Abstract
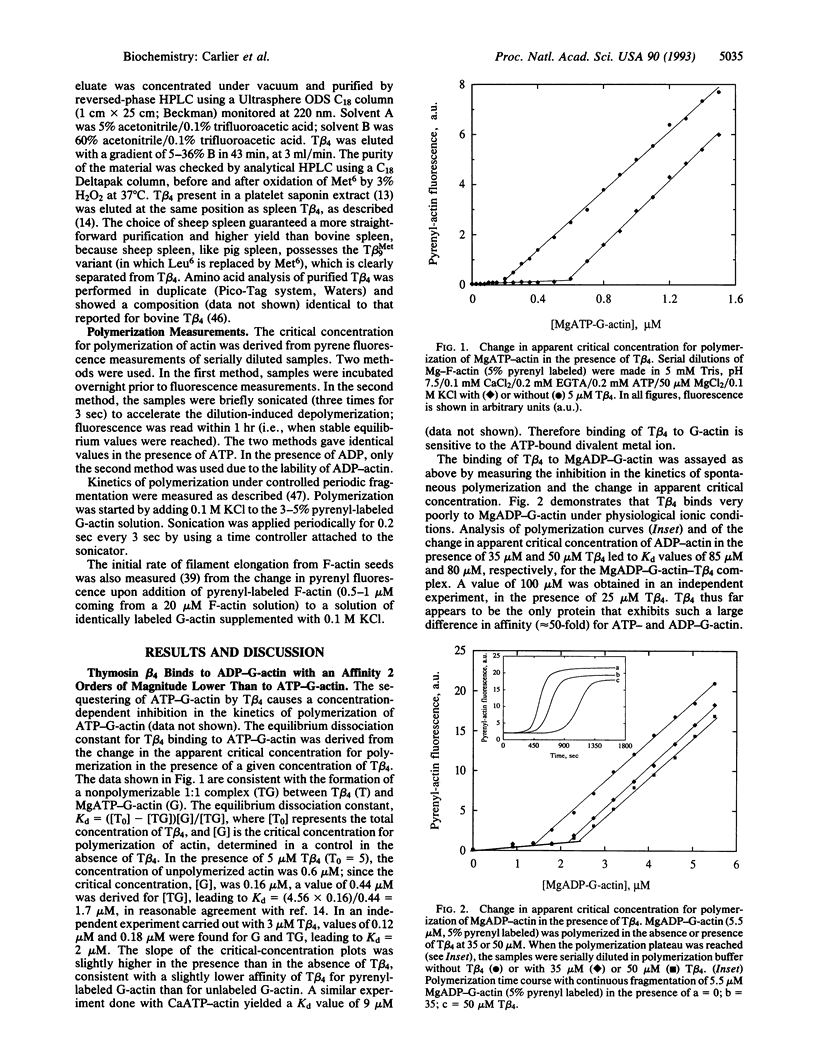
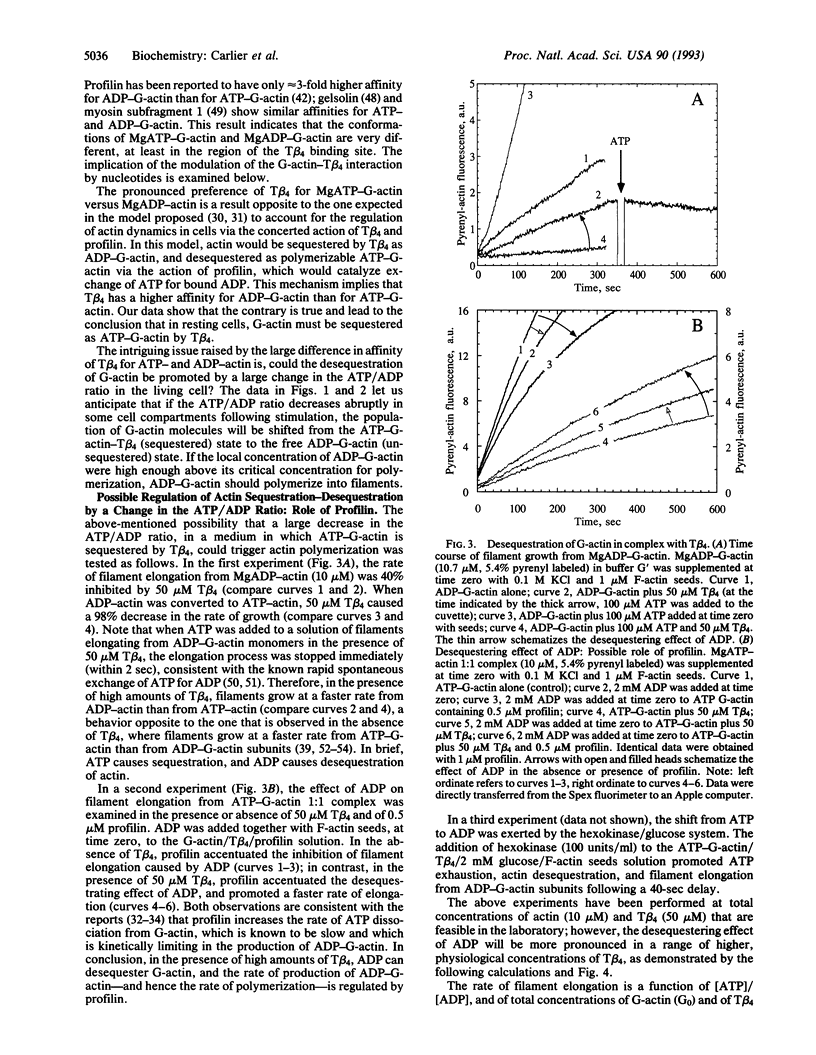
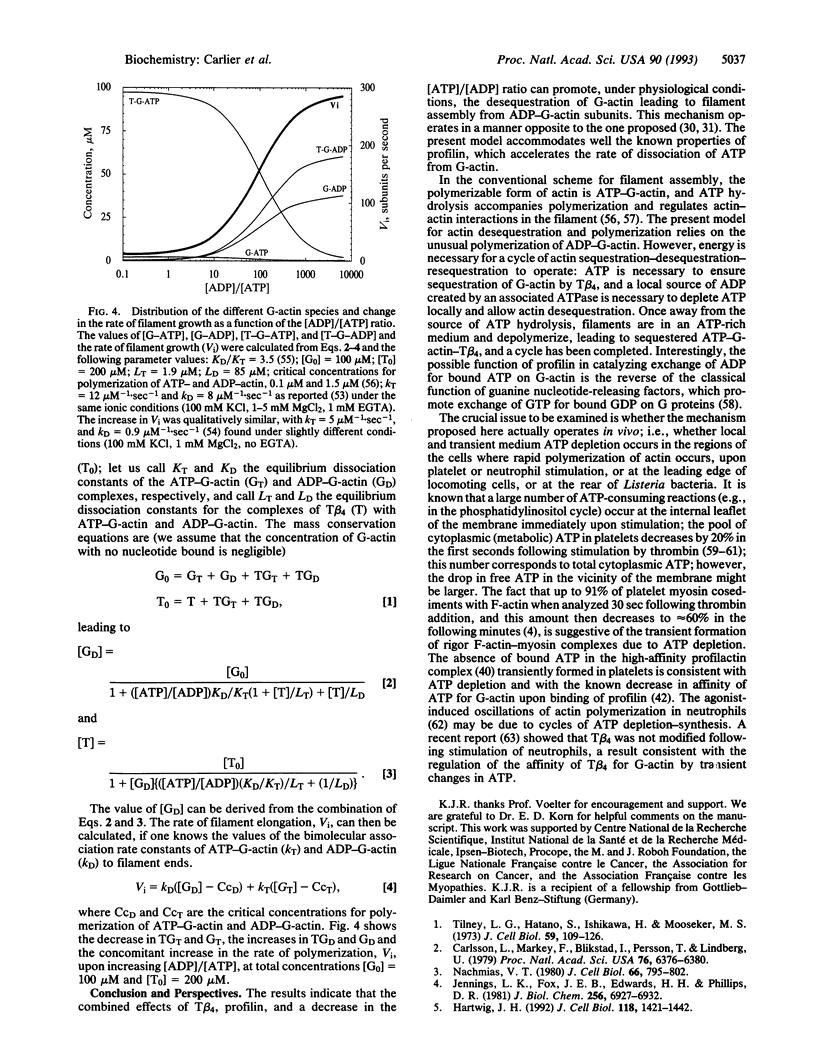
The interaction of G-actin with thymosin beta 4 (T beta 4), the major G-actin-sequestering protein in motile and proliferating cells, has been analyzed in vitro. T beta 4 is found to have a 50-fold higher affinity for MgATP-actin than for MgADP-actin. These results imply that in resting platelets and neutrophils, actin is sequestered by T beta 4 as MgATP-G-actin. Kinetic experiments and theoretical calculations demonstrate that this ATP/ADP dependence of T beta 4 affinity for G-actin can generate a mechanism of desequestration of G-actin by ADP, in the presence of physiological concentrations of T beta 4 (approximately 0.1 mM). The desequestration of G-actin by ADP is kinetically enhanced by profilin, which accelerates the dissociation of ATP from G-actin. Whether a local drop in the ATP/ADP ratio can allow local, transient desequestration and polymerization of actin either close to the plasma membrane, following platelet or neutrophil stimulation, or behind the Listeria bacterium in the host cell, while the surrounding cytoplasm contains sequestered ATP-G-actin, is an open issue raised by the present work.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. Signal transduction and the actin cytoskeleton: the roles of MARCKS and profilin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akkerman J. W., Holmsen H. Interrelationships among platelet responses: studies on the burst in proton liberation, lactate production, and oxygen uptake during platelet aggregation and Ca2+ secretion. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):956–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L. G., Babcock G. G., Rubenstein P. A., Wang Y. L. Effects of profilin and profilactin on actin structure and function in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1023–1029. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. Evidence for an ATP cap at the ends of actin filaments and its regulation of the F-actin steady state. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):9983–9986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. Polymerization of ADP-actin and ATP-actin under sonication and characteristics of the ATP-actin equilibrium polymer. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6565–6571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. The effects of Mg2+ at the high-affinity and low-affinity sites on the polymerization of actin and associated ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10785–10792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Markey F., Blikstad I., Persson T., Lindberg U. Reorganization of actin in platelets stimulated by thrombin as measured by the DNase I inhibition assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Safer D., Nachmias V. T., Zigmond S. H. Thymosin beta 4 sequesters the majority of G-actin in resting human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1261–1270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coué M., Korn E. D. Interaction of plasma gelsolin with ADP-actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3628–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Zigmond S. H. Changes in cytoskeletal proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by chemotactic peptides. Cell Motil. 1983;3(4):349–361. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden C., Patane K. Mechanism for nucleotide exchange in monomeric actin. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3812–3820. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Holmsen H., Salganicoff L. Adenine nucleotide metabolism of blood platelets. IX. Time course of secretion and changes in energy metabolism in thrombin-treated platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 22;444(3):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Furman M. I., Wachsstock D., Safer D., Nachmias V. T., Pollard T. D. The control of actin nucleotide exchange by thymosin beta 4 and profilin. A potential regulatory mechanism for actin polymerization in cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Sep;3(9):1015–1024. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.9.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Doberstein S. K., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of the interaction of human platelet profilin with actin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1081–1089. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Richardson M., Furuichi Y., Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Horecker B. L. Sequence of a cloned 523-bp cDNA for thymosin beta 4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):445–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90646-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillon C., Rieger K., Bakala J., Schott D., Morgat J. L., Hannappel E., Voelter W., Lenfant M. Involvement of thymosin beta 4 and endoproteinase Asp-N in the biosynthesis of the tetrapeptide AcSerAspLysPro a regulator of the hematopoietic system. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 12;274(1-2):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81322-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. L., Schlein A., Condeelis J. Relationship of pseudopod extension to chemotactic hormone-induced actin polymerization in amoeboid cells. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul;37(3):285–299. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240370304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Leibold W. Biosynthesis rates and content of thymosin beta 4 in cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jul;240(1):236–241. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E. One-step procedure for the determination of thymosin beta 4 in small tissue samples and its separation from other thymosin beta 4-like peptides by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Xu G. J., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 4: a ubiquitous peptide in rat and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., van Kampen M. Determination of thymosin beta 4 in human blood cells and serum. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 26;397:279–285. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)85010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Chambers K. A., Hopcia K. L., Kwiatkowski D. J. Association of profilin with filament-free regions of human leukocyte and platelet membranes and reversible membrane binding during platelet activation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1571–1579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H. Mechanisms of actin rearrangements mediating platelet activation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1421–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Fox J. E., Edwards H. H., Phillips D. R. Changes in the cytoskeletal structure of human platelets following thrombin activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. A., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Levine B. A., Pollard T. D. Characterization of renatured profilin purified by urea elution from poly-L-proline agarose columns. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(2):251–262. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D., Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Actin polymerization and ATP hydrolysis. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):638–644. doi: 10.1126/science.3672117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Fluorimetry study of N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide-labelled F-actin. Local structural change of actin protomer both on polymerization and on binding of heavy meromyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal A. A., Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. Preparation and polymerization of skeletal muscle ADP-actin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13061–13065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal A. A., Korn E. D. Reinvestigation of the inhibition of actin polymerization by profilin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10132–10138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson H., Lindberg U. The effect of divalent cations on the interaction between calf spleen profilin and different actins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 2;953(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant M., Wdzieczak-Bakala J., Guittet E., Prome J. C., Sotty D., Frindel E. Inhibitor of hematopoietic pluripotent stem cell proliferation: purification and determination of its structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Schutt C. E., Hellsten E., Tjäder A. C., Hult T. The use of poly(L-proline)-Sepharose in the isolation of profilin and profilactin complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 15;967(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Lin C. Y., Pan T. L., Chiou A. J., Tsugita A. Structure and immunological properties of thymosin beta 9 Met, a new analog of thymosin beta 4 isolated from porcine thymus. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Dec;36(6):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S., Pollard T. D. Identification of a factor in conventional muscle actin preparations which inhibits actin filament self-association. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey F., Lindberg U., Eriksson L. Human platelets contain profilin, a potential regulator of actin polymerisability. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockrin S. C., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba profilin interacts with G-actin to increase the rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5359–5362. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Cytoskeleton of human platelets at rest and after spreading. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E. Opposite effects of cofilin and profilin from porcine brain on rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1160–1164. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak E., Goody R. S. Kinetics of adenosine 5'-triphosphate and adenosine 5'-diphosphate interaction with G-actin. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8613–8617. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Porasik M. M., Sklar L. A. Oscillating actin polymerization/depolymerization responses in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16355–16358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Quantitative analysis of the effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on actin filament nucleation and elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6631–6641. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Elzinga M., Nachmias V. T. Thymosin beta 4 and Fx, an actin-sequestering peptide, are indistinguishable. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4029–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Golla R., Nachmias V. T. Isolation of a 5-kilodalton actin-sequestering peptide from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2536–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D. The interaction of actin with thymosin beta 4. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Jun;13(3):269–271. doi: 10.1007/BF01766454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöbitz B., Netzker R., Hannappel E., Brand K. Cell-cycle-regulated expression of thymosin beta 4 in thymocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöbitz B., Netzker R., Hannappel E., Brand K. Rapid induction of thymosin beta 4 in concanavalin A-stimulated thymocytes by translational control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15387–15391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Actin microfilament dynamics in locomoting cells. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):126–131. doi: 10.1038/352126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The nucleation-release model of actin filament dynamics in cell motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Hatano S., Ishikawa H., Mooseker M. S. The polymerization of actin: its role in the generation of the acrosomal process of certain echinoderm sperm. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):109–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Ranc C., Combeau C., Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Myosin subfragment-1 interacts with two G-actin molecules in the absence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17872–17879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven A. J., Tysnes O. B., Horvli O., Cook C. A., Holmsen H. Stimulation of phosphate uptake in human platelets by thrombin and collagen. Changes in specific 32P labeling of metabolic ATP and polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7047–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Nachmias V. T., Pennise C. R., Pring M., Safer D. Interaction of thymosin beta 4 with muscle and platelet actin: implications for actin sequestration in resting platelets. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 14;31(27):6179–6185. doi: 10.1021/bi00142a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



