Abstract
The current treatments of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) face a limited choice of vaccine, antibody and antiviral agents. The development of additional antiviral agents is still needed for improvement of CHB therapy. In this study, we established a screening system in order to identify compounds inhibiting the core promoter activity of hepatitis B virus (HBV). We prepared 80 extracts of marine organisms from the coral reefs of Indonesia and screened them by using this system. Eventually, two extracts showed high inhibitory activity (>95%) and low cytotoxicity (66% to 77%). Solvent fractionation, column chromatography and NMR analysis revealed that 3,5-dibromo-2-(2,4-dibromophenoxy)-phenol (compound 1) and 3,4,5-tribromo-2-(2,4-dibromophenoxy)-phenol (compound 2), which are classified as polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), were identified as anti-HBV agents in the extracts. Compounds 1 and 2 inhibited HBV core promoter activity as well as HBV production from HepG2.2.15.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The EC50 values of compounds 1 and 2 were 0.23 and 0.80 µM, respectively, while selectivity indexes of compound 1 and 2 were 18.2 and 12.8, respectively. These results suggest that our cell-based HBV core promoter assay system is useful to determine anti-HBV compounds, and that two PBDE compounds are expected to be candidates of lead compounds for the development of anti-HBV drugs.
Keywords: marine organism, hepatitis B virus, HBV, HBV core promoter, high-throughput screening, antiviral agent
1. Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a serious public health problem worldwide, with more than 240 million people estimated to be chronically infected [1]. Chronic infection with HBV leads to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, which are adverse outcomes seen in untreated patients [2,3].
HBV is an enveloped DNA virus that belongs to the genus Orthohepadnavirus of the Hepadnaviridae family [4]. The infectious virion of HBV contains incompletely double-stranded and relaxed circular DNA (rcDNA), surrounded with a lipid bilayer and viral surface proteins. Following virus entry into hepatocytes, rcDNA migrates into the nucleus and is then converted into a covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), which encodes overlapping open reading frames (ORFs). The viral genes are transcribed under the control of four promoters (core, preS1, preS2/S, and X promoters) and two enhancer regions (enhancer I and enhancer II also referred as the core upstream regulatory sequence: CURS), and translated into the core protein (Hepatitis B core antigen: HBcAg), precore protein (Hepatitis B e antigen: HBeAg), surface proteins (Large S, Middle S and Small S protein), polymerase (reverse transcriptase and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase) and X protein. These viral regulatory elements play a role in transcriptions of 3.5, 2.4, 2.1 and 0.7 kb mRNAs. The mRNA with a size of 3.5 kb, which is termed pregenomic RNA (pgRNA), is packaged with the viral polymerase into a viral capsid consisting of core proteins. The pgRNA is enclosed with capsid proteins in cytoplasm and then reverse-transcribed into a negative-strand DNA in the cytoplasmic capsid. The transcription of pgRNA is regulated under the control of the core promoter, which consists of the basic core promoter and the upper regulatory region including negative regulatory region and CURS. Thus, the core promoter is responsible for HBV replication as well as the viral particle formation and is capable of being targeted for development of an effective HBV therapy [5,6,7,8,9,10].
The currently available antiviral agents for the treatment of chronic HBV infection are classified as follows: (1) immunomodulatory agents, such as conventional interferon-alpha and pegylated interferon-alpha; and (2) oral nucleoside/nucleotide analogues (NAs), such as three nucleoside (lamivudine, entecavir and telbivudine) and two nucleotide analogues (adefovir and tenofovir). Treatments with these agents are capable of preventing disease progression to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, resulting in improvement of the survival rate of patients with chronic HBV infections [11,12,13]. However, interferon therapy is associated with major problems such as serious side effects, genotype-dependent treatment response and moderate antiviral activity, while long-term therapy using NAs promotes the emergence of drug-resistant viruses. In addition, the most serious problem is that currently available agents do not eradicate cccDNA, the template in transcription of HBV pgRNA and mRNA. Safer and more effective anti-HBV agents are still needed for efficient therapy [14,15].
Natural products including terrestrial plants and microbes have historically been sources for the development of various drugs targeting human diseases. Research on natural products has often included marine organisms because of the chemical and biological novelties of marine natural products. trabectedin (Yondelis®) and eribulin (Halaven®) are derived from chemical compounds isolated from marine organisms, and approved for anticancer therapy [16,17]. Ara-A (vidarabine) is a semisynthetic anti-herpes drug made from spongouridine isolated from the Caribbean sponge Tethya crypta [18,19].
In this study, we established a screening system to identify compounds inhibiting HBV core promoter activity and then screened 80 extracts of marine organisms collected from the coral reefs of Indonesia in order to identify anti-HBV agents.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Establishment of HBV Core Promoter Reporter Cell Line
The core promoter consists of CURS and basal core promoter (BCP) (Figure 1A) and is responsible for transcription of 3.5 kb mRNA, pgRNA [4]. CURS negatively and positively regulates the promoter activity [4]. The region composed of both CURS and BCP or BCP only was cloned into pGL4.18 [luc2P/Neo] plasmid (Figure 1A). The resulting plasmids were designated as pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS (CURS BCP) or pGL4.18 BC_AeUS (BCP) in this study (Figure 1A). The plasmid pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS or pGL4.18 BC_AeUS was transfected with phRG-TK into human hepatoma cell line Huh7, human cervical cancer cell line HeLa, and human fibrosarcoma cell line HT-1080. The resulting cells were harvested 48 h post-transfection and suspended in lysis buffer in order to estimate luciferase activity. Previous findings suggested that HBV core promoter (CURS and BCP) is more active in hepatoma cell lines than other cell lines [6,20,21,22,23]. In this study, Huh7 cell line exhibited the highest luciferase activity under the control of CURS BCP or BCP among tested cell lines (Figure 1B). Moreover, the Huh7 cells transfected with pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS exhibited 5-time higher luciferase activity than the cells transfected with pGL4.18 BC_AeUS (Figure 1B). These results suggest its potential for establishment of a cell-based screening assay based on HBV promoter activity. The plasmid pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS was introduced into Huh7 cells again for establishment of a stable cell line. The transfected cells were incubated in the presence of G418 until colony formation. The Huh7 cell line exhibiting the highest luciferase activity was selected by colony isolation, and designated as Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS.
Figure 1.
Development of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) core promoter reporter system. (A) Schematic representation of the firefly luciferase reporter plasmid pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS and pGL4.18 BC_AeUS; (B) HBV core promoter activity in three cell lines. Each plasmid described above was transfected with phRG-TK into hepatic (Huh7) and non-hepatic (HeLa and HT-1080) cells. Luciferase activity was measured at 48 h post-transfection as described in the Experimental Section. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized with Renilla luciferase activity. Luciferase activity was expressed as a fold induction compared with the value of cells transfected with pGL4.18 [luc2P/Neo] empty control vector (control). The data shown in this panel are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
2.2. Validation of Cell-Based HBV Core Promoter Assay
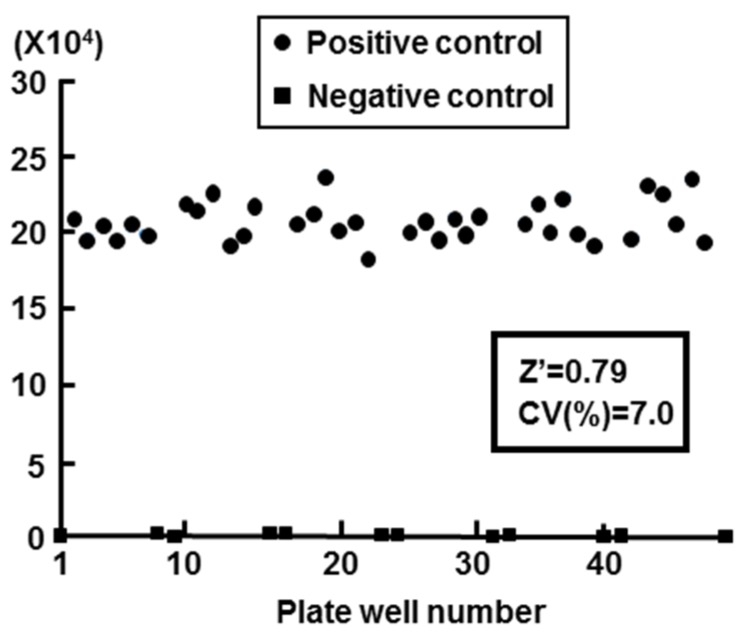
We calculated the Z′ factor in order to evaluate the Huh7 G4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cell line for high-throughput screening. The Z′ factor is a useful tool for measurement of the quality or suitability of high throughput screening, and the value spanning from 0.5 to 1.0 exhibits an appropriate assay [24,25]. In this study, the value of Z′ factor was 0.79 (n = 48) using Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells (Figure 2). The coefficient of variation (CV), which represents unevenness of the screening system, should be less than 10% for a correct assay [24]. The CV value of our system was 7.0% (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Validation of cell based HBV core promoter reporter assay. Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells (positive control) and Huh7 GL4.18 cells (negative control) were harvested at 72 h. The luciferase activity was determined as described in the Experimental Section. The Z′ factor and coefficient of variation (CV) value was calculated as described in the Experimental Section.
HepG2.2.15 cell line is generally used to screen for anti-HBV agents, although HepG2.2.15 cell-based drug screening assay requires at least 10 days for screening. However, cell-based HBV core promoter assay was completed for 3 days for screening. The cell-based HBV core promoter assay is more advantageous than the assay using HepG2.2.15 cell in high-throughput screening of anti HBV agents. Thus, the cell-based HBV core promoter assay was employed in this study for high-throughput screening of extracts prepared from marine organisms.
2.3. High-Throughput Screening for Extracts of Marine Organisms Inhibiting HBV Core Promoter Activity
We collected marine organisms from coral reefs of Indonesia and prepared 80 extracts from them with methanol (MeOH). We then screened them in order to discover anti-HBV agents using our screening system. Each extract was added at a final concentration of 25 µg/mL to the culture supernatant of Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells. Luciferase activity and cell viability were measured 48 h after treatment. Among them, extracts of samples code named 00A14 and 00X18 exhibited high inhibitory activity of more than 95% and low cytotoxicity of 66% to 77% (Table 1, Figure 3). The 00A14 extract was prepared from the marine sponge Dysidea granulosa collected from the coral reefs of Simua Island, while the 00X18 extract was prepared from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. collected from the coral reefs of Buton strait. Dysidea granulosa of 00A14 was similar to Dysidea sp. of 00X18 regarding morphological features. The 00X18 extract, but not the 00A14 extract, was further analyzed in this study because of the much smaller amount of Dysidea granulosa than of Dysidea sp.
Table 1.
Effect of marine organism extracts on HBV core promoter activity and cell viability.
| Sample No. | Sample Code Name | Specimen | Phylum | Inhibitory Activity (%) | Cell Viability (% of Control) | Collection Site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00A01 | Callyspongia sp. | Porifera | 0 | 101.5 | Simua Island |
| 2 | 00A05 | Xestospongia sp. | Porifera | 2.3 | 97.7 | Simua Island |
| 3 | 00A07 | Ircinia ramosa | Porifera | 0 | 177.4 | Simua Island |
| 4 | 00A08 | Liosina sp. | Porifera | 99.4 | 0 | Simua Island |
| 5 | 00A09 | Clathria sp. | Porifera | 98.6 | 0 | Simua Island |
| 6 | 00A10 | Unidentified | Chordata | 18.1 | 108.3 | Simua Island |
| 7 | 00A11 | Hippospongia sp. | Porifera | 40.3 | 97.7 | Simua Island |
| 8 | 00A12 | Petrosia sp. | Porifera | 6.9 | 92.8 | Simua Island |
| 9 | 00A13 | Callyspongia cf. aerizusa | Porifera | 5.4 | 119.1 | Simua Island |
| 10 | 00A14 | Dysidea granulosa | Porifera | 96.5 | 77.3 | Simua Island |
| 11 | 00B15 | Spheciospongia vagabunda | Porifera | 0 | 104.8 | Kajuongia Island |
| 12 | 00B16 | Callyspongia sp. | Porifera | 0 | 101.3 | Kajuongia Island |
| 13 | 00B17 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 91.2 | Kajuongia Island |
| 14 | 00J85 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 96.6 | Buton Island |
| 15 | 00J86 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 97.6 | Buton Island |
| 16 | 00J87 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 95.2 | Buton Island |
| 17 | 00J88 | Phyllospongia sp. | Porifera | 17.9 | 90.7 | Buton Island |
| 18 | 00J89 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 101.3 | Buton Island |
| 19 | 00J90 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 96.3 | Buton Island |
| 20 | 00J91 | Parazoanthus sp. | Cnidaria | 24.2 | 90.1 | Buton Island |
| 21 | 00K92 | Unidentified | Porifera | 14.8 | 95.9 | Buton Island |
| 22 | 00K94 | Ianthella basta | Porifera | 94.2 | 28.8 | Tobea Island |
| 23 | 00K95 | Unidentified | Chordata | 9.2 | 92.4 | Tobea Island |
| 24 | 00K97 | Higginsia mixta | Porifera | 16.1 | 84.5 | Tobea Island |
| 25 | 00L00 | Thrinacophora cervicornis | Porifera | 0 | 85.7 | Magintin Island |
| 26 | 00L02 | Unidentified | Chordata | 3.1 | 76.6 | Magintin Island |
| 27 | 00M03 | Gelliodes fibulata | Porifera | 13.7 | 98.2 | Masaloka Island |
| 28 | 00M04 | Clavularia viridis | Cnidaria | 99.6 | 1.4 | Masaloka Island |
| 29 | 00M05 | Coelocarteria sp. | Porifera | 15.1 | 91.1 | Masaloka Island |
| 30 | 00M06 | Mycale sp. | Porifera | 37.6 | 87.6 | Masaloka Island |
| 31 | 00M07 | Unidentified | Porifera | 28.2 | 94.2 | Masaloka Island |
| 32 | 00M08 | Unidentified | Porifera | 96.3 | 24.3 | Masaloka Island |
| 33 | 00N09 | Unidentified | Porifera | 15.3 | 83.7 | Buton strait |
| 34 | 00N10 | Myrmekioderma granulatum | Porifera | 0 | 92.9 | Buton strait |
| 35 | 00N11 | Callyspongia samarensis | Porifera | 0 | 95.5 | Buton strait |
| 36 | 00N12 | Biemna sp. | Porifera | 6.8 | 87.5 | Buton strait |
| 37 | 00N13 | Biemna triraphis | Porifera | 24.1 | 92.6 | Buton strait |
| 38 | 00N14 | Xestospongia exigua | Porifera | 99.4 | 1.6 | Buton strait |
| 39 | 00P16 | Unidentified | Cnidaria | 0 | 101.0 | Muna Island |
| 40 | 00Q17 | Unidentified | Porifera | 16.1 | 101.9 | Buton strait |
| 41 | 00Q18 | Unidentified | Porifera | 2.5 | 84.8 | Buton strait |
| 42 | 00Q19 | Axinyssa sp. | Porifera | 51.5 | 104.0 | Buton strait |
| 43 | 00Q20 | Mycale sp. | Porifera | 22.7 | 86.0 | Buton strait |
| 44 | 00R22 | Clavularia inflate | Cnidaria | 22.1 | 107.0 | Buton Island |
| 45 | 00R23 | Paralemnalia sp. | Cnidaria | 19.2 | 99.0 | Buton Island |
| 46 | 00R24 | Junceella fragilis | Cnidaria | 18.6 | 102.9 | Buton Island |
| 47 | 00R25 | Nephthea sp. | Cnidaria | 0 | 94.6 | Buton Island |
| 48 | 00S26 | Svenzea sp. | Porifera | 25.5 | 88.5 | Tobea Island |
| 49 | 00S27 | Unidentified | Cnidaria | 32.0 | 97.3 | Tobea Island |
| 50 | 00S28 | Coelogorgia sp. | Cnidaria | 0 | 97.7 | Tobea Island |
| 51 | 00T29 | Theonella sp. | Porifera | 35.3 | 85.4 | Tobea Island |
| 52 | 00T30 | Unidentified | Porifera | 47.6 | 93.6 | Tobea Island |
| 53 | 00T31 | Higginsia cf. mixta | Porifera | 14.7 | 142.0 | Tobea Island |
| 54 | 00T32 | Paratelesto sp. | Cnidaria | 0 | 94.7 | Tobea Island |
| 55 | 00U33 | Pycnoclabella sp. | Chordata | 25.8 | 91.9 | Muna Island |
| 56 | 00U34 | Lissoclinum patella | Chordata | 27.8 | 87.2 | Muna Island |
| 57 | 00X01 | Polycarpa contecta | Chordata | 25.9 | 93.6 | Simua Island |
| 58 | 00X02 | Dysidea sp. | Porifera | 56.8 | 73.4 | Tobea Island |
| 59 | 00X04 | Nephthea sp. | Cnidaria | 0 | 99.2 | Beromasidi Island |
| 60 | 00X05 | Haliclona fascigera | Porifera | 7.8 | 98.7 | Torobulu |
| 61 | 00X06 | Axinyssa sp. | Porifera | 98.9 | 4.9 | Torobulu |
| 62 | 00X07 | Unidentified | Porifera | 16.7 | 86.0 | Torobulu |
| 63 | 00X08 | Unidentified | Cnidaria | 12.9 | 87.0 | Torobulu |
| 64 | 00X10 | Niphates olemda | Porifera | 70.2 | 38.5 | Buton Island |
| 65 | 00X11 | Unidentified | Porifera | 99.7 | 1.1 | Tobea Island |
| 66 | 00X12 | Unidentified | Porifera | 70.6 | 63.9 | Tobea Island |
| 67 | 00X13 | Unidentified | Porifera | 13.9 | 108.7 | Magintin Island |
| 68 | 00X14 | Xestospongia sp. | Porifera | 21.1 | 105.6 | Magintin Island |
| 69 | 00X15 | Dysidea/Euryspongia | Porifera | 10.2 | 114.4 | Magintin Island |
| 70 | 00X16 | Unidentified | Chordata | 0 | 130.3 | Buton strait |
| 71 | 00X17 | Dysidea cf. arenaria | Porifera | 14.7 | 80.0 | Buton strait |
| 72 | 00X18 | Dysidea sp. | Porifera | 95.0 | 65.3 | Buton strait |
| 73 | 00X19 | Unidentified | Porifera | 23.0 | 92.5 | Buton strait |
| 74 | 00X21 | Gelliodes/Niphates | Porifera | 36.7 | 80.9 | Buton strait |
| 75 | 00X22 | Amphimedon/Haliclona | Porifera | 31.2 | 90.9 | Buton strait |
| 76 | 00X23 | Dysidea cf. arenaria | Porifera | 0 | 92.8 | Buton strait |
| 77 | 00X24 | Unidentified | Porifera | 0 | 99.2 | Buton strait |
| 78 | 00X26 | Anthelia sp. | Cnidaria | 61.5 | 107.4 | Buton strait |
| 79 | 00X27 | Unidentified | Chordata | 14.8 | 85.2 | Tobea Island |
| 80 | 00X28 | Clathria sp. | Porifera | 58.9 | 82.0 | Tobea Island |
Figure 3.
Correlation between the inhibitory activity of each marine organism extract against HBV core promoter and the cell viability of each marine organism extract. Each closed circle represents one marine organism extract. The x-axis indicates inhibitory activity against HBV core promoter, while the y-axis indicates cell viability.
2.4. Identification of PBDEs as the Inhibitory Compounds of HBV Production via HBV Core Promoter Activity
The extract of 00X18 was separated with several chromatographic steps to give two polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), 3,5-dibromo-2-(2,4-dibromophenoxy)-phenol (compound 1) and 3,4,5-tribromo-2-(2,4-dibromophenoxy)-phenol (compound 2) as major constituents (Figure 4A). The compounds were identified by comparing the NMR data with those published. Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells were incubated with each of those compounds to evaluate their effects on the core promoter activity. Both compounds inhibited the core promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 4B). IC50 values of compounds 1 and 2 are 2.3 µM and 4.9 µM, respectively, suggesting that compounds 1 and 2 included in the 00X18 extract inhibit HBV core promoter activity.
Figure 4.
Effect of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) on HBV core promoter activity. (A) Structure of 3,5-dibromo-2-(2,4-dibromo-phenoxy)-phenol (Compound 1) and 3,4,5-tribromo-2-(2,4-dibromo-phenoxy)-phenol (Compound 2); (B) Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells were incubated for 48 h in the medium containing various concentrations of PBDEs. Luciferase and cytotoxicity assays were carried out by the method described in the Experimental section. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
We next addressed the effects of compounds 1 and 2 on HBV production and cell viability. HBV-producing cultured cells, HepG2.2.15.7, were incubated in culture medium containing various concentrations of compound 1 or 2. Entecavir was used as the positive control for anti-HBV activities of compound 1 and 2. The amount of supernatant HBV DNA and cell viability were measured by using real-time PCR and MTS assay, respectively. Treatment with compound 1 or 2 impaired production of HBV DNA in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 5). The IC50 and CC50 values of compound 1 were 0.23 µM and 4.19 µM, respectively, while the EC50 and CC50 values of compound 2 were 0.80 µM and 10.26 µM, respectively. Thus, the selectivity indexes of compounds 1 and 2 were 18.2 and 12.8, respectively (Table 2). These results suggest that compounds 1 and 2 possess anti-HBV activity. However, IC50 values of compound 1 and 2 were higher than that of entecavir, while compounds 1 and 2 were more toxic than entecavir (Table 2).
Figure 5.
Effect of PBDEs on HBV production. HepG2.2.15.7 cells were incubated with various concentrations of compound 1 or 2. Supernatant HBV DNA and cytotoxicity were estimated by real-time qPCR and MTS assay, respectively, as described in the Experimental section. The data were representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Table 2.
Anti HBV activity and cytotoxicity of Compound 1, 2 and entecavir in HepG2.2.15.7 cells.
| Compound | EC50 a (µM) | CC50 b (µM) | Selectivity c Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 4.19 ± 0.12 | 18.2 |
| Compound 2 | 0.80 ± 0.34 | 10.26 ± 3.69 | 12.8 |
| Entecavir | 0.021 ± 0.003 | >100 | >4761 |
a Fifty percent effective concentration based on the inhibition of the HBV viral DNA release; b Fifty percent cytotoxicity concentration based on the reduction of cell viability; c Selectivity index (CC50/EC50).
HepG2.2.15 cells have generally been used to screen chemical compounds for anti-HBV agents, but the disadvantage of HepG2.2.15 cell-based drug screening assay requires at least 10 days for screening. However, cell-based HBV core promoter assay was completed for 2 days for screening. Thus, cell-based HBV core promoter assay offers an advantage in high-throughput screening of anti HBV agents.
PBDEs were recently isolated from marine sponges and biologically synthesized by their associated microorganisms [26,27]. Several groups reported multifunctional properties containing antibacterial, antifungal, anti-microalgal and anti-inflammatory activities of PBDEs [28,29,30]. Treatment with PBDEs also inhibited the enzymatic activities of endogenous and viral proteins [31,32,33]. Compound 1 suppressed activity of Tie2 kinase, which is associated with angiogenesis essential for tumor growth and survival [34]. The data reported by Zhang et al., indicate that compound 1 induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest in MCF-7 cells (a breast cancer cell line) [35], although HBV could infect and replicate in non-dividing cells [36]. These reports indicate that endogenous factors are associated with the inhibitory effect of PBDEs on HBV propagation. Further studies will reveal the mechanism of PBDE-related suppression of HBV production, and will be required for the development of more effective and safe anti-HBV agents based on PBDEs.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture
HepG2.2.15.7 cell line was subcloned from HepG2.2.15 cell line, which is stably transfected with the HBV genome (genotype D) [37,38]. HepG2.2.15.7 cell line produced HBV at a higher level than HepG2.2.15 cell line. This cell lines were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium/Ham’s Nutrient Mixture F12 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL Penicillin, 100 µg/mL Streptomycin, 2 mM l-Glutamine, 400 µg/mL G418, 50 µM hydrocortisone and 5 µg/mL Insulin. Huh7 cells, HeLa cells and HT-1080 cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal calf serum, 100 U/mL Penicillin and 100 µg/mL Streptomycin.
3.2. Plasmid Construction and Transient or Stable Expression
The HBV CURS BCP and BCP fragment was amplified from pUC19 HBV AeUS plasmid [39] by PCR using the following primers: CURS BCP: 5′-GCTAGCGATCCTGCCCAAGGTCTTACATAA-3′ (the underlined region indicates Nhe I site) and 5′-AGATCTAAGAGATGATTAGGCAGAGGT-GAA-3′ (underlined region indicates Bgl II site); BCP: 5′-GCTAGCTGGGGGAGGAGATTAGGT-TAAAGG-3′ (the underlined region indicates Nhe I site) and 5′-AGATCTAAGAGATGATTAGGC-AGAGGTGAA-3′ (underlined region indicates Bgl II site). These PCR products were cloned into a TA cloning vector, pTA2 (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). After sequence confirmation, these PCR fragments were introduced between Nhe I and Bgl II sites of pGL4.18 [luc2P/Neo] (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The resulting plasmid was designated as pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS and pGL4.18 BC_AeUS in this study.
Huh7, HeLa and HT-1080 cell lines were co-transfected with pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS and phRG-TK using Lipofectamine LTX reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). To standardize transfection efficiency and cell recovery, we used the phRG-TK plasmid (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) encoding Renilla luciferase under the control of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase promoter. The plasmid pGL4.18 [luc2P/Neo] was used as a negative control instead of pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS. The transfected cells were harvested 48 h post-transfection and then were lysed in Passive lysis buffer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Luciferase activity was measured using a Dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The resulting luminescence was detected by a Luminescencer-JNR AB-2100 (ATTO, Tokyo, Japan).
The pGL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS or pGL4.18 [luc2P/Neo] plasmid was transfected into Huh7 cells using Lipofectamine LTX reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). These transfected cells were seeded on the plate and then incubated until colonies formed. The stable cell lines were established by colony isolation. The clone exhibiting the highest activity among the isolated clone was designated as Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS, and the negative control clone was designated as Huh7 GL4.18.
3.3. Validation of Screening Method
Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS and Huh7 cells were seeded at 2 × 104 cells per well in a 48-well plate. Luciferase activity was measured after 72 h of incubation. The Z′ factor was calculated as follows:
SD: Standard Deviation.
The minimal acceptable value for a high-throughput screening assay is usually considered to be 0.5. The theoretical maximum is 1 [24,25].
The CV is calculated using the formula:
SD: Standard Deviation.
The acceptable value of CV for a high-throughput screening assay is less than 10% [24].
3.4. Cell-Based HBV Promoter Assay
Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells were seeded at 2 × 104 cells per well in a 48-well plate and then treated with 25 µg/mL each extracts 24 h after seeding cells. The treated cells were harvested 48 h post-treatment and then lysed with Cell culture lysis buffer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Luciferase activity was measured by using Luciferase assay systems (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The resulting luminescence was detected as described above.
3.5. Determination of Cytotoxicity
Huh7 GL4.18 CURS_BC_AeUS cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well in a 96-well plate and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Each extract was added at 25 µg/mL to the culture supernatant. The treated cells were harvested 48 h post-treatment. Cell viability was estimated by dimethylthiazol carboxymethoxy-phenylsulfophenyl tetrazolium (MTS) assay using a Celltiter 96 aqueous one-solution cell proliferation assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
3.6. Preparation of Extracts from Marine Organisms
The marine organisms were collected at coral reefs around Sulawesi, Muna, and Buton Islands, Indonesia, in August 2000. Marine sponge No. 10 was identified as Dysidea granulosa in this study and deposited at the Netherlands Centre for Biodiversity with code RMNH POR 10013. Each specimen was preserved with a small amount of ethanol until use. After decantation of ethanol solution, each specimen was extracted three times with MeOH. A crude extract was prepared by concentrating the combined solution under vacuum and then kept at −20 °C until use. A portion of each extract was solubilized in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) after measuring its weight.
3.7. Separation of PBDEs
A crude MeOH extract (1.24 g) of specimen No. 72 was partitioned between EtOAc and water. The lipophilic layer yielded 481 mg after concentration and it was applied to a silica gel column and separated into six fractions. A portion of the third fraction (185 mg) was subjected to silica HPLC (hexane-CH2Cl2 or hexane-EtOAc). Finally, two PBDEs, 3,5-dibromo-2-(2,4-dibromo-phenoxy)-phenol (Compound 1, 2.5 mg) and 3,4,5-tribromo-2-(2,4-dibromo-phenoxy)-phenol (Compound 2, 7.3 mg), were identified by checking NMR data as follows:
Compound 1: 1H NMR (acetone-d6) δ 7.83 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-3′), 7.43 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, H-5′), 7.39 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz, H-4), 7.26 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz, H-6), 6.59 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-6′).
Compound 2: 1H NMR (acetone-d6) δ 7.83 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-3′), 7.51 (1H, s, H-6), 7.42 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, H-5′), 6.63 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-6′).
3.8. Determination of Anti HBV Activity and Cytotoxicity in HepG2.2.15.7 Cells
HepG2.2.15.7 cells were seeded at 1 × 104 cells per well in a collagen coated 96-well plate (Corning, Corning, NY, USA) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h before treatment. The tested compound was added to the culture medium at the indicated concentrations. The culture medium was exchanged every 3 days for fresh medium containing the compound. The treated cells and culture supernatants were harvested 9 days post-treatment and were subjected to MTS assay and estimation of HBV DNA, respectively. The culture supernatant was mixed with an equal volume of Sidestep lysis and stabilization buffer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The viral DNA included in the mixture was estimated by real-time quantitative PCR using the THUNDERBIRD Probe qPCR Mix (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). The forward and reverse primers targeting HBV surface region are 5′-ACTCACCAACCTCCTGTCCT-3′ and 5′-GACAAACGGGCAACATACCT-3′, respectively. The fluorogenic probe was 5′-FAM-TATCGCTGGATGTGTCTGCGGCGT-TAMRA-3 [40].
3.9. Reagents
Entecavir and hydrocortisone were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). G418 and insulin were purchased from Wako (Osaka, Japan).
4. Conclusions
We developed a cell-based assay based on HBV core promoter activity, screened marine products using this assay system and finally identified two PBDEs as anti-HBV compounds.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Furugori for her secretarial work and C. Endoh for technical assistance. We also thank M. Mizokami for kindly providing a plasmid. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan (H24-Bsou-kanen-012 and -005) and from the Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Science and Technology of Japan (26350973 and 15K08493).
Author Contributions
Atsuya Yamashita, Junichi Tanaka, Masaaki Toyama, Masanori Baba, and Kohji Moriishi designed all of the experiments. Mayumi Tamaki, Andi Setiawan, and Junichi Tanaka collected marine organisms, purified the materials and identified compounds. Nicole J. De Voogd identified marine sponges. Tomohisa Tanaka, Kaori Okuyama-Dobashi, Hirotake Kasai, Koichi Watashi, Takaji Wakita, Shinya Maekawa and Nobuyuki Enomoto analyzed the data. Atsuya Yamashita and Yuusuke Fujimoto conducted other experiments. Atsuya Yamashita, Junichi Tanaka and Kohji Moriishi wrote the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Ott J.J., Stevens G.A., Groeger J., Wiersma S.T. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: New estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–2219. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Liaw Y.F., Chu C.M. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373:582–592. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Trepo C., Chan H.L., Lok A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2014;384:2053–2063. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Locarnini S., Littlejohn M., Aziz M.N., Yuen L. Possible origins and evolution of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013;23:561–575. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beck J., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007;13:48–64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kramvis A., Kew M.C. The core promoter of hepatitis B virus. J. Viral Hepat. 1999;6:415–427. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1999.00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Moolla N., Kew M., Arbuthnot P. Regulatory elements of hepatitis B virus transcription. J. Viral Hepat. 2002;9:323–331. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2002.00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus replication: Novel roles for virus-host interactions. Intervirology. 1999;42:100–116. doi: 10.1159/000024970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seeger C., Mason W.S. Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000;64:51–68. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.64.1.51-68.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tang H., Banks K.E., Anderson A.L., McLachlan A. Hepatitis B virus transcription and replication. Drug News Perspect. 2001;14:325–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lok A.S. Personalized treatment of hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2015;21:1–6. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.You C.R., Lee S.W., Jang J.W., Yoon S.K. Update on hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014;20:13293–13305. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zoulim F., Durantel D. Antiviral therapies and prospects for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015;5 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gish R., Jia J.D., Locarnini S., Zoulim F. Selection of chronic hepatitis B therapy with high barrier to resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012;12:341–353. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grimm D., Thimme R., Blum H.E. HBV life cycle and novel drug targets. Hepatol. Int. 2011;5:644–653. doi: 10.1007/s12072-011-9261-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cragg G.M., Newman D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1830:3670–3695. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Molinski T.F., Dalisay D.S., Lievens S.L., Saludes J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009;8:69–85. doi: 10.1038/nrd2487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Donia M., Hamann M.T. Marine natural products and their potential applications as anti-infective agents. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003;3:338–348. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(03)00655-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sagar S., Kaur M., Minneman K.P. Antiviral lead compounds from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs. 2010;8:2619–2638. doi: 10.3390/md8102619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guo W., Chen M., Yen T.S., Ou J.H. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the hepatitis B virus core promoter depends on both positive and negative regulation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993;13:443–448. doi: 10.1128/MCB.13.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J. Virol. 1989;63:919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yee J.K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989;246:658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yuh C.H., Ting L.P. The genome of hepatitis B virus contains a second enhancer: Cooperation of two elements within this enhancer is required for its function. J. Virol. 1990;64:4281–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4281-4287.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fatokun A.A., Liu J.O., Dawson V.L., Dawson T.M. Identification through high-throughput screening of 4′-methoxyflavone and 3′,4′-dimethoxyflavone as novel neuroprotective inhibitors of parthanatos. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013;169:1263–1278. doi: 10.1111/bph.12201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang J.H., Chung T.D., Oldenburg K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999;4:67–73. doi: 10.1177/108705719900400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agarwal V., El Gamal A.A., Yamanaka K., Poth D., Kersten R.D., Schorn M., Allen E.E., Moore B.S. Biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds by marine bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014;10:640–647. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Teuten E.L., Xu L., Reddy C.M. Two abundant bioaccumulated halogenated compounds are natural products. Science. 2005;307:917–920. doi: 10.1126/science.1106882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Handayani D., Edrada R.A., Proksch P., Wray V., Witte L., van Soest R.W., Kunzmann A., Soedarsono Four new bioactive polybrominated diphenyl ethers of the sponge Dysidea herbacea from west sumatra, indonesia. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:1313–1316. doi: 10.1021/np970271w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hanif N., Tanaka J., Setiawan A., Trianto A., de Voogd N.J., Murni A., Tanaka C., Higa T. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the indonesian sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2007;70:432–435. doi: 10.1021/np0605081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sionov E., Roth D., Sandovsky-Losica H., Kashman Y., Rudi A., Chill L., Berdicevsky I., Segal E. Antifungal effect and possible mode of activity of a compound from the marine sponge Dysidea herbacea. J. Infect. 2005;50:453–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2004.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fu X., Schmitz F.J., Govindan M., Abbas S.A., Hanson K.M., Horton P.A., Crews P., Laney M., Schatzman R.C. Enzyme inhibitors: New and known polybrominated phenols and diphenyl ethers from four indo-pacific Dysidea sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 1995;58:1384–1391. doi: 10.1021/np50123a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Salam K.A., Furuta A., Noda N., Tsuneda S., Sekiguchi Y., Yamashita A., Moriishi K., Nakakoshi M., Tani H., Roy S.R., et al. Pbde: Structure-activity studies for the inhibition of hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase. Molecules. 2014;19:4006–4020. doi: 10.3390/molecules19044006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yamazaki H., Sumilat D.A., Kanno S., Ukai K., Rotinsulu H., Wewengkang D.S., Ishikawa M., Mangindaan R.E., Namikoshi M. A polybromodiphenyl ether from an indonesian marine sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea and its chemical derivatives inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, an important target for diabetes treatment. J. Nat. Med. 2013;67:730–735. doi: 10.1007/s11418-012-0735-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu Y.M., Johnson R.K., Hecht S.M. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers from a sponge of the Dysidea genus that inhibit Tie2 kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005;13:657–659. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2004.10.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang H., Skildum A., Stromquist E., Rose-Hellekant T., Chang L.C. Bioactive polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008;71:262–264. doi: 10.1021/np070244y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cohen D., Adamovich Y., Reuven N., Shaul Y. Hepatitis B virus activates deoxynucleotide synthesis in nondividing hepatocytes by targeting the R2 gene. Hepatology. 2010;51:1538–1546. doi: 10.1002/hep.23519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ogura N., Watashi K., Noguchi T., Wakita T. Formation of covalently closed circular DNA in Hep38.7-Tet cells, a tetracycline inducible hepatitis B virus expression cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014;452:315–321. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sells M.A., Chen M.L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1987;84:1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sugiyama M., Tanaka Y., Kato T., Orito E., Ito K., Acharya S.K., Gish R.G., Kramvis A., Shimada T., Izumi N., et al. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the intra- and extracellular expression of viral DNA and antigens. Hepatology. 2006;44:915–924. doi: 10.1002/hep.21345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu Y., Hussain M., Wong S., Fung S.K., Yim H.J., Lok A.S. A genotype-independent real-time PCR assay for quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007;45:553–558. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00709-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]