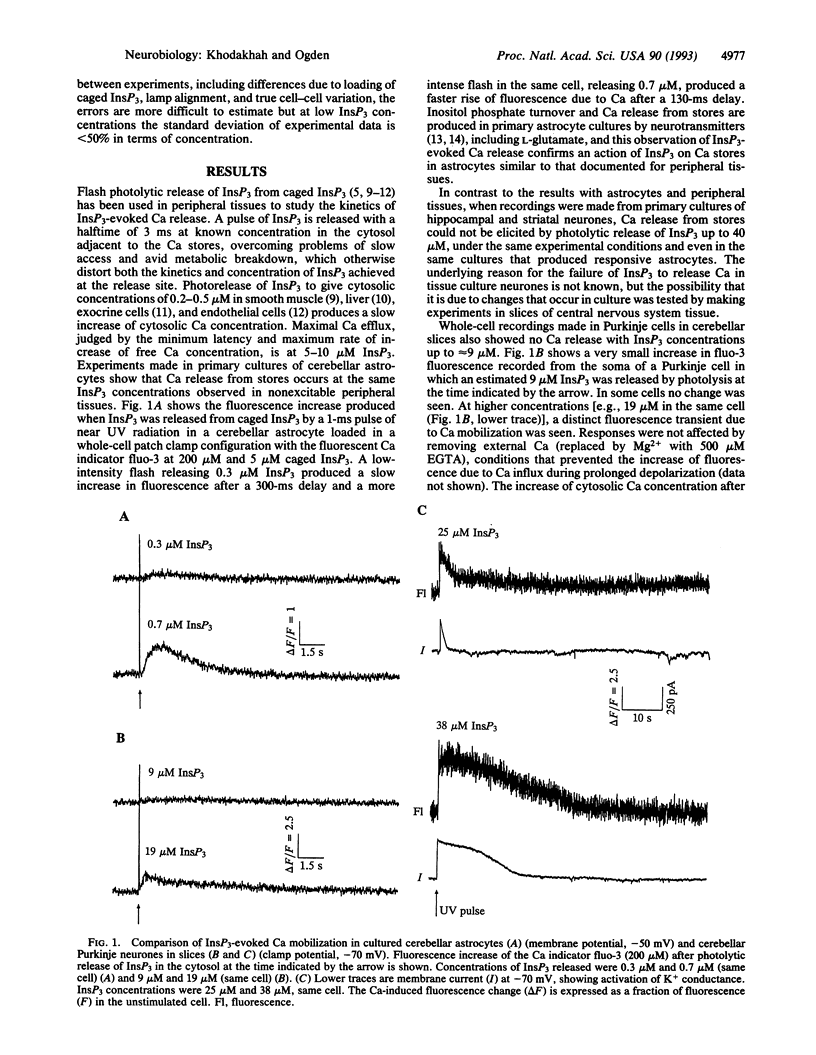
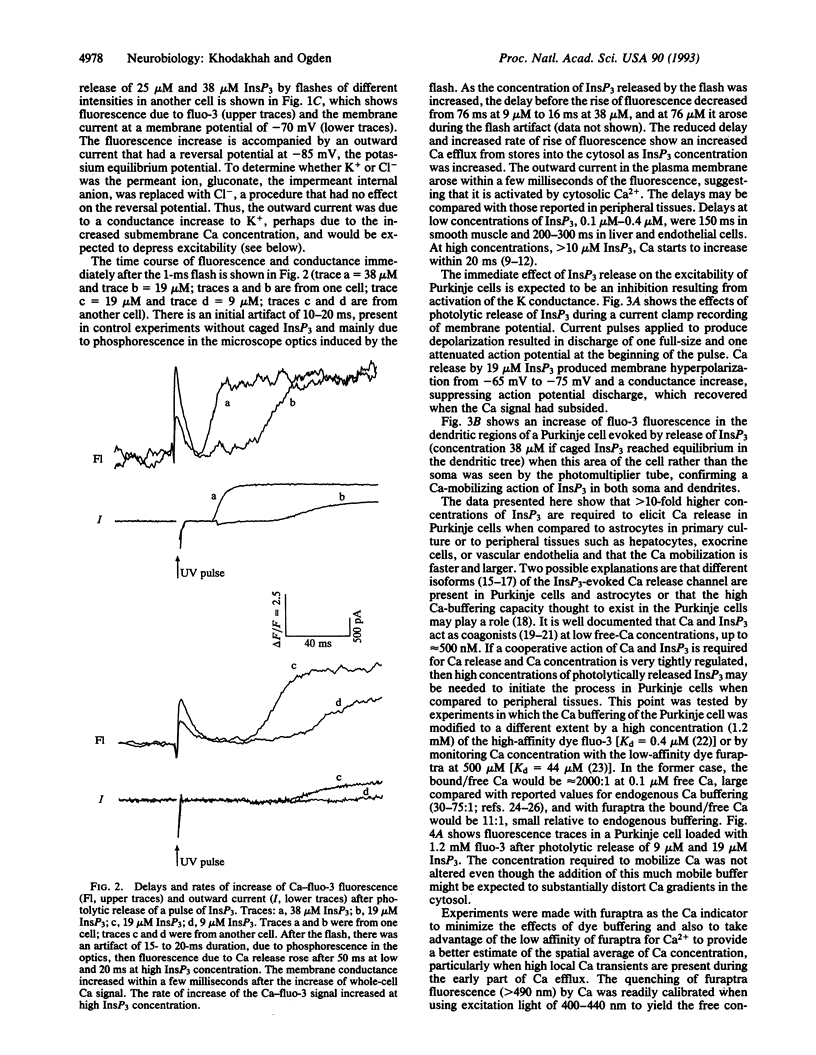
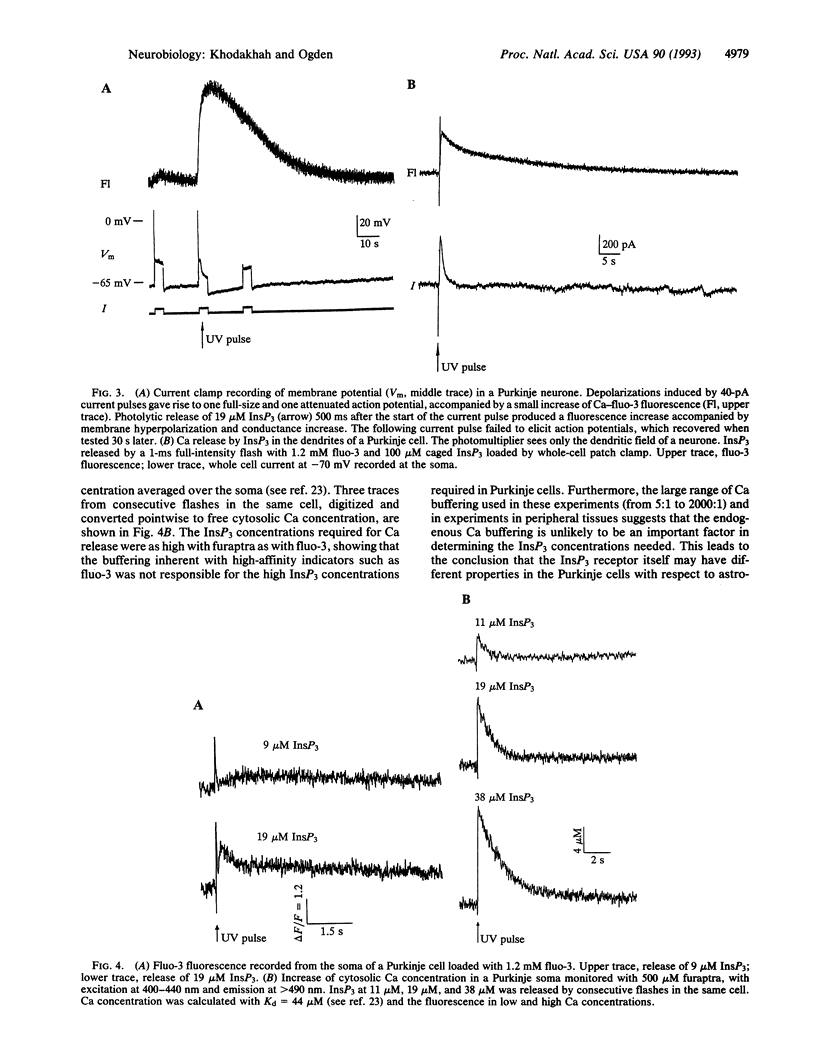
Abstract
Purkinje neurones of the cerebellar cortex are rich in receptors for the Ca-mobilizing second messenger inositol trisphosphate (InsP3) in association with intracellular Ca stores. Cytosolic Ca ions are important in regulating neuronal excitability but it has proved difficult to demonstrate InsP3-evoked release of Ca in mammalian central neurones directly. Intracellular release of InsP3 by flash photolysis of caged InsP3, combined with whole-cell patch clamp and microspectrofluorimetry of Ca indicators, allows comparison of InsP3-evoked Ca release in single Purkinje cells in cerebellar slices with the same process in cultured astrocytes and peripheral tissues. In astrocytes, hepatocytes, exocrine cells, and vascular endothelium, minimal Ca release from stores requires photorelease of InsP3 at concentrations of 0.2-0.5 microM, and maximal efflux as judged by the rate of increase of Ca concentration is seen with 5-10 microM InsP3. In contrast in Purkinje cells, InsP3 concentrations of > or = 9 microM were required to produce minimal Ca release from stores under the same conditions, and Ca efflux increased with InsP3 concentrations up to 70-80 microM. Furthermore, the rate of increase and size of the Ca concentration in Purkinje cells are 10- to 30-fold greater than in astrocytes and peripheral tissues. The InsP3 sensitivity was not affected by changing exogenous cytosolic Ca buffering, suggesting that endogenous Ca binding cannot account for the difference. The results show a functional difference in InsP3-evoked Ca release between Purkinje cells and peripheral tissues.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Calcium regulation by and buffer capacity of molluscan neurons during calcium transients. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. D., Ogden D. Kinetics of intracellular calcium release by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and extracellular ATP in porcine cultured aortic endothelial cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Dec 22;250(1329):235–241. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danoff S. K., Ferris C. D., Donath C., Fischer G. A., Munemitsu S., Ullrich A., Snyder S. H., Ross C. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: distinct neuronal and nonneuronal forms derived by alternative splicing differ in phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B., Takahashi T. A thin slice preparation for patch clamp recordings from neurones of the mammalian central nervous system. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):600–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00580998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enkvist M. O., Holopainen I., Akerman K. E. Glutamate receptor-linked changes in membrane potential and intracellular Ca2+ in primary rat astrocytes. Glia. 1989;2(6):397–402. doi: 10.1002/glia.440020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1103–1122. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers monitored with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):271–301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Dreessen J., Kano M., Konnerth A. Intradendritic release of calcium induced by glutamate in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90370-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. A glutamate receptor regulates Ca2+ mobilization in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Okano H., Furuichi T., Aruga J., Mikoshiba K. The subtypes of the mouse inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor are expressed in a tissue-specific and developmentally specific manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6244–6248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Capiod T., Walker J. W., Trentham D. R. Kinetics of the conductance evoked by noradrenaline, inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+ in guinea-pig isolated hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:585–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce B., Albrecht J., Morrow C., Murphy S. Astrocyte glutamate receptor activation promotes inositol phospholipid turnover and calcium flux. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 23;72(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90537-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp G., Güth K. A low cost high intensity flash device for photolysis experiments. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):200–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00582315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Danoff S. K., Schell M. J., Snyder S. H., Ullrich A. Three additional inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors: molecular cloning and differential localization in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4265–4269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Meldolesi J., Milner T. A., Satoh T., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor localized to endoplasmic reticulum in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):468–470. doi: 10.1038/339468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa A., Podini P., Clegg D. O., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Intracellular Ca2+ stores in chicken Purkinje neurons: differential distribution of the low affinity-high capacity Ca2+ binding protein, calsequestrin, of Ca2+ ATPase and of the ER lumenal protein, Bip. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):779–791. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Feeney J., Trentham D. R. Photolabile precursors of inositol phosphates. Preparation and properties of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl esters of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3272–3280. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Somlyo A. V., Goldman Y. E., Somlyo A. P., Trentham D. R. Kinetics of smooth and skeletal muscle activation by laser pulse photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):249–252. doi: 10.1038/327249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



