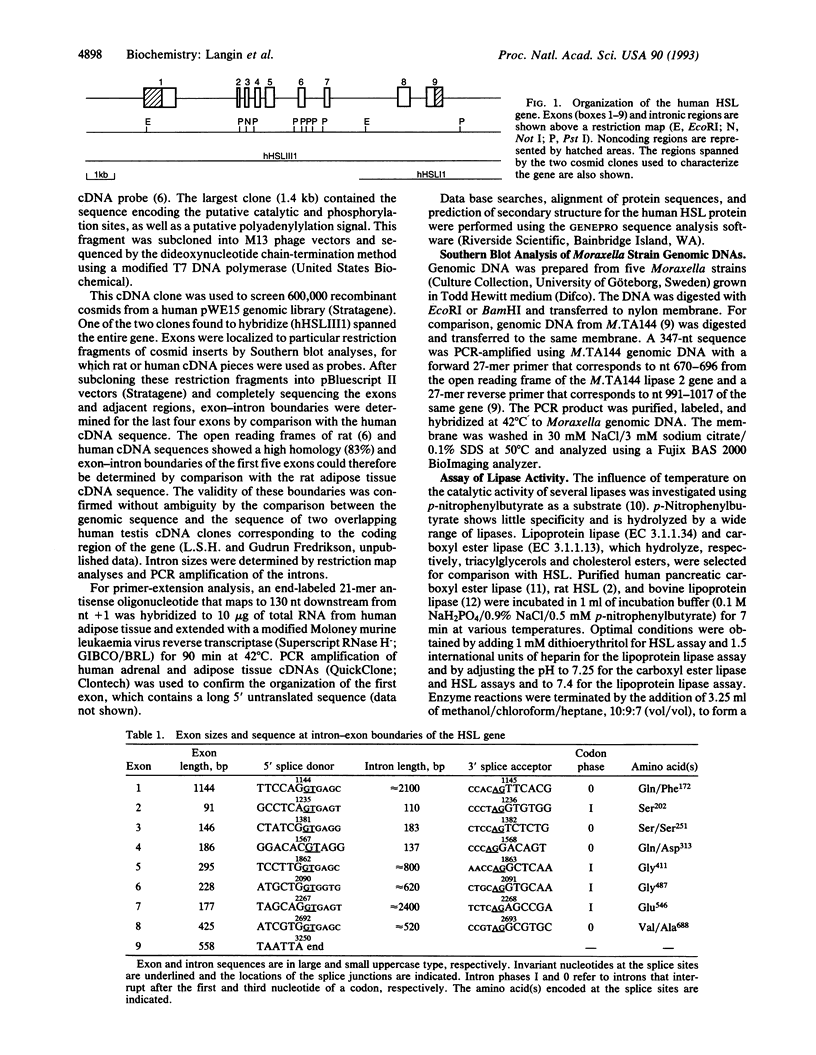
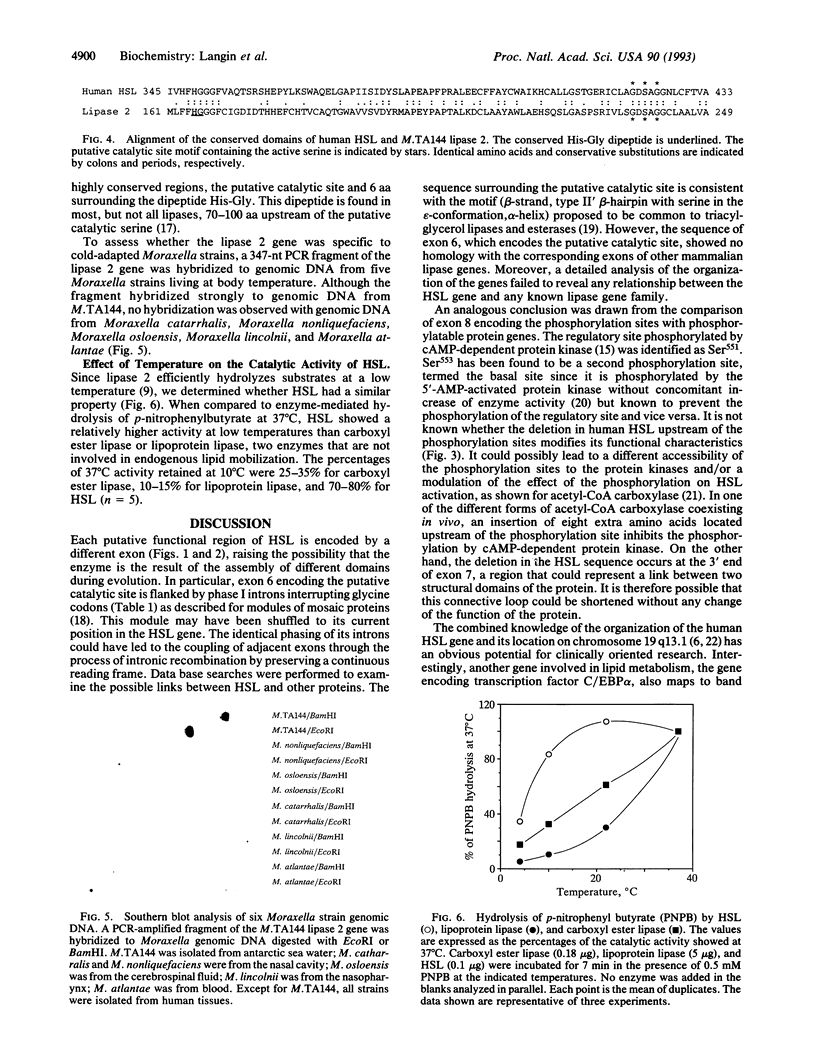
The human hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) gene encodes a 786-aa polypeptide (85.5 kDa). It is composed of nine exons spanning approximately 11 kb, with exons 2-5 clustered in a 1.1-kb region. The putative catalytic site (Ser423) and a possible lipid-binding region in the C-terminal part are encoded by exons 6 and 9, respectively. Exon 8 encodes the phosphorylation site (Ser551) that controls cAMP-mediated activity and a second site (Ser553) that is phosphorylated by 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase. Human HSL showed 83% identity with the rat enzyme and contained a 12-aa deletion immediately upstream of the phosphorylation sites with an unknown effect on the activity control. Besides the catalytic site motif (Gly-Xaa-Ser-Xaa-Gly) found in most lipases, HSL shows no homology with other known lipases or proteins, except for a recently reported unexpected homology between the region surrounding its catalytic site and that of the lipase 2 of Moraxella TA144, an antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium. The gene of lipase 2, which catalyses lipolysis below 4 degrees C, was absent in the genomic DNA of five other Moraxella strains living at 37 degrees C. The lipase 2-like sequence in HSL may reflect an evolutionarily conserved cold adaptability that might be of critical survival value when low-temperature-mobilized endogenous lipids are the primary energy source (e.g., in poikilotherms or hibernators). The finding that HSL at 10 degrees C retained 3- to 5-fold more of its 37 degrees C catalytic activity than lipoprotein lipase or carboxyl ester lipase is consistent with this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambid L., Berlan M., Agid R. Contribution de la graisse brune à la mobilisation des lipides au cours des réveils périodiques chez un hibernant, le lérot (Eliomys quercinus L. J Physiol (Paris) 1971 Jun-Jul;63(4):505–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au-Young J., Fielding C. J. Synthesis and secretion of wild-type and mutant human plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein in baculovirus-transfected insect cells: the carboxyl-terminal region is required for both lipoprotein binding and catalysis of transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with heparin-Sepharose. Evaluation of conditions for affinity binding. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):109–119. doi: 10.1042/bj1670109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. G., Yeaman S. J., Strålfors P., Fredrikson G., Belfrage P. Direct evidence that cholesterol ester hydrolase from adrenal cortex is the same enzyme as hormone-sensitive lipase from adipose tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampes F., Beauville M., Riviere D., Garrigues M. Effect of physical training in humans on the response of isolated fat cells to epinephrine. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Jul;61(1):25–29. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda Z. S., Derewenda U. Relationships among serine hydrolases: evidence for a common structural motif in triacylglyceride lipases and esterases. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;69(12):842–851. doi: 10.1139/o91-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller G., Thiry M., Gerday C. Nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene lip2 from the antarctic psychrotroph Moraxella TA144 and site-specific mutagenesis of the conserved serine and histidine residues. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):381–388. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrikson G., Strålfors P., Nilsson N. O., Belfrage P. Hormone-sensitive lipase of rat adipose tissue. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6311–6320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii J., Otsu K., Zorzato F., de Leon S., Khanna V. K., Weiler J. E., O'Brien P. J., MacLennan D. H. Identification of a mutation in porcine ryanodine receptor associated with malignant hyperthermia. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):448–451. doi: 10.1126/science.1862346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garton A. J., Campbell D. G., Carling D., Hardie D. G., Colbran R. J., Yeaman S. J. Phosphorylation of bovine hormone-sensitive lipase by the AMP-activated protein kinase. A possible antilipolytic mechanism. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garton A. J., Campbell D. G., Cohen P., Yeaman S. J. Primary structure of the site on bovine hormone-sensitive lipase phosphorylated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks-Taylor L. R., Bachinski L. L., Siciliano M. J., Fertitta A., Trask B., de Jong P. J., Ledbetter D. H., Darlington G. J. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP alpha) gene (CEBPA) maps to human chromosome 19q13.1 and the related nuclear factor NF-IL6 (C/EBP beta) gene (CEBPB) maps to human chromosome 20q13.1. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Belfrage P., Fredrikson G. Human adipose tissue hormone-sensitive lipase: identification and comparison with other species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Fredrikson G., Nilsson S., Miller C. G., Shively J. E., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T. Hormone-sensitive lipase: sequence, expression, and chromosomal localization to 19 cent-q13.3. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1503–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.3420405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., Chuat J. C., Heinzmann C., Etienne J., Guilhot S., Svenson K., Ameis D., Pilon C., d'Auriol L., Andalibi A. Organization of the human lipoprotein lipase gene and evolution of the lipase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9647–9651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong I. S., López-Casillas F., Kim K. H. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase mRNA species with or without inhibitory coding sequence for Ser-1200 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13695–13701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt R. C., McKusick V. A., Fletcher J. E., Rosenberg H. Gene candidate. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):297–298. doi: 10.1038/345297b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnqvist F., Nyberg B., Wahrenberg H., Arner P. Catecholamine-induced lipolysis in adipose tissue of the elderly. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1614–1621. doi: 10.1172/JCI114612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliorini R. H., Lima-Verde J. S., Machado C. R., Cardona G. M., Garofalo M. A., Kettelhut I. C. Control of adipose tissue lipolysis in ectotherm vertebrates. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):R857–R862. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.4.R857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard J., Cannon B. Preferential utilization of brown adipose tissue lipids during arousal from hibernation in hamsters. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):R506–R512. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.3.R506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonk D., van Dijk P., Riegmann P., Trapman J., Holm C., Willcocks T. C., Sillekens P., van Venrooij W., Wimmer E., Geurts van Kessel A. Assignment of seven genes to distinct intervals on the midportion of human chromosome 19q surrounding the myotonic dystrophy gene region. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;54(1-2):15–19. doi: 10.1159/000132946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai K., Jackson R. L. Lipoprotein lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl butyrate. Interfacial activation by phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1253–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Belfrage P. Phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15146–15152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Björgell P., Belfrage P. Hormonal regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase in intact adipocytes: identification of phosphorylated sites and effects on the phosphorylation by lipolytic hormones and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S. Purification of human milk bile salt-activated lipase by cholic acid-coupled Sepharose 4B affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. E., Deeb S., Florant G. L. Seasonal changes in hormone-sensitive and lipoprotein lipase mRNA concentrations in marmot white adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):R177–R181. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.262.2.R177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., D'Arcy A., Hunziker W. Structure of human pancreatic lipase. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):771–774. doi: 10.1038/343771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oort M. G., Deveer A. M., Dijkman R., Tjeenk M. L., Verheij H. M., de Haas G. H., Wenzig E., Götz F. Purification and substrate specificity of Staphylococcus hyicus lipase. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9278–9285. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




