Abstract
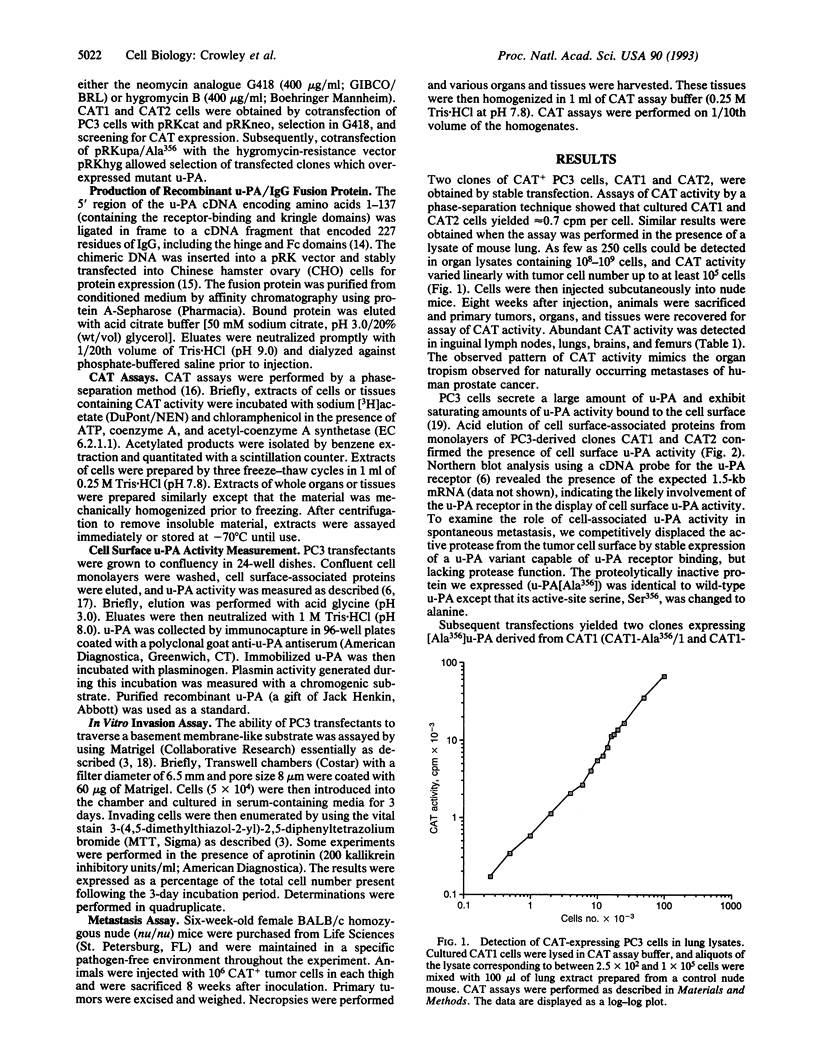
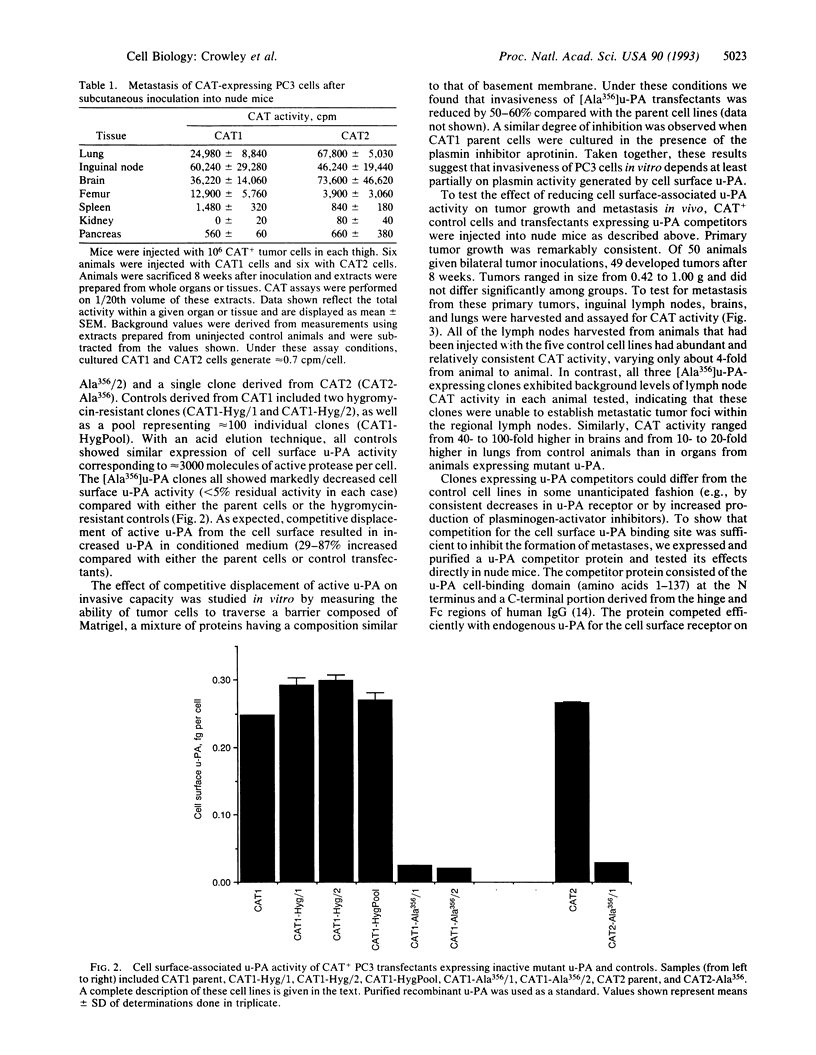
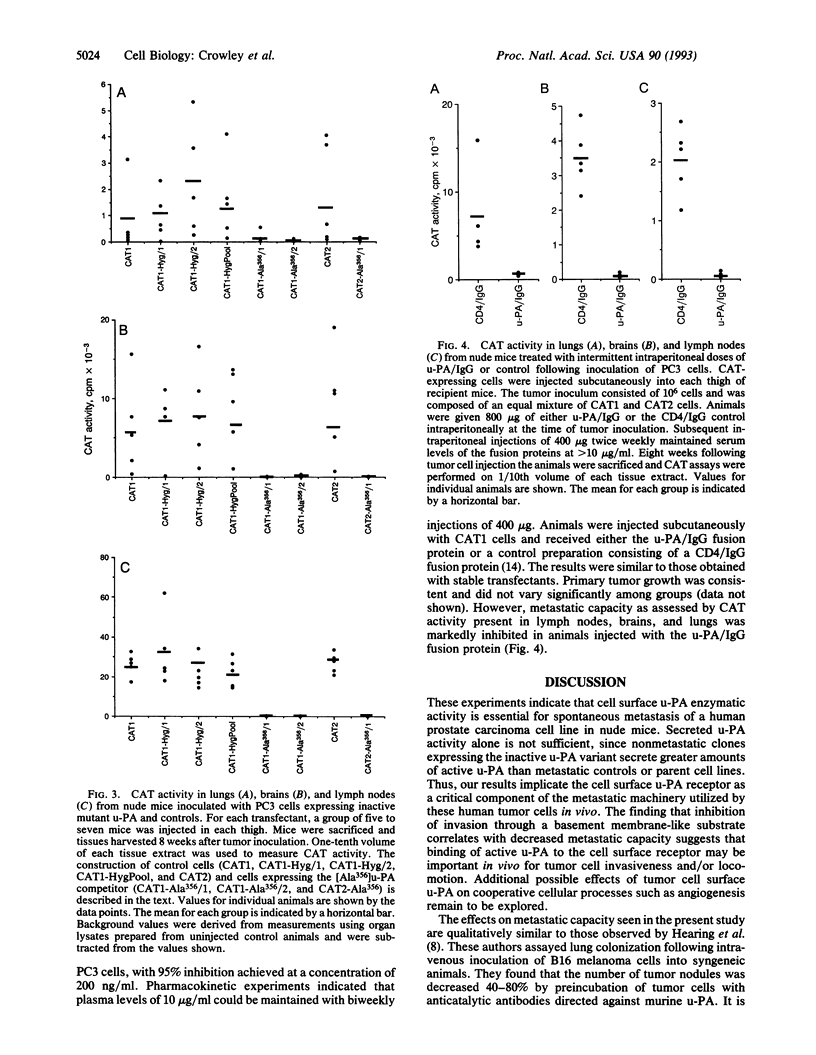
The plasminogen activator urokinase (u-PA) mediates proteolysis by a variety of human tumor cells. Competitive displacement of u-PA from cellular binding sites results in decreased proteolysis in vitro, suggesting that the cell surface is the preferred site for u-PA-mediated protein degradation. We studied the effect of u-PA receptor blockade on the metastatic capacity of human PC3 prostate carcinoma cells, using transfectants which expressed chloramphenicol acetyl-transferase (CAT). Eight weeks after subcutaneous inoculation of these cells into nude mice, CAT activity was detected in regional lymph nodes, femurs, lungs, and brain, thereby mimicking the organ tropism observed for naturally occurring metastases of prostate cancer. In a second transfection, CAT-expressing PC3 cells received cDNA encoding a mutant u-PA (Ser356-->Ala) which lacks enzymatic activity but which retains full receptor binding affinity. Three mutant u-PA expressors, each with < 5% of wild-type cell-associated u-PA activity, were compared in vivo with independently derived controls. Primary tumor growth was similar in each group of animals and all tumors expressed comparable CAT activity. In contrast, metastasis (as assessed by CAT activity) was markedly inhibited when cell surface u-PA activity was blocked. Levels of CAT activity were reduced by a factor of > 300 in regional lymph nodes, 40-100 in brain tissue, and 10-20 in lung tissue. Metastatic capacity was inhibited similarly when animals were given intermittent intraperitoneal injections of a u-PA/IgG fusion protein capable of displacing u-PA activity from the tumor cell surface. Our results indicate that cell surface u-PA activity is essential to the metastatic process. In addition, the assay system employed in these experiments may be generally useful in testing other therapeutic modalities to limit the spread of primary tumors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Cassani G., Blasi F. The receptor-binding sequence of urokinase. A biological function for the growth-factor module of proteases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4437–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. D., Bennett G. L., Vitangcol R. V., Jewett J. R., Burnier J., Henzel W., Lowe D. G. Extracellular domain-IgG fusion proteins for three human natriuretic peptide receptors. Hormone pharmacology and application to solid phase screening of synthetic peptide antisera. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23060–23067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. L., Xi X. P., Crowley C. W., Lucas B. K., Levinson A. D., Shuman M. A. Effects of urokinase receptor occupancy on plasmin generation and proteolysis of basement membrane by human tumor cells. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):479–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6130–6138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Law L. W., Corti A., Appella E., Blasi F. Modulation of metastatic potential by cell surface urokinase of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1270–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoosein N. M., Boyd D. D., Hollas W. J., Mazar A., Henkin J., Chung L. W. Involvement of urokinase and its receptor in the invasiveness of human prostatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Commun. 1991 Aug;3(8):255–264. doi: 10.3727/095535491820873146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Green P. P., 3rd, Fowlkes D. M. A rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive assay for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):173–178. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Russo-Payne H., Wilson E. L. Inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by antibodies: the effect on dissemination of a human tumor in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Leeuwen R. T., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H. Protein and messenger RNA levels of plasminogen activators and inhibitors analyzed in 22 human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1488–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repesh L. A. A new in vitro assay for quantitating tumor cell invasion. Invasion Metastasis. 1989;9(3):192–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A. L., Cubellis M. V., Masucci M. T., Behrendt N., Lund L. R., Danø K., Appella E., Blasi F. Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):467–474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlechte W., Brattain M., Boyd D. Invasion of extracellular matrix by cultured colon cancer cells: dependence on urokinase receptor display. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(5):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suva L. J., Winslow G. A., Wettenhall R. E., Hammonds R. G., Moseley J. M., Diefenbach-Jagger H., Rodda C. P., Kemp B. E., Rodriguez H., Chen E. Y. A parathyroid hormone-related protein implicated in malignant hypercalcemia: cloning and expression. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):893–896. doi: 10.1126/science.3616618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



