Abstract
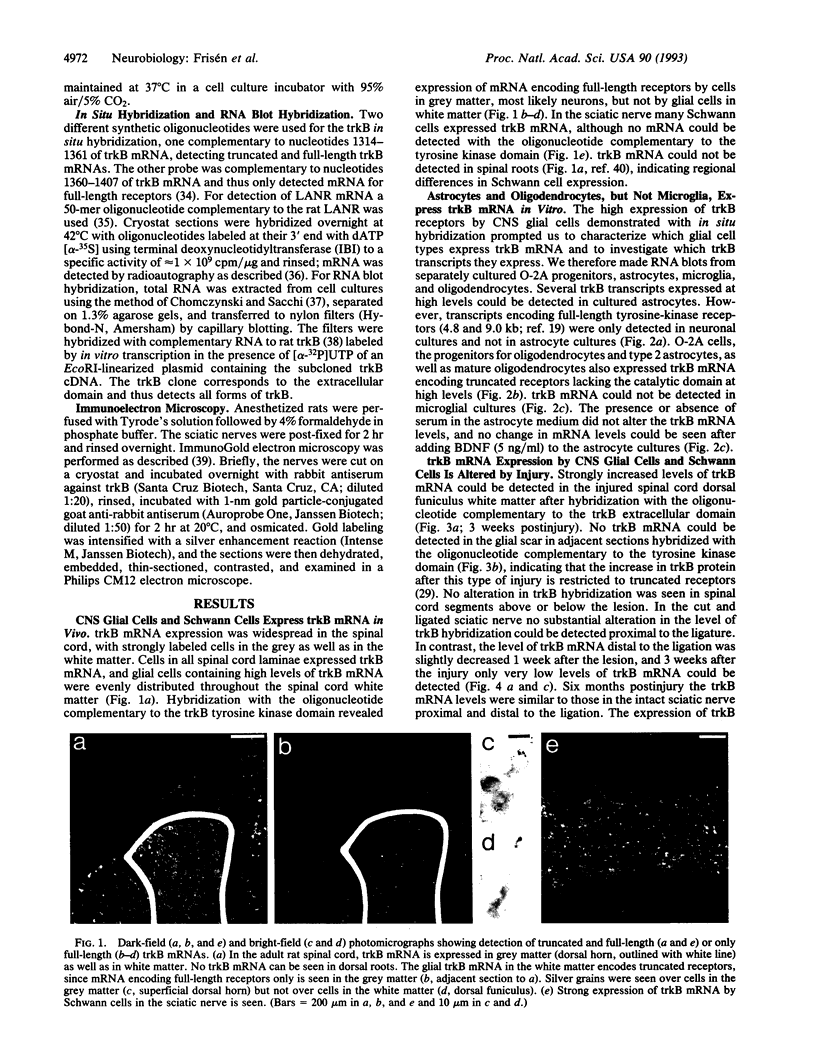
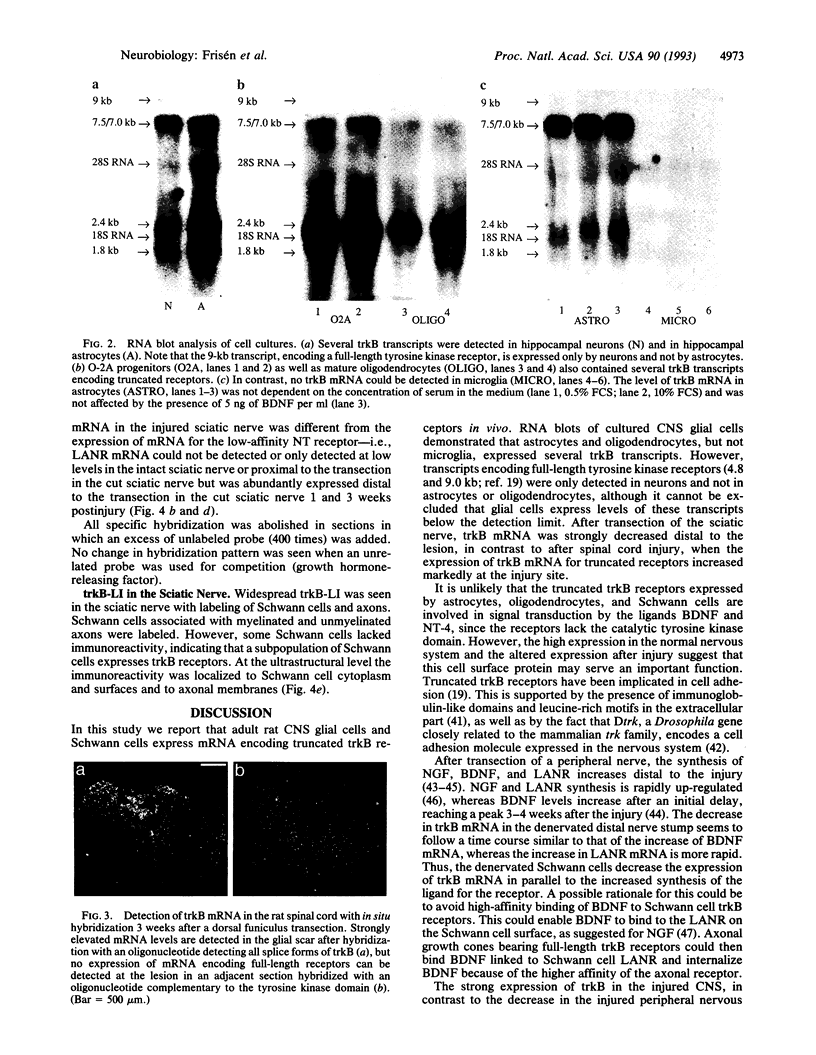
In situ hybridization on sections from the adult rat peripheral and central nervous systems demonstrated that trkB mRNA was expressed not only by neurons but also by cells in central nervous system white matter as well as by Schwann cells in the sciatic nerve. In situ hybridization with an oligonucleotide complementary to the trkB tyrosine kinase domain could only demonstrate mRNA in neurons, indicating expression of truncated trkB receptors lacking the tyrosine kinase domain by glial cells. RNA blot analysis was performed on separately cultured central nervous system glial cells to study which cell types express trkB mRNA. Several transcripts encoding truncated trkB receptors were expressed at high levels in O-2A progenitors, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, but not trkB mRNA could be detected in microglia. The expression of trkB mRNA by glial cells in vivo was also investigated after injury; strongly elevated levels of mRNA encoding truncated receptors were detected in the glial scar formed after an incision in the spinal cord dorsal funiculus. In contrast, in the cut sciatic nerve, trkB mRNA decreased distal to the transection, and by 3 weeks only very low levels of mRNA could be detected. Immunoelectron microscopy located trkB-like immunoreactivity to axons and Schwann cells in the sciatic nerve. The expression of truncated trkB receptors by astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells and the altered levels in response to injury indicate that glial trkB receptors may serve an important function in the intact and injured nervous system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Thoenen H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):549–553. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. M., Sternberg D. W., Hempstead B. L., Chao M. V. The low-affinity p75 nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor mediates NGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7106–7110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier L. R., Winslow J. W., Kaplan D. R., Nikolics K., Goeddel D. V., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bögler O., Wren D., Barnett S. C., Land H., Noble M. Cooperation between two growth factors promotes extended self-renewal and inhibits differentiation of oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte (O-2A) progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6368–6372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrén E., Zafra F., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Light regulates expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in rat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9444–9448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Henschen A., Olson L., Persson H. Expression of nerve growth factor receptor mRNA is developmentally regulated and increased after axotomy in rat spinal cord motoneurons. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1605–1613. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Olson L., Persson H. Molecular cloning and neurotrophic activities of a protein with structural similarities to nerve growth factor: developmental and topographical expression in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisén J., Verge V. M., Cullheim S., Persson H., Fried K., Middlemas D. S., Hunter T., Hökfelt T., Risling M. Increased levels of trkB mRNA and trkB protein-like immunoreactivity in the injured rat and cat spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11282–11286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallbök F., Ibáez C. F., Persson H. Evolutionary studies of the nerve growth factor family reveal a novel member abundantly expressed in Xenopus ovary. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):845–858. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Patil N., Thiel B., Chao M. V. Deletion of cytoplasmic sequences of the nerve growth factor receptor leads to loss of high affinity ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9595–9598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann R., Korsching S., Bandtlow C., Thoenen H. Changes of nerve growth factor synthesis in nonneuronal cells in response to sciatic nerve transection. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1623–1631. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann R., Lindholm D., Bandtlow C., Meyer M., Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Shooter E., Thoenen H. Differential regulation of mRNA encoding nerve growth factor and its receptor in rat sciatic nerve during development, degeneration, and regeneration: role of macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8735–8739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn A., Leibrock J., Bailey K., Barde Y. A. Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):339–341. doi: 10.1038/344339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Ibáez C. F., Nye S. H., McClain J., Jones P. F., Gies D. R., Belluscio L., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Squinto S. P. Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, Taniuchi M., DiStefano P. S. Expression and possible function of nerve growth factor receptors on Schwann cells. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. Molecular cloning of a human gene that is a member of the nerve growth factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaisho Y., Yoshimura K., Nakahama K. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding a novel human neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81536-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Conway D., Parada L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase gene codes for a second neurogenic receptor that lacks the catalytic kinase domain. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):647–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90476-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Lamballe F., Bryant S., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for neurotrophin-4. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90209-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Li E., Huber L. J., Landis S. C., Sharpe A. H., Chao M. V., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the gene encoding the low affinity NGF receptor p75 leads to deficits in the peripheral sensory nervous system. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):737–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90286-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., Hofer M., Hengerer B., Masiakowski P., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):149–152. doi: 10.1038/341149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Castrén E., Kiefer R., Zafra F., Thoenen H. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 in the rat brain: increase after injury and inhibition of astrocyte proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(2):395–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindå H., Cullheim S., Risling M. A light and electron microscopic study of intracellularly HRP-labeled lumbar motoneurons after intramedullary axotomy in the adult cat. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Apr 8;318(2):188–208. doi: 10.1002/cne.903180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlio J. P., Ernfors P., Kokaia Z., Middlemas D. S., Bengzon J., Kokaia M., Smith M. L., Siesjö B. K., Hunter T., Lindvall O. Increased production of the TrkB protein tyrosine kinase receptor after brain insults. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90307-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Matsuoka I., Wetmore C., Olson L., Thoenen H. Enhanced synthesis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the lesioned peripheral nerve: different mechanisms are responsible for the regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNA. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):45–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemas D. S., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. trkB, a neural receptor protein-tyrosine kinase: evidence for a full-length and two truncated receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):143–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido D., Campuzano S., Koda T., Modolell J., Barbacid M. Dtrk, a Drosophila gene related to the trk family of neurotrophin receptors, encodes a novel class of neural cell adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):391–404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risling M., Cullheim S., Hildebrand C. Reinnervation of the ventral root L7 from ventral horn neurons following intramedullary axotomy in adult cats. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 28;280(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risling M., Fried K., Lindå H., Cullheim S., Meier M. Changes in nerve growth factor receptor-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord after ventral funiculus lesion in adult cats. J Neurocytol. 1992 Feb;21(2):79–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01189007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Tébar A., Dechant G., Barde Y. A. Binding of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to the nerve growth factor receptor. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90107-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Tébar A., Dechant G., Götz R., Barde Y. A. Binding of neurotrophin-3 to its neuronal receptors and interactions with nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):917–922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Goeddel D. V., Nguyen T., Lewis M., Shih A., Laramee G. R., Nikolics K., Winslow J. W. Primary structure and biological activity of a novel human neurotrophic factor. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90203-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Schweiger M. A novel modular mosaic of cell adhesion motifs in the extracellular domains of the neurogenic trk and trkB tyrosine kinase receptors. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1807–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Clark H. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Induction of nerve growth factor receptor in Schwann cells after axotomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J., Bitter-Suermann D., Schachner M. Differentiation-regulated loss of the polysialylated embryonic form and expression of the different polypeptides of the neural cell adhesion molecule by cultured oligodendrocytes and myelin. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Apr;22(4):369–383. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verge V. M., Merlio J. P., Grondin J., Ernfors P., Persson H., Riopelle R. J., Hökfelt T., Richardson P. M. Colocalization of NGF binding sites, trk mRNA, and low-affinity NGF receptor mRNA in primary sensory neurons: responses to injury and infusion of NGF. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4011–4022. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04011.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Hengerer B., Leibrock J., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Activity dependent regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNAs in the rat hippocampus is mediated by non-NMDA glutamate receptors. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3545–3550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]