Abstract
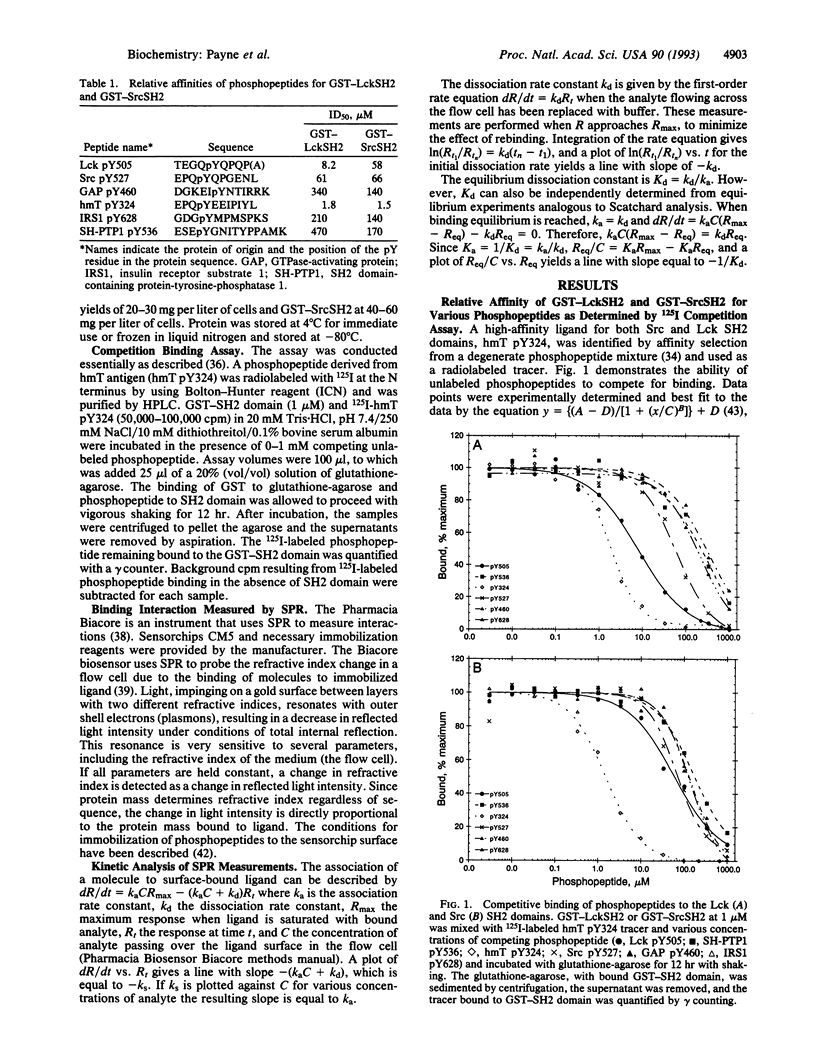
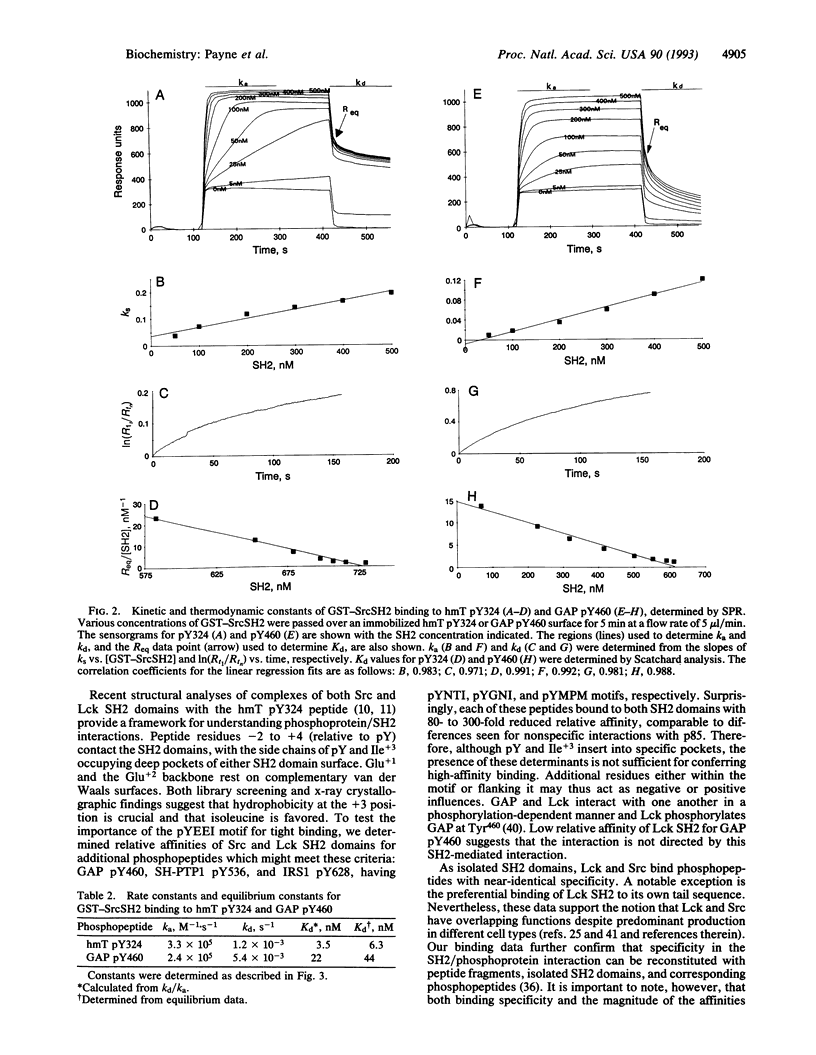
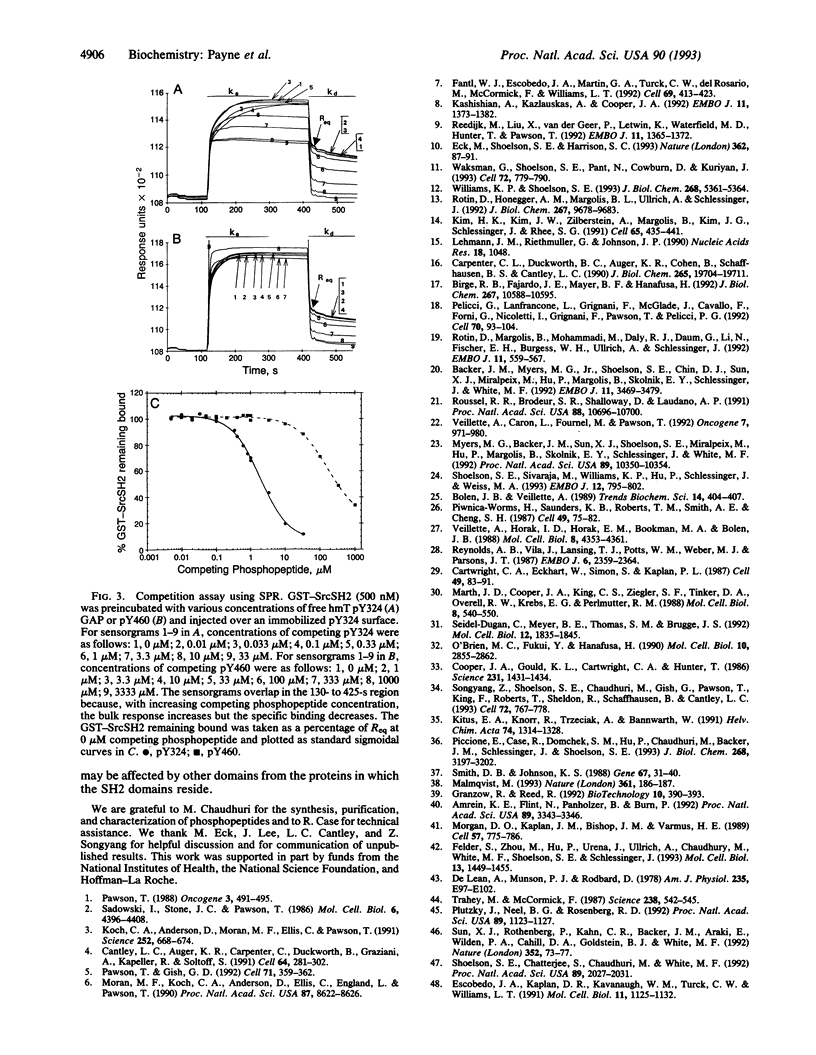
Src homology 2 (SH2) domains are phosphotyrosine-binding modules found within various signal-transducing proteins. We have determined by 125I competition assay and surface plasmon resonance that the SH2 domains of Src and Lck bind to a variety of phosphopeptides with similar affinity and specificity. Both bound with highest affinity [Kd(app) approximately 3.7 nM; ka = 2.4 x 10(5) M-1 x s-1; kd = 1.2 x 10(-3) s-1] a phosphopeptide having a Tyr(P)-Glu-Glu-Ile motif found in the hamster polyomavirus middle-sized tumor antigen. Intermediate affinity (5- to 40-fold lower) was observed with phosphopeptides corresponding to the regulatory domains of Src and Lck, containing Tyr527 and Tyr505, respectively. Lowest affinity (80- to 300-fold lower) was observed with phosphopeptides corresponding to phosphorylated tyrosines of GTPase-activating protein, insulin receptor substrate 1, and SH2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase 1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Flint N., Panholzer B., Burn P. Ras GTPase-activating protein: a substrate and a potential binding protein of the protein-tyrosine kinase p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3343–3346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cellular p130 provide high affinity binding substrates to analyze Crk-phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10588–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A. A function for the lck proto-oncogene. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Oct;14(10):404–407. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Shoelson S. E., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):87–91. doi: 10.1038/362087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder S., Zhou M., Hu P., Ureña J., Ullrich A., Chaudhuri M., White M., Shoelson S. E., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains exhibit high-affinity binding to tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides yet also exhibit rapid dissociation and exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granzow R., Reed R. Interactions in the fourth dimension. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Apr;10(4):390–393. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashishian A., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation sites in the PDGF receptor with different specificities for binding GAP and PI3 kinase in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1373–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Riethmüller G., Johnson J. P. Nck, a melanoma cDNA encoding a cytoplasmic protein consisting of the src homology units SH2 and SH3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1048–1048. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist M. Biospecific interaction analysis using biosensor technology. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):186–187. doi: 10.1038/361186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Kaplan J. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of p60c-src by p34cdc2-associated protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):775–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccione E., Case R. D., Domchek S. M., Hu P., Chaudhuri M., Backer J. M., Schlessinger J., Shoelson S. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85 SH2 domain specificity defined by direct phosphopeptide/SH2 domain binding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3197–3202. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutzky J., Neel B. G., Rosenberg R. D. Isolation of a src homology 2-containing tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X., van der Geer P., Letwin K., Waterfield M. D., Hunter T., Pawson T. Tyr721 regulates specific binding of the CSF-1 receptor kinase insert to PI 3'-kinase SH2 domains: a model for SH2-mediated receptor-target interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Honegger A. M., Margolis B. L., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Presence of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1 enhances substrate phosphorylation by increasing the affinity toward the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9678–9683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel R. R., Brodeur S. R., Shalloway D., Laudano A. P. Selective binding of activated pp60c-src by an immobilized synthetic phosphopeptide modeled on the carboxyl terminus of pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10696–10700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel-Dugan C., Meyer B. E., Thomas S. M., Brugge J. S. Effects of SH2 and SH3 deletions on the functional activities of wild-type and transforming variants of c-Src. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1835–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Chatterjee S., Chaudhuri M., White M. F. YMXM motifs of IRS-1 define substrate specificity of the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Sivaraja M., Williams K. P., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Weiss M. A. Specific phosphopeptide binding regulates a conformational change in the PI 3-kinase SH2 domain associated with enzyme activation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):795–802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Caron L., Fournel M., Pawson T. Regulation of the enzymatic function of the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck by the non-catalytic SH2 and SH3 domains. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):971–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Shoelson S. E., Pant N., Cowburn D., Kuriyan J. Binding of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide to the Src SH2 domain: crystal structures of the complexed and peptide-free forms. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90405-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Shoelson S. E. A photoaffinity scan maps regions of the p85 SH2 domain involved in phosphoprotein binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5361–5364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



