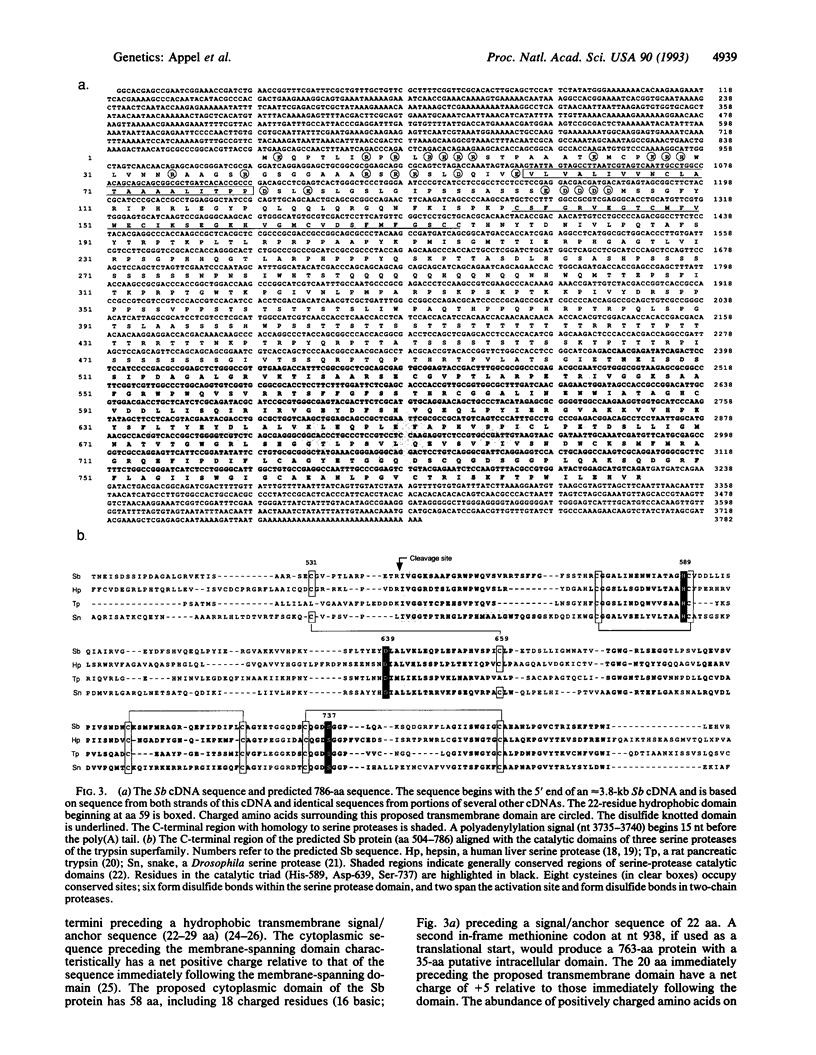
Abstract
The Stubble-stubbloid (Sb-sbd) gene is required for hormone-dependent epithelial morphogenesis of imaginal discs of Drosophila, including the formation of bristles, legs, and wings. The gene has been cloned by using Sb-sbd-associated DNA lesions in a 20-kilobase (kb) region of a 263-kb genomic walk. The region specifies an approximately 3.8-kb transcript that is induced by the steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone in imaginal discs cultured in vitro. The conceptually translated protein is an apparent 786-residue type II transmembrane protein (N terminus in, C terminus out), including an intracellular N-terminal domain of at least 35 residues and an extracellular C-terminal trypsin-like serine protease domain of 244 residues. Sequence analyses indicate that the Sb-sbd-encoded protease could activate itself by proteolytic cleavage. Consistent with the cell-autonomous nature of the Sb-sbd bristle phenotype, a disulfide bond between cysteine residues in the noncatalytic N-terminal fragment and the C-terminal catalytic fragment could tether the protease to the membrane after activation. Both dominant Sb and recessive sbd mutations affect the organization of microfilament bundles during bristle morphogenesis. We propose that the Sb-sbd product has a dual function. (i) It acts through its proteolytic extracellular domain to detach imaginal disc cells from extracellular matrices, and (ii) it transmits an outside-to-inside signal to its intracellular domain to modify the cytoskeleton and facilitate cell shape changes underlying morphogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S., Zett B., Anderson B., Fraley D. S. Effect of volume expansion on renal citrate and ammonia metabolism in KCl-deficient rats. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):391–400. doi: 10.1172/JCI108104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews D. W., Young J. C., Mirels L. F., Czarnota G. J. The role of the N region in signal sequence and signal-anchor function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7761–7769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaton A. H., Kiss I., Fristrom D., Fristrom J. W. Interaction of the Stubble-stubbloid locus and the Broad-complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):453–464. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Chen Z., Bartels K., Kutzbach C., Schmidt-Kastner G., Bartunik H. Refined 2 A X-ray crystal structure of porcine pancreatic kallikrein A, a specific trypsin-like serine proteinase. Crystallization, structure determination, crystallographic refinement, structure and its comparison with bovine trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):237–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Dautricourt J. P., Maulik S., Relph J. Improved sensitivity of biological sequence database searches. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jul;6(3):237–245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condic M. L., Fristrom D., Fristrom J. W. Apical cell shape changes during Drosophila imaginal leg disc elongation: a novel morphogenetic mechanism. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):23–33. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLotto R., Spierer P. A gene required for the specification of dorsal-ventral pattern in Drosophila appears to encode a serine protease. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):688–692. doi: 10.1038/323688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Bing D. H., Feldmann R. J., Robison D. J., Burnier J. P., Furie B. C. Computer-generated models of blood coagulation factor Xa, factor IXa, and thrombin based upon structural homology with other serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3875–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golic K. G. Site-specific recombination between homologous chromosomes in Drosophila. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):958–961. doi: 10.1126/science.2035025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S., Brown J. R., Kauffman D. L., Smillie L. B. Evolutionary similarities between pancreatic proteolytic enzymes. Nature. 1965 Sep 11;207(5002):1157–1159. doi: 10.1038/2071157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A., Lodish H. F. Predicting the orientation of eukaryotic membrane-spanning proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Moolenaar W. H. Thrombin receptor activation causes rapid neural cell rounding and neurite retraction independent of classic second messengers. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):411–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS E. B. Pseudoallelism and gene evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:159–174. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Loeb K. R., Hagen F. S., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. A novel trypsin-like serine protease (hepsin) with a putative transmembrane domain expressed by human liver and hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Stary S. J., Swift G. H. Two similar but nonallelic rat pancreatic trypsinogens. Nucleotide sequences of the cloned cDNAs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9724–9732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muta T., Hashimoto R., Miyata T., Nishimura H., Toh Y., Iwanaga S. Proclotting enzyme from horseshoe crab hemocytes. cDNA cloning, disulfide locations, and subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22426–22433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Intracellular proclotting enzyme in limulus (Tachypleus tridentatus) hemocytes: its purification and properties. J Biochem. 1985 Jun;97(6):1561–1574. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton J. The fine structure of developing bristles in wild type and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Morphol. 1967 Aug;122(4):367–379. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051220406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Topology of eukaryotic type II membrane proteins: importance of N-terminal positively charged residues flanking the hydrophobic domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90507-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pino-Heiss S., Schubiger G. Extracellular protease production by Drosophila imaginal discs. Dev Biol. 1989 Apr;132(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Hedman K., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Vaheri A. Ultrastructural localization of plasma membrane-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator at focal contacts. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):87–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The structure and insertion of integral proteins in membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:247–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., DeLotto R. A common domain within the proenzyme regions of the Drosophila snake and easter proteins and Tachypleus proclotting enzyme defines a new subfamily of serine proteases. Protein Sci. 1992 Sep;1(9):1225–1226. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Torres-Rosado A., Arai T., Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Chou S. H., Kurachi K. Hepsin, a cell membrane-associated protease. Characterization, tissue distribution, and gene localization. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16948–16953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]